当前位置:网站首页>2022-07-07: the original array is a monotonic array with numbers greater than 0 and less than or equal to K. there may be equal numbers in it, and the overall trend is increasing. However, the number
2022-07-07: the original array is a monotonic array with numbers greater than 0 and less than or equal to K. there may be equal numbers in it, and the overall trend is increasing. However, the number
2022-07-08 00:53:00 【Fuda frame constructor daily question】
2022-07-07: The original array is greater than 0、 Less than or equal to k The number of , Is a monotonic array ,
There may be equal numbers , The overall trend is increasing .
But the numbers in some of these positions have been replaced by 0, We need to find out all the pieces 0 Number of alternatives :
1) Each number filled can be greater than or equal to the previous number , Less than or equal to the next number ;
2) Each number filled cannot be greater than k.
From Tencent music .
answer 2022-07-07:
Method 1 : Dynamic programming .
Method 2 : Mathematical methods . Use combination ,C(b-a+m,m).
The code to use rust To write . The code is as follows :
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
let nn: i64 = 20;
let kk: i64 = 30;
let test_time: i32 = 10000;
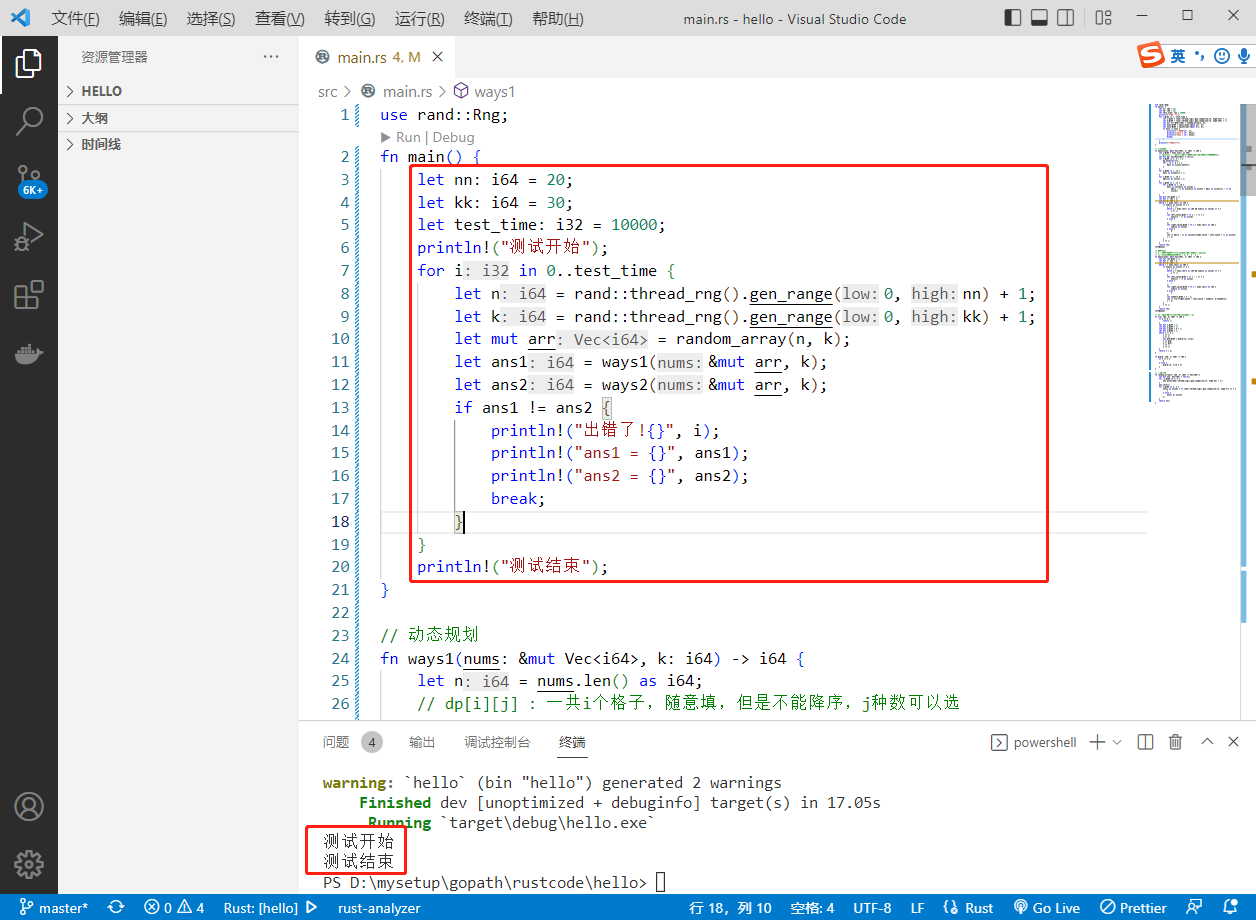
println!(" Beginning of the test ");
for i in 0..test_time {
let n = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, nn) + 1;
let k = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, kk) + 1;
let mut arr = random_array(n, k);
let ans1 = ways1(&mut arr, k);
let ans2 = ways2(&mut arr, k);
if ans1 != ans2 {
println!(" Something went wrong !{}", i);
println!("ans1 = {}", ans1);
println!("ans2 = {}", ans2);
break;
}
}
println!(" End of test ");
}
// Dynamic programming
fn ways1(nums: &mut Vec<i64>, k: i64) -> i64 {
let n = nums.len() as i64;
// dp[i][j] : altogether i Lattice , Fill in at will , But not in descending order ,j The number of species can be selected
let mut dp: Vec<Vec<i64>> = vec![];
for i in 0..n + 1 {
dp.push(vec![]);
for _ in 0..k + 1 {
dp[i as usize].push(0);
}
}
for i in 1..=n {
dp[i as usize][1] = 1;
}
for i in 1..=k {
dp[1][i as usize] = i;
}
for i in 2..=n {
for j in 2..=k {
dp[i as usize][j as usize] =
dp[(i - 1) as usize][j as usize] + dp[i as usize][(j - 1) as usize];
}
}
let mut res = 1;
let mut i: i64 = 0;
let mut j: i64 = 0;
while i < nums.len() as i64 {
if nums[i as usize] == 0 {
j = i + 1;
while j < nums.len() as i64 && nums[j as usize] == 0 {
j += 1;
}
let left_value = if i - 1 >= 0 {
nums[(i - 1) as usize]
} else {
1
};
let right_value = if j < nums.len() as i64 {
nums[j as usize]
} else {
k
};
res *= dp[(j - i) as usize][(right_value - left_value + 1) as usize];
i = j;
}
i += 1;
}
return res;
}
// Mathematical methods
// a ~ b Choose any number in the range , You can choose the number of repetitions , Co selection m individual
// Select the number of schemes in the ordered sequence :C ( m, b - a + m )
fn ways2(nums: &mut Vec<i64>, k: i64) -> i64 {
let mut res = 1;
let mut i: i64 = 0;
let mut j: i64 = 0;
while i < nums.len() as i64 {
if nums[i as usize] == 0 {
j = i + 1;
while j < nums.len() as i64 && nums[j as usize] == 0 {
j += 1;
}
let left_value = if i - 1 >= 0 {
nums[(i - 1) as usize]
} else {
1
};
let right_value = if j < nums.len() as i64 {
nums[j as usize]
} else {
k
};
let numbers = j - i;
res *= c(right_value - left_value + numbers, numbers);
i = j;
}
i += 1;
}
return res;
}
// From total a A few miles , choose b Number , What is the number of methods
fn c(a: i64, b: i64) -> i64 {
if a == b {
return 1;
}
let mut x = 1;
let mut y = 1;
let mut i = b + 1;
let mut j = 1;
while i <= a {
x *= i;
y *= j;
let gcd = gcd(x, y);
x /= gcd;
y /= gcd;
i += 1;
j += 1;
}
return x / y;
}
fn gcd(m: i64, n: i64) -> i64 {
if n == 0 {
m
} else {
gcd(n, m % n)
}
}
// In order to test
fn random_array(n: i64, k: i64) -> Vec<i64> {
let mut ans: Vec<i64> = vec![];
for _i in 0..n {
ans.push(rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, k) + 1);
}
ans.sort();
for i in 0..n {
ans[i as usize] = if rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, 2) == 0 {
0
} else {
ans[i as usize]
};
}
return ans;
}
The results are as follows :
边栏推荐
- RPA cloud computer, let RPA out of the box with unlimited computing power?
- STL--String类的常用功能复写
- Is it safe to open an account on the official website of Huatai Securities?
- Summary of the third course of weidongshan
- Leetcode brush questions
- How can CSDN indent the first line of a paragraph by 2 characters?
- The weight of the product page of the second level classification is low. What if it is not included?
- Class head up rate detection based on face recognition
- 浪潮云溪分布式数据库 Tracing(二)—— 源码解析
- 应用实践 | 数仓体系效率全面提升!同程数科基于 Apache Doris 的数据仓库建设
猜你喜欢

SDNU_ ACM_ ICPC_ 2022_ Summer_ Practice(1~2)
Class head up rate detection based on face recognition
Jouer sonar
ThinkPHP kernel work order system source code commercial open source version multi user + multi customer service + SMS + email notification
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)(A~D)
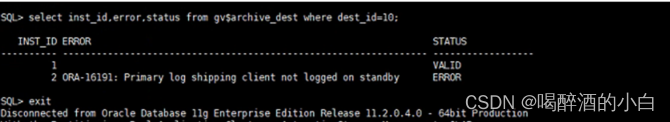
The standby database has been delayed. Check that the MRP is wait_ for_ Log, apply after restarting MRP_ Log but wait again later_ for_ log

51 communicates with the Bluetooth module, and 51 drives the Bluetooth app to light up
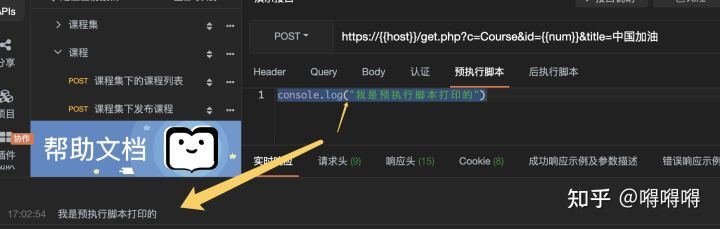
接口测试进阶接口脚本使用—apipost(预/后执行脚本)
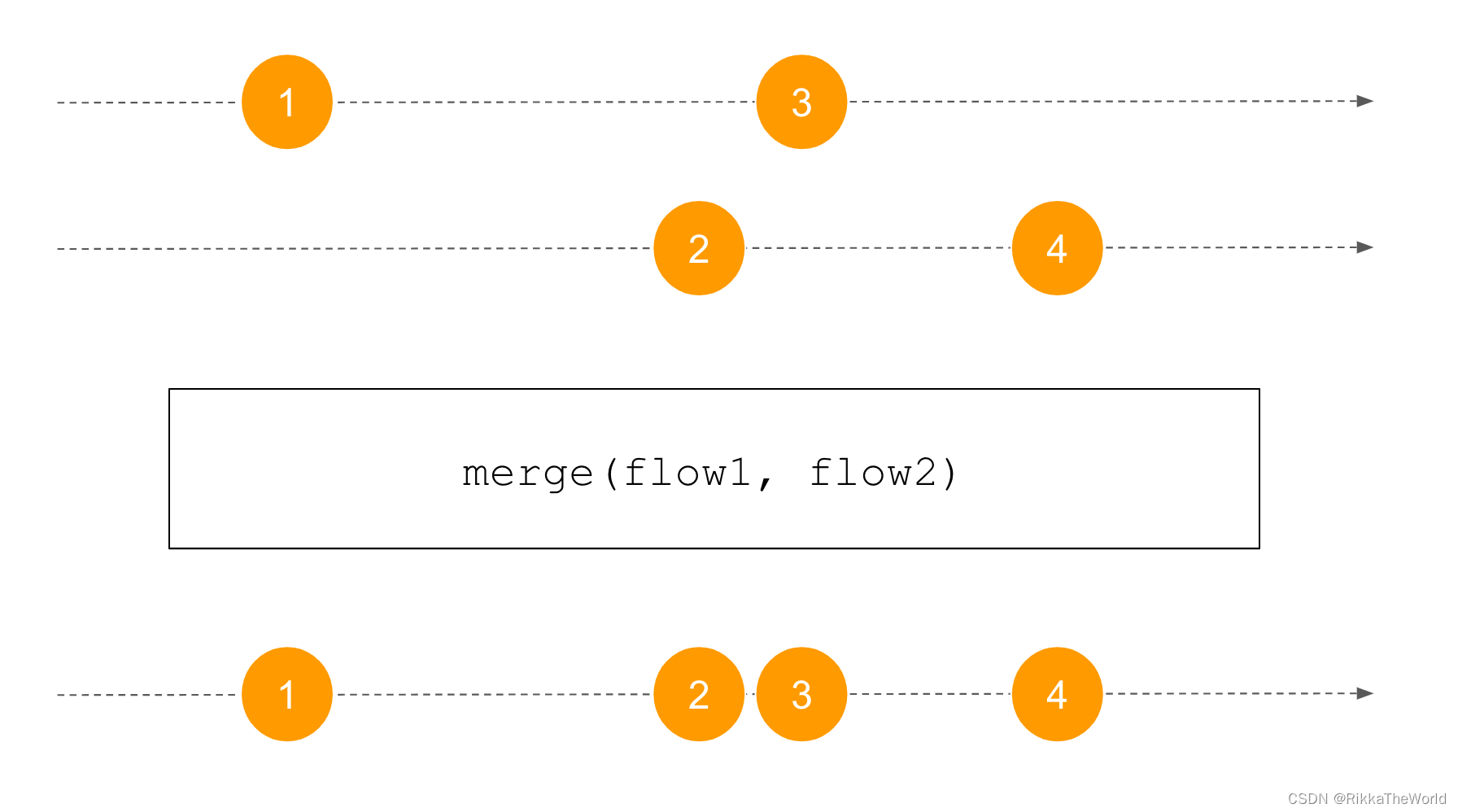
深潜Kotlin协程(二十二):Flow的处理
Lecture 1: the entry node of the link in the linked list
随机推荐
基于微信小程序开发的我最在行的小游戏
[OBS] the official configuration is use_ GPU_ Priority effect is true
炒股开户怎么最方便,手机上开户安全吗
QT adds resource files, adds icons for qaction, establishes signal slot functions, and implements
接口测试进阶接口脚本使用—apipost(预/后执行脚本)
What is load balancing? How does DNS achieve load balancing?
RPA cloud computer, let RPA out of the box with unlimited computing power?
大二级分类产品页权重低,不收录怎么办?
After going to ByteDance, I learned that there are so many test engineers with an annual salary of 40W?
They gathered at the 2022 ecug con just for "China's technological power"
Prompt configure: error: required tool not found: libtool solution when configuring and installing crosstool ng tool
ReentrantLock 公平锁源码 第0篇
fabulous! How does idea open multiple projects in a single window?
Jouer sonar
手机上炒股安全么?
Letcode43: string multiplication
C# 泛型及性能比较
Su embedded training - day4
QT establish signal slots between different classes and transfer parameters
The standby database has been delayed. Check that the MRP is wait_ for_ Log, apply after restarting MRP_ Log but wait again later_ for_ log