当前位置:网站首页>Reflection (II)
Reflection (II)
2022-07-07 07:08:00 【Cold Snowflakes】
Static loading and dynamic loading
Static loading : Load related classes at compile time , If it is not found, an error is reported .
Dynamic loading : Load the required classes at runtime .
Reflection is dynamic loading , Only when it is executed , To load the class .
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]) throws ClassNotFoundException{
// Static loading , Load when compiling , If you don't find it, you will report an error , Strong dependence
Cat cat = new Cat();
// Dynamic loading , Don't worry about it when compiling , I won't check Whether the loaded class exists
// The code will not be loaded until it is actually run and executed
Class.forName("com.itheima.Cat");
}
}
Class loading
When a program wants to use a class , If the class has not been loaded into memory , Then the system will go through Class loading , Class connection , Class initialization These three steps are used to initialize the class .
In general ,JVM These three steps will be completed in succession , So sometimes these three steps are collectively referred to as class loading .
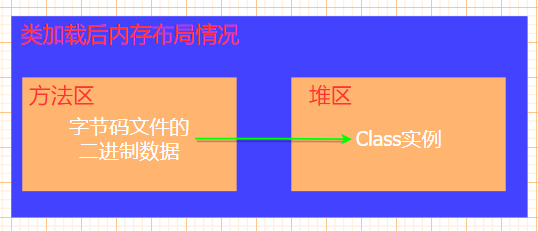
Class loading :JVM Take bytecode from different data sources (class file ,jar package , Network, etc. ) Convert to binary byte stream to load into memory , And generate Class Instance object .
Class connection
Validation phase : Make sure .class The byte stream of the file contains information that meets the requirements of the current virtual machine , Does not harm the security of virtual machine itself .
Preparation stage : by static Decorated field variables allocate memory and set default initial values , Not included final Embellished static, because final It will be allocated at compile time .
Analytic stage : It mainly replaces the symbolic reference in the constant pool with a direct reference .
Class initialization : Last stage of class loading , Actually start executing what's defined in the class Java Program code , This stage is the implementation of < clinit >() Method process .
< clinit >() Method is created by the compiler in the order in which statements appear in the source file , Automatically collect the assignment actions of all static variables in the class and the statements in the static code block in turn , And merge .
Virtual opportunity guarantees a class of < clinit >() Methods are properly locked in a multithreaded environment , Sync , If multiple threads are initializing a class at the same time , There will only be one thread to execute this class < clinit >() Method , All other threads need to block and wait , Until the active thread executes < clinit >() Methods to complete .
If this class has a superclass , Then initialize it , Perform static initializer and static initialization member variables .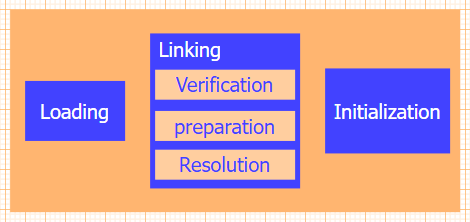
@SuppressWarnings({
"all"})
public class lambdademo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fun.num);
}
}
/** * stay Linking Of Preparation Stage , Yes num Allocate memory , Initialize to 0 * stay Initialization Stage , collect Static variables , Static code block to <clinit> In the method , And implement <clinit> Method */
class fun {
static{
System.out.println(" Static code blocks are executed ");
num = 300;
}
static int num = 100;
public fun(){
System.out.println(" The constructor is executed ");
}
}
// Output
Static code blocks are executed
100
// The results of the analysis , It is obvious that , What is done in class loading , Of course, we didn't create objects , So the constructor is not called
// The general process should be like this
1. load fun class , And generate a corresponding Class example , And in the method area Bytecode binary data
2. Linking Stage , by num Allocate memory , Initialize to 0
3. Initialization Stage , In the order it appears in the source file , Collect the assignment actions of all static variables and the statements in the static code block in turn , Merge to <clinit> In the method , And implement .
clinit() {
/// Statements in static code blocks /
System.out.println(" Static code blocks are executed ");
num = 300;
/// Static variable assignment statement //
num = 100;
}
Field Some other of the class API
getModifiers(): default/0 , public/1 , private/2 , protected/4 , static/8 , final/16
// have access to Modifier.toString(cls.getModifiers()) Convert a number to a string
getType(): Return to one Class object , Represents the type of the property
getName(): Return property name
Class<fun> funClass = fun.class;
Field[] fields = funClass.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field f : fields){
System.out.println(f.getModifiers()); // The returned value represents its access modifier
System.out.println(f.getType()); // int/double/java.lang.String ...
System.out.println(f.getName()); // Property name
}
Mehod class
getModifiers() // Access modifier
getReturnType() // return Class object , Represents the return type
getName() // Method name
getParameterTypes() // return Class[], Represents an array of parameter types
Create objects by reflection
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.itheima.fun");
// 1. Using a parameterless constructor
Object o1 = cls.newInstance();
// 2. Through a parametric constructor ( Specify the parameter list )
Constructor<?> cons1 = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
Object o2 = cons1.newInstance("xxx");
// 3. You can also use private Constructor
Constructor<?> cons2 = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class);
cons2.setAccessible(true);
Object o3 = cons2.newInstance(100, "fang_shou_ba..");
Class Objects are generated as follows :
1、 Class name .class
JVM Class loader will be used , Load classes into memory , Do not do class initialization , return Class The object of .
2、Class.forName(“ The fully qualified name of the class ”)
Load class , And do class initialization ( Will execute static code blocks and initialize static variables ), return Class The object of .
Usually use new When you create an object , The class will be loaded first , After performing Non static code block , Then execute the constructor .
Several generation Class The difference between instance methods
边栏推荐
- 数据资产管理与数据安全国内外最新趋势
- Exception of DB2 getting table information: caused by: com ibm. db2.jcc. am. SqlException: [jcc][t4][1065][12306][4.25.13]
- Implementation of AVL tree
- 详解机器翻译任务中的BLEU
- CompletableFuture使用详解
- Learning records on July 4, 2022
- Answer to the second stage of the assignment of "information security management and evaluation" of the higher vocational group of the 2018 Jiangsu Vocational College skills competition
- $parent(获取父组件) 和 $root(获取根组件)
- 子组件传递给父组件
- 带你刷(牛客网)C语言百题(第一天)
猜你喜欢

Mysql---- import and export & View & Index & execution plan
子组件传递给父组件

Can 7-day zero foundation prove HCIA? Huawei certification system learning path sharing
The latest trends of data asset management and data security at home and abroad
2022年全国所有A级景区数据(13604条)
SolidWorks的GB库(钢型材库,包括铝型材、铝管等结构)安装及使用教程(生成铝型材为例)
Bus消息总线
$refs:组件中获取元素对象或者子组件实例:

大促过后,销量与流量兼具,是否真的高枕无忧?
Use of completable future
随机推荐
Leetcode T1165: 日志分析
【JDBC以及内部类的讲解】
Big coffee gathering | nextarch foundation cloud development meetup is coming
异步组件和Suspense(真实开发中)
How can clothing stores make profits?
Matlab tips (29) polynomial fitting plotfit
一条慢SQL拖死整个系统
Graduation design game mall
Answer to the first stage of the assignment of "information security management and evaluation" of the higher vocational group of the 2018 Jiangsu Vocational College skills competition
服装门店如何盈利?
How Oracle backs up indexes
readonly 只读
算法---比特位计数(Kotlin)
使用TCP/IP四层模型进行网络传输的基本流程
main函数在import语句中的特殊行为
Stack and queue-p78-8 [2011 unified examination true question]
Esxi attaching mobile (Mechanical) hard disk detailed tutorial
如何给目标机器人建模并仿真【数学/控制意义】
MOS管参数μCox得到的一种方法
[noi simulation] regional division (conclusion, structure)