当前位置:网站首页>【第30天】给定一个整数 n ,求它的因数之和
【第30天】给定一个整数 n ,求它的因数之和
2022-07-06 00:51:00 【执 梗】
学习指引
序、专栏前言
本专栏开启,目的在于帮助大家更好的掌握学习Java,特别是一些Java学习者难以在网上找到系统地算法学习资料帮助自身入门算法,同时对于专栏内的内容有任何疑问都可在文章末尾添加我的微信给你进行一对一的讲解。
但最最主要的还是需要独立思考,对于本专栏的所有内容,能够进行完全掌握,自己完完全全将代码写过一遍,对于算法入门肯定是没有问题的。
算法的学习肯定不能缺少总结,这里我推荐大家可以到高校算法社区将学过的知识进行打卡,以此来进行巩固以及复习。
学好算法的唯一途径那一定是题海战略,大量练习的堆积才能练就一身本领。专栏的任何题目我将会从【题目描述】【解题思路】【模板代码】【代码解析】等四板块进行讲解。
一、【例题1】
1、题目描述
给定一个整数 n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 e 9 ) n(1\leq n\leq1e9) n(1≤n≤1e9),求它的约数之和,答案对 1 e 9 + 7 1e9+7 1e9+7取模
2、解题思路
( 1 ) (1) (1)可以根据求因数个数的代码来求,有 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)和 O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n)复杂的做法。
( 2 ) (2) (2)也可以约数之和定理求解,重点讲解该定理
3、模板代码
1)朴素O(n)做法
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int mod=1000000007;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
long ans=0;
for (int i = 1; i <=n; i++) {
if (n%i==0) ans=(ans+i)%mod;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
2)优化根号n做法
import java.util.*;
public class test {
static int mod=1000000007;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
long ans=0;
for (int i = 1; i <=n/i; i++) {
if (n%i==0){
if (i!=n/i){
ans=(ans+i)%mod;
ans=(ans+n/i)%mod;
}else{
ans=(ans+i)%mod;
}
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
3)约数之和定理
import java.util.*;
public class test {
static int mod=1000000007;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
long sum=1;
for (int i = 2; i <=n/i; i++) {
if (n%i==0){
int c=0;
while (n%i==0){
c++;
n/=i;
}
long t=1;
while (c-->0) t=(t*i+1)%mod;
sum=(sum*t)%mod;
}
}
if (n>1) sum=(sum*(n+1)%mod);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
4、代码解析
- ( 1 ) (1) (1)前面讲过,对于一个正整数 n n n,由算式基本定理可得:
n = ∏ i = 1 k p i i = p 1 a 1 × p 2 a 2 × p 3 a 3 . . . . . . p k a k ( p 1 , p 2 . . . . p k 均 为 质 数 ) n=\prod_{i=1}^{k} p_i^{^i}=p_1^{a^1}\times p_2^{a^2}\times p_3^{a^3}......p_k^{a^k}(p_1,p_2....p_k均为质数) n=i=1∏kpii=p1a1×p2a2×p3a3......pkak(p1,p2....pk均为质数)
那么记 n n n的约束之和为 f ( n ) f(n) f(n),则有:
f ( n ) = ( p 1 0 + p 1 1 + . . . + p 1 a 1 ) ∗ ( p 2 0 + p 2 1 + . . . + p 2 a 2 ) ∗ . . . ( p k 0 + p k 1 + . . . + p k a k ) f(n)=(p_1^0+p_1^1+...+p_1^{a_1})*(p_2^0+p_2^1+...+p_2^{a_2})*...(p_k^0+p_k^1+...+p_k^{a_k}) f(n)=(p10+p11+...+p1a1)∗(p20+p21+...+p2a2)∗...(pk0+pk1+...+pkak) - ( 2 ) (2) (2)证明:
首先计算 p 1 a 1 p_1^{a_1} p1a1的约数之和,可知为 ( p 1 0 + p 1 1 + . . . + p 1 a 1 ) (p_1^0+p_1^1+...+p_1^{a_1}) (p10+p11+...+p1a1)
其次再算 p 2 a 2 p_2^{a_2} p2a2的约数之和,可知为 ( p 2 0 + p 2 1 + . . . + p 2 a 2 ) (p_2^0+p_2^1+...+p_2^{a_2}) (p20+p21+...+p2a2)
…
最后算出 p k a k p_k^{a^k} pkak的约数之和,可知为 ( p k 0 + p k 1 + . . . + p k a k ) (p_k^0+p_k^1+...+p_k^{a_k}) (pk0+pk1+...+pkak)
根据乘法原理可得, n n n的约数之和 f ( n ) 为 : f(n)为: f(n)为:
f ( n ) = ( p 1 0 + p 1 1 + . . . + p 1 a 1 ) ∗ ( p 2 0 + p 2 1 + . . . + p 2 a 2 ) ∗ . . . ( p k 0 + p k 1 + . . . + p k a k ) f(n)=(p_1^0+p_1^1+...+p_1^{a_1})*(p_2^0+p_2^1+...+p_2^{a_2})*...(p_k^0+p_k^1+...+p_k^{a_k}) f(n)=(p10+p11+...+p1a1)∗(p20+p21+...+p2a2)∗...(pk0+pk1+...+pkak)
二、【例题2】
1、题目描述
给定 n n n 个正整数 a i a_i ai,请你输出这些数的乘积的约数之和,答案对 1 0 9 + 7 10^9+7 109+7 取模。
2、解题思路
( 1 ) (1) (1)在上一题上,由一个数的因数之和拓展为多个数,但本质上乘积的最后仍然为一个数。
( 2 ) (2) (2)我们可以将这 n n n个数的都进行质因数的分解,统计每个质因数出现的总次数,最后使用约数之和定理即可。
3、模板代码
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static final int mod = 1000000007;
static Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
static long ans = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
while (n-- > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
getNums(a);
}
for (Integer a : map.keySet()) {
long sum=1;
int k=map.get(a);
while(k-->0) sum=(sum*a+1)%mod;
ans=(ans*sum)%mod;
}
System.out.print(ans);
}
//求质因数公式
static void getNums(int n) {
for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i++) {
while (n % i == 0) {
map.put(i, map.getOrDefault(i, 0) + 1);
n /= i;
}
}
if (n > 1) map.put(n, map.getOrDefault(n, 0) + 1);
}
}
三、推荐专栏
四、课后习题
| 序号 | 题目链接 | 难度评级 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 约数求和 | 2 |
边栏推荐
- The value of applet containers
- XML Configuration File
- MCU realizes OTA online upgrade process through UART
- Intranet Security Learning (V) -- domain horizontal: SPN & RDP & Cobalt strike
- Power query data format conversion, Split Merge extraction, delete duplicates, delete errors, transpose and reverse, perspective and reverse perspective
- 如何利用Flutter框架开发运行小程序
- STM32按键消抖——入门状态机思维
- NLP generation model 2017: Why are those in transformer
- Pointer - character pointer
- VSphere implements virtual machine migration
猜你喜欢

Cf:c. the third problem

The third season of ape table school is about to launch, opening a new vision for developers under the wave of going to sea
Arduino六足机器人
95后CV工程师晒出工资单,狠补了这个,真香...
Cannot resolve symbol error
SAP Spartacus home 页面读取 product 数据的请求的 population 逻辑
Spark SQL null value, Nan judgment and processing
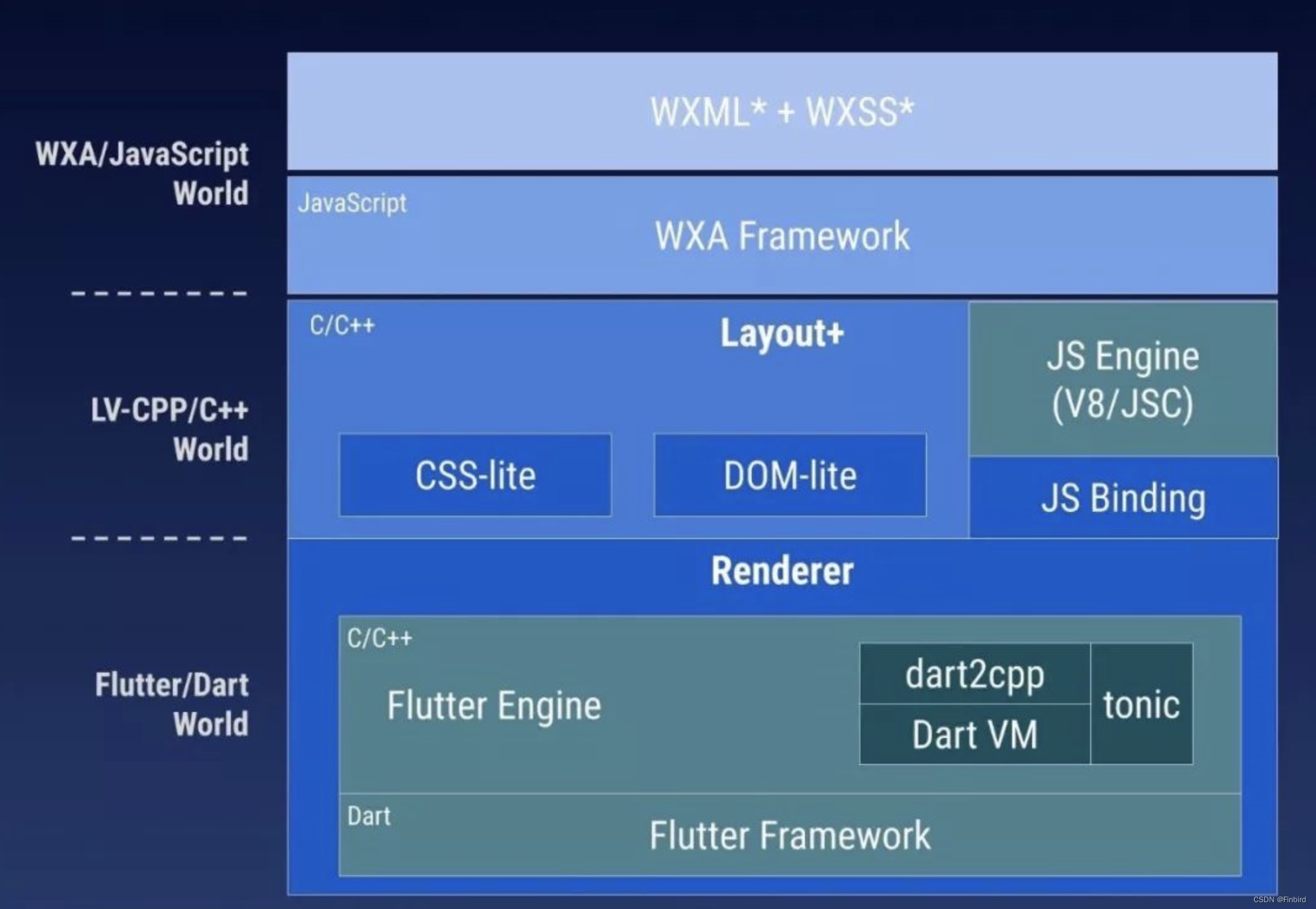
How to use the flutter framework to develop and run small programs
Recoverable fuse characteristic test
Set data real-time update during MDK debug
随机推荐
Leetcode 44 Wildcard matching (2022.02.13)
Beginner redis
Spark获取DataFrame中列的方式--col,$,column,apply
[groovy] XML serialization (use markupbuilder to generate XML data | set XML tag content | set XML tag attributes)
Zhuhai laboratory ventilation system construction and installation instructions
Pointer - character pointer
Power query data format conversion, Split Merge extraction, delete duplicates, delete errors, transpose and reverse, perspective and reverse perspective
For a deadline, the IT fellow graduated from Tsinghua suddenly died on the toilet
KDD 2022 | EEG AI helps diagnose epilepsy
[groovy] JSON serialization (convert class objects to JSON strings | convert using jsonbuilder | convert using jsonoutput | format JSON strings for output)
小程序容器可以发挥的价值
An understanding of & array names
Folding and sinking sand -- weekly record of ETF
The third season of ape table school is about to launch, opening a new vision for developers under the wave of going to sea
Getting started with devkit
Set data real-time update during MDK debug
Arduino hexapod robot
[groovy] compile time metaprogramming (compile time method interception | find the method to be intercepted in the myasttransformation visit method)
时间戳的拓展及应用实例
Browser reflow and redraw