当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to paddle - using lenet to realize image classification method I in MNIST
Introduction to paddle - using lenet to realize image classification method I in MNIST
2022-07-08 00:17:00 【Vertira】
MNIST The data set realizes image classification
One 、 Configuration environment
import paddle
print(paddle.__version__)
How to configure paddle You can search online , My blog also has , Here is a little
Load data : There are two ways : Custom data loading ( My previous blog has ), load paddled Data prepared on the official website
We are looking for the second way , Because it's convenient
Handwritten numbers MNIST Data sets , contain 60,000 Examples and for training 10,000 An example for testing . These numbers have been dimensioned and located in the center of the image , The image is a fixed size (28x28 Pixels ), Its value is 0 To 1. The official address of the data set is :http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist .
We use the built-in... Of the propeller frame paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST complete mnist Data set loading .
from paddle.vision.transforms import Compose, Normalize
transform = Compose([Normalize(mean=[127.5],
std=[127.5],
data_format='CHW')])
# Use transform Normalize the data set
print('download training data and load training data')
train_dataset = paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST(mode='train', transform=transform)
test_dataset = paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST(mode='test', transform=transform)
print('load finished')
Take a piece of data from the training set and have a look .
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
train_data0, train_label_0 = train_dataset[0][0],train_dataset[0][1]
train_data0 = train_data0.reshape([28,28])
plt.figure(figsize=(2,2))
plt.imshow(train_data0, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
print('train_data0 label is: ' + str(train_label_0))
3、 ... and 、 networking
use paddle.nn Under the API, Such as Conv2D、MaxPool2D、Linear complete LeNet The construction of .
import paddle
import paddle.nn.functional as F
class LeNet(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2)
self.max_pool1 = paddle.nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv2 = paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5, stride=1)
self.max_pool2 = paddle.nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.linear1 = paddle.nn.Linear(in_features=16*5*5, out_features=120)
self.linear2 = paddle.nn.Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84)
self.linear3 = paddle.nn.Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.max_pool1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.max_pool2(x)
x = paddle.flatten(x, start_axis=1,stop_axis=-1)
x = self.linear1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.linear2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.linear3(x)
return x
Four 、 The way 1: Based on high-level API, Complete the training and prediction of the model
adopt paddle Provided Model Build instance , Use the encapsulated training and test interface , Quickly complete model training and testing .
4.1 Use Model.fit To train the model
from paddle.metric import Accuracy
model = paddle.Model(LeNet()) # use Model Packaging model
optim = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001, parameters=model.parameters())
# Configuration model
model.prepare(
optim,
paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),
Accuracy()
)
# Training models
model.fit(train_dataset,
epochs=2,
batch_size=64,
verbose=1
)
Training results
The loss value printed in the log is the current step, and the metric is the average value of previous steps.
Epoch 1/2
step 938/938 [==============================] - loss: 0.0329 - acc: 0.9399 - 10ms/step
Epoch 2/2
step 938/938 [==============================] - loss: 0.0092 - acc: 0.9798 - 10ms/step
4.2 Use Model.evaluate To predict the model
model.evaluate(test_dataset, batch_size=64, verbose=1)
Eval begin...
step 157/157 [==============================] - loss: 4.4728e-04 - acc: 0.9857 - 8ms/step
Eval samples: 10000
{'loss': [0.0004472804], 'acc': 0.9857}
Way one ends
That's way one , Can quickly 、 Efficiently complete network model training and prediction .
Reference resources :
边栏推荐
- If an exception is thrown in the constructor, the best way is to prevent memory leakage?
- “一个优秀程序员可抵五个普通程序员”,差距就在这7个关键点
- 浪潮云溪分布式数据库 Tracing(二)—— 源码解析
- [basis of recommendation system] sampling and construction of positive and negative samples
- The function is really powerful!
- 80%的人答错,苹果logo上的叶子到底朝左还是朝右?
- Robomaster visual tutorial (0) Introduction
- Stm32f1 and stm32cubeide programming example - rotary encoder drive
- DNS 系列(一):为什么更新了 DNS 记录不生效?
- 3年经验,面试测试岗20K都拿不到了吗?这么坑?
猜你喜欢

STM32F1与STM32CubeIDE编程实例-旋转编码器驱动
![[leetcode] 20. Valid brackets](/img/42/5a2c5ec6c1a7dbcdfb2226cdea6a42.png)
[leetcode] 20. Valid brackets
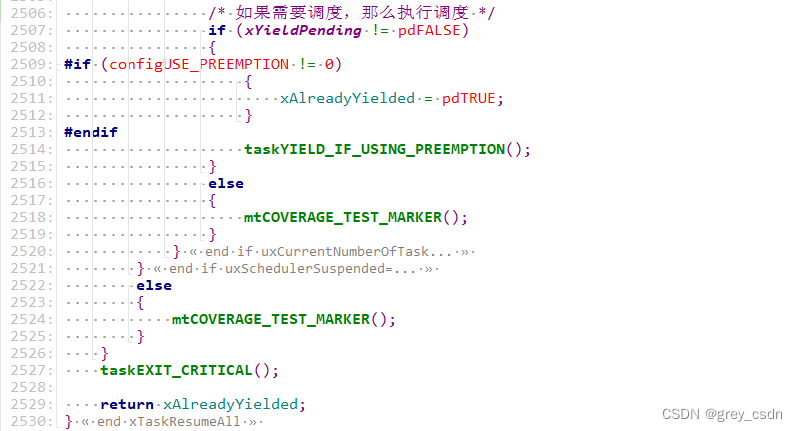
1293_FreeRTOS中xTaskResumeAll()接口的实现分析
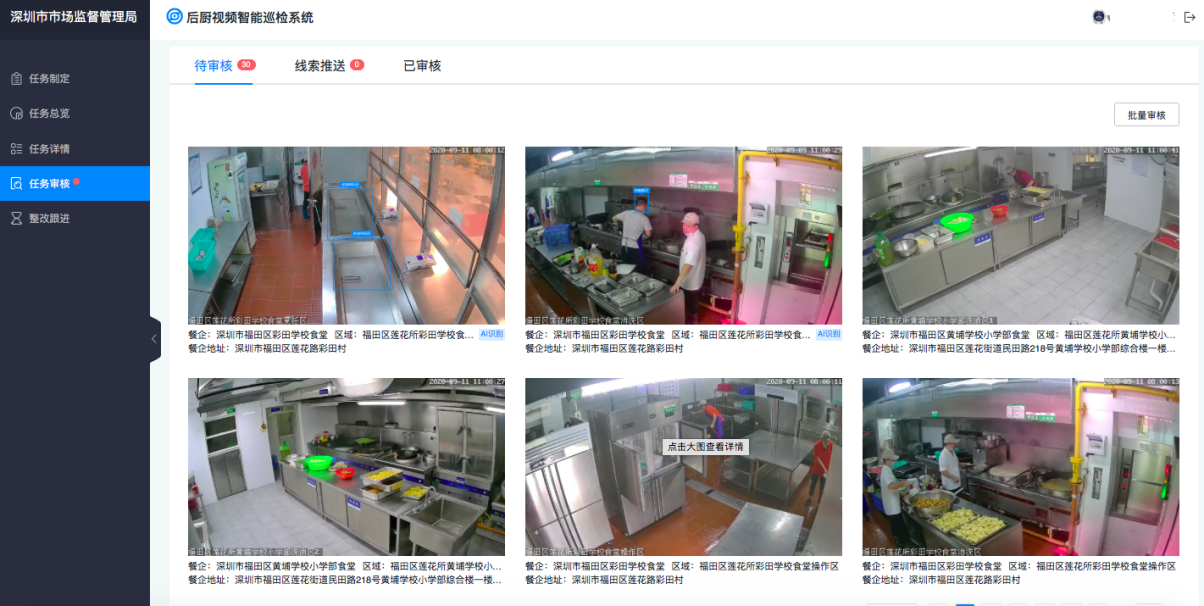
Smart regulation enters the market, where will meituan and other Internet service platforms go

The result of innovation in professional courses such as robotics (Automation)
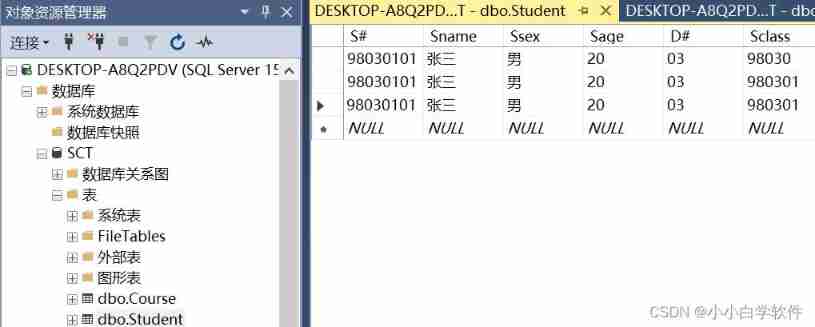
Basic learning of SQL Server -- creating databases and tables with code

Stm32f1 and stm32cubeide programming example - rotary encoder drive
Development of a horse tourism website (optimization of servlet)

智慧监管入场,美团等互联网服务平台何去何从

从Starfish OS持续对SFO的通缩消耗,长远看SFO的价值
随机推荐
应用实践 | 数仓体系效率全面提升!同程数科基于 Apache Doris 的数据仓库建设
RPA云电脑,让RPA开箱即用算力无限?
Common selectors are
The difference between -s and -d when downloading packages using NPM
The function is really powerful!
Introduction to programming hardware
在网页中打开展示pdf文件
【编程题】【Scratch二级】2019.09 制作蝙蝠冲关游戏
某马旅游网站开发(对servlet的优化)
面试题详解:用Redis实现分布式锁的血泪史
商品的设计等整个生命周期,都可以将其纳入到产业互联网的范畴内
QT and OpenGL: load 3D models using the open asset import library (assimp)
全自动化处理每月缺卡数据,输出缺卡人员信息
How does starfish OS enable the value of SFO in the fourth phase of SFO destruction?
Trust orbtk development issues 2022
Automated testing: robot framework is a practical skill that 90% of people want to know
【编程题】【Scratch二级】2019.09 绘制雪花图案
去了字节跳动,才知道年薪 40w 的测试工程师有这么多?
从Starfish OS持续对SFO的通缩消耗,长远看SFO的价值
How does the markdown editor of CSDN input mathematical formulas--- Latex syntax summary