当前位置:网站首页>Bubble sort [C language]
Bubble sort [C language]
2022-07-06 11:57:00 【Weiyuan escort agency】
Bubble sort Is the simplest sort method , It's easy to understand . Although it has many calculation steps , Not the fastest , But it is the most basic , Beginners must master .
The principle of bubble sort is : From left to right , Compare adjacent elements . Compare one round at a time , You will find the largest or smallest in the sequence . This number will appear from the far right of the sequence .
Take sorting from small to large as an example , After the first round of comparison , The largest of all numbers will float to the far right ; After the second round of comparison , The second largest of all numbers will float to the penultimate position …… Just compare it round by round , Finally, sort from small to large .
For example, sort the following sequence from small to large :
90 21 132 -58 34 The first round :
1、90 and 21 Than ,90>21, Then they exchange positions :
21 90 132 -58 342、90 and 132 Than ,90<132, Then there is no need to exchange positions .
3、132 and –58 Than ,132>–58, Then they exchange positions :
21 90 -58 132 344、132 and 34 Than ,132>34, Then they exchange positions :
21 90 -58 34 132 The first round of comparison is over . The result of the first round is to find the largest number in the sequence , And float to the far right .
When comparing , No. in each round n The second comparison is the n Elements and number n+1 Comparison of elements ( If n from 1 Start ).
The second round :
1、21 and 90 Than ,21<90, Then there is no need to exchange positions .
2、90 and –58 Than ,90>–58, Then they exchange positions :
21 -58 90 34 1323、90 and 34 Than ,90>34, Then they exchange positions :
21 -58 34 90 132 This is the end of the second round . The result of the second round is to find the second largest number in the sequence , And float to the second position on the far right .
The third round :
1、21 and –58 Than ,21>–58, Then they exchange positions :
-58 21 34 90 1322) 21 and 34 Than ,21<34, Then there is no need to exchange positions .
The third round will be over . The result of the third round is to find the third largest number in the sequence , And float to the third position on the far right .
The fourth round :
1、–58 and 21 Than ,–58<21, Then there is no need to exchange positions .
thus , The whole sequence is sorted . The sequence from small to large is “–58 21 34 90 132”. From this example, we can also conclude that , If there is n Data , Then just compare n–1 round . And besides the first round , There is no need to compare every round . Because after the previous rounds of comparison , The rounds that have been compared have found the largest number in the round and floated to the right , So the number on the right is big without comparison .
Write a program below :
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int a[] = {900, 2, 3, -58, 34, 76, 32, 43, 56, -70, 35, -234, 532, 543, 2500};
int n; // Store array a The number of elements in
int i; // The number of rounds compared
int j; // The number of comparisons per round
int buf; // It is used to store intermediate data when exchanging data
n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); /*a[0] yes int type , Occupy 4 byte , So the total number of bytes divided by 4 Equal to the number of elements */
for (i=0; i<n-1; ++i) // Compare n-1 round
{
for (j=0; j<n-1-i; ++j) // Each round of comparison n-1-i Time ,
{
if (a[j] < a[j+1])
{
buf = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = buf;
}
}
}
for (i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
printf("%d\x20", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}The output is :
2500 900 543 532 76 56 43 35 34 32 3 2 -58 -70 -234 In the program , Why is the number of comparisons per round j<n–1–i, instead of j<n–1?
Because bubble sorting has a feature , This program is sorted from large to small , So after the first round of sorting , The smallest number will float to the far right ; After the second round of sorting , The second smallest number will float to the penultimate position ; After the third round of sorting , The third smallest number will float to the penultimate position …… in other words , How many rounds to sort , How many numbers have been arranged according to the sorting requirements , They don't need to be compared . Write j<n–1 It's fine too , It's just that the program does a lot of useless work during execution .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
小天才电话手表 Z3工作原理
高通&MTK&麒麟 手機平臺USB3.0方案對比

機器學習--線性回歸(sklearn)
Correspondence between STM32 model and contex M

Machine learning -- linear regression (sklearn)

{one week summary} take you into the ocean of JS knowledge
MongoDB
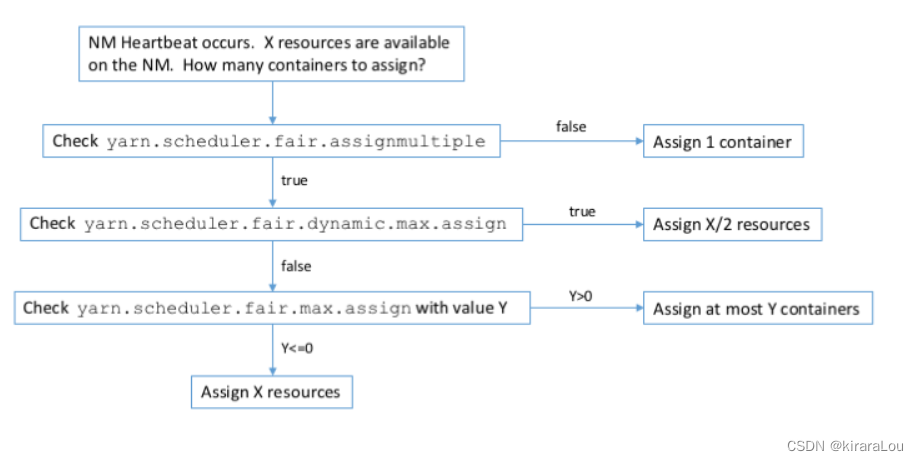
【CDH】CDH5.16 配置 yarn 任务集中分配设置不生效问题
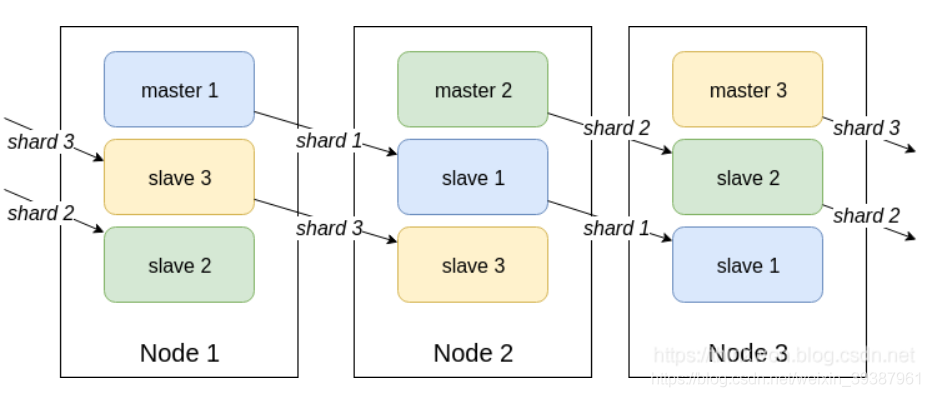
Redis interview questions
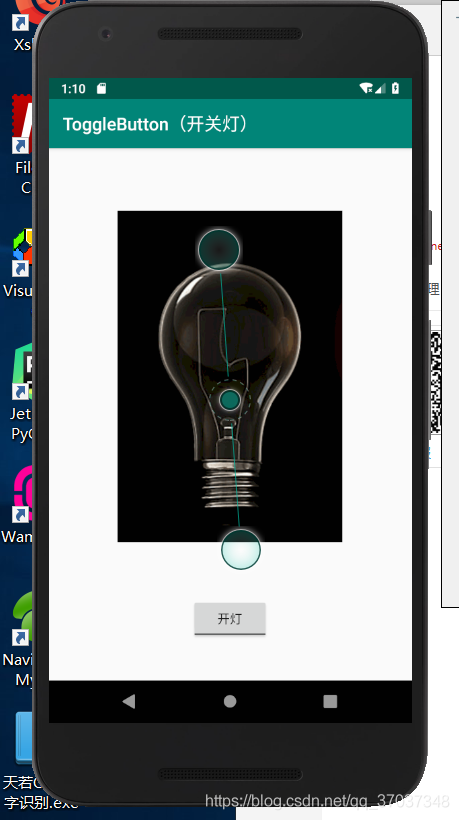
Togglebutton realizes the effect of switching lights
随机推荐
【Flink】CDH/CDP Flink on Yarn 日志配置
Apprentissage automatique - - régression linéaire (sklearn)
Principle and implementation of MySQL master-slave replication
{一周总结}带你走进js知识的海洋
[CDH] modify the default port 7180 of cloudera manager in cdh/cdp environment
SQL时间注入
互聯網協議詳解
Password free login of distributed nodes
高通&MTK&麒麟 手机平台USB3.0方案对比
[template] KMP string matching
C语言函数之可变参数原理:va_start、va_arg及va_end
Encodermappreduce notes
Pytorch-温度预测
【CDH】CDH5.16 配置 yarn 任务集中分配设置不生效问题
yarn安装与使用
XML file explanation: what is XML, XML configuration file, XML data file, XML file parsing tutorial
Machine learning -- decision tree (sklearn)
Détails du Protocole Internet
【CDH】CDH/CDP 环境修改 cloudera manager默认端口7180
express框架详解