当前位置:网站首页>Go 语言使用 MySQL 的常见故障分析和应对方法
Go 语言使用 MySQL 的常见故障分析和应对方法
2022-07-05 09:27:00 【百度Geek说】

导读:很多同学在使用Go和数据库打交道的过程中,经常会遇到一些异常不知道为什么,本文从SQL连接池的原理进行分析,模拟了一些例子对异常的现象进行解读分析,并给出一些常见的应对手段,期望能帮助到大家。
全文12795字,预计阅读时间32分钟
有很多同学遇到了 MySQL 查询缓慢的问题,其可能表现为 SQL 语句很简单,但是查询耗时很长。可能是由于这样一些原因所致。
1、资源未及时释放
Go 的 sql 包使用的是长连接方式让 Client 和 SQL Server 交互,为了避免 SQL Server 链接过多,一般会在 Client 端限定最大连接数。
下面是sql 的连接池的状态图(设置了最大打开连接数的情况):
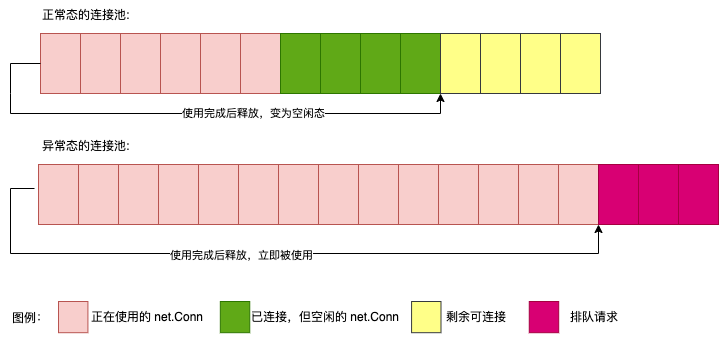
SQL Client 和 Server 交互后,有些结果返回的是一个流(Stream),此时的网络连接(Conn)是被 Stream 对象继续使用的,Client 需要迭代读取结果,读取完成后应立即关闭流以回收资源(释放 conn)。
比如最长用的DB.QueryContext 方法即是如此:
// QueryContext 查询一些结果
// query:select * from test limit 10
func (db *DB) QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
type Rows struct{
Close( ) error
ColumnTypes( ) ( [ ]*ColumnType, error)
Columns( ) ( [ ]string, error)
Err( ) error
Next( ) bool
NextResultSet( ) bool
Scan(dest ...any) error
}
当还有结果的时候(即Rows.Next()==true 时),说明还有结果未读取出来,此时必须调用 Rows.Close() 方法来对流进行关闭以释放连接(让当前连接变为空闲状态以 让其他逻辑可以使用该连接)。
1.1 实验1-不调用 Rows.Close()
若不调用 Close 又会怎样呢?下面做一个实验来观察一下:
select * from user;
+----+-------+---------------------+----------+--------+
| id | email | register_time | password | status |
+----+-------+---------------------+----------+--------+
| 2 | dw | 2011-11-11 11:01:00 | d | 0 |
+----+-------+---------------------+----------+--------+
1 row in set (0.03 sec)
package main
import (
"context"
"database/sql"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"sync"
"time"
_ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql"
)
func main() {
db, err := sql.Open("mysql", "root:@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/test")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
db.SetMaxOpenConns(1)
// 启动一个单独的协程,用于输出 DB 的状态信息
go func() {
tk := time.NewTicker(3 * time.Second)
defer tk.Stop()
for range tk.C {
bf, _ := json.Marshal(db.Stats())
fmt.Println("db.Stats=", string(bf))
}
}()
// 启动 10 个协程,同时查询数据
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go func(id int) {
defer wg.Done()
queryOne(id, db)
}(i)
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println("finish")
}
func queryOne(id int, db *sql.DB) {
start := time.Now()
rows, err := db.QueryContext(context.Background(), "select * from user limit 1")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// defer rows.Close()
// 没有从 Rows 里读取结果,也没有调用 rows.Close
fmt.Println("id=", id, "hasNext=", rows.Next(), "cost=", time.Since(start))
}
执行后将输入如下内容:
id= 0 hasNext= true cost= 9.607371ms
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
解读一下状态数据:
{
"MaxOpenConnections": 1, // 最大打开连接数,和代码设置的一致,是 1
"OpenConnections": 1, // 已打开的连接数
"InUse": 1, // 正在使用的连接数
"Idle": 0, // 空闲连接数
"WaitCount": 9, // 等待连接数
"WaitDuration": 0, // 等待总耗时(在等待退出时才计数)
"MaxIdleClosed": 0, // 超过最大 idle 数所关闭的连接总数
"MaxIdleTimeClosed": 0, // 超过追到 idle 时间所关闭的连接总数
"MaxLifetimeClosed": 0 // 超过最大生命周期所关闭的连接总数
}
从上面的输出可以看出,总共启动了 10 个协程,只有一个协程的 queryOne 方法成功执行了,其他 9 个协程的都是处于等待状态。
1.2 实验2-调用 Rows.Close()
若将 queryOne 方法的,“// defer rows.Close()” 的注释去掉,即变为:
func queryOne(id int, db *sql.DB) {
start := time.Now()
rows, err := db.QueryContext(context.
Background(), "select * from user limit 1")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer rows.Close() // 打开了此处的注释,Close 方法会释放资源
fmt.Println("id=", id, "hasNext=", rows.Next(), "cost=", time.Since(start))
}
执行后,会输出如下内容:
# go run main.go
id= 9 hasNext= true cost= 4.082448ms
id= 3 hasNext= true cost= 5.670052ms
id= 8 hasNext= true cost= 5.745443ms
id= 5 hasNext= true cost= 6.238615ms
id= 6 hasNext= true cost= 6.520818ms
id= 7 hasNext= true cost= 6.697782ms
id= 4 hasNext= true cost= 6.953454ms
id= 1 hasNext= true cost= 7.1079ms
id= 0 hasNext= true cost= 7.3036ms
id= 2 hasNext= true cost= 7.464726ms
finish
上述输出结果说明所有的 10 个协程都成功执行完成。
1.3 实验3- 使用带超时的 Context
补充,上述调用 QueryContext 方法的时候,使用的是context.Background(),所以是一致阻塞的效果。实际在使用的时候,传入的 context 一般是有超时时间或者支持取消的,类似这样:
func queryOne(id int, db *sql.DB) {
start := time.Now()
ctx,cancel:=context.WithTimeout(context.Background(),time.Second) // 关键
defer cancel() // 关键。若将此行替换为 _=cancel,又是另外一种结果了
rows, err := db.QueryContext(ctx , "select * fro m user limit 1")
if err != nil {
// panic (err)
fmt.Println("BeginTx failed:",err)
return
}
// defer rows.Close () // 打开了此处的注 释,Close 方法会释放资源
fmt.Println("id=" , id, "hasNext=", rows.Next(), "cost=", time.Since (start))
}
运行后可以观察到,所有的 10 个协程也都执行成功了:
id= 9 hasNext= true cost= 1.483715ms
id= 3 hasNext= true cost= 175.675µs
id= 6 hasNext= true cost= 1.277596ms
id= 1 hasNext= true cost= 174.307µs
id= 7 hasNext= true cost= 108.061µs
id= 4 hasNext= true cost= 115.072µs
id= 2 hasNext= true cost= 104.046µs
id= 0 hasNext= true cost= 96.833µs
id= 8 hasNext= true cost= 123.758µs
id= 5 hasNext= true cost= 92.791µs
finish
由于 context 是带超时的,而且执行完成后会调用 defer cancel() 将 ctx 取消,所以即使没有使用 rows.Close 释放资源,ctx 在被cancel后也会立即释放资源。
若是将 defer cancel() 换为 _=cancel ,又是另外一种结果了,我们将看到的是:
d= 9 hasNext= true cost= 2.581813ms
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
1.4 解决方案
小结:
我们应该使用QueryContext 这类支持传入 context 的函数,并且传入带超时控制的 context,并且在逻辑执行完成后,应使用 defer 方法将 context 取消。
对于返回一个流类型的结果,使用完成后一定需要调用 Close 方法以释放资源。
所有 *sql.DB、*sql.Tx、*sql.Stmt 的返回 *Conn、*Stmt、*Rows 这几种类型的都需要 Close:
type DB/Tx/Stmt struct{
Conn(ctx context.Context) (*Conn, error)
Prepare(query string) (*Stmt, error)
PrepareContext(ctx context.Context, query string) (*Stmt, error)
Query(query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
}
要避免该问题出现,一般只需要如上例,添加上 defer rows.Close() 即可。
若是使用的 GDP 框架,读取 Rows 结果,可以使用 mysql.ReadRowsClose 方法,在读取完成后,会自动的 Close。比如:
type user struct {
ID int64 `ddb:"id"`
Status uint8 `ddb:"status"`
}
func readUsers(ctx context.Context)([]*user,error)
rows, err := cli.QueryContext(ctx, "select * from user where status=1 limit 5")
if err != nil {
return nil,err
}
var userList []*user
err=mysql.ReadRowsClose(rows, &userList)
return userList,err
}
或者是 QueryWithBuilderScan:
b := &SimpleBuilder{
SQL: "SELECT id,name from user where id=1",
}
type user struct{
Name string `ddb:"name"`
ID int `ddb:"id"`
}
var us []*user
err = mysql.QueryWithBuilderScan(ctx, client, b, &us)
2、事务不完整
打开一个事务(Tx)后,必须提交(Commit)或者回滚(Rollback),否则会事务不完整,也会导致 Client 端资源(连接)不释放。
func (db *DB) BeginTx(ctx context.Context, opts *TxOptions) (*Tx, error)
type Tx
func (tx *Tx) Commit() error // 提交事务
func (tx *Tx) Rollback ( ) error // 回滚事务
func (tx *Tx) Exec(query string, args ...any) (Result, error)
func (tx *Tx) ExecContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (Result, error)
func (tx *Tx) Prepare(query string) (*Stmt, error)
func (tx *Tx) PrepareContext(ctx context.Context, query string) (*Stmt, error)
func (tx *Tx) Query(query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
func (tx *Tx) QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
func (tx *Tx) QueryRow(query string, args ...any) *Row
func (tx *Tx) QueryRowContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) *Row
func (tx *Tx) Stmt(stmt *Stmt) *Stmt
func (tx *Tx) StmtContext(ctx context.Context, stmt *Stmt) *Stmt
2.1 和 PHP 的区别
另外需要注意的是,使用 Go标准库的 DB.BeginTx 方法开启一个事务后,会得到一个事务对象 Tx,要让一批 SQL 在一个事务里执行需要让这些 SQL 在此 Tx 对象上执行。这点和 PHP 的是不一样的,比如在 PHP 中是这样使用事务:
<?php
/* 开始一个事务,关闭自动提交 */
$dbh->beginTransaction();
/* 在全有或全无的基础上插入多行记录(要么全部插入,要么全部不插入) */
$sql = 'INSERT INTO fruit(name, colour, calories) VALUES (?, ?, ?)';
$sth = $dbh->prepare($sql);
foreach ($fruits as $fruit) {
$sth->execute(array(
$fruit->name,
$fruit->colour,
$fruit->calories,
));
}
/* 提交更改 */
$dbh->commit();
// 此代码来自 https://www.php.net/manual/zh/pdo.commit.php
而使用 Go 的事务是这样的:
import (
"context"
"database/sql"
"log"
)
var (
ctx context.Context
db *sql.DB
)
func main() {
tx, err := db.BeginTx(ctx, &sql.TxOptions{Isolation: sql.LevelSerializable})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
id := 37
// 使用 Tx 执行 Update 语句,而不是继续使用 db.Exec
_, execErr := tx.Exec(`UPDATE users SET status = ? WHERE id = ?`, "paid", id)
if execErr != nil {
_ = tx.Rollback()
log.Fatal(execErr)
}
if err := tx.Commit(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
// 此代码来自于:https://pkg.go.dev/database/[email protected]#example-DB.BeginTx
2.2 实验
下面继续实验事务不完整的影响,主体部分和上述一样,queryOne 方法变成如下这样:
func queryOne(id int, db *sql.DB) {
tx,err:=db.BeginTx(context.Background(),nil)
if err!=nil{
panic(err)
}
// defer tx.Rollback()
start := time.Now()
rows, err := tx.QueryContext(context.Background(), "select * from user limit 1")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer rows.Close()
// 事务没有回滚、提交
fmt.Println("id=", id, "hasNext=", rows.Next(), "cost=", time.Since(start))
}
执行后输入和上述没有 rows.Close 类似:
id= 9 hasNext= true cost= 11.670369ms
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
同样,总共启动了 10 个协程,只有一个协程的 queryOne 方法成功执行了,其他 9 个协程的都是处于等待状态。
若将上述queryOne 方法中的 // defer tx.Rollback() 的注释打开,则所有 10 个协程都可以成功执行完成。
2.3 解决方案
要避免事务不完整,要保证事务要么被 Commit,要么被 Rollback。
若是使用的 GDP 框架,可以使用 mysql.BeginTx 方法来使用事务。该方案可以更安全的使用事务,会自动的依据 函数返回值来决定是 Commit 还是 Rollback,若业务函数出现了 panic 也会自动的 Rollback。
// 业务逻辑函数的定义,在此函数内实现事务内的增删改查
// 返回 error==nil 则 tx.Commit(),否则 tx.Rollback()
type doFunc func(ctx context.Context, qe QueryExecuto r) error
func BeginTx(ctx context.Context, cli CanBeginTx, opts *sql.TxOptions, do doFunc) error
var cli mysql.Client
updateUserNameByID := func(ctx context.Context, id uint64, name string) error {
// 使用 BeginTx 方法,能更省心的处理事务
err := mysql.BeginTx(ctx, cli, nil, func(ctx context.Context, qe mysq.QueryExecutor) error {
// 其他的数据库更新逻辑略
b1 := &mysql.SimpleBuilder{}
b1.Append("select name from user where uid=?", id)
var oldName string
if err := mysql.QueryRowWithBuilderScan(ctx, qe, b1, &oldName); err != nil {
return err
}
if oldName == "诸葛亮" || oldName == name {
// 返回 err,mysql.BeginTx 方法将会回滚事务
return fmt.Errorf("不需要更新,事务整体回滚")
}
b2 := &mysql.SimpleBuilder{}
b2.Append("update user set name=? where id=?", name, id)
_, err := mysql.ExecWithBuilder(ctx, qe, b2)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 返回 nil,mysql.BeginTx 方法将会提交事务
return nil
})
return err
}
3、其他原因
3.1 不支持预处理
默认一般会使用预处理的方式来提升 SQL 的安全性,避免产生 SQL 注入的问题。
若是在厂内使用集群版MySQL:DDBS(DRDS),其对 prepare 支持的并不好,使用后会导致性能特别差。可能表现为,本应该几毫秒返回的查询,实际上要数百毫秒甚至数秒才能返回。此时需要在参数中添加上配置项 interpolateParams=true ,关闭 prepare 功能来解决。
Name = "demo"
# 其他配置项略
[MySQL]
Username = "example"
# 其他参数略
DSNParams ="charset=utf8&timeout=90s&collation=utf8mb4_unicode_ci&parseTime=true&interpolateParams=true"
4、如何排查
我们可以利用 DB 的 Stats() 接口返回的数据来分析是否存在上述问题。在上述章节中,我们就是打印此数据来观察 Client 的状态信息。
{
"MaxOpenConnections" : 1 , // 最大打开连接数,和代码设置的一致,是 1
"OpenConnections" : 1 , // 已打开的连接数
"InUse" : 1 , // 正在使用的连接数
"Idle" : 0 , // 空闲连接数
"WaitCount" : 9 , // 等待连接数
"WaitDuration" : 0 , // 等待总耗时(在等待退出时才计数)
"MaxIdleClosed" : 0 , // 超过最大 idle 数所关闭的连接总数
"MaxIdleTimeClosed" : 0 , // 超过追到 idle 时间所关闭的连接总数
"MaxLifetimeClosed" : 0 // 超过最大生命周期所关闭的连接总数
}
若使用的是 GDP 框架,我们可以通过如下几种手段来观察此数据。
4.1 集成 GDP 应用面板
在百度厂内,GDP 框架(百度内部的 Go Develop Platform,具有易用性好、易扩展、易观察、稳定可靠的特点,被数千模块使用)提供了一个叫做"GDP应用面板"的功能模块,该模块提供了可视化的 UI 让我们可以非常方便的查看、观察应用的各种状态信息。比如可以查看系统信息、文件系统信息、网络状态信息、编译信息、go runtime信息、框架里各种组件的状态信息(如服务发现的运转状态、MySQL、Redis 等 各种 Client 的连接池信息等)。
集成该功能非常简单,只需要添加 2 行配置性代码。
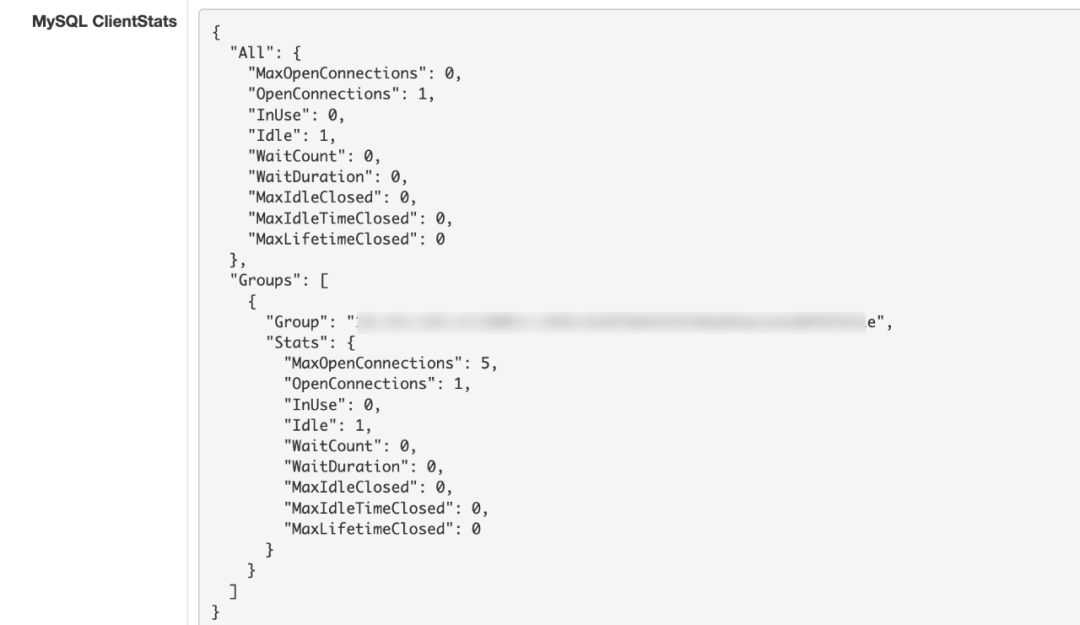
完成集成后,可以通过 http://ip:port/debug/panel/?tab=servicer 来访问此面板,找到对应的 servicer 后(页面的地址是 /debug/panel/?tab=servicer&key={servicer_name} ),页面上的 “MySQL ClientStats”段落即为当前 MySQL Client 的 Stats 信息。比如:
4.2 集成监控
GDP 框架的标准化指标监控能力已经将所有 MySQL Client 的 Stats 信息进行了采集输出。可以以 prometheus 或者 bvar 格式输出。
完成集成后,访问 http://ip:port/metrics/service 即可查看到对应的指标项,大致是这样的:
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="ConnType"} 1
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="IPTotal"} 1
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="InUseAvg"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="InUseMax"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="InUseTotal"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="NumOpenAvg"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="NumOpenCfg"} 100
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="NumOpenMax"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="NumOpenTotal"} 0
可以对上述指标添加报警,以帮我们更快发现并定位到问题。
4.3 输出到日志
若不采用上述 2 种方案,还可以采用启动一个异步协程,定期将 Stats 信息输出到日志的方案,以方便我们分析定位问题。
————————END————————
推荐阅读:
边栏推荐
- Android privacy sandbox developer preview 3: privacy, security and personalized experience
- Uni app implements global variables
- Ministry of transport and Ministry of Education: widely carry out water traffic safety publicity and drowning prevention safety reminders
- 生成对抗网络
- 【PyTorch Bug】RuntimeError: Boolean value of Tensor with more than one value is ambiguous
- Applet network data request
- 云计算技术热点
- 【ManageEngine】如何利用好OpManager的报表功能
- [beauty of algebra] solution method of linear equations ax=0
- My life
猜你喜欢
LeetCode 503. Next bigger Element II
Node の MongoDB Driver
Introduction Guide to stereo vision (6): level constraints and polar correction of fusiello method
![[ctfhub] Title cookie:hello guest only admin can get flag. (cookie spoofing, authentication, forgery)](/img/78/d9d1a66fc239e7c62de1fce426d30d.jpg)
[ctfhub] Title cookie:hello guest only admin can get flag. (cookie spoofing, authentication, forgery)
Confusion matrix
利用请求头开发多端应用
Applet customization component
Node collaboration and publishing
高性能Spark_transformation性能
项目实战 | Excel导出功能
随机推荐
Talking about the difference between unittest and pytest
顶会论文看图对比学习(GNN+CL)研究趋势
Thermometer based on STM32 single chip microcomputer (with face detection)
Kotlin introductory notes (I) kotlin variables and non variables
【阅读笔记】图对比学习 GNN+CL
2309. 兼具大小写的最好英文字母
Shutter uses overlay to realize global pop-up
Huber Loss
Applet (subcontracting)
.NET服务治理之限流中间件-FireflySoft.RateLimit
Unity skframework framework (XXIII), minimap small map tool
Node collaboration and publishing
uni-app---uni.navigateTo跳转传参使用
一文详解图对比学习(GNN+CL)的一般流程和最新研究趋势
[Yugong series] go teaching course 003-ide installation and basic use in July 2022
Kotlin introductory notes (VIII) collection and traversal
nodejs_ fs. writeFile
初识结构体
MySQL does not take effect in sorting string types
A detailed explanation of the general process and the latest research trends of map comparative learning (gnn+cl)