当前位置:网站首页>[flask] obtain request information, redirect and error handling
[flask] obtain request information, redirect and error handling
2022-07-06 01:28:00 【Coriander Chrysanthemum】
Preface article :
- 【Flask】Web Departure and implementation are based on Flask The smallest application
- 【Flask】 Static file and template rendering
Get request data
We know , about Web Applications , It is important to respond to the data sent by the client to the server . stay Flask in , This information is determined by the overall situation request The object provides .
request object
The first step in using it is from flask Import in module :
from flask import request
In the previous article, I introduced , stay httpt Agreement , There are many possibilities for a request , Such as GET,POST etc. . We can go through request.method To get . stay html Sometimes we use form Forms (POST,PUT Method will make data request ) To submit data , Then the server gets form The way of data in the form is through form Property acquisition . A simple case is as follows :
@app.route('/login', methods=['POST', 'GET'])
def login():
error = None
if request.method == 'POST':
if valid_login(request.form['username'],
request.form['password']):
return log_the_user_in(request.form['username'])
else:
error = 'Invalid username/password'
# the code below is executed if the request method
# was GET or the credentials were invalid
return render_template('login.html', error=error)
When key Not in the form In the middle of the day , Will pack KeyError It's abnormal . Then align according to the specific situation try except Operation to capture .
about html End in URL In the middle of the transmission (?key=value), We can use args Get parameters for properties of :
searcgword=request.args.get('key', '')
Upload files
Another data type is file . Use Flask It's also more convenient . We just need to guarantee form Set... In the form enctype='multipart/form-data', Otherwise, the file cannot be transferred .
The uploaded files are stored in transit or temporary files in the file system . This data is obtained using request Of files attribute . Every uploaded file will be saved in that dictionary . Its behavior is Python Of file object , But with save() Method to allow you to store data in the file system of the server . A simple case is as follows :
from flask import request
@app.route('/upload', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def upload_file():
if request.method == 'POST':
f = request.files['the_file']
f.save('/var/www/uploads/uploaded_file.txt')
...
If you want to know how files are named on the client before uploading to your application , You can visit filename attribute . But remember , This value can be forged , So never believe that value . If you want to use the file name of the client to store the file on the server , adopt Werkzeug For you secure_filename() The function passes it , as follows :
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
@app.route('/upload', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def upload_file():
if request.method == 'POST':
file = request.files['the_file']
file.save(f"/var/www/uploads/{
secure_filename(file.filename)}")
...
Cookies
If you want to visit cookies Data in , We can go through cookies attribute . If you want to set cookies, We need to borrow set_cookie Method . Again cookies The attribute is request A dictionary of objects . If you want to use Session, Please do not use it directly cookie, But use Flask Medium Session, It will be cookie Add some security to it .
Read cookies Cases in :
from flask import request
@app.route('/')
def index():
username = request.cookies.get('username')
# use cookies.get(key) instead of cookies[key] to not get a
# KeyError if the cookie is missing.
Storage cookies Content case :
from flask import make_response
@app.route('/')
def index():
resp = make_response(render_template(...))
resp.set_cookie('username', 'the username')
return resp
Please note that ,cookie Is set on the response object . Because you usually only return strings from view functions , therefore Flask They will be converted into response objects for you . If you clearly want to do this , You can use make_response() function , It is then modified . Sometimes you may want to set in a location where the response object does not already exist cookie. This can be achieved by using the deferred request callback pattern . For these things , You need to know more about the official documents .
Redirection and error handling
To redirect the user to another endpoint , Please use redirect() function ; To abort a request in advance with an error code , Please use abort() function :
from flask import abort, redirect, url_for
@app.route('/')
def index():
return redirect(url_for('login'))
@app.route('/login')
def login():
abort(401)
this_is_never_executed()
This is a rather pointless example , Because users will redirect from the index to pages they cannot access (401 Access denied ), But it shows how it works .
By default , Each error code will display a black and white error page . If you want to customize the error page , have access to errorhandler() Decorator :
from flask import render_template
@app.errorhandler(404)
def page_not_found(error):
return render_template('page_not_found.html'), 404
Be careful render_template() After calling 404. This tells Flask The status code of this page should be 404, This means that no . By default, it is assumed to be 200, It means : Deo gratias .
边栏推荐
- 282. Stone consolidation (interval DP)
- [技术发展-28]:信息通信网大全、新的技术形态、信息通信行业高质量发展概览
- Vulhub vulnerability recurrence 75_ XStream
- UE4 unreal engine, editor basic application, usage skills (IV)
- Xunrui CMS plug-in automatically collects fake original free plug-ins
- Opinions on softmax function
- Leetcode 208. Implement trie (prefix tree)
- 干货!通过软硬件协同设计加速稀疏神经网络
- 基於DVWA的文件上傳漏洞測試
- 【已解决】如何生成漂亮的静态文档说明页
猜你喜欢
c#网页打开winform exe
Folio.ink 免费、快速、易用的图片分享工具
Dede collection plug-in free collection release push plug-in
Pbootcms plug-in automatically collects fake original free plug-ins

C web page open WinForm exe
![[understanding of opportunity-39]: Guiguzi - Chapter 5 flying clamp - warning 2: there are six types of praise. Be careful to enjoy praise as fish enjoy bait.](/img/3c/ec97abfabecb3f0c821beb6cfe2983.jpg)
[understanding of opportunity-39]: Guiguzi - Chapter 5 flying clamp - warning 2: there are six types of praise. Be careful to enjoy praise as fish enjoy bait.
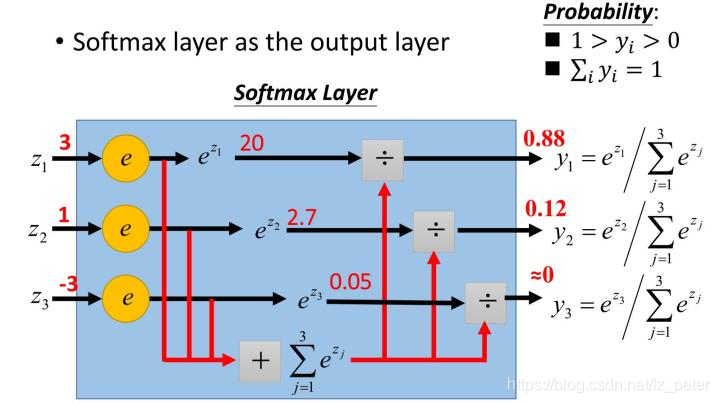
Opinions on softmax function
SSH login is stuck and disconnected
Kotlin basics 1

Vulhub vulnerability recurrence 75_ XStream
随机推荐
Docker compose configures MySQL and realizes remote connection
有谁知道 达梦数据库表的列的数据类型 精度怎么修改呀
SSH login is stuck and disconnected
A Cooperative Approach to Particle Swarm Optimization
A Cooperative Approach to Particle Swarm Optimization
ORA-00030
3D模型格式汇总
【全网最全】 |MySQL EXPLAIN 完全解读
ThreeDPoseTracker项目解析
记一个 @nestjs/typeorm^8.1.4 版本不能获取.env选项问题
Recommended areas - ways to explore users' future interests
internship:项目代码所涉及陌生注解及其作用
MCU lightweight system core
2022 Guangxi Autonomous Region secondary vocational group "Cyberspace Security" competition and its analysis (super detailed)
In the era of industrial Internet, we will achieve enough development by relying on large industrial categories
Test de vulnérabilité de téléchargement de fichiers basé sur dvwa
Leetcode skimming questions_ Sum of squares
How does Huawei enable debug and how to make an image port
Leetcode sword finger offer 59 - ii Maximum value of queue
Leetcode1961. 检查字符串是否为数组前缀
