当前位置:网站首页>The first time to tear the code by hand, how to solve the problem of full arrangement
The first time to tear the code by hand, how to solve the problem of full arrangement
2022-08-02 04:04:00 【dumb papa】
面试官:Here is a programming question,need you to do it……
求职者:哎,好
面试官:probably for you 10 分钟
7 minutes later……
求职者:面试官,For this question I think it is possible to usefor循环,First find the number of times you need to loop,Then the amount
面试官:Is there any way to solve this problem using recursion?
求职者:这个呢…

一、Brainless loop solution?
拿到这个问题,Of course my first thought was for 循环,比如这样:
for(int i = 1; i < n+1; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < n+1; j++){
for(int k = 1; k < n+1; k++){
……From now on in endless loop
}
}
}
可是,问题大了,How many cycles are there?n 个?
又或者是 while loop to control the number of loops:
while(i < n){
for(int j = 1; j < n+1; j++){
……so in the cycle again
}
i++;
}
十分钟内,The whole mind is how to control the number of loops to solve this problem.其实,If you understand the backtracking algorithm,not to take for Loop to deal with the interviewer,Let's analyze this problem.
二、全排列的个数
首先,Questions about the whole arrangement,It is easy to get the number of answers to the question as n!个:
当 n = 2 时,全排列的个数为 2 个:
[1,2]、[2,1]
当 n = 3 时,全排列的个数为 3*2 ,即 6 个:
[1,2,3]、[1,3,2]、[2,1,3]、[2,3,1]、[3,1,2]、[3,2,1]
当 n = 4 时,The total number of slices is 4*3*2 ,即 24 个
[1, 2, 3, 4]、[1, 2, 4, 3]、[1, 3, 2, 4]、[1, 3, 4, 2]、[1, 4, 2, 3]、[1, 4, 3, 2]、
[2, 1, 3, 4]、[2, 1, 4, 3]、[2, 3, 1, 4]、[2, 3, 4, 1]、[2, 4, 1, 3]、[2, 4, 3, 1]、
[3, 1, 2, 4]、[3, 1, 4, 2]、[3, 2, 1, 4]、[3, 2, 4, 1]、[3, 4, 1, 2]、[3, 4, 2, 1]、
[4, 1, 2, 3]、[4, 1, 3, 2]、[4, 2, 1, 3]、[4, 2, 3, 1]、[4, 3, 1, 2]、[4, 3, 2, 1]
很容易推出 n 个数字时,全排列的个数为 n! 个.
三、Backtracking algorithm for the problem solving
Next, we use the backtracking algorithm to solve this problem.,还是比较简单的.首先,We need to construct a fully permuted solution space.Similarly, here we first study the smaller problems,假设 n 为 3 solution space:

The solution space of the backtracking algorithm is a polytree,Usually the root node is empty.In this polytree,Leaf nodes are called non-extendable nodes,Non-leaf nodes are called extensible nodes.
接下来,You need to pass depth traversal traversal many forks tree,Each traversal to the leaf node,to get a corresponding solution.

Backtracking happens during traversal,When encountering a non-scalable node,You need to go back to the tree layer,Continue to traverse other extensible nodes.
Then you can use the code to achieve,There are two main ways to implement the backtracking algorithm:
1、Recursive implementation of backtracking algorithm
递归实现思路:function self-tuning,Continue to traverse the depth of the tree through the self-tuning function;而通过 for 循环,to find the right node,and temporarily in the result set.递归终止时,i.e. get a complete result!
/** * * @param t 起始层数,初始值为 1 * @param n 数的个数,the last layer of the tree * @param ls 结果集 */
public static void backTrack(int t, int n, ArrayList<Integer> ls) {
if(t > n) {
System.out.println(ls.toString());
}else {
for(int i = 1; i < n+1; i++) {
if(ls.contains(i))
continue;
else
ls.add(i);
backTrack(t+1, n, ls);
ls.remove(t-1);
}
}
}
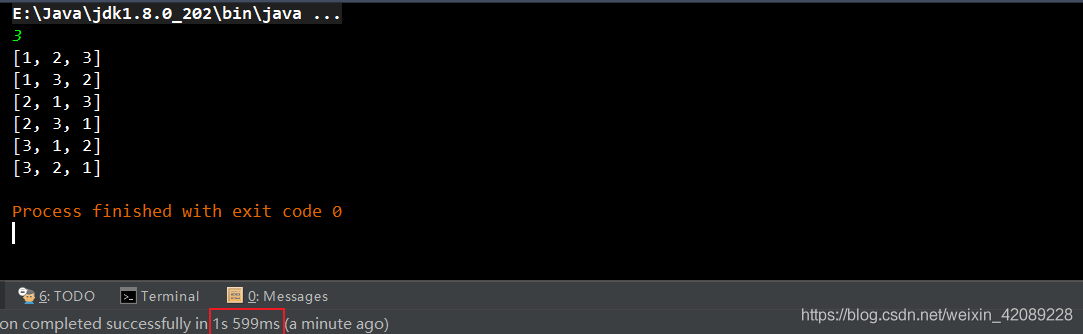
Below is the abstract procedure of recursive call:
观察这个过程,You will find that recursion has a natural advantage over backtracking algorithms,In other words, recursion is a process of continuous backtracking.;The iterative implementation of the backtracking algorithm is more difficult to understand.
2、Iteratively implement the backtracking algorithm
递归实现思路:Backtracking using iteration,like plunging into a dead end,Then step back,After back again into a dead end.until back out of the alley,Exit the whole back process.
/** * @param n 数的个数 * @param ls 结果集 */
public static void iterativeBacktrack(int n, ArrayList<Integer> ls) {
int t = 1;
int left = 1;
while(t > 0) {
if(left <= n) {
for(int i = left; i <= n; i++) {
if(ls.contains(i)) {
continue;
}else {
if(ls.size() == t){
ls.set(t-1, i);
}else{
ls.add(t-1, i);
}
i = 0;
}
if(t == n) {
System.out.println(ls.toString());
}else {
t++;
i=0;
}
}
}
if (t > 0){
ls.remove(t-1);
}
t--;
if(t > 0)
left = ls.get(t-1);
}
}

Actually there is backtracking algorithm最后一步,Trim excess branches with constraints and boundary control,To improve the efficiency of the backtracking algorithm.这里,no pruning……
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

hackmyvm-bunny walkthrough

hackmyvm: may walkthrough

DarkHole: 2 vulnhub walkthrough

GreenOptic: 1 vulnhub walkthrough
Shuriken: 1 vulnhub walkthrough

(4) Function, Bug, Class and Object, Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism, Copy

Pycharm packages the project as an exe file

C language uses stack to calculate infix expressions
![WeChat applet development video loading: [Rendering layer network layer error] Failed to load media](/img/24/e12a1312aee28a43428b2ae0bfbe00.png)
WeChat applet development video loading: [Rendering layer network layer error] Failed to load media

v-bind usage: class dynamic binding object array style style and function method
随机推荐
vim edit mode
hackmyvm: juggling walkthrough
12. What is JS
Activity
Masashi: 1 vulnhub walkthrough
SQL注入(7)
文件包含漏洞
(5) Modules and packages, encoding formats, file operations, directory operations
[league/flysystem] An elegant and highly supported file operation interface
(8) requests, os, sys, re, _thread
Offensive and defensive world - novice MISC area 1-12
Using PHPMailer send mail
Phonebook
Add a full image watermark to an image in PHP
(2) 顺序结构、对象的布尔值、选择结构、循环结构、列表、字典、元组、集合
PHP反序列化漏洞
file contains vulnerabilities
web安全之目录遍历
DarkHole: 2 vulnhub walkthrough
Solve the problem of Zlibrary stuck/can't find the domain name/reached the limit, the latest address of Zlibrary