当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode(417)——太平洋大西洋水流问题
Leetcode(417)——太平洋大西洋水流问题
2022-07-06 22:50:00 【SmileGuy17】
Leetcode(417)——太平洋大西洋水流问题
题目
有一个 m × n m \times n m×n 的矩形岛屿,与 太平洋 和 大西洋 相邻。 “太平洋” 处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而 “大西洋” 处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
这个岛被分割成一个由若干方形单元格组成的网格。给定一个 m × n m \times n m×n 的整数矩阵 heights , heights[r][c] 表示坐标 (r, c) 上单元格 高于海平面的高度 。
岛上雨水较多,如果相邻单元格的高度 小于或等于 当前单元格的高度,雨水可以直接向北、南、东、西流向相邻单元格。水可以从海洋附近的任何单元格流入海洋。
返回网格坐标 result 的 2D 列表 ,其中 result[i] = [ri, ci] 表示雨水从单元格 (ri, ci) 流动 既可流向太平洋也可流向大西洋 。
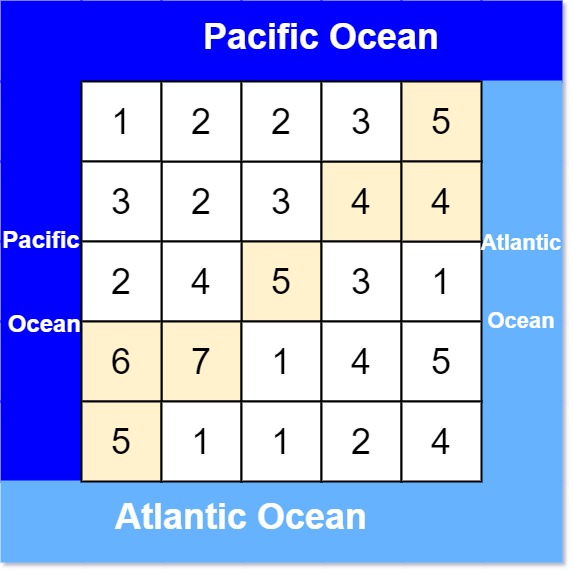
示例 1:
输入: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
输出: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
示例 2:
输入: heights = [[2,1],[1,2]]
输出: [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
提示:
- m == heights.length
- n == heights[r].length
- 1 1 1 <= m, n <= 200 200 200
- 0 0 0 <= heights[r][c] <= 1 0 5 10^5 105
题解
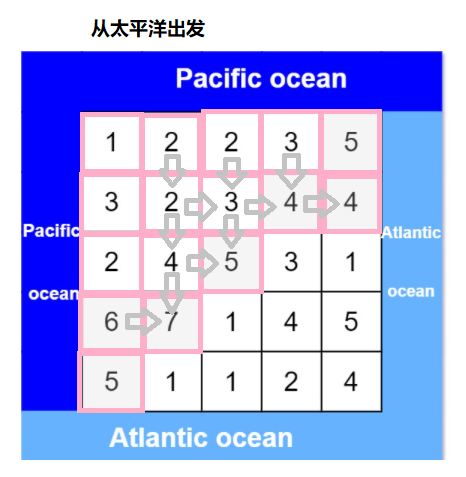
从边界开始反向搜索,以减少时间复杂度
方法一:DFS
思路
雨水的流动方向是从高到低,每个单元格上的雨水只能流到高度小于等于当前单元格的相邻单元格。从一个单元格开始,通过搜索的方法模拟雨水的流动,则可以判断雨水是否可以从该单元格流向海洋。
如果直接以每个单元格作为起点模拟雨水的流动,则会重复遍历每个单元格,导致时间复杂度过高。为了降低时间复杂度,可以从矩阵的边界开始反向搜索寻找雨水流向边界的单元格,反向搜索时,每次只能移动到高度相同或更大的单元格。
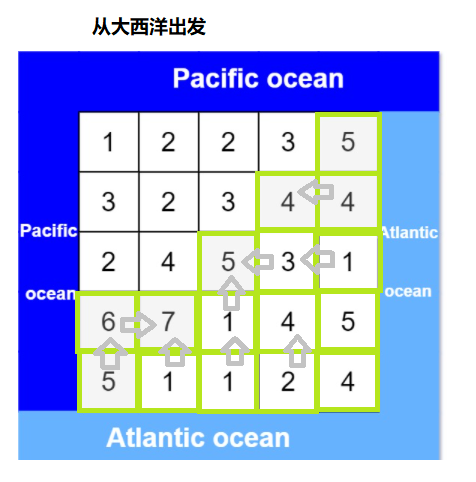
由于矩阵的左边界和上边界是太平洋,矩阵的右边界和下边界是大西洋,因此从矩阵的左边界和上边界开始反向搜索即可找到雨水流向太平洋的单元格,从矩阵的右边界和下边界开始反向搜索即可找到雨水流向大西洋的单元格。
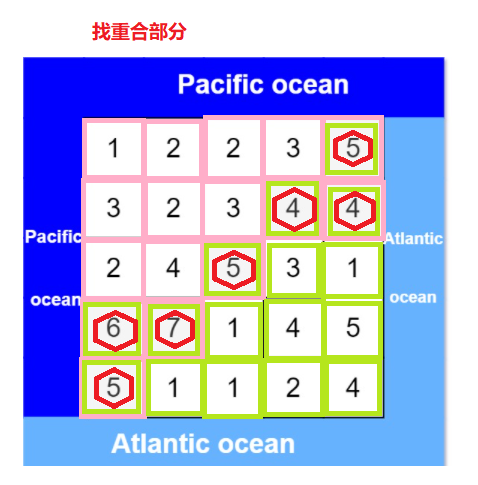
可以使用深度优先搜索实现反向搜索,搜索过程中需要记录每个单元格是否可以从太平洋反向到达以及是否可以从大西洋反向到达。反向搜索结束之后,遍历每个网格,如果一个网格既可以从太平洋反向到达也可以从大西洋反向到达,则该网格满足太平洋和大西洋都可以到达,将该网格添加到答案中。
代码实现
Leetcode 官方题解:
static const int dirs[4][2] = {
{
-1, 0}, {
1, 0}, {
0, -1}, {
0, 1}};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> heights;
void dfs(int row, int col, vector<vector<bool>> & ocean) {
int m = ocean.size();
int n = ocean[0].size();
if (ocean[row][col]) {
return;
}
ocean[row][col] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newRow = row + dirs[i][0], newCol = col + dirs[i][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < m && newCol >= 0 && newCol < n && heights[newRow][newCol] >= heights[row][col]) {
dfs(newRow, newCol, ocean);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
this->heights = heights;
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> pacific(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(i, 0, pacific);
}
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dfs(0, j, pacific);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(i, n - 1, atlantic);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
dfs(m - 1, j, atlantic);
}
vector<vector<int>> result;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
vector<int> cell;
cell.emplace_back(i);
cell.emplace_back(j);
result.emplace_back(cell);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
我自己的:(递归)
class Solution {
vector<int> direction{
-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; //用于遍历四个方位
void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& ocean, int a, int b){
ocean[a][b] = true;
int p1, p2;
for(int n = 0; n < 4; n++){
p1 = a + direction[n];
p2 = b + direction[n+1];
if(0 > p1 || p1 >= heights.size() || 0 > p2 || p2 >= heights[0].size())
continue;
if(heights[p1][p2] >= heights[a][b] && ocean[p1][p2] == false)
DFS(heights, ocean, p1, p2);
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
// 从外到内
int n = heights.size(), m = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<vector<bool>> Pacific_Ocean(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
vector<vector<bool>> Atlantic_Ocean(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
// 上下
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
DFS(heights, Pacific_Ocean, 0, i);
DFS(heights, Atlantic_Ocean, n -1, i);
}
// 左右
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
DFS(heights, Pacific_Ocean, i, 0);
DFS(heights, Atlantic_Ocean, i, m - 1);
}
for(int a = 0; a < n; a++){
for(int b = 0; b < m; b++){
if(Pacific_Ocean[a][b] && Atlantic_Ocean[a][b])
ans.push_back(vector<int>{
a, b});
}
}
return ans;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),其中 m m m 和 n n n 分别是矩阵 heights \textit{heights} heights 的行数和列数。深度优先搜索最多遍历每个单元格两次,寻找太平洋和大西洋都可以到达的单元格需要遍历整个矩阵,因此时间复杂度是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn)。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),其中 m m m 和 n n n 分别是矩阵 heights \textit{heights} heights 的行数和列数。深度优先搜索的递归调用层数是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),记录每个单元格是否可以到达太平洋和大西洋需要 O ( 2 × m n ) O(2 \times mn) O(2×mn) 的空间,因此空间复杂度是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn)。
方法二:BFS
思路
反向搜索也可以使用广度优先搜索实现。搜索过程中同样需要记录每个单元格是否可以从太平洋反向到达以及是否可以从大西洋反向到达。反向搜索结束之后,遍历每个网格,如果一个网格既可以从太平洋反向到达也可以从大西洋反向到达,则该网格满足太平洋和大西洋都可以到达,将该网格添加到答案中。
代码实现
Leetcode 官方题解:
static const int dirs[4][2] = {
{
-1, 0}, {
1, 0}, {
0, -1}, {
0, 1}};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> heights;
void bfs(int row, int col, vector<vector<bool>> & ocean) {
if (ocean[row][col]) {
return;
}
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
ocean[row][col] = true;
queue<pair<int, int>> qu;
qu.emplace(row, col);
while (!qu.empty()) {
auto [row, col] = qu.front();
qu.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newRow = row + dirs[i][0], newCol = col + dirs[i][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < m && newCol >= 0 && newCol < n && heights[newRow][newCol] >= heights[row][col] && !ocean[newRow][newCol]) {
ocean[newRow][newCol] = true;
qu.emplace(newRow, newCol);
}
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
this->heights = heights;
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> pacific(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
bfs(i, 0, pacific);
}
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
bfs(0, j, pacific);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
bfs(i, n - 1, atlantic);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
bfs(m - 1, j, atlantic);
}
vector<vector<int>> result;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
vector<int> cell;
cell.emplace_back(i);
cell.emplace_back(j);
result.emplace_back(cell);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
我自己的:
class Solution {
vector<int> direction{
-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; //用于遍历四个方位
void BFS(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& ocean, int a, int b){
queue<pair<int, int>> qu;
ocean[a][b] = true;
qu.push(make_pair(a, b));
int n, m, nextn, nextm;
while(!qu.empty()){
n = qu.front().first;
m = qu.front().second;
qu.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
nextn = n + direction[i];
nextm = m + direction[i+1];
if(0 > nextn || nextn >= heights.size() || 0 > nextm || nextm >= heights[0].size())
continue;
if(heights[nextn][nextm] >= heights[n][m] && ocean[nextn][nextm] == false){
ocean[nextn][nextm] = true;
qu.push(make_pair(nextn, nextm));
}
}
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
// 从外到内
int n = heights.size(), m = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<vector<bool>> Pacific_Ocean(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
vector<vector<bool>> Atlantic_Ocean(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
// 上下
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
BFS(heights, Pacific_Ocean, 0, i);
BFS(heights, Atlantic_Ocean, n - 1, i);
}
// 左右
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
BFS(heights, Pacific_Ocean, i, 0);
BFS(heights, Atlantic_Ocean, i, m - 1);
}
for(int a = 0; a < n; a++){
for(int b = 0; b < m; b++){
if(Pacific_Ocean[a][b] && Atlantic_Ocean[a][b])
ans.push_back(vector<int>{
a, b});
}
}
return ans;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),其中 m m m 和 n n n 分别是矩阵 heights \textit{heights} heights 的行数和列数。广度优先搜索最多遍历每个单元格两次,寻找太平洋和大西洋都可以到达的单元格需要遍历整个矩阵,因此时间复杂度是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn)。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),其中 m m m 和 n n n 分别是矩阵 heights \textit{heights} heights 的行数和列数。广度优先搜索的队列空间是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),记录每个单元格是否可以到达太平洋和大西洋需要 O ( 2 × m n ) O(2 \times mn) O(2×mn) 的空间,因此空间复杂度是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn)。
方法三:并查集
思路
其中维护连通性部分可以使用「并查集」来做:起始将与太平洋相邻的边缘格子与 Pacific_Ocean 连通,将与大西洋相邻的边缘格子与 Atlantic_Ocean 连通,然后运行一遍方法一或方法二中的 DFS/BFS,最后将既和 Pacific_Ocean 连通又和 Atlantic_Ocean 连通的格子加入答案。
代码实现
我自己的:
无,忘记写了
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),其中 m m m 和 n n n 分别是矩阵 heights \textit{heights} heights 的行数和列数。DFS 和 BFS 最多遍历每个单元格两次,寻找太平洋和大西洋都可以到达的单元格需要遍历整个矩阵,因此时间复杂度是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn)。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),其中 m m m 和 n n n 分别是矩阵 heights \textit{heights} heights 的行数和列数。BFS 的队列空间是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),而 DFS 的递归栈空间或辅助栈空间是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn)。记录每个单元格是否可以到达太平洋和大西洋需要 O ( 2 × m n ) O(2 \times mn) O(2×mn) 的空间,因此空间复杂度是 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn)。
边栏推荐
- How to design API interface and realize unified format return?
- 一文搞懂常见的网络I/O模型
- Mysql database (basic)
- Inventory host list in ansible (I wish you countless flowers and romance)
- 最全常用高数公式
- Run the command once per second in Bash- Run command every second in Bash?
- 【数模】Matlab allcycles()函数的源代码(2021a之前版本没有)
- [Yugong series] go teaching course 005 variables in July 2022
- [line segment tree practice] recent requests + area and retrieval - array modifiable + my schedule I / III
- 一个酷酷的“幽灵”控制台工具
猜你喜欢
Introduction to namespace Basics
AttributeError: module ‘torch._C‘ has no attribute ‘_cuda_setDevice‘
sublime使用技巧
acwing 843. N-queen problem
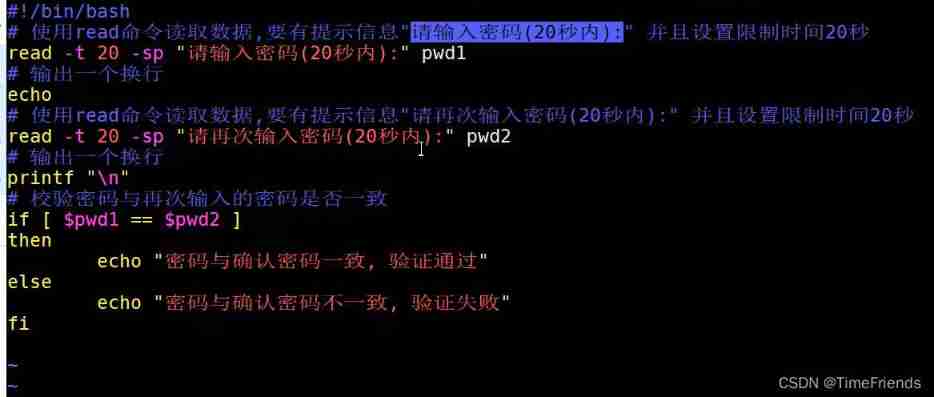
Read of shell internal value command
![[736. LISP syntax parsing]](/img/62/5e2aeec150096aa3fd81025d146255.png)
[736. LISP syntax parsing]

CentOS 7.9安装Oracle 21c历险记
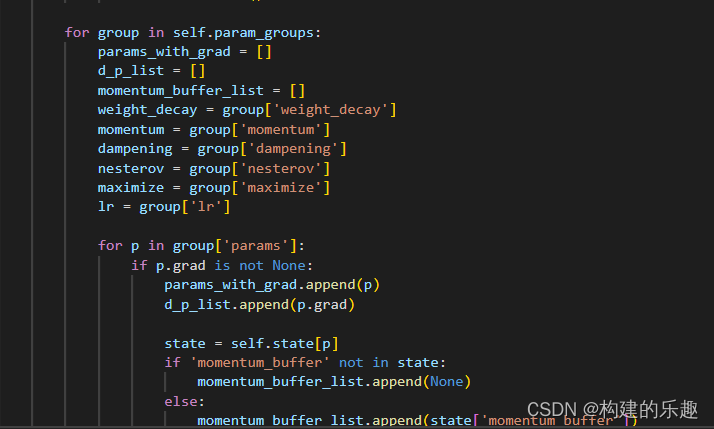
torch optimizer小解析
![[line segment tree practice] recent requests + area and retrieval - array modifiable + my schedule I / III](/img/13/d598bb53b71fbadd4a97c603152124.png)
[line segment tree practice] recent requests + area and retrieval - array modifiable + my schedule I / III
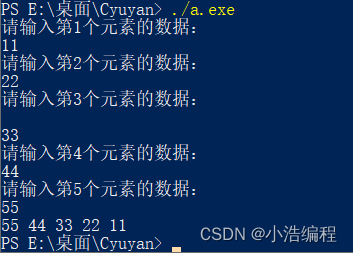
Pointer and array are input in function to realize reverse order output
随机推荐
最全常用高数公式
深入解析Kubebuilder
File upload vulnerability summary
关于01背包个人的一些理解
Addressable 预下载
Batch normalization (Standardization) processing
Operand of null-aware operation ‘!‘ has type ‘SchedulerBinding‘ which excludes null.
01 machine learning related regulations
第一篇论文的写作流程
Programmers go to work fishing, so play high-end!
Code source de la fonction [analogique numérique] MATLAB allcycles () (non disponible avant 2021a)
How to design API interface and realize unified format return?
谈谈讲清楚这件事的重要性
Why do many people misunderstand technical debt
STM32 encapsulates the one key configuration function of esp8266: realize the switching between AP mode and sta mode, and the creation of server and client
JS variable case
Flex layout and usage
JS variable plus
Ansible报错:“msg“: “Invalid/incorrect password: Permission denied, please try again.“
Inventory host list in ansible (I wish you countless flowers and romance)