当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode 31. Next spread
LeetCode 31. Next spread
2022-07-05 09:26:00 【Sasakihaise_】


【 analysis 】 If you want to get an element larger than the current number , We need to exchange the next larger number with the previous smaller number , And the bits exchanged in front should be as low as possible , The numbers exchanged later should be as small as possible , But it has to be bigger than the front . Then it needs to be done in two steps :
1. Find the position of the previous element to be exchanged .
2. Look for the smallest element larger than him from the back .
about 1, Let's look at a situation 5,4,3,2,1, We find that this number is already the largest arrangement , That is, you can't find the position you can exchange in front . But for permutations 3,5,4,2,1, If you cover up 3, hinder 5,4,2,1 It is already the maximum , however 3 This position can be changed , So it is not difficult to find , When a sequence is arranged in reverse order , His composition is already the maximum . If such two elements are found (i, j),nums[i] < nums[j], Explain that you can change nums[i] To make the element bigger . In this way, we find the minimum bit of the element to be exchanged .
about 2, Suppose the insertion position is i, that [i + 1, n) It must be in descending order , Continue traversing from back to front , Just look for the first element larger than the insertion position , This element is greater than i The smallest element of the element at .
After exchange , because [i + 1, n) Or in descending order , He is still a big number , But because of the exchange i Cause of , No matter how they are arranged in the back , Are bigger than the previous one , In order to make the result smaller , Also change this part into ascending order .( You can directly reverse , It's fine too sort)
class Solution {
// Monotonic stack 10:12 10:30
// Looking back and forth , If it's in ascending order , The description cannot be changed later, for example 4 6 5 3 2 1, We cannot change 65321 From your location
// Find the next one
// however 4 6 It's in reverse order , Explain that you can find a comparison in the back 4 Large element exchange to make the exchange larger than before
// The first ratio found from the back 4 The big one is 5, In exchange for 4 and 5 And then get 5 6 4 3 2 1, But now it's not the smallest element
// It can only be said that 5 The element at the beginning must be larger than that just now 4 At the beginning , So we have to deal with 5 The following elements are arranged in order from small to large
// current 5 1 2 3 4 6 Is the next smallest element
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, i, j;
for (i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {
break;
}
}
if (i == -1) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return;
}
for (j = n - 1; j > i; j--) {
if (nums[j] > nums[i]) {
break;
}
}
var t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
Arrays.sort(nums, i + 1, n);
}
}class Solution {
// Monotonic stack 10:12 10:30
// Looking back and forth , If it's in ascending order , The description cannot be changed later, for example 4 6 5 3 2 1, We cannot change 65321 From your location
// Find the next one
// however 4 6 It's in reverse order , Explain that you can find a comparison in the back 4 Large element exchange to make the exchange larger than before
// The first ratio found from the back 4 The big one is 5, In exchange for 4 and 5 And then get 5 6 4 3 2 1, But now it's not the smallest element
// It can only be said that 5 The element at the beginning must be larger than that just now 4 At the beginning , So we have to deal with 5 The following elements are arranged in order from small to large
// current 5 1 2 3 4 6 Is the next smallest element
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, i, j;
for (i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {
break;
}
}
if (i == -1) {
i = 0; j = n - 1;
while (i < j) {
int t = nums[i];
nums[i++] = nums[j];
nums[j--] = t;
}
return;
}
for (j = n - 1; j > i; j--) {
if (nums[j] > nums[i]) {
break;
}
}
int t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
i++;
j = n - 1;
while (i < j) {
t = nums[i];
nums[i++] = nums[j];
nums[j--] = t;
}
}
}边栏推荐
- fs. Path module
- [beauty of algebra] solution method of linear equations ax=0
- SMT32H7系列DMA和DMAMUX的一点理解
- Causes and appropriate analysis of possible errors in seq2seq code of "hands on learning in depth"
- Thermometer based on STM32 single chip microcomputer (with face detection)
- 什么是防火墙?防火墙基础知识讲解
- Applet network data request
- 一题多解,ASP.NET Core应用启动初始化的N种方案[上篇]
- . Net service governance flow limiting middleware -fireflysoft RateLimit
- Principle and performance analysis of lepton lossless compression
猜你喜欢
图神经网络+对比学习,下一步去哪?
什么是防火墙?防火墙基础知识讲解
Kotlin introductory notes (V) classes and objects, inheritance, constructors
An article takes you into the world of cookies, sessions, and tokens
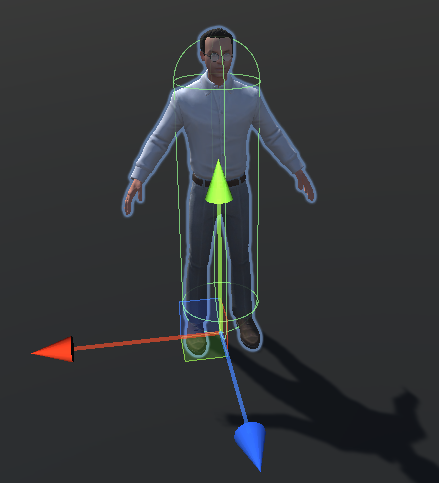
Unity SKFramework框架(二十四)、Avatar Controller 第三人称控制
VS Code问题:长行的长度可通过 “editor.maxTokenizationLineLength“ 进行配置
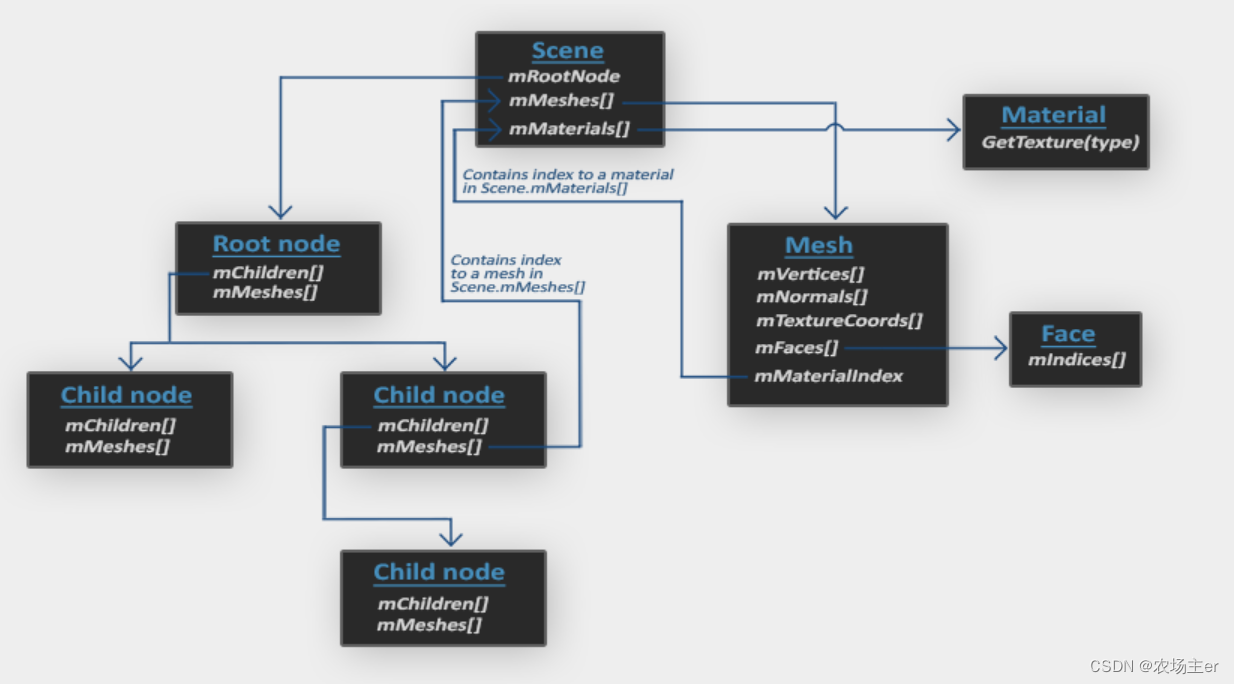
OpenGL - Model Loading
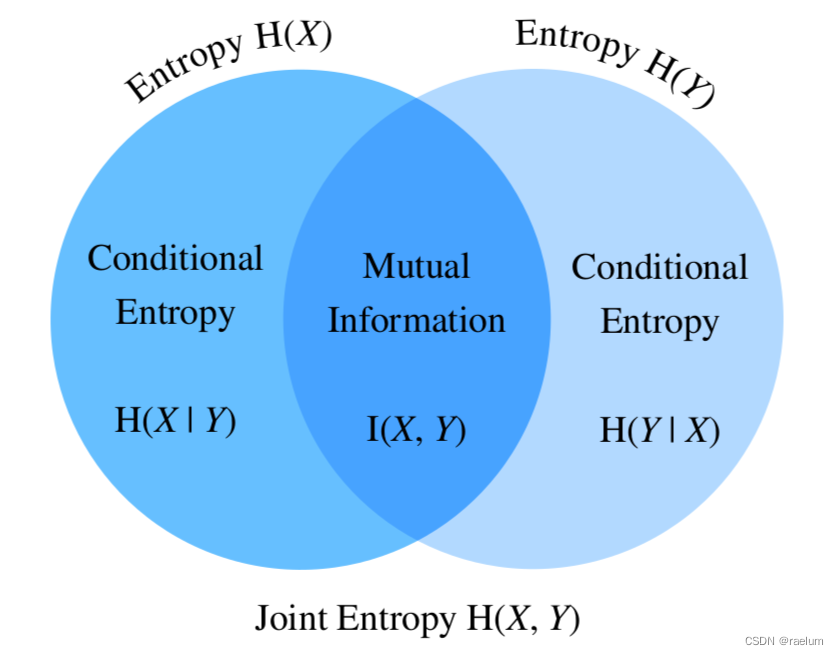
Information and entropy, all you want to know is here
Can't find the activitymainbinding class? The pit I stepped on when I just learned databinding
Attention is all you need
随机推荐
Introduction Guide to stereo vision (6): level constraints and polar correction of fusiello method
Nips2021 | new SOTA for node classification beyond graphcl, gnn+ comparative learning
一文详解图对比学习(GNN+CL)的一般流程和最新研究趋势
2011-11-21 training record personal training (III)
Principle and performance analysis of lepton lossless compression
[code practice] [stereo matching series] Classic ad census: (6) multi step parallax optimization
Multiple solutions to one problem, asp Net core application startup initialization n schemes [Part 1]
Newton iterative method (solving nonlinear equations)
微信小程序获取住户地区信息
Attention is all you need
Unity SKFramework框架(二十二)、Runtime Console 运行时调试工具
Node collaboration and publishing
Talking about label smoothing technology
一次 Keepalived 高可用的事故,让我重学了一遍它
Svg optimization by svgo
Jenkins Pipeline 方法(函数)定义及调用
Wechat applet obtains household area information
Kotlin introductory notes (III) kotlin program logic control (if, when)
Unity skframework framework (24), avatar controller third person control
. Net service governance flow limiting middleware -fireflysoft RateLimit