当前位置:网站首页>[understand series after reading] 6000 words teach you to realize interface automation from 0 to 1
[understand series after reading] 6000 words teach you to realize interface automation from 0 to 1
2022-07-05 03:54:00 【Little brother said test】
Last time I mentioned that if I had time, I would share the interface automation I was working on recently , Today I will start from the framework 、 Design 、 The test class is shared in three aspects . There may be deficiencies or areas that can be optimized , Welcome to correct , Friends with ideas can contact me backstage !
The framework is introduced
What I use here is Java Language , be based on TestNG The test framework , Support continuous integration , Automatic build and test . It mainly has the following characteristics :
Data driven design , Use TestNG Medium @DataProvider Read Excel Automated test cases stored in .
Use HttpClient send out Http request , And unified interface response The return value is String
Use fastJson Data analysis
AssertJ For checkpoint settings
Maven Project 、 Dependency management
Design
I am responsible for the interface automation of the withholding Group , In fact, I'm not very familiar with business , But it doesn't make much difference , Simply walk through the process and you can basically start .

java Interface code
structure

api:http Interface
common: Utility class
dto: Data transmission object , Used for data transmission objects between presentation layer and service layer .
decompose
api

The interface automation of the withholding group should maintain both the client and Web End , So I stepped on some pits in the early stage , I wanted to encapsulate one request And a response, Distinguish the end in the test class , Finally, it was found that this method was not desirable , Because the login method is completely different , Later, I simply wrote it separately .
common

dto

Basically, I have a clear idea here , The content mainly focuses on common Utility class , Let's take a detailed look at what each class encapsulates .
common Detailed explanation
Following pair common Analyze each class in , Because it involves business , So I can only take appropriate screenshots + touch on lightly , Believe that smart as you , At a glance .
One 、【 client 】
HttpKhdRequest Login request of the client
Requested URL And port number from config.properties take ;
The requested user information is from user.properties

Request interface

Because the login client needs to obtain security authentication and obtain token, therefore AuthorizationHq and tokenhqbyTyrk Take it out and write it alone .
AuthorizationHq

tokenhqbyTyrk

remarks :dto Under the UserDTO Here we use .
ApiKhdResponse The client returns Check the interface document , Return the basic information .

So the encapsulation of my return class mainly includes the following :
public class ApiKhdResponse {
private String type;
private Object data;
private String errorCode;
private String errorMessage;
private String reason;
public JSONObject convert2JsonObject() {
String dataText = JSON.toJSONString(data, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue);
JSONObject dataObject = JSON.parseObject(dataText);
return dataObject;
}
public JSONArray convert2JsonArray() {
String dataText = JSON.toJSONString(data, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue);
JSONArray dataArray = JSON.parseArray(dataText);
return dataArray;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public void assertSuccess(){
String type=getType();
assertEquals("SUCCESS", type);
}
public void assertFailed() {
String type=getType();
// Some return failed interfaces ,type return ERROR
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(type)) {
assertTrue(true);
return;
}
assertTrue(!type.equals("SUCCESS") && !type.contains("ERROR"));
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String getErrorCode() {
return errorCode;
}
public void setErrorCode(String errorCode) {
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public String getErrorMessage() {
return errorMessage;
}
public void setErrorMessage(String errorMessage) {
this.errorMessage = errorMessage;
}
public String getReason() {
return reason;
}
public void setReason(String reason) {
this.reason = reason;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ApiResponse{" +
"type='" + type + '\'' +
", data=" + data +
", errorCode='" + errorCode + '\'' +
", errorMessage='" + errorMessage + '\'' +
", reason='" + reason + '\'' +
'}';
}
public <T> T getBodyBean(Class<T> clazz) { return JSON.parseObject(data.toString(), clazz); }
}
remarks :

Don't write this content by hand , It's easy to make mistakes ,IDEA It can be brought out automatically .

RestUtil Client security verification
What I mainly use here is Hmac Encryption algorithms and AES encryption algorithm .
TokenUtil Client generation token
Two 、【Web End 】
HttpWebRequest Web Login request of client

Request interface

getAuthorizationToken It is written in combination with our actual situation ( There is one MOCK platform ), We authorize login through the interface platform .
ApiWebResponse Web End return
Check the interface document , Return the basic information .

So the encapsulation of my return class mainly includes the following :
public class ApiWebResponse<T extends Object> {
@Getter
private String code;
@Getter
private Object[] params;
@Getter
private String message;
@Getter
private Object data;
@Getter
private String appCodeForEx;
@Getter
private String originalErrorCode;
/**
* rid
*/
@Setter
@Getter
private String rid;
/**
* @param code
* @return
*/
public ApiWebResponse<T> setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
return this;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
/**
* @param message
* @return
*/
public ApiWebResponse<T> setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
return this;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
/**
* @param data
* @return
*/
public ApiWebResponse<T> setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
return this;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
/**
* @param params
* the params to set
*/
public ApiWebResponse<T> setParams(Object[] params) {
this.params = params;
return this;
}
public Object[] getParams() {
return params;
}
public JSONObject convert2JsonObject() {
String dataText = JSON.toJSONString(data, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue);
JSONObject dataObject = JSON.parseObject(dataText);
return dataObject;
}
public JSONArray convert2JsonArray() {
String dataText = JSON.toJSONString(data, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue);
JSONArray dataArray = JSON.parseArray(dataText);
return dataArray;
}
public static boolean isSuccess(ApiWebResponse<?> apiResponse) {
boolean success = false;
if (apiResponse == null) {
return success;
}
if ("SUCCESS".equals(apiResponse.getCode())) {
success = true;
}
return success;
}
}
XmlParserUtil Parsing tool
The encapsulation of this class mainly includes the basic path 、 Get account information 、 Get file path information .
Basic path

Get account information

remarks :dto Under the ZhxxDTO Here we use .
Get file path information

3、 ... and 、【 database 】
DBUnitBaseTest

Database information, if there is a new database or the database is split in the process of business iteration, you need to dataBase.xml and DBUnitBaseTest maintain , Otherwise, the implementation of the example will fail . My colleagues have other suggestions about this content , I will learn from it later .
resources
api

zhxx What is maintained here is Web Accounts in different environments on the end , The corresponding is java Interface code dto, Each project is different , Not always .
Test class
In fact, we wrote so much code just to write less code when writing test class interfaces , Don't believe it. :

Next, let's practice writing a withholding Web End interface .
1. First, review the structure

2. Start writing interfaces
2.1 stay web End request interface , Packet capture interface .

2.2 View interface documentation .

2.3 Start writing
2.3.1 Add test class
Right click Add Package, Add layer by layer , Until the last layer, right-click to add Java Class.

2.3.2 Write interface code
package com.XXX.api.kjweb.zrr.XXXX;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.XXX.common.ApiWebResponse;
import com.XXX.common.DBUnitBaseTest;
import com.XXX.common.HttpWebRequest;
import com.XXX.api.util.AssertUtil;
import junitx.framework.Assert;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import ru.yandex.qatools.allure.annotations.Title;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Objects;
import static org.testng.AssertJUnit.assertEquals;
/**
* create by lxl01 on 2021/5/18
*/
@Title(" Basic information query of natural person ")
public class QueryTest extends HttpWebRequest {
@Test(dataProvider = "excel", groups = {"kjweb_http"})
public void testQuery(String run, String testname, String yhm, String device,String data, String expectData) {
// Interface request
String Api = "/web/zrr/XXXX/query";
// Interface to return
ApiWebResponse response = requestKjd(Api, HttpMethod.GET, JSON.parseObject(data, HashMap.class), yhm,device);
// Verify that the actual returned results are consistent with the expected results ( Check only data)
assertEquals(Objects.toString(response.getData(), ""), expectData);
}
}
2.4 Details
2.4.1 Package import , Import whatever you reference .
2.4.2 Table fields contain run、testName、yhm、device、data、expectData, See below , Add... As needed .

2.4.3 Interface request Put... Directly URL Put it on
2.4.4 Interface to return
ApiWebResponse It is separately sealed as withholding Web End of the return check class , stay common Next .
requestKjd It is separately sealed as withholding Web End of the request class , stay common Next .
2.4.5 check
Verify what content can be based on business needs + Write interface documents . Let's first look at the returned data of this interface .

Here are some common verifications I use
A. Check all return - The first verification method
Assert.assertEquals(Objects.toString(response, ""), expectData);
The result is

B. Check all return - The second verification method
AssertUtil.isJsonEquals(response, expectData,false);
The result is

A and B When using, you need to import different packages , The difference between the two can be seen by left clicking on the corresponding class , Are common classes encapsulated at the bottom .
A Import import junitx.framework.Assert;

B Import import com.xqy.api.util.AssertUtil;

C Verify that the returned data data
assertEquals(Objects.toString(response.getData(), ""), expectData);
The result is

among getData It's me. ApiWebResponse Class

D Check the database
JsonUtils.assertDBEquals(jdbcTemplateOfSb, returnSql, returnDB);
Debugging and execution
After writing, click execute in the test class , If an error is reported during execution , Follow the prompts on the console debug.
As for how to deal with problems debug You can read the article I wrote before , The title is 《 how debug Troubleshoot problems and resolve conflicts 》.
This article can be read upside down , First look at the test class , Look at the previous content . The reason why this test class can pass is because of the previous building foundation ; And why should we build the foundation in front , Because the later maintenance test class is very simple 、 convenient .
All right. , The content of the article is updated here , I will be off work soon. .
Learning resource sharing
Finally, thank everyone who reads my article carefully , Watching the rise and attention of fans all the way , Reciprocity is always necessary , Although it's not very valuable , If you can use it, you can take it
These materials , For thinking 【 Advanced test development 】 For our friends, it should be the most comprehensive and complete war preparation warehouse , This warehouse also accompanied me through the most difficult journey , I hope it can help you ! Everything should be done as soon as possible , Especially in the technology industry , We must improve our technical skills . I hope that's helpful …….

边栏推荐
- ABP vNext microservice architecture detailed tutorial - distributed permission framework (Part 2)
- 一文带你了解BI的前世今身与企业数字化转型的关系
- Soul 3: what is interface testing, how to play interface testing, and how to play interface automation testing?
- grandMA2 onPC 3.1.2.5的DMX参数摸索
- [web Audit - source code disclosure] obtain source code methods and use tools
- [deep learning] deep learning reference materials
- 花了2晚,拿到了吴恩达@斯坦福大学的机器学习课程证书
- Subversive cognition: what does SRE do?
- 灵魂三问:什么是接口测试,接口测试怎么玩,接口自动化测试怎么玩?
- Use of vscode software
猜你喜欢
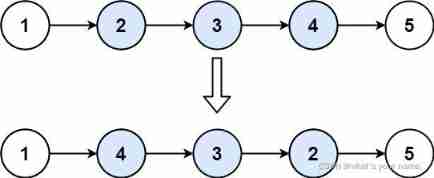
Leetcode92. reverse linked list II
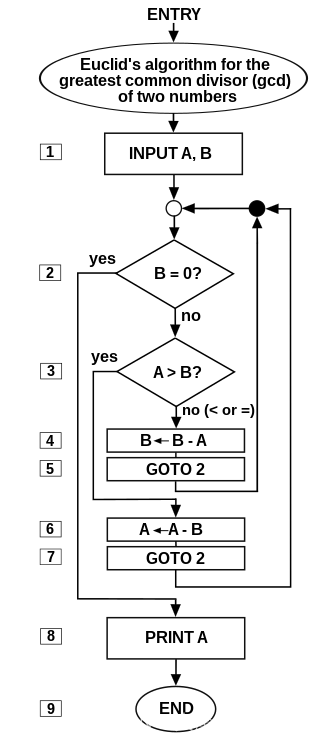
An elegant program for Euclid‘s algorithm
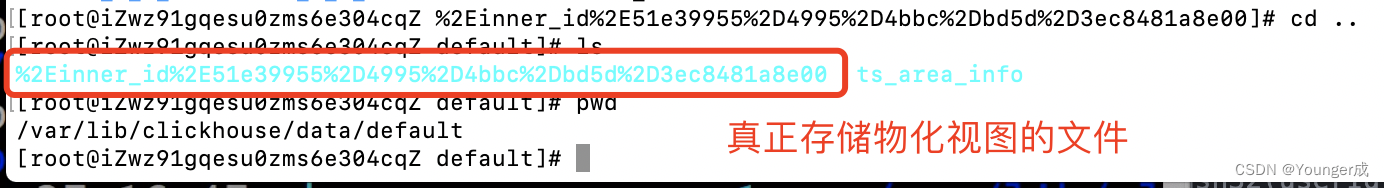
Clickhouse materialized view

Test d'automatisation de l'interface utilisateur télécharger manuellement le pilote du navigateur à partir de maintenant
![[web source code code code audit method] audit skills and tools](/img/7c/2c26578da084b3cd15d8f252b0e132.png)
[web source code code code audit method] audit skills and tools

About the recent experience of writing questions

How to use jedis of redis
![[vérification sur le Web - divulgation du code source] obtenir la méthode du code source et utiliser des outils](/img/ea/84e67a1fca0e12cc4452c744c242b4.png)
[vérification sur le Web - divulgation du code source] obtenir la méthode du code source et utiliser des outils
【无标题】
面试字节,过关斩将直接干到 3 面,结果找了个架构师来吊打我?
随机推荐
Why is there a reincarnation of 60 years instead of 120 years in the tiangan dizhi chronology
Necessary fonts for designers
[Chongqing Guangdong education] 2777t green space planning reference questions of National Open University in autumn 2018
Official announcement! The third cloud native programming challenge is officially launched!
51 independent key basic experiment
In MySQL Association query, the foreign key is null. What if the data cannot be found?
How is the entered query SQL statement executed?
Deflocculant aminoiodotide eye drops
IronXL for .NET 2022.6
[groovy] string (string splicing | multi line string)
【web源码-代码审计方法】审计技巧及审计工具
Anti debugging (basic principles of debugger Design & NT NP and other anti debugging principles)
Multimedia query
我就一写代码的,王总整天和我谈格局...
PlasticSCM 企业版Crack
Solve the problem that sqlyog does not have a schema Designer
Why do some programmers change careers before they are 30?
[punch in questions] integrated daily 5-question sharing (phase III)
[deep learning] deep learning reference materials
[wp]bmzclub writeup of several questions