当前位置:网站首页>Interview: is bitmap pixel memory allocated in heap memory or native
Interview: is bitmap pixel memory allocated in heap memory or native
2022-07-05 10:11:00 【A bird carved in the desert】
I met a classmate in the interview today who said that he had done memory optimization , So I usually ask that Bitmap Where does the pixel memory exist ? Most of the students answered in java heap Inside , It's embarrassing , In theory, you do memory optimization , If you don't even know where the picture memory is , It's hard to say .
Bitmap It can be said that it is the most common memory consumer in Android , We encountered in the development process oom Many problems are caused by it . Google officials have also been iterating over its pixel memory management strategy . from Android 2.3.3 The previous assignment was at native On , To 2.3 - 7.1 The distribution between java Pile it up , To 8.0 And then back native On . Several changes , Its recycling methods are also changing .
Android 2.3.3 before
2.3.3 before Bitmap The pixel memory is allocated in natvie On , And I'm not sure when it will be recycled . According to the official documentation, we need to manually call Bitmap.recycle() To recycle :
https://developer.android.com/topic/performance/graphics/manage-memory
stay Android 2.3.3(API Level 10) And earlier , The backup pixel data of the bitmap is stored in local memory . It is stored in Dalvik The bitmaps in the heap themselves are separate . Pixel data in local memory is not released in a predictable manner , It may cause the application to briefly exceed its memory limit and crash .
stay Android 2.3.3(API Level 10) And earlier , It is recommended to use recycle(). If you display a large amount of bitmap data in your application , You may encounter OutOfMemoryError error . utilize recycle() Method , Applications can reclaim memory as soon as possible .
Be careful : Use only if you are sure that the bitmap is no longer in use recycle(). If you call recycle() And try to draw a bitmap later , You will receive an error :"Canvas: trying to use a recycled bitmap".
2.Android 3.0~Android 7.1
although 3.0~7.1 Version of Bitmp The pixel memory is allocated in java On the pile , But the reality is natvie Layer for decode Of , And it will be there. native Layer to create a c++ The object and java Layer of Bitmap Object to associate .
from BitmapFactory We can see that it calls all the way to nativeDecodeStream This native Method :
// BitmapFactory.java
public static Bitmap decodeFile(String pathName, Options opts) {
...
stream = new FileInputStream(pathName);
bm = decodeStream(stream, null, opts);
...
return bm;
}
public static Bitmap decodeStream(InputStream is, Rect outPadding, Options opts) {
...
bm = decodeStreamInternal(is, outPadding, opts);
...
return bm;
}
private static Bitmap decodeStreamInternal(InputStream is, Rect outPadding, Options opts) {
...
return nativeDecodeStream(is, tempStorage, outPadding, opts);
}
nativeDecodeStream In fact, it will pass through jni establish java Heap memory , Then read io Stream decode the picture and save the pixel data to this java In the heap memory :
// BitmapFactory.cpp
static jobject nativeDecodeStream(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jobject is, jbyteArray storage,
jobject padding, jobject options) {
...
bitmap = doDecode(env, bufferedStream, padding, options);
...
return bitmap;
}
static jobject doDecode(JNIEnv* env, SkStreamRewindable* stream, jobject padding, jobject options) {
...
// outputAllocator Is the allocator of pixel memory , Will be in java Create memory on the heap for pixel data , Can pass BitmapFactory.Options.inBitmap Reuse previous bitmap Pixel memory
SkBitmap::Allocator* outputAllocator = (javaBitmap != NULL) ?
(SkBitmap::Allocator*)&recyclingAllocator : (SkBitmap::Allocator*)&javaAllocator;
...
// Set the memory allocator to the decoder
decoder->setAllocator(outputAllocator);
...
// decode
if (decoder->decode(stream, &decodingBitmap, prefColorType, decodeMode)
!= SkImageDecoder::kSuccess) {
return nullObjectReturn("decoder->decode returned false");
}
...
return GraphicsJNI::createBitmap(env, javaAllocator.getStorageObjAndReset(),
bitmapCreateFlags, ninePatchChunk, ninePatchInsets, -1);
}
// Graphics.cpp
jobject GraphicsJNI::createBitmap(JNIEnv* env, android::Bitmap* bitmap,
int bitmapCreateFlags, jbyteArray ninePatchChunk, jobject ninePatchInsets,
int density) {
// java Layer of Bitmap The object is actually natvie layer new Coming out
// native The layer will also create a android::Bitmap Object and the java Layer of Bitmap Object binding
// bitmap->javaByteArray() Code bitmap The pixel data actually exists java Layer of byte Array
jobject obj = env->NewObject(gBitmap_class, gBitmap_constructorMethodID,
reinterpret_cast<jlong>(bitmap), bitmap->javaByteArray(),
bitmap->width(), bitmap->height(), density, isMutable, isPremultiplied,
ninePatchChunk, ninePatchInsets);
...
return obj;
}
We can see that in the end, we will call javaAllocator.getStorageObjAndReset() Create a android::Bitmap Type of native layer Bitmap object , And then through jni call java Layer of Bitmap Constructor to create java Layer of Bitmap object , At the same time native Layer of Bitmap Object to save to mNativePtr:
// Bitmap.java
// Convenience for JNI access
private final long mNativePtr;
/**
* Private constructor that must received an already allocated native bitmap
* int (pointer).
*/
// called from JNI
Bitmap(long nativeBitmap, byte[] buffer, int width, int height, int density,
boolean isMutable, boolean requestPremultiplied,
byte[] ninePatchChunk, NinePatch.InsetStruct ninePatchInsets) {
...
mNativePtr = nativeBitmap;
...
}
We can also see from the above source code ,Bitmap The pixels are present java Heaped , So if bitmap No one used , The garbage collector can automatically reclaim this memory , But in native created nativeBitmap How to recycle ? from Bitmap We can see the source code in Bitmap The constructor will also create a BitmapFinalizer To manage nativeBitmap:
/**
* Private constructor that must received an already allocated native bitmap
* int (pointer).
*/
// called from JNI
Bitmap(long nativeBitmap, byte[] buffer, int width, int height, int density,
boolean isMutable, boolean requestPremultiplied,
byte[] ninePatchChunk, NinePatch.InsetStruct ninePatchInsets) {
...
mNativePtr = nativeBitmap;
mFinalizer = new BitmapFinalizer(nativeBitmap);
...
}
BitmapFinalizer The principle is very simple .Bitmap When the object is destroyed BitmapFinalizer Will also be destroyed synchronously , And then you can do it in BitmapFinalizer.finalize() Inside destroy native Layer of nativeBitmap:
private static class BitmapFinalizer {
private long mNativeBitmap;
...
BitmapFinalizer(long nativeBitmap) {
mNativeBitmap = nativeBitmap;
}
...
@Override
public void finalize() {
try {
super.finalize();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Ignore
} finally {
setNativeAllocationByteCount(0);
nativeDestructor(mNativeBitmap);
mNativeBitmap = 0;
}
}
}3.Android 8.0 after
8.0 After that, the pixel memory is put back native On , So it is still necessary to java Layer of Bitmap After the object is recycled, it is recycled synchronously native Of memory .
although BitmapFinalizer The same thing can be done , however Java Of finalize Method is actually not recommended , So Google also changed NativeAllocationRegistry To achieve :
/**
* Private constructor that must received an already allocated native bitmap
* int (pointer).
*/
// called from JNI
Bitmap(long nativeBitmap, int width, int height, int density,
boolean isMutable, boolean requestPremultiplied,
...
mNativePtr = nativeBitmap;
long nativeSize = NATIVE_ALLOCATION_SIZE + getAllocationByteCount();
NativeAllocationRegistry registry = new NativeAllocationRegistry(
Bitmap.class.getClassLoader(), nativeGetNativeFinalizer(), nativeSize);
registry.registerNativeAllocation(this, nativeBitmap);
}
locationRegistry The bottom layer actually uses sun.misc.Cleaner, You can register a clean up for the object Runnable. When object memory is reclaimed jvm It will be called .
import sun.misc.Cleaner;
public Runnable registerNativeAllocation(Object referent, Allocator allocator) {
...
CleanerThunk thunk = new CleanerThunk();
Cleaner cleaner = Cleaner.create(referent, thunk);
..
}
private class CleanerThunk implements Runnable {
...
public void run() {
if (nativePtr != 0) {
applyFreeFunction(freeFunction, nativePtr);
}
registerNativeFree(size);
}
...
}This Cleaner The principle of is also very violent , First, it is a virtual reference ,registerNativeAllocation It actually creates a Bitmap The virtual quotation of :
// Cleaner.java
public class Cleaner extends PhantomReference {
...
public static Cleaner create(Object ob, Runnable thunk) {
...
return add(new Cleaner(ob, thunk));
}
...
private Cleaner(Object referent, Runnable thunk) {
super(referent, dummyQueue);
this.thunk = thunk;
}
...
public void clean() {
...
thunk.run();
...
}
...
}
We all know that we need to cooperate with a ReferenceQueue Use , When a reference to an object is recycled ,jvm This virtual reference will be thrown into ReferenceQueue Inside . and ReferenceQueue When inserting, I passed instanceof I have judged whether it is Cleaner:
// ReferenceQueue.java
private boolean enqueueLocked(Reference<? extends T> r) {
...
if (r instanceof Cleaner) {
Cleaner cl = (sun.misc.Cleaner) r;
cl.clean();
...
}
...
}
in other words Bitmap Object is recycled , It will trigger Cleaner This virtual reference is dropped into ReferenceQueue, and ReferenceQueue It will determine whether the dropped virtual reference is Cleaner, If so, call Cleaner.clean() Method . and clean The method will perform the cleaning of our registration Runnable.
边栏推荐
- 如何获取GC(垃圾回收器)的STW(暂停)时间?
- Cross process communication Aidl
- 硬核,你见过机器人玩“密室逃脱”吗?(附代码)
- The comparison of every() and some() in JS uses a power storage plan
- 剪掉ImageNet 20%数据量,模型性能不下降!Meta斯坦福等提出新方法,用知识蒸馏给数据集瘦身...
- 面试:List 如何根据对象的属性去重?
- Dedecms website building tutorial
- Tianlong Babu TLBB series - single skill group injury
- RMS TO EAP通过MQTT简单实现
- Wechat applet - simple diet recommendation (4)
猜你喜欢
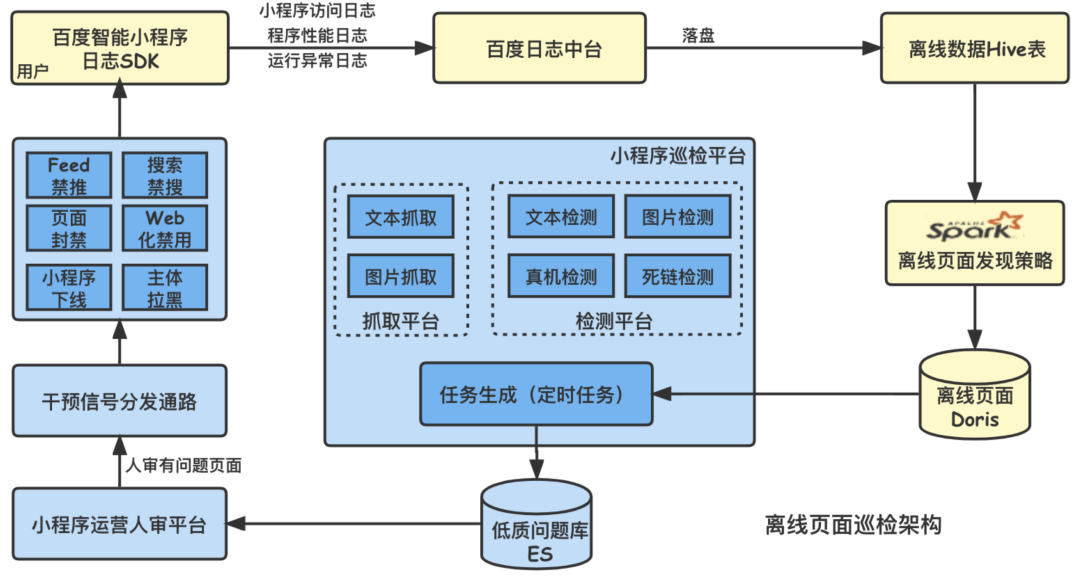
Evolution of Baidu intelligent applet patrol scheduling scheme
QT realizes signal transmission and reception between two windows
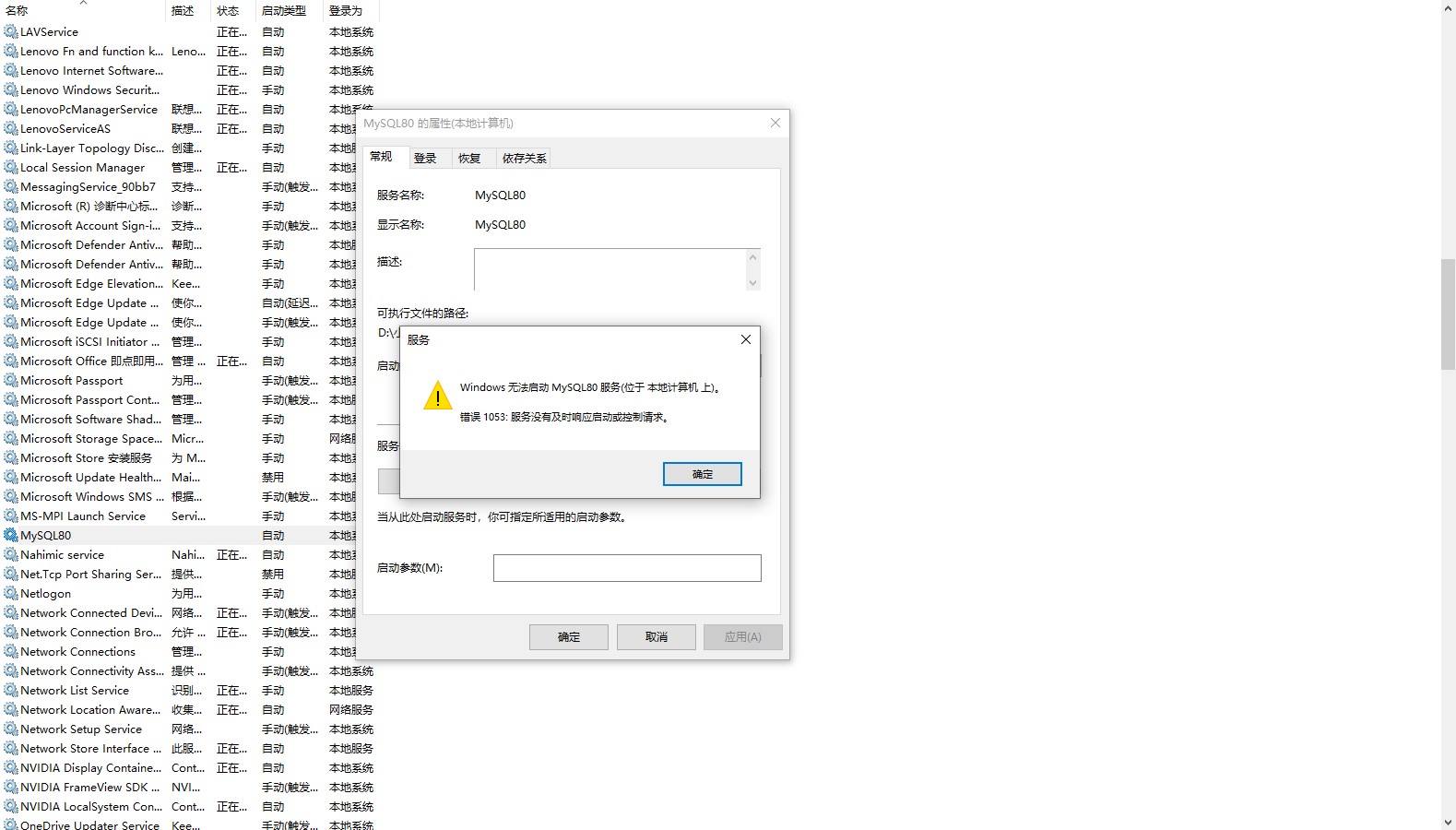
Mysql80 service does not start
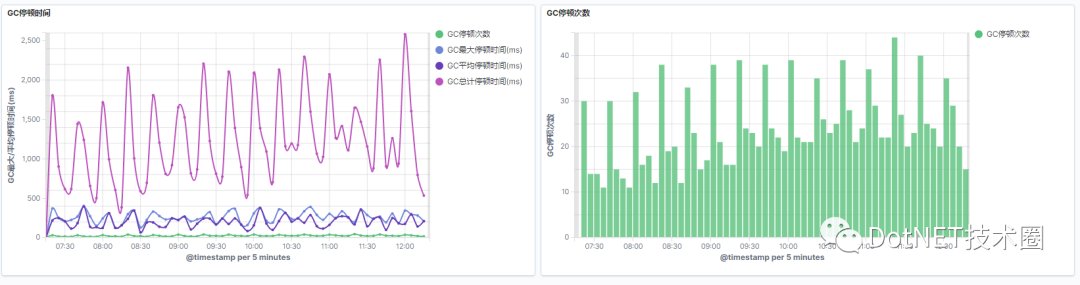
如何获取GC(垃圾回收器)的STW(暂停)时间?
![[tips] get the x-axis and y-axis values of cdfplot function in MATLAB](/img/08/2d039df6ea3ace8685512b2af8281d.png)
[tips] get the x-axis and y-axis values of cdfplot function in MATLAB
Roll up, break through 35 year old anxiety, and animate the CPU to record the function call process
MySQL character type learning notes
硬核,你见过机器人玩“密室逃脱”吗?(附代码)
最全是一次I2C总结
.Net之延迟队列
随机推荐
Data visualization platform based on template configuration
程序员搞开源,读什么书最合适?
The comparison of every() and some() in JS uses a power storage plan
硬核,你见过机器人玩“密室逃脱”吗?(附代码)
QT realizes signal transmission and reception between two windows
学习笔记5--高精地图解决方案
90%的人都不懂的泛型,泛型的缺陷和应用场景
How Windows bat script automatically executes sqlcipher command
@SerializedName注解使用
uniapp + uniCloud+unipay 实现微信小程序支付功能
剪掉ImageNet 20%数据量,模型性能不下降!Meta斯坦福等提出新方法,用知识蒸馏给数据集瘦身...
Apache DolphinScheduler 系统架构设计
The Alipay in place function can't be found, and the Alipay in place function is offline
Android SQLite database encryption
Fluent development: setting method of left and right alignment of child controls in row
StaticLayout的使用详解
【 conseils 】 obtenir les valeurs des axes X et y de la fonction cdfplot dans MATLAB
卷起來,突破35歲焦慮,動畫演示CPU記錄函數調用過程
《剑来》语句摘录(七)
Kotlin Compose 与原生 嵌套使用