当前位置:网站首页>Langchao Yunxi distributed database tracing (II) -- source code analysis
Langchao Yunxi distributed database tracing (II) -- source code analysis
2022-07-08 00:28:00 【Inspur Yunxi database】
according to 【 Yunxi database Tracing( One )】 Introduce the use of opentracing requirement , This paper mainly introduces Yunxi database Tracing How to implement in the module Span,SpanContexts and Tracer Of .
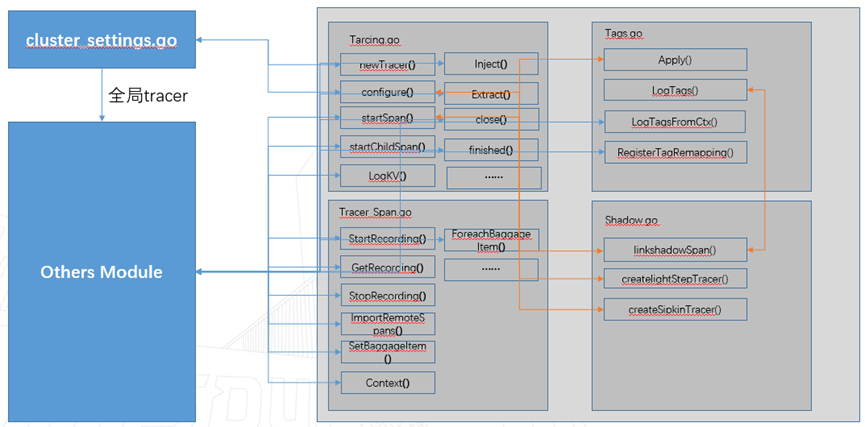
Part 1 - Tracing Module call relation
1.1 Traincg List of files included in the module
Tracer.go : Defined opentracing Medium trace Implementation of related interfaces .Tracer_span.go : Defined opentracing Medium span Implementation of related operations .Tags.go : Defined opentracing About China tags Related interfaces of .Shadow.go : No opentracing The concept of , Here, we mainly realize and zipkin Communication for , be used for tracing Information is pushed to the outside zipkin in .
1.2 The calling relationship between various files
stay cluster_settings.go China will create tracer, For global use , Use this in other modules Tracer Realization span Creation and other operations of , For example, setting span name 、 Set up tag 、 increase log Wait for the operation .
Part 2 - Opentracing
Implementation in Yunxi database
The following is just a list of some interface implementations , Not all of them .
2.1 Span Interface implementation :
GetContext Realization :API Used to get Span Medium SpanContext, The main function is to create a map[string]string Type of baggageCopy, take span Medium mu.Baggage Read write baggageCopy, Create a new spanContext, And back to .
func (s *span) Context() opentracing.SpanContext {s.mu.Lock()defer s.mu.Unlock()baggageCopy := make(map[string]string, len(s.mu.Baggage))for k, v := range s.mu.Baggage {baggageCopy[k] = v}sc := &spanContext{spanMeta: s.spanMeta,Baggage: baggageCopy,}if s.shadowTr != nil {sc.shadowTr = s.shadowTrsc.shadowCtx = s.shadowSpan.Context()}if s.isRecording() {sc.recordingGroup = s.mu.recordingGroupsc.recordingType = s.mu.recordingType}return sc}
Finished Realization :API Used to end a Span Recording and tracking of .
func (s *span) Finish() {s.FinishWithOptions(opentracing.FinishOptions{})}
SetTag Realization : Used to direct the specified Span add to Tag Information .
func (s *span) SetTag(key string, value interface{}) opentracing.Span {return s.setTagInner(key, value, false /* locked */)}
Log Realization : Used to direct the specified Span add to Log Information .
func (s *span) LogKV(alternatingKeyValues ...interface{}) {fields, err := otlog.InterleavedKVToFields(alternatingKeyValues...)if err != nil {s.LogFields(otlog.Error(err), otlog.String("function", "LogKV"))return}s.LogFields(fields...)}
SetBaggageItem Realization : Used to direct the specified Span increase Baggage Information , It is mainly used for cross process tracking .
func (s *span) SetBaggageItem(restrictedKey, value string) opentracing.Span {s.mu.Lock()defer s.mu.Unlock()return s.setBaggageItemLocked(restrictedKey, value)}
BaggageItem Realization : Used to get the specified Baggage Information .
func (s *span) BaggageItem(restrictedKey string) string {s.mu.Lock()defer s.mu.Unlock()return s.mu.Baggage[restrictedKey]}
SetOperationName Realization : Used to set Span The name of .
func (s *span) SetOperationName(operationName string) opentracing.Span { if s.shadowTr != nil { s.shadowSpan.SetOperationName(operationName) } s.operation = operationName return s}Tracer Realization : Used to get Span Which is it? Tracer.
// Tracer is part of the opentracing.Span interface.func (s *span) Tracer() opentracing.Tracer {return s.tracer}
2.2 SpanContext Interface implementation :
ForeachBaggageItem Realization : Used to traverse the spanContext Medium baggage Information .
func (sc *spanContext) ForeachBaggageItem(handler func(k, v string) bool) {for k, v := range sc.Baggage {if !handler(k, v) {break}}}
2.3 Tracer Interface implementation :
Inject Realization : Used to direct to carrier In the injection SpanContext Information
// Inject is part of the opentracing.Tracer interface.func (t *Tracer) Inject(osc opentracing.SpanContext, format interface{}, carrier interface{},) error {……// We onlysupport the HTTPHeaders/TextMap format.if format != opentracing.HTTPHeaders && format != opentracing.TextMap {return opentracing.ErrUnsupportedFormat}mapWriter, ok := carrier.(opentracing.TextMapWriter)if !ok {return opentracing.ErrInvalidCarrier}sc, ok := osc.(*spanContext)if !ok {return opentracing.ErrInvalidSpanContext}mapWriter.Set(fieldNameTraceID, strconv.FormatUint(sc.TraceID, 16))mapWriter.Set(fieldNameSpanID, strconv.FormatUint(sc.SpanID, 16))for k, v := range sc.Baggage {mapWriter.Set(prefixBaggage+k, v)}……return nil}
Extract Realization : For from carrier To take out SpanContext Information .
func (t *Tracer) Extract(format interface{}, carrier interface{}) (opentracing.SpanContext, error) {// We onlysupport the HTTPHeaders/TextMap format.if format != opentracing.HTTPHeaders && format != opentracing.TextMap {return noopSpanContext{}, opentracing.ErrUnsupportedFormat}mapReader, ok := carrier.(opentracing.TextMapReader)if !ok {return noopSpanContext{}, opentracing.ErrInvalidCarrier}var sc spanContext……err :=mapReader.ForeachKey(func(k, v string) error {switch k = strings.ToLower(k); k {case fieldNameTraceID:var err errorsc.TraceID, err = strconv.ParseUint(v, 16, 64)if err != nil {return opentracing.ErrSpanContextCorrupted}case fieldNameSpanID:var err errorsc.SpanID, err = strconv.ParseUint(v, 16, 64)if err != nil {return opentracing.ErrSpanContextCorrupted}case fieldNameShadowType:shadowType = vdefault:if strings.HasPrefix(k, prefixBaggage) {if sc.Baggage == nil {sc.Baggage = make(map[string]string)}sc.Baggage[strings.TrimPrefix(k, prefixBaggage)] = v} else if strings.HasPrefix(k, prefixShadow) {if shadowCarrier == nil {shadowCarrier = make(opentracing.TextMapCarrier)}// We build ashadow textmap with the original shadow keys.shadowCarrier.Set(strings.TrimPrefix(k, prefixShadow), v)}}return nil})if err != nil {return noopSpanContext{}, err}if sc.TraceID == 0 &&sc.SpanID == 0 {return noopSpanContext{}, nil}……return &sc, nil}
StartSpan Interface implementation : Used to create a new Span, It can be different according to the incoming opts To make a difference Span The initialization .
func (t *Tracer) StartSpan(operationName string, opts ...opentracing.StartSpanOption,) opentracing.Span {// Fast paths toavoid the allocation of StartSpanOptions below when tracing// is disabled: if we have no optionsor a single SpanReference (the common// case) with a noop context, return anoop span now.if len(opts) == 1 {if o, ok := opts[0].(opentracing.SpanReference); ok {if IsNoopContext(o.ReferencedContext) {return &t.noopSpan}}}shadowTr := t.getShadowTracer()……return s}
2.4 noop span Realization :
noop span Realization : Make the monitoring code independent Tracer and Span The return value of , Prevent abnormal exit of program .
type noopSpan struct {tracer *Tracer}var _ opentracing.Span = &noopSpan{}func (n *noopSpan) Context() opentracing.SpanContext { return noopSpanContext{} }func (n *noopSpan) BaggageItem(key string) string { return "" }func (n *noopSpan) SetTag(key string, value interface{}) opentracing.Span { return n }func (n *noopSpan) Finish() {}func (n *noopSpan) FinishWithOptions(opts opentracing.FinishOptions) {}func (n *noopSpan) SetOperationName(operationName string) opentracing.Span { return n }func (n *noopSpan) Tracer() opentracing.Tracer { return n.tracer }func (n *noopSpan) LogFields(fields ...otlog.Field) {}func (n *noopSpan) LogKV(keyVals ...interface{}) {}func (n *noopSpan) LogEvent(event string) {}func (n *noopSpan) LogEventWithPayload(event string, payload interface{}) {}func (n *noopSpan) Log(data opentracing.LogData) {}func (n *noopSpan) SetBaggageItem(key, val string) opentracing.Span {if key == Snowball {panic("attempting to set Snowball on a noop span; use the Recordable optionto StartSpan")}return n}
Part3 - Yunxi database
Opentracing Simple use examples
3.1 Turn on Tracer Recording test
Yunxi database Started span It's all no operator span, Manual call required StartRecording, take span Convert to executable record state , Can be normal to span To operate .
func TestTracerRecording(t *testing.T) {tr := NewTracer()noop1 := tr.StartSpan("noop")if _, noop := noop1.(*noopSpan); !noop {t.Error("expected noop span")}noop1.LogKV("hello", "void")noop2 := tr.StartSpan("noop2", opentracing.ChildOf(noop1.Context()))if _, noop := noop2.(*noopSpan); !noop {t.Error("expected noop child span")}noop2.Finish()noop1.Finish()s1 := tr.StartSpan("a", Recordable)if _, noop := s1.(*noopSpan); noop {t.Error("Recordable (but not recording) span should not be noop")}if !IsBlackHoleSpan(s1) {t.Error("Recordable span should be black hole")}// Unless recording is actually started, child spans are still noop.noop3 := tr.StartSpan("noop3", opentracing.ChildOf(s1.Context()))if _, noop := noop3.(*noopSpan); !noop {t.Error("expected noop child span")}noop3.Finish()s1.LogKV("x", 1)StartRecording(s1, SingleNodeRecording)s1.LogKV("x", 2)s2 := tr.StartSpan("b", opentracing.ChildOf(s1.Context()))if IsBlackHoleSpan(s2) {t.Error("recording span should not be black hole")}s2.LogKV("x", 3)if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(s1), `span a:tags: unfinished=x: 2span b:tags: unfinished=x: 3`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(s2), `span b:tags: unfinished=x: 3`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}s3 := tr.StartSpan("c", opentracing.FollowsFrom(s2.Context()))s3.LogKV("x", 4)s3.SetTag("tag", "val")s2.Finish()if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(s1), `span a:tags: unfinished=x: 2span b:x: 3span c:tags: tag=val unfinished=x: 4`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}s3.Finish()if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(s1), `span a:tags: unfinished=x: 2span b:x: 3span c:tags: tag=valx: 4`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}StopRecording(s1)s1.LogKV("x", 100)if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(s1), ``); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}// The child span is still recording.s3.LogKV("x", 5)if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(s3), `span c:tags: tag=valx: 4x: 5`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}s1.Finish()}
3.2 establish childSpan test
test StartChildSpan, According to the existing span Create a new span, For already span The son of span.
func TestStartChildSpan(t *testing.T) {tr := NewTracer()sp1 := tr.StartSpan("parent", Recordable)StartRecording(sp1, SingleNodeRecording)sp2 := StartChildSpan("child", sp1, nil /* logTags */, false /*separateRecording*/)sp2.Finish()sp1.Finish()if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(sp1), `span parent:span child:`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}sp1 = tr.StartSpan("parent", Recordable)StartRecording(sp1, SingleNodeRecording)sp2 = StartChildSpan("child", sp1, nil /* logTags */, true /*separateRecording*/)sp2.Finish()sp1.Finish()if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(sp1), `span parent:`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(sp2), `span child:`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}sp1 = tr.StartSpan("parent", Recordable)StartRecording(sp1, SingleNodeRecording)sp2 = StartChildSpan("child", sp1, logtags.SingleTagBuffer("key", "val"), false, /*separateRecording*/)sp2.Finish()sp1.Finish()if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(sp1), `span parent:span child:tags: key=val`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}}
3.3 Cross process tracking test
Test the cross process tracking function , It's mainly about testing inject Interface and extract Interface ,Inject Used to direct to carrier In the injection SpanContext Information ,Extract For from carrier To take out SpanContext Information .
func TestTracerInjectExtract(t *testing.T) {tr := NewTracer()tr2 := NewTracer()// Verify that noop spans become noop spans on the remote side.noop1 := tr.StartSpan("noop")if _, noop := noop1.(*noopSpan); !noop {t.Fatalf("expected noop span: %+v", noop1)}carrier := make(opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier)if err := tr.Inject(noop1.Context(), opentracing.HTTPHeaders, carrier); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}if len(carrier) != 0 {t.Errorf("noop span has carrier: %+v", carrier)}wireContext, err := tr2.Extract(opentracing.HTTPHeaders, carrier)if err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}if _, noopCtx := wireContext.(noopSpanContext); !noopCtx {t.Errorf("expected noop context: %v", wireContext)}noop2 := tr2.StartSpan("remote op", opentracing.FollowsFrom(wireContext))if _, noop := noop2.(*noopSpan); !noop {t.Fatalf("expected noop span: %+v", noop2)}noop1.Finish()noop2.Finish()// Verify that snowball tracing is propagated and triggers recording on the// remote side.s1 := tr.StartSpan("a", Recordable)StartRecording(s1, SnowballRecording)carrier = make(opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier)if err := tr.Inject(s1.Context(), opentracing.HTTPHeaders, carrier); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}wireContext, err = tr2.Extract(opentracing.HTTPHeaders, carrier)if err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}s2 := tr2.StartSpan("remote op", opentracing.FollowsFrom(wireContext))// Compare TraceIDstrace1 := s1.Context().(*spanContext).TraceIDtrace2 := s2.Context().(*spanContext).TraceIDif trace1 != trace2 {t.Errorf("TraceID doesn't match: parent %d child %d", trace1, trace2)}s2.LogKV("x", 1)s2.Finish()// Verify that recording was started automatically.rec := GetRecording(s2)if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(rec, `span remote op:tags: sb=1x: 1`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(s1), `span a:tags: sb=1 unfinished=`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}if err := ImportRemoteSpans(s1, rec); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}s1.Finish()if err := TestingCheckRecordedSpans(GetRecording(s1), `span a:tags: sb=1span remote op:tags: sb=1x: 1`); err != nil {t.Fatal(err)}}
边栏推荐
- 应用实践 | 数仓体系效率全面提升!同程数科基于 Apache Doris 的数据仓库建设
- 哪个券商公司开户佣金低又安全,又靠谱
- Daily question brushing record (16)
- 测试流程不完善,又遇到不积极的开发怎么办?
- Fully automated processing of monthly card shortage data and output of card shortage personnel information
- 深潜Kotlin协程(二十二):Flow的处理
- How to measure whether the product is "just needed, high frequency, pain points"
- ROS from entry to mastery (IX) initial experience of visual simulation: turtlebot3
- 关于组织2021-2022全国青少年电子信息智能创新大赛西南赛区(四川)复赛的通知
- Database query - what is the highest data?
猜你喜欢

Detailed explanation of interview questions: the history of blood and tears in implementing distributed locks with redis
Kubernetes Static Pod (静态Pod)
Binder核心API
![[question de programmation] [scratch niveau 2] oiseaux volants en décembre 2019](/img/5e/a105f8615f3991635c9ffd3a8e5836.png)
[question de programmation] [scratch niveau 2] oiseaux volants en décembre 2019

C # generics and performance comparison
![[programming problem] [scratch Level 2] 2019.09 make bat Challenge Game](/img/81/c84432a7d7c2fe8ef377d8c13991d6.png)
[programming problem] [scratch Level 2] 2019.09 make bat Challenge Game
玩轉Sonar
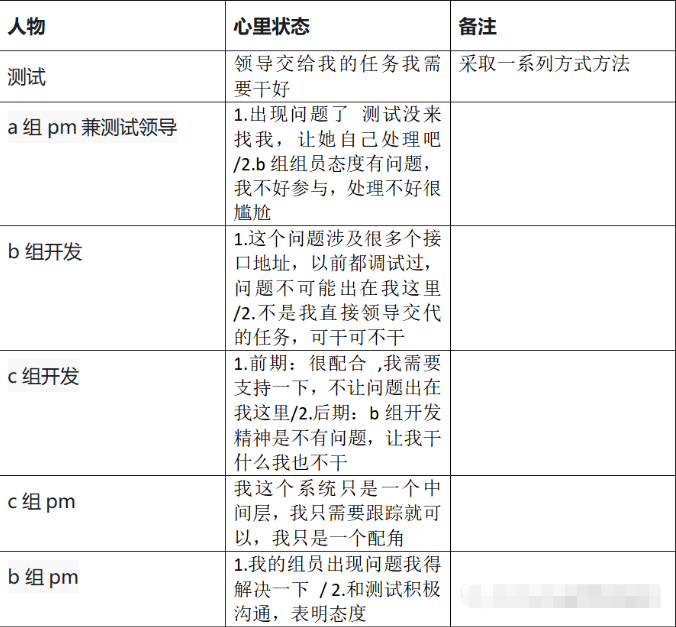
What if the testing process is not perfect and the development is not active?
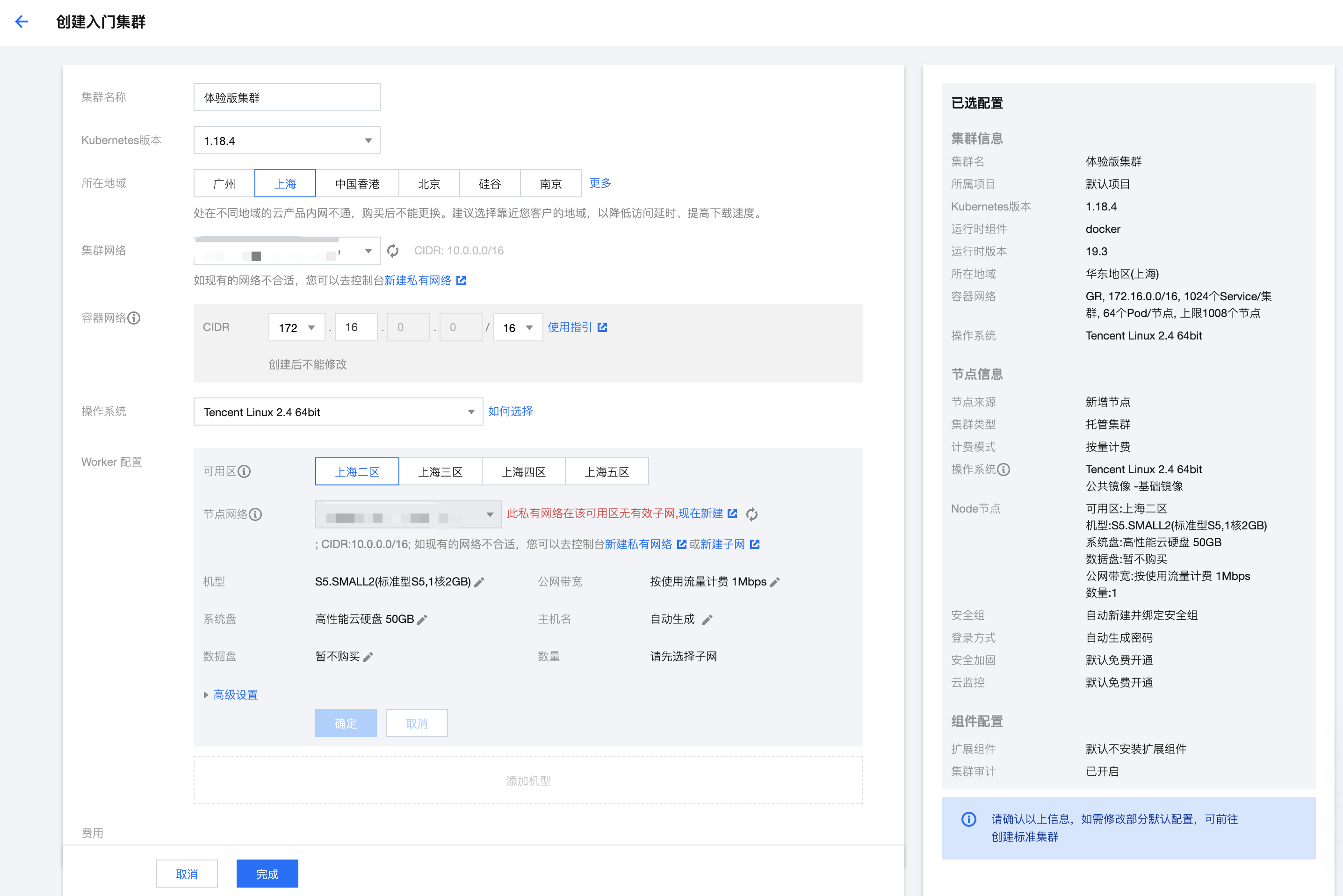
从服务器到云托管,到底经历了什么?
某马旅游网站开发(对servlet的优化)
随机推荐
"An excellent programmer is worth five ordinary programmers", and the gap lies in these seven key points
华为交换机S5735S-L24T4S-QA2无法telnet远程访问
Introduction to paddle - using lenet to realize image classification method I in MNIST
The difference between get and post
When creating body middleware, express Is there any difference between setting extended to true and false in urlencoded?
22年秋招心得
Sqlite数据库存储目录结构邻接表的实现2-目录树的构建
52岁的周鸿祎,还年轻吗?
大数据开源项目,一站式全自动化全生命周期运维管家ChengYing(承影)走向何方?
Robomaster visual tutorial (1) camera
Single machine high concurrency model design
51 communicates with the Bluetooth module, and 51 drives the Bluetooth app to light up
Tapdata 的 2.0 版 ,开源的 Live Data Platform 现已发布
Teach you to make a custom form label by hand
【编程题】【Scratch二级】2019.09 制作蝙蝠冲关游戏
Binder核心API
【obs】官方是配置USE_GPU_PRIORITY 效果为TRUE的
取消select的默认样式的向下箭头和设置select默认字样
从服务器到云托管,到底经历了什么?
paddle一个由三个卷积层组成的网络完成cifar10数据集的图像分类任务