当前位置:网站首页>Rsync remote synchronization
Rsync remote synchronization
2022-07-05 23:35:00 【Oranges are delicious】
List of articles
One 、rsync
1、rsync brief introduction
rsync(Remote Sync, Remote synchronization ) Is an open source fast backup tool , It can mirror and synchronize the whole directory tree between different hosts , Support incremental backup , And keep links and permissions , And the optimized synchronization algorithm is used , Perform compression before transmission , So it is very suitable for remote backup 、 Image server and other applications .
rsync The website of our official website is https://rsync.samba.org/, The latest version is 3.1.3, from Wayne Davison For maintenance . As one of the most commonly used file backup tools ,rsync Tend to be Linux and UNIX System silence Recognize one of the basic components installed .
2、rsync characteristic
- Support for copying special files , Such as connection file 、 Equipment etc. .
- It can exclude the synchronization of specified files or directories , It's like a pack order tar The exclusion function of .
- Can do to maintain the original file or directory permissions 、 Time 、 Hard and soft links 、 Belong to 、 All attributes such as group do not change –p.
- Incremental synchronization can be achieved , It only synchronizes the changed data , So data transmission efficiency is very high (tar-N).
- have access to rcp、rsh、ssh And so on (rsync It doesn't encrypt data itself ).
- Can pass socket( Process mode ) Transfer files and data ( Server and client ).
- Support anonymous live Authentication ( No need for system users ) Process mode transfer of , Can achieve convenient and safe data backup and mirror .
Two 、rsync Synchronization source
In the remote synchronization task , Responsible for initiating rsync The client of the synchronous operation is called the initiator , And is responsible for responding to requests from clients rsync The server that synchronizes is called the synchronization source .
- Synchronize in the downlink ( download ) in , The synchronization source is responsible for providing the original location of the document , The initiator should have read permission to this location .
- Synchronize on the uplink ( Upload ) in , The synchronization source is responsible for providing the target location of the document , The initiator should have write permission to this location .
3、 ... and 、 To configure rsync Downlink synchronization
1、 To configure rsync Source
The source server :20.0.0.12
The client ( Originator ):20.0.0.5
systemctl stop firewalld.service
setenforce 0
rpm -q rsync
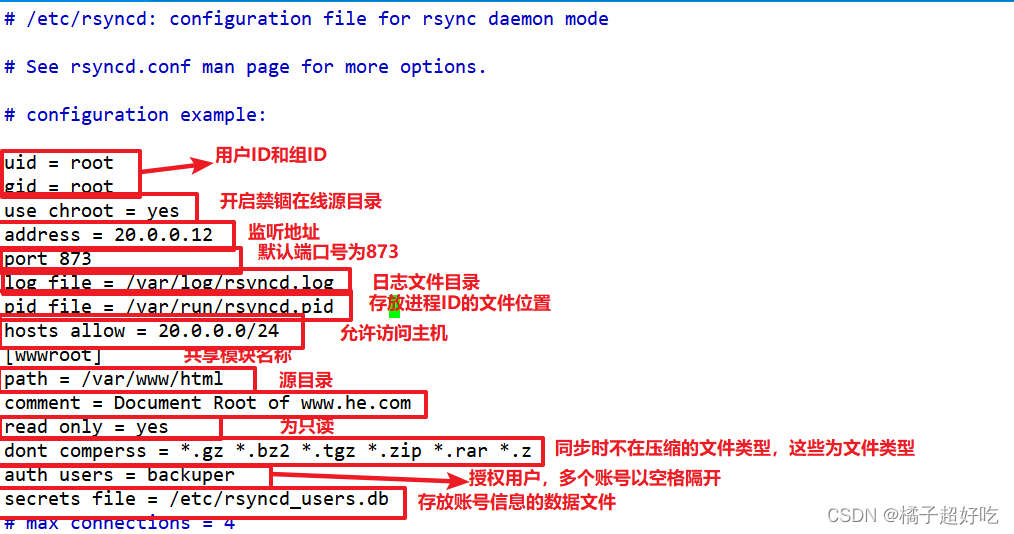
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
uid = nobody
gid = nobody
use chroot = yes
address = 20.0.0.12
port 873
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
hosts allow = 20.0.0.0/24
[wwwroot]
path = /var/www/html
comment = Document Root of www.he.com
read only = yes
dont comperss = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z
auth users = backuper
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db
vim /etc/rsyncd_users.db
backuper:abc123
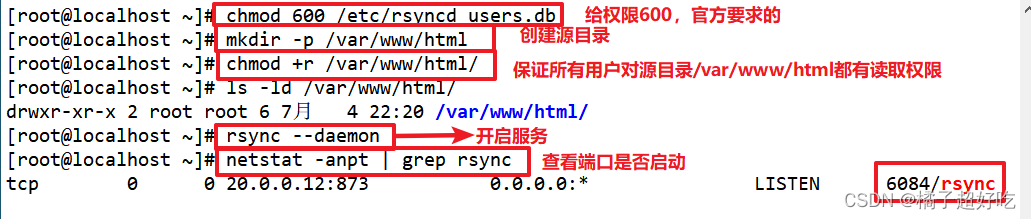
chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd_users.db
mkdir -p /var/www/html
chmod +r /var/www/html/
ls -ld /var/www/html/
rsync --daemon
netstat -natp | grep rsync

2、 Initiator configuration
The basic format :rsync [ Options ] Original location Target location
Common options
| Options | explain |
|---|---|
| -r | Recursive mode , Contains all the files in the directory and subdirectories . |
| -l | For symbolic link files, still copy as symbolic link files . |
| -v | Show details of the synchronization process (verbose) Information . |
| -z | Compress when transferring files (compress). |
| -a | Archiving mode , Keep file permissions 、 Properties and other information , Equivalent to combination options “-rlptgop". |
| -p | Keep the permission tag of the file .-t Keep the time stamp of the file . |
| -g | Keep the group tag of the file ( For super users only ). |
| -o | Keep the owner tag of the file ( For super users only ). |
| -H | Keep hard connection files . |
| -A | Retain ACL Attribute information . |
| -D | Keep equipment files and other special files . |
| –delete | Delete files that exist in the target location but not in the original location . |
| –checksum | According to the check sum ( Not the file size 、 Modification time ) To decide whether to skip the file . |
3、 There are two ways to download to local
Format 1 : user name @ The host address :: Share module name
rsync -avz [email protected]20.0.0.12::wwwroot /opt/
Format two : rsync:/ user name @ The host address / Share module name
rsync -avz rsync://[email protected]/wwwroot /opt/
## No interactive format configuration :
echo "abc123" > /etc/server.pass
chmod 600 /etc/server.pass
Timing synchronization
crontab -e
30 22 * * * /usr/bin/rsync -az --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass [email protected]20.0.0.12::wwwroot /opt/
# In order not to enter a password during synchronization , Need to create a password file , preservation backuper User's password , Such as /etc/server.pass. In execution rsync Use options when synchronizing “--password-file=/etc/server.pass” Just specify .
systemctl restart crond
systemctl enable crond
Four 、 Initiator configuration
1、rsync+inotify
Use inotify Notification interface , It can be used to monitor various changes in the file system , Such as file access 、 Delete 、 Move 、 Modify etc. . Using this mechanism , It is very convenient to realize file change alarm 、 Incremental backup , And respond to changes in directories or files in a timely manner .
take inotify Mechanism and rsync Combination of tools , You can achieve triggered backup ( Real time synchronization ), That is, as long as the document in the original location changes , Start the incremental backup operation immediately ; Otherwise, it will be in a state of silent waiting . such , This avoids the latency when backing up according to a fixed cycle 、 The period is too dense and so on .
because inotify The notification mechanism consists of Linux Provided by kernel , Therefore, it is mainly used for local monitoring , It is more suitable for uplink synchronization when applied in triggered backup .
2、 To configure rsync Real time synchronization ( Uplink synchronization )
## modify rsync Source server configuration file
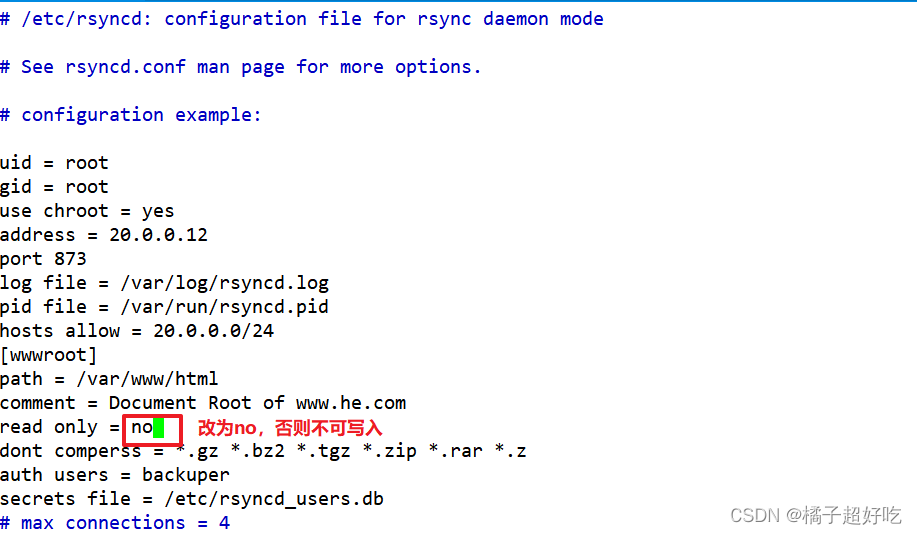
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
......
read only = no ## Turn off read-only , Uplink synchronization needs to be able to write
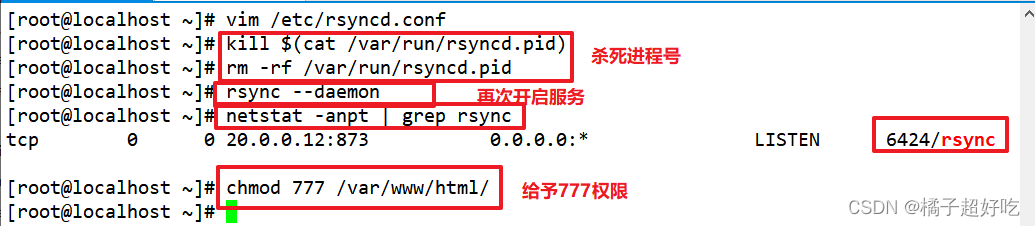
kill $(cat /var/run/rsyncd.pid)
rm -rf /var/run/rsyncd.pid
rsync --daemon
netstat -anpt | grep rsync
chmod 777 /var/www/html/
adjustment inotify Kernel parameters
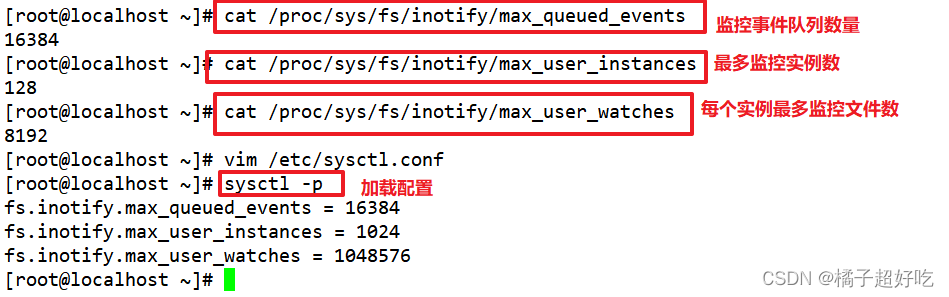
stay Linux The kernel , default inotify The mechanism provides three regulatory parameters :
- max_queue_events( Monitor the event queue , The default value is 16384)
- max_user_instances( The maximum number of monitoring instances , The default value is 128)
- max_user_watches( The maximum number of monitoring files per instance , The default value is 8192).
When you want to monitor the directory 、 When the number of files is large or changes frequently , It is suggested to increase the values of these three parameters .
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
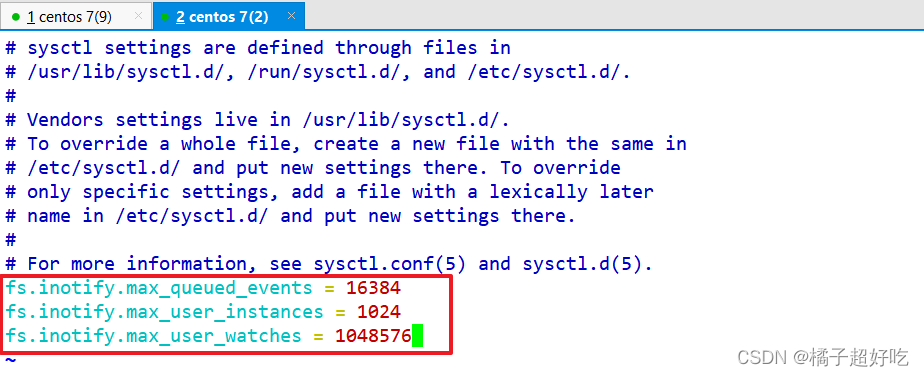
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 16384
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576
sysctl -p
3、 install inotify-tools
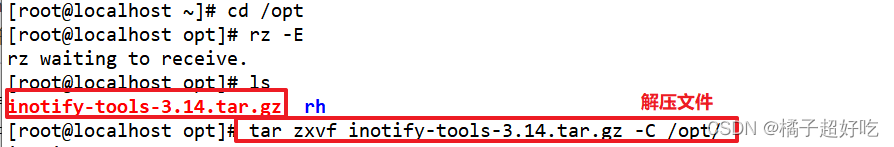
use inotify The mechanism also needs to be installed inotify-tools, To provide inotifywait、inotifywatch Auxiliary tool program , Used for monitoring 、 Summarize the changes .
inotifywait: Can be monitored modify( modify )、create( establish )、move( Move )、delete( Delete )、attrib( Property changes ) And so on , Output results as soon as there is a change .
inotifywatch: It can be used to collect file system changes , At the end of the run, output the change of the summary .
tar zxvf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz -C /opt/
cd /opt/inotify-tools-3.14
./configure
make && make install
# You can do it first “inotifywait” command , Then open a new terminal to /var/www/html Add files to directory 、 Moving files , Track the screen output results in the original terminal .
inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,move,delete /var/www/html
# Options “-e”: Used to specify which events to monitor
# Options “-m”: Continuous monitoring
# Options “-r”: Represents recursion of the entire directory
# Options “-q”: Simplify the output
Write trigger synchronization script at another terminal ( Be careful , Script name cannot contain rsync character string , Otherwise the script may not take effect )
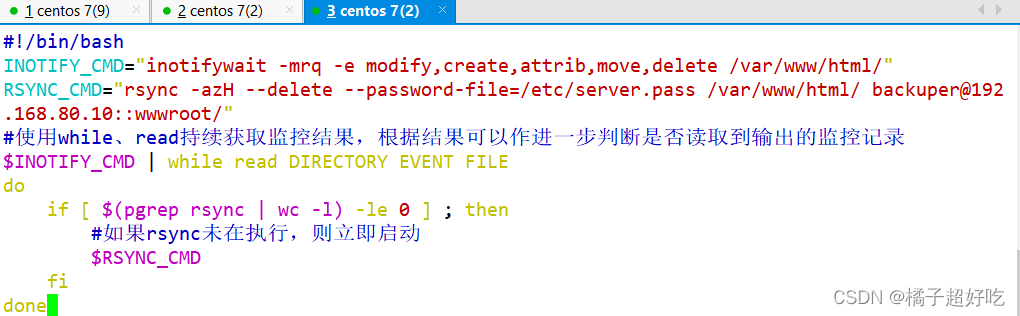
vim /opt/inotify.sh
#!/bin/bash
INOTIFY_CMD="inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,attrib,move,delete /var/www/html/"
RSYNC_CMD="rsync -azH --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass /var/www/html/ [email protected]::wwwroot/"
# Use while、read Continuously obtain monitoring results , According to the result, it can be further judged whether the output monitoring record is read
$INOTIFY_CMD | while read DIRECTORY EVENT FILE
do
if [ $(pgrep rsync | wc -l) -le 0 ] ; then
# If rsync Not executing , Start immediately
$RSYNC_CMD
fi
done
chmod +x /opt/inotify.sh
chmod 777 /var/www/html/
chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
echo '/opt/inotify.sh' >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local ## Add boot auto execution
The above script is used to detect native /var/www/html Changes in the catalogue , Once there is an update trigger rsync Synchronous operation , Upload backup to server 20.0.0.12 Of wwwroot Share Directory .
The verification process of triggered uplink synchronization is as follows :
- (1) Running on local machine /opt/inotify.sh Script program .
- (2) Switch to the local /var/www/html Catalog , Execution increase 、 Delete 、 Modify files and other operations .
- (3) View the in the remote server wwwroot Changes in the directory .
5、 ... and 、 Use rsync To quickly delete a large number of files
If you want to be in linux Delete a large number of files under , such as 100 ten thousand 、1000 ten thousand , image /usr/local/nginx/proxy_temp Of nginx Cache, etc , that rm -rf * It may not be easy to use , Because it takes a long time . In this case, we can use rsync To deal with .rsync The principle of substitution is actually used .
## First create an empty folder :
mkdir /home/blank
## use rsync Delete target directory :
rsync --delete-before -a -H -v --progress --stats /home/blank/ /usr/local/nginx/proxy_temp
So the target directory is quickly cleared
Option description :
--delete-before The receiver deletes during transmission
-a Archiving mode , Indicates that files are transferred recursively , And keep all file properties
-H Keep hard connected files
-v Detailed output mode
--progress Display the transmission process during transmission
--stats Give the transfer status of some files
边栏推荐
- 如何提升口才
- Krypton Factor purple book chapter 7 violent solution
- 帶外和帶內的區別
- SpreadJS 15.1 CN 与 SpreadJS 15.1 EN
- Judge whether the binary tree is a complete binary tree
- Idea rundashboard window configuration
- TVS管和ESD管的技術指標和選型指南-嘉立創推薦
- 2022.6.20-6.26 AI行业周刊(第103期):新的小生命
- 2022.6.20-6.26 AI industry weekly (issue 103): new little life
- 4点告诉你实时聊天与聊天机器人组合的优势
猜你喜欢

Rasa 3.x 学习系列-Rasa X 社区版(免费版) 更改
![[original] what is the core of programmer team management?](/img/11/d4b9929e8aadcaee019f656cb3b9fb.png)
[original] what is the core of programmer team management?

成为程序员的你,后悔了吗?

Go language introduction detailed tutorial (I): go language in the era

Dynamic memory management (malloc/calloc/realloc)
MySQL replace primary key delete primary key add primary key

Neural structured learning - Part 2: training with natural graphs
Southeast Asia e-commerce guide, how do sellers layout the Southeast Asia market?

保研笔记四 软件工程与计算卷二(8-12章)
LabVIEW打开PNG 图像正常而 Photoshop打开得到全黑的图像
随机推荐
Neural structured learning - Part 2: training with natural graphs
2022.6.20-6.26 AI industry weekly (issue 103): new little life
Development specification: interface unified return value format [resend]
The PNG image is normal when LabVIEW is opened, and the full black image is obtained when Photoshop is opened
Basic knowledge of database (interview)
Spécifications techniques et lignes directrices pour la sélection des tubes TVS et ESD - Recommandation de jialichuang
帶外和帶內的區別
98. 验证二叉搜索树 ●●
Go语言实现原理——Map实现原理
ORB_ SLAM2/3
(4) UART application design and simulation verification 2 - RX module design (stateless machine)
[Yu Yue education] NC machining technology reference materials of Shaanxi University of science and technology
STM32__06—单通道ADC
QCombox(重写)+QCompleter(自动补全,自动加载qcombox的下拉选项,设置背景颜色)
TVS管和ESD管的技術指標和選型指南-嘉立創推薦
20.移植Freetype字体库
SpreadJS 15.1 CN 与 SpreadJS 15.1 EN
Sum of two numbers, sum of three numbers (sort + double pointer)
Creative mode 1 - single case mode
Rasa 3.x 学习系列-Rasa X 社区版(免费版) 更改