当前位置:网站首页>Confusion matrix
Confusion matrix
2022-07-05 08:59:00 【Wanderer001】
Reference resources Confusion matrix (Confusion Matrix) - cloud + Community - Tencent cloud
brief introduction
The confusion matrix is ROC The basis of curve drawing , At the same time, it is also the most basic method to measure the accuracy of classification model , Most intuitive , The simplest way to calculate .
Explain the version in one sentence :
The confusion matrix is the error classification of the statistical classification model , The number of observations classified into pairs , Then show the results in a table . This table is the confusion matrix .
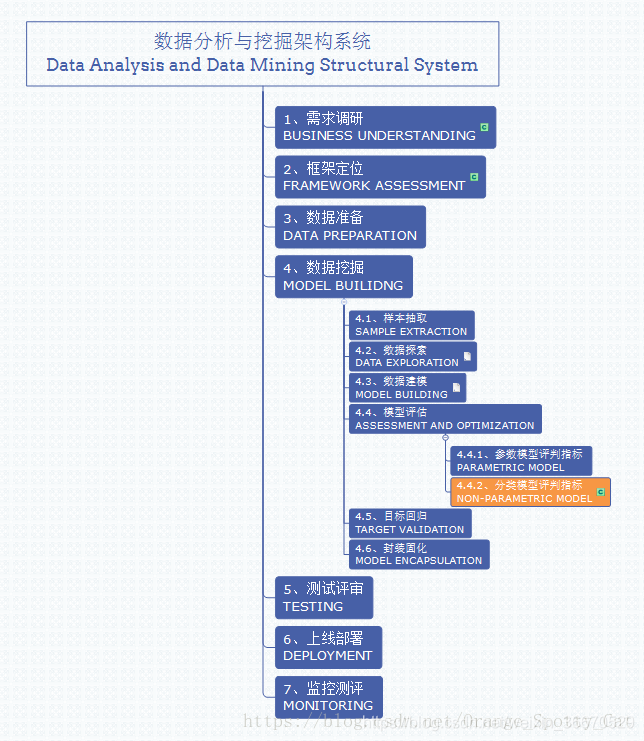
Data analysis and mining system location
Confusion matrix is the index to judge the results of the model , Part of the model evaluation . Besides , Confusion matrix is often used to judge classifiers (Classifier) The advantages and disadvantages of , It is applicable to the data model of different types , Such as classification tree (Classification Tree)、 Logical regression (Logistic Regression)、 Linear discriminant analysis (Linear Discriminant Analysis) Other methods .
In the evaluation index of classification model , There are three common methods :
- Confusion matrix ( Also known as error matrix ,Confusion Matrix)
- ROC curve
- AUC area
This article mainly introduces the first method , Confusion matrix , Also known as error matrix .
The position of this method in the whole data analysis and mining system is shown in the figure below .
Definition of confusion matrix
Definition of confusion matrix
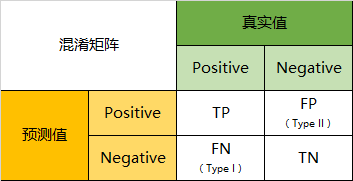
Confusion matrix (Confusion Matrix), Its essence is far less popular than its name sounds . matrix , It can be understood as a table , The confusion matrix is actually just a table .
Take the simplest binary classification in the classification model as an example , For this kind of problem , Our model ultimately needs to judge that the result of the sample is 0 still 1, Or rather, positive still negative.
We collect samples , Can directly know the real situation , What data results are positive, What are the results negative. meanwhile , We use the sample data to run out the results of the classification model , You can also know what the model thinks these data are positive, Which are negative.
therefore , We can get these four basic indicators , I call them primary indicators ( At the bottom of the ):
The real value is positive, The model considers that positive The number of (True Positive=TP)
The real value is positive, The model considers that negative The number of (False Negative=FN): This is the first type of statistical error (Type I Error)
The real value is negative, The model considers that positive The number of (False Positive=FP): This is the second type of statistical error (Type II Error)
The real value is negative, The model considers that negative The number of (True Negative=TN)
Present these four indicators together in the table , We can get such a matrix , We call it the confusion matrix (Confusion Matrix):
Index of confusion matrix
Predictive classification model , I must hope that the more accurate the better . that , Corresponding to the confusion matrix , That must be hope TP And TN A large number of , and FP And FN The number is small . So when we get the confusion matrix of the model , You need to see how many observations are in the second 、 The position corresponding to the four quadrants , The more values here, the better ; conversely , In the first place 、 The less the observed values in the corresponding positions of the three and four quadrants, the better .
Two level index
however , The confusion matrix counts numbers , Sometimes faced with a lot of data , Just count the numbers , It's hard to measure the quality of the model . Therefore, the confusion matrix extends the basic statistical results as follows 4 Indicators , I call them secondary indicators ( Obtained by adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing the lowest index ):
Accuracy rate (Accuracy)—— For the whole model
Accuracy (Precision)
sensitivity (Sensitivity): It's the recall rate (Recall)
Specificity (Specificity)
I use tables to define these four indicators 、 Calculation 、 The understanding is summarized :
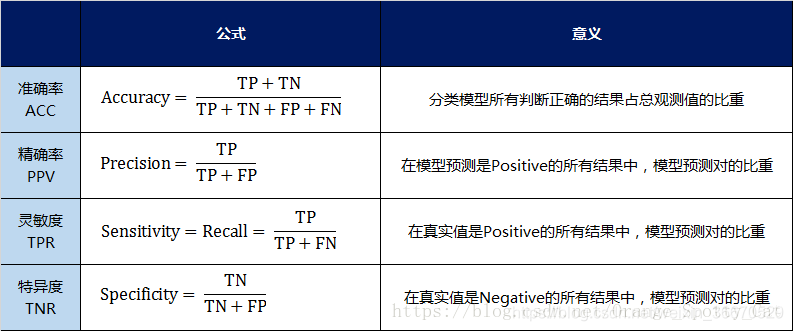
Through the above four secondary indicators , The result of the number in the confusion matrix can be transformed into 0-1 The ratio between . It's easy to make standardized measurements .
Expand on the basis of these four indicators , Another three-level indicator of the production order
Third level index
This indicator is called F1 Score. His formula is :
among ,P representative Precision,R representative Recall.
F1-Score The indicators synthesize Precision And Recall The result of the output .F1-Score The value range of is from 0 To 1 Of ,1 The output representing the model is the best ,0 The output of representative model is the worst .
Examples of confusion matrices
When the classification problem is dichotomous, the problem is , The confusion matrix can be calculated by the above method . When the results of classification are more than two , The confusion matrix also applies .
Take the following confusion matrix as an example , The purpose of our model is to predict what animals the sample is , This is our result :
Through the confusion matrix , We can draw the following conclusion :
Accuracy
In total 66 Of the animals , We're right in all 10 + 15 + 20=45 Samples , So the accuracy (Accuracy)=45/66 = 68.2%.
Take the cat for example , We can combine the above diagram into a bipartite problem :
Precision
therefore , Take the cat for example , The results of the model tell us ,66 There are... In the animals 13 It's just cats , But actually it's 13 The cat has only 10 Only the prediction is right . The model thinks it's a cat's 13 In an animal , Yes 1 A dog , Two pigs . therefore ,Precision( cat )= 10/13 = 76.9%
Recall
Take the cat for example , In total 18 A real cat , Our model thinks that there are only 10 It's just cats , The rest 3 Just a dog ,5 All pigs . this 5 Eighty percent of them are orange cats , Can understand . therefore ,Recall( cat )= 10/18 = 55.6%
Specificity
Take the cat for example , In total 48 Among animals that are not cats , According to the model, there are 45 It's not a cat . therefore ,Specificity( cat )= 45/48 = 93.8%.
Although in 45 In an animal , The model still thinks it's wrong 6 A dog and 4 Cats , But from a cat's point of view , There is nothing wrong with the judgment of the model .
( Here is the reference Wikipedia,Confusion Matrix The explanation of ,https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Confusion_matrix)
F1-Score
Through the formula , You can calculate that , For cats ,F1-Score=(2 * 0.769 * 0.556)/( 0.769 + 0.556) = 64.54%
Again , We can also calculate the secondary and tertiary index values of pigs and dogs respectively .
边栏推荐
- Count of C # LINQ source code analysis
- Causes and appropriate analysis of possible errors in seq2seq code of "hands on learning in depth"
- golang 基础 ——map、数组、切片 存放不同类型的数据
- Multiple linear regression (gradient descent method)
- [beauty of algebra] singular value decomposition (SVD) and its application to linear least squares solution ax=b
- 驾驶证体检医院(114---2 挂对应的医院司机体检)
- AdaBoost use
- [formation quotidienne - Tencent Selection 50] 557. Inverser le mot III dans la chaîne
- 一题多解,ASP.NET Core应用启动初始化的N种方案[上篇]
- RT-Thread内核快速入门,内核实现与应用开发学习随笔记
猜你喜欢
优先级队列(堆)

Beautiful soup parsing and extracting data
Halcon shape_ trans
Ros-10 roslaunch summary

Halcon color recognition_ fuses. hdev:classify fuses by color

微信H5公众号获取openid爬坑记

AUTOSAR从入门到精通100讲(103)-dbc文件的格式以及创建详解
容易混淆的基本概念 成员变量 局部变量 全局变量

Halcon clolor_ pieces. Hedv: classifier_ Color recognition
ROS learning 4 custom message
随机推荐
Applet (use of NPM package)
uni-app 实现全局变量
[牛客网刷题 Day4] JZ32 从上往下打印二叉树
生成对抗网络
ROS learning 4 custom message
ABC#237 C
什么是防火墙?防火墙基础知识讲解
Rebuild my 3D world [open source] [serialization-3] [comparison between colmap and openmvg]
kubeadm系列-00-overview
Introduction Guide to stereo vision (7): stereo matching
Array,Date,String 对象方法
Dynamic dimensions required for input: input, but no shapes were provided. Automatically overriding
Use and programming method of ros-8 parameters
Hello everyone, welcome to my CSDN blog!
驾驶证体检医院(114---2 挂对应的医院司机体检)
某公司文件服务器迁移方案
12、动态链接库,dll
【日常訓練--騰訊精選50】557. 反轉字符串中的單詞 III
JS asynchronous error handling
[code practice] [stereo matching series] Classic ad census: (4) cross domain cost aggregation