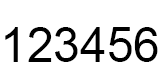当前位置:网站首页>Reading BMP file with C language
Reading BMP file with C language
2022-07-06 11:25:00 【imxlw00】
BMP Image coding
BMP namely bitmap, It's a bitmap , Generally by 4 Part of it is made up of : Header information block 、 Image description information block 、 color table ( No color table in true color mode ) And image data area .
Before the image data , As shown in the figure , share 54 Bit data 
among ,0x424d In the decimal system is 19778, Corresponding ASCII Code for BM, It means it's a bitmap file .
Windows The data is read backwards , This is a PC Computer features . If a piece of data is 42 4D, Read it backwards 4D 42, namely 0x4D42.
therefore , If bfSize The data is A2 1E 04 00, In fact, it becomes 0x00041EA2, That is to say 0x41EA2.
File header [14 byte ]
Storing file types , File size and other information
// File header structure
typedef struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER{
unsigned short bfType; // Must be "BM"
unsigned int bfSize; // File Bytes (2-5)
unsigned int bfReserved; // Bitmap file reserved word , Must be 0(6-9)
unsigned int bfOffBits; // Pixel data offset (10-13)
} bmpHeader;
Image description information [40 byte ]
#define uint unsigned int
#define ushort unsigned short
// Image header structure
typedef struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER{
uint biSize; // Structure size (14-17)
int biWidth; // The width of the image (18-21)
int biHeight; // Height of the image (22-25)
ushort biPlanes; // The level of the target device , by 1(26-27)
ushort biBitCount; // Pixel digits , by 1、4、8 or 24(28-29)
uint biCompression; // Bitmap compression type ,0 For no compression 、1 by BI_RLE8、2 by BI_RLE4(30-33)
uint biSizeImage; // Single pixel data size , be equal to bfSize-bfOffBits (34-37)
int biXPelsPerMeter; // Horizontal resolution , It's usually 0 (38-41)
int biYPelsPerMeter; // Vertical resolution , It's usually 0 (42-45)
uint biClrUsed; // The number of colors in the bitmap color table ,0 Indicates that all palette items are used (46-49)
uint biClrImportant; // Number of important color indexes ,0 It means that everything is important (50-53)
} infoHeader;
Pixel information structure
typedef struct _PixelInfo {
unsigned char rgbBlue; // Blue weight (0-255)
unsigned char rgbGreen; // Green component (0-255)
unsigned char rgbRed; // Red component (0-255)
//unsigned char rgbReserved;// Retain , It has to be for 0
} PixelInfo;
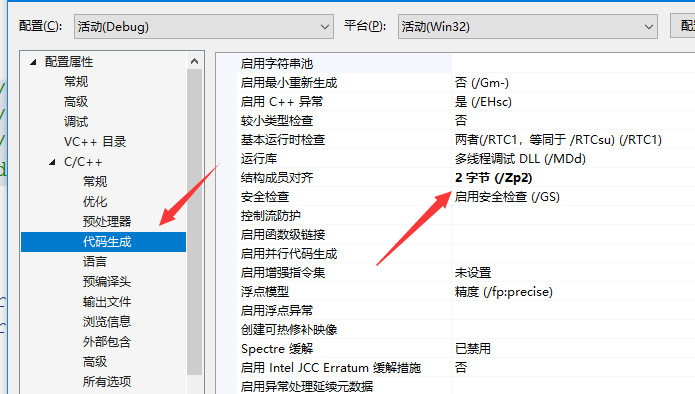
vs 2019 Set the structure alignment rules
The sample picture
Read images
int main()
{
BITMAPFILEHEADER fileHeader;
BITMAPINFOHEADER infoHeader;
PixelInfo pixel;
FILE* fp;
fp = fopen("images/123456.bmp", "rb");
//fp = fopen("images/b44.bmp", "rb");
fread(&fileHeader, sizeof(fileHeader), 1, fp);
fread(&infoHeader, sizeof(infoHeader), 1, fp);
if (fileHeader.bfType != 19778)
{
printf("%s", "err");
}
printf("%d\n", fileHeader.bfType);
printf("%d\n", fileHeader.bfSize);
unsigned char b;
unsigned char g;
unsigned char r;
unsigned char gray;
int x, y, count = 0;
int w = infoHeader.biWidth;
int h = infoHeader.biHeight;
char info[] = "* ";
int len = w * h + h + 1;
char* out = (char*)malloc(len * sizeof(char));
for (y = 0; y < h; y++)
{
for (x = 0; x < w; x++)
{
fread(&pixel, sizeof(pixel), 1, fp);
//printf("%d, %d , %d \n", pixel.rgbRed, pixel.rgbGreen, pixel.rgbBlue);
b = pixel.rgbBlue;
g = pixel.rgbGreen;
r = pixel.rgbRed;
gray = (int)(r * 0.299 + g * 0.587 + b * 0.114);
out[count++] = info[gray * strlen(info) / 256];
}
out[count++] = '\n';
}
out[count] = '\0';
printf("%s\n", out);
printf("helloWorld\n");
return 0;
}

Due to different coordinate systems , You need to modify the order of reading pixels
int main3()
{
BITMAPFILEHEADER fileHeader;
BITMAPINFOHEADER infoHeader;
PixelInfo pixel;
FILE* fp;
fp = fopen("images/123456.bmp", "rb");
//fp = fopen("images/b44.bmp", "rb");
fread(&fileHeader, sizeof(fileHeader), 1, fp);
fread(&infoHeader, sizeof(infoHeader), 1, fp);
if (fileHeader.bfType != 19778)
{
printf("%s", "err");
}
printf("%d\n", fileHeader.bfType);
printf("%d\n", fileHeader.bfSize);
unsigned char b;
unsigned char g;
unsigned char r;
unsigned char gray;
int x, y,count=0;
int w = infoHeader.biWidth;
int h = infoHeader.biHeight;
char info[] = "* ";
int len = w * h + h+1;
char* out = (char*)malloc(len * sizeof(char));
for (y = h - 1; y >= 0; y--)
{
count = (w + 1) * y;
for (x = 0; x < w; x++)
{
fread(&pixel, sizeof(pixel), 1, fp);
b = pixel.rgbBlue;
g = pixel.rgbGreen;
r = pixel.rgbRed;
gray = (int)(r * 0.299 + g * 0.587 + b * 0.114);
out[count++] = info[gray * strlen(info) / 256];
}
out[count++] = '\n';
}
out[len-1] = '\0';
printf("%s\n", out);
printf("helloWorld\n");
return 0;
}

Image distortion
Windows Specifies that the number of bytes occupied by a scan line must be 4 Multiple ( That is to long In units of ), Not enough to 0 fill .
How to calculate the number of bytes occupied by a scan line :
DataSizePerLine= (biWidth* biBitCount+31)/8;
// The number of bytes occupied by a scan line
DataSizePerLine= DataSizePerLine/44; // The number of bytes must be 4 Multiple
The size of bitmap data ( Without compression ):
DataSize= DataSizePerLine biHeight;
int main()
{
BITMAPFILEHEADER fileHeader;
BITMAPINFOHEADER infoHeader;
PixelInfo pixel;
FILE* fp;
fp = fopen("images/123456.bmp", "rb");
//fp = fopen("images/b44.bmp", "rb");
fread(&fileHeader, sizeof(fileHeader), 1, fp);
fread(&infoHeader, sizeof(infoHeader), 1, fp);
if (fileHeader.bfType != 19778)
{
printf("%s", "err");
}
printf("%d\n", fileHeader.bfType);
printf("%d\n", fileHeader.bfSize);
unsigned char b;
unsigned char g;
unsigned char r;
unsigned char gray;
int x, y,count=0;
int w = infoHeader.biWidth;
int h = infoHeader.biHeight;
int DataSizePerLine = (w * infoHeader.biBitCount + 31) / 8 / 4 * 4; // The number of bytes must be 4 Multiple
char info[] = "* ";
int len = w * h + h+1;
char* out = (char*)malloc(len * sizeof(char));
for (y = h - 1; y >= 0; y--)
{
count = (w + 1) * y;
for (x = 0; x < w; x++)
{
fread(&pixel, sizeof(pixel), 1, fp);
b = pixel.rgbBlue;
g = pixel.rgbGreen;
r = pixel.rgbRed;
gray = (int)(r * 0.299 + g * 0.587 + b * 0.114);
out[count++] = info[gray * strlen(info) / 256];
}
if (w % 4 != 0)
{
fseek(fp, DataSizePerLine - 3 * w,SEEK_CUR);
}
out[count++] = '\n';
}
out[len-1] = '\0';
printf("%s\n", out);
printf("helloWorld\n");
return 0;
}
Reference link https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39400113/article/details/104750460
Refer to Daniel video https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1n5411N7T4?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0
边栏推荐
- AcWing 1294. Cherry Blossom explanation
- Principes JDBC
- How to configure flymcu (STM32 serial port download software) is shown in super detail
- 02 staff information management after the actual project
- Request object and response object analysis
- Asp access Shaoxing tourism graduation design website
- QT creator design user interface
- Rhcsa certification exam exercise (configured on the first host)
- Install MySQL for Ubuntu 20.04
- MySQL主从复制、读写分离
猜你喜欢
MySQL master-slave replication, read-write separation

QT creator test
double转int精度丢失问题

QT creator design user interface

One click extraction of tables in PDF
QT creator runs the Valgrind tool on external applications
![[recommended by bloggers] background management system of SSM framework (with source code)](/img/7f/a6b7a8663a2e410520df75fed368e2.png)
[recommended by bloggers] background management system of SSM framework (with source code)
Install mongdb tutorial and redis tutorial under Windows
![[Thesis Writing] how to write function description of jsp online examination system](/img/f8/13144e0febf4a576bbcc3290192079.jpg)
[Thesis Writing] how to write function description of jsp online examination system
Pytorch基础
随机推荐
MySQL与c语言连接(vs2019版)
MySQL的一些随笔记录
QT creator create button
AI benchmark V5 ranking
软件测试-面试题分享
[recommended by bloggers] C WinForm regularly sends email (with source code)
Remember the interview algorithm of a company: find the number of times a number appears in an ordered array
Aborted connection 1055898 to db:
Install MySQL for Ubuntu 20.04
Data dictionary in C #
[Thesis Writing] how to write function description of jsp online examination system
Antlr4 uses keywords as identifiers
Ansible practical Series III_ Task common commands
Project practice - background employee information management (add, delete, modify, check, login and exit)
MySQL主從複制、讀寫分離
Ansible实战系列二 _ Playbook入门
Swagger, Yapi interface management service_ SE
Test objects involved in safety test
数据库高级学习笔记--SQL语句
打开浏览器的同时会在主页外同时打开芒果TV,抖音等网站