当前位置:网站首页>Two traversal sequences are known to construct binary trees
Two traversal sequences are known to construct binary trees
2022-07-02 15:39:00 【-Xiaoxiaobai-】
The traversal order of binary tree is : Access the root node first , The preorder then traverses the left subtree , Traverse the right subtree again in the preceding order .
The order of traversal is : The middle order traverses the left subtree of the root node , Then access the root node , Finally, the middle order traverses the right subtree .
The order of subsequent traversal is : Then traverse the left subtree of the root node , Then the post order traverses the right subtree , Finally, the root node is accessed .
One , Known before , Middle order traversal sequence to construct binary tree

【 Main idea 】
1. Traverse through the preamble , Know the root
2. Traverse through the middle order , Know the length of the left subtree .
3. Only the unknown of the right subtree is left , Just use recursion to build
// Auxiliary function
struct TreeNode* build(int* preorder, int l1, int r1, int* inorder, int l2, int r2){
if (l1 > r1) return NULL;
struct TreeNode* root = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->val = preorder[l1]; // Preorder traversal tells where the root is
int mid = l2;
while (inorder[mid] != root->val) mid++;
int leftSize = mid - l2; // The middle order traversal tells the length of the left subtree ( Just before the root )
// Recursively build
root->left = build(preorder, l1 + 1, l1 + leftSize, inorder, l2, mid - 1);
root->right = build(preorder, l1 + leftSize + 1, r1, inorder, mid + 1, r2);
return root;
}
struct TreeNode* buildTree(int* preorder, int preorderSize, int* inorder, int inorderSize){
return build(preorder, 0, preorderSize - 1, inorder, 0, inorderSize - 1) ;
} Two , Known , After traversing the binary sequence tree 
【 Main idea 】
1. The key is to figure out how the postorder traversal represents the left subtree 、 Right subtree 、 root
· The former sequence traversal : root / The left subtree / Right subtree -> Root in the head
· In the sequence traversal : The left subtree / root / Right subtree -> The length of the left subtree
· After the sequence traversal : The left subtree / Right subtree / root -> Root in tail
The relationship :
Determine the length of the left subtree by traversing the middle order : leftSize = left_in - mid
Before the order preorder Middle preface inorder In the following order postorder
The left subtree (left_pr + 1, left_pr + leftSize) || (left_in, mid - 1) || (left_po, left_po + leftSize - 1)
Right subtree (left_pr + leftSize + 1, right_pr) || (mid + 1, right_in) || (po + leftSize, right_po - 1)
*mid Because it was born in the middle order traversal , It can only be used in middle order traversal
* Why should the left subtree in post order traversal - 1? Because this is from “0” Array of starting numbers , Its subscript is to “ - 1”
* It can be inferred that the left subtree in preorder traversal does not need - 1. Because the head of preorder traversal is root , To make into “ from 1 Start ” Array of
// Auxiliary function
struct TreeNode* build(int* inorder, int left_in, int right_in, int* postorder, int left_po, int right_po) {
if (left_in > right_in) return NULL;
struct TreeNode* root = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->val = postorder[right_po];
int mid = left_in;
while (inorder[mid] != root->val) mid++;
int leftSize = mid - left_in;
root->left = build(inorder, left_in, mid - 1, postorder, left_po, left_po + leftSize - 1);
root->right = build(inorder, mid + 1, right_in, postorder, left_po + leftSize, right_po - 1);
return root;
}
struct TreeNode* buildTree(int* inorder, int inorderSize, int* postorder, int postorderSize){
return build(inorder, 0, inorderSize - 1, postorder, 0, postorderSize - 1);
}3、 ... and , Known before , After traversing the binary sequence tree
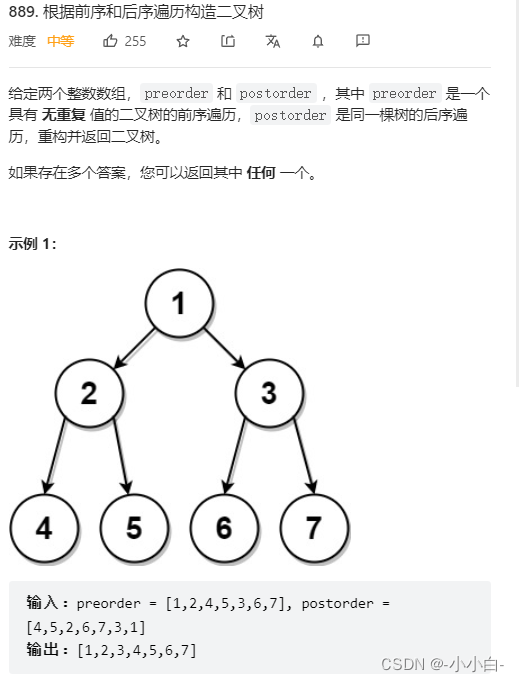
【 Main idea 】
1. First build the root , Then calculate the length of the left subtree , Build the left subtree , Finally, the right subtree . The whole process can be realized by recursion
2. The final root is easy to find , It is the first of the preorder traversal .
3. How to calculate the length of the left subtree ? According to the definition of preorder traversal and postorder traversal , I.e. preamble : root -> Left -> Right , In the following order : Left -> Right -> root , set up mid The pointer moves successively on the subsequent traversal , wait until mid The corresponding value is equal to the value of the root on the preorder traversal , At this moment mid Subtract the subscript at the beginning of traversal and add 1, You get the length of the left subtree
4. The length of the left subtree is obtained , Besides the root , The rest are right subtrees
【 Attention to detail 】
1. Pay attention to special situations , For example, the preorder traversal has only one node
2. use C When the language establishes a node , Remember to initialize . For example, a root spot , Remember root->left = NULL, root->right = NULL
// Auxiliary function
struct TreeNode* build(int* preorder, int left_pr, int right_pr, int* postorder, int left_po, int right_po) {
if (left_pr > right_pr) return NULL; Special circumstances that cannot be saved ①
struct TreeNode* root = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); //C Language establishment node method
root->val = preorder[left_pr];
root->left = NULL, root->right = NULL; // initialization root node , Omitting this step will report an error
if (left_pr == right_pr) return root; // Special circumstances that cannot be saved ②
int mid = left_po;
while (mid < right_po && postorder[mid] != preorder[left_pr + 1]) mid++;
int leftSize = mid - left_po + 1; // Get the length of the left subtree
// Recursive construction of left and right subtrees
root->left = build(preorder, left_pr + 1, left_pr + leftSize, postorder, left_po, mid);
root->right = build(preorder, left_pr + leftSize + 1, right_pr, postorder, mid + 1, right_po - 1);
return root;
}
struct TreeNode* constructFromPrePost(int* preorder, int preorderSize, int* postorder, int postorderSize){
return build(preorder, 0, preorderSize - 1, postorder, 0, postorderSize - 1);
}边栏推荐
- [leetcode] 19 delete the penultimate node of the linked list
- LeetCode刷题——统计各位数字都不同的数字个数#357#Medium
- 微信支付宝账户体系和支付接口业务流程
- 语义分割学习笔记(一)
- Beijing rental data analysis
- MySQL calculate n-day retention rate
- Facing the challenge of "lack of core", how can Feiling provide a stable and strong guarantee for customers' production capacity?
- Infra11199 database system
- NBA player analysis
- 6092. 替换数组中的元素
猜你喜欢

Guangzhou Emergency Management Bureau issued a high temperature and high humidity chemical safety reminder in July
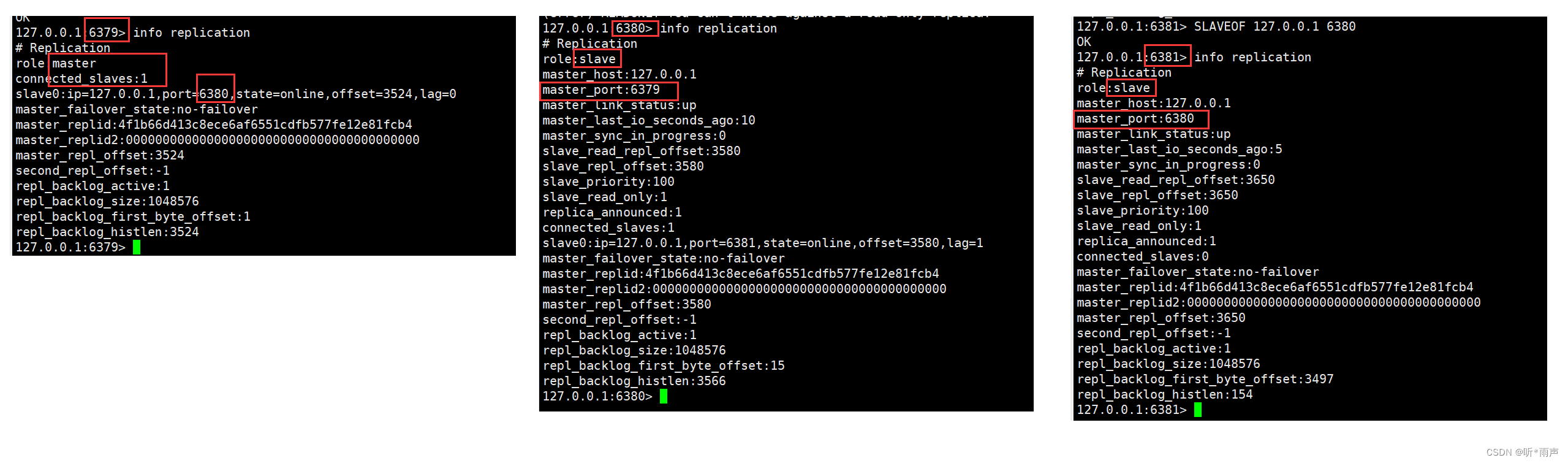
19_ Redis_ Manually configure the host after downtime

Leetcode skimming - remove duplicate letters 316 medium

2022 年辽宁省大学生数学建模A、B、C题(相关论文及模型程序代码网盘下载)

百变大7座,五菱佳辰产品力出众,人性化大空间,关键价格真香

飞凌嵌入式RZ/G2L处理器核心板及开发板上手评测

03.golang初步使用
How does the computer set up speakers to play microphone sound
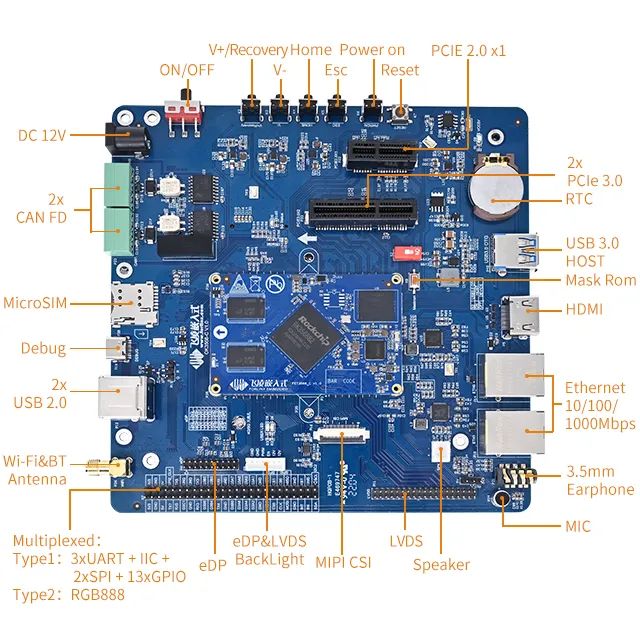
工程师评测 | RK3568开发板上手测试

. Net again! Happy 20th birthday
随机推荐
Let your HMI have more advantages. Fet-g2ld-c core board is a good choice
终于搞懂了JS中的事件循环,同步/异步,微任务/宏任务,运行机制(附笔试题)
16_ Redis_ Redis persistence
基于RZ/G2L | OK-G2LD-C开发板存储读写速度与网络实测
Bing. Site Internet
Custom exception
02.面向容器化后,必须面对golang
. Net again! Happy 20th birthday
LeetCode刷题——验证二叉树的前序序列化#331#Medium
20_ Redis_ Sentinel mode
[leetcode] 977 square of ordered array
【LeetCode】577-反转字符串中的单词 III
LeetCode_ String_ Simple_ 412.Fizz Buzz
[leetcode] 877 stone game
Infra11199 database system
6095. 强密码检验器 II
Leetcode skimming -- verifying the preorder serialization of binary tree # 331 # medium
[leetcode] 417 - Pacific Atlantic current problem
02. After containerization, you must face golang
List of sergeant schools