当前位置:网站首页>(5) Introduction to R language bioinformatics -- ORF and sequence analysis
(5) Introduction to R language bioinformatics -- ORF and sequence analysis
2022-07-06 12:21:00 【EricFrenzy】
notes : This blog aims to share personal learning experience , Please forgive me for any irregularities !
The concept is introduced
In the human body , To express DNA Genes on , This gene contains DNA Is transcribed as pre-mRNA After further processing, it becomes mature mRNA,mRNA Then it will be used by ribosomes to synthesize proteins , So as to control the response of organisms . stay mRNA On , Every three bases form a codon , Corresponding to an amino acid . The following figure shows the comparison table of codons and amino acids :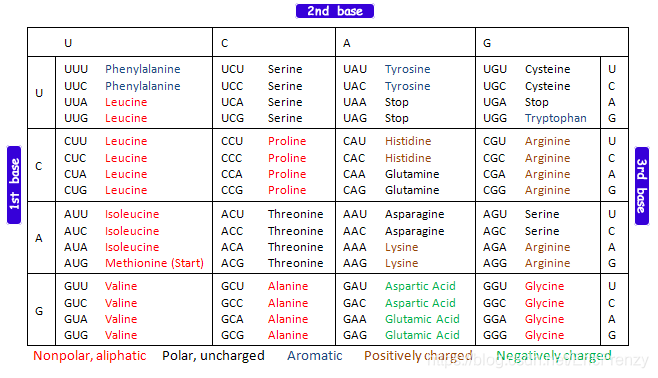
To synthesize a normal protein ,mRNA Both ends of the sequence need to have a starting codon ( Marked with start) And a stop codon ( Marked with stop). But in DNA There are many start and stop codons like this on , Produce many different sequence combinations . In order to be in DNA Find all possible sequence combinations that can be used to make a certain protein , We use open reading frames (ORF,Open Reading Frame) To find all sequences that have the potential to encode proteins .
look for ORF Code implementation of
stay R Find in language ORF The procedure flow of is as follows :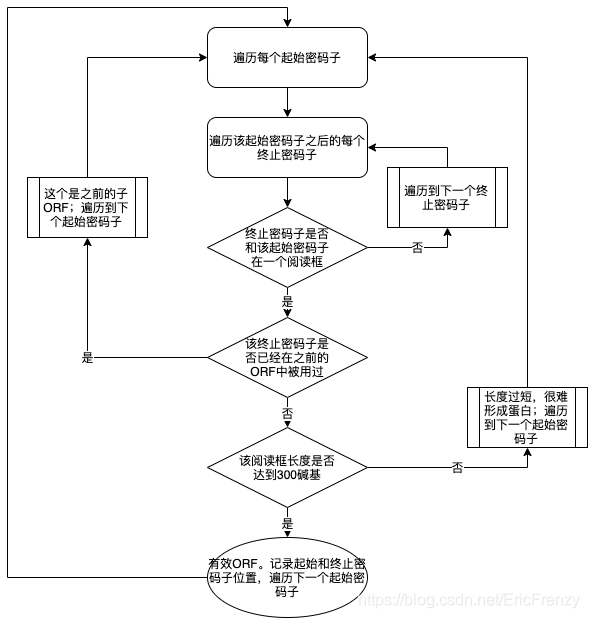
Here is the specific code :
findORF <- function(seq){
# The incoming parameter is DNA Sequence , Pay attention to the direction. It must be 5' To 3'
findStartCodons <- function(seq){
# Find the function of starting codon
startcodons <- numeric(0) # Create an empty function
k <- 1
for(i in 1:(length(seq)-5)){
# Calculate by the first base position of the codon , The last five do not need to be checked , Because the length is too short
if(seq[i] == "a" && seq[i+1] == "t" && seq[i+2] == "g"){
#ATG Corresponding to the starting codon
startcodons[k] <- i # Record location
k <- k + 1 # Position subscript plus one
}
}
return(startcodons) # Return results
}
findStopCodons <- function(seq){
# Find the function that terminates the codon
stopcodons <- numeric(0) # Create an empty function
k <- 1
for(i in 1:(length(seq)-2)){
# Calculate by the first base position of the codon
if((seq[i] == "t" && seq[i+1] == "a" && seq[i+2] == "a") || (seq[i] == "t" && seq[i+1] == "a" && seq[i+2] == "g") || (seq[i] == "t" && seq[i+1] == "g" && seq[i+2] == "a")){
#TAA TAG TGA Corresponding to the stop codon
stopcodons[k] <- i # Record location
k <- k + 1 # Position subscript plus one
}
}
return(stopcodons) # Return results
}
startcodon <- findStartCodons(seq) # Find all the starting codons
stopcodon <- findStopCodons(seq) # Find all the stop codons
usedStop <- numeric(0) # Record used stop codons
ORFs <- character(0) # Record effective open reading frames
k <- 1
for(i in startcodon){
# Traverse all start codons
for(j in stopcodon){
# Traverse all termination codons
if((j-i)%%3==0 && j > i){
# If in a reading box , That is, the position between the two codons is 3 The integer of
if(j %in% usedStop){
# If the stop codon is used
break # Jump out of this cycle , To the next starting codon
}else if(j-i < 300){
# If the sequence length between codons is too short
break # ditto
}else{
ORFs[k] <- paste(i, "to", j) # Generate string , The recorded results are as follows "1 to 3001"
usedStop[k] <- j # Record used stop codons
k <- k + 1 # Position subscript plus one
break # Jump out of this cycle , To the next starting codon
}
}
}
}
return(ORFs) # Return results
}
This kind of search ORF Our algorithm is relatively simple and fast , But the accuracy will decrease accordingly . stay NCBI Official website There is a more accurate algorithm .
Conclusion
Find ORF after , Can put the ORF Compare with the known sequence in the database , Thus, useful information such as the composition and function of genes in this species can be predicted . Next time we will introduce Needleman-Wunsch This sequence global alignment algorithm , Coming soon ! And any questions or ideas are welcome to leave messages and comments !
边栏推荐
- I2C bus timing explanation
- Gravure sans fil Bluetooth sur micro - ordinateur à puce unique
- Keyword inline (inline function) usage analysis [C language]
- Who says that PT online schema change does not lock the table, or deadlock
- Embedded startup process
- JS function promotion and declaration promotion of VaR variable
- Esp8266 uses Arduino to connect Alibaba cloud Internet of things
- RuntimeError: cuDNN error: CUDNN_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED
- @The difference between Autowired and @resource
- arduino获取随机数
猜你喜欢
基於Redis的分布式ID生成器
Redis 缓存更新策略,缓存穿透、雪崩、击穿问题
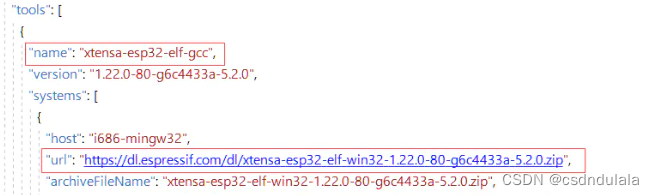
ESP学习问题记录

Générateur d'identification distribué basé sur redis
编译原理:源程序的预处理及词法分析程序的设计与实现(含代码)
![[Red Treasure Book Notes simplified version] Chapter 12 BOM](/img/ff/0ad410b5b556c0e16a4076a2a0577b.jpg)
[Red Treasure Book Notes simplified version] Chapter 12 BOM

Pytorch: tensor operation (I) contiguous
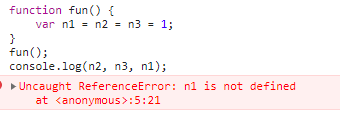
JS 函数提升和var变量的声明提升

ES6 grammar summary -- Part 2 (advanced part es6~es11)
Reno7 60W super flash charging architecture
随机推荐
C language callback function [C language]
JS object and event learning notes
The first simple case of GNN: Cora classification
Knowledge summary of request
JS variable types and common type conversions
ESP学习问题记录
Kconfig Kbuild
STM32 how to locate the code segment that causes hard fault
如何给Arduino项目添加音乐播放功能
Symbolic representation of functions in deep learning papers
Pat 1097 duplication on a linked list (25 points)
Keyword inline (inline function) usage analysis [C language]
Understanding of AMBA, AHB, APB and Axi
RT thread API reference manual
arduino JSON数据信息解析
MySQL replacement field part content
程序设计大作业:教务管理系统(C语言)
Amba, ahb, APB, Axi Understanding
Programmers can make mistakes. Basic pointers and arrays of C language
JS 函数提升和var变量的声明提升