当前位置:网站首页>Su embedded training - day4
Su embedded training - day4
2022-07-08 00:13:00 【Light chasing rain】
List of articles
One 、 Array
1.1 The concept of array
Array :
Save a set of data of the same type
Whether it's a multi-dimensional array , Is to open up a continuous memory space
Array is a construction data type ( Array , Structure , Shared body )
1.2 One dimensional array
1.2.1 The definition of one-dimensional array
< Storage type > < data type > < Array name > [ The array subscript ]
Storage type :auto,register,static,extern
data type : Basic data type :int,char,float.... etc.
Array name : Is an identifier , Meet the naming rules of identifiers
The array subscript : Determine the number of elements in the array
for example :
int a[10];
meaning : Define a name a Array of , altogether 10 Elements , Every element is int type .
1.2.2 Properties of one-dimensional array
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a[4];
a[0] = 222;
a[1] = 333;
a[2] = 444;
a[3] = 555;
printf("%d %d %d\n",a[0],a[1],a[2]);
// When defining and using arrays , Try not to use variables in the following table of array
// Prevent later variable changes from affecting the operation of the array , Generally, array subscripts are constants or constant form Masters , The macro definition itself is also a constant expression , So it can be used as an array subscript
#if 0
int num = 10;
int b[num];
b[2] = 5;
int n =3;
b[n] = 888;
printf("%d %d\n",b[2],b[n]);
#endif
printf("sizeof(a) = %ld %ld\n",sizeof(a),sizeof(int)*4);
printf("%p\n",&a[0]);
printf("%p\n",&a[0]+1);
printf("%p\n",a);
printf("%p\n",a+1);
printf("%p\n",&a);
printf("%p\n",&a+1);
a++; // Array names are constant pointers , Do not modify
return 0;
}
1.3 Initialization and traversal of one-dimensional array
1. All initialization
2. Local initialization
3. Initialize all without specifying array subscripts
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
// If you define an array inside a function without initializing , Then every element is a random value
//int a[5];
//a = {1,2,3,4,5}; // Wrong writing
// All initialization
//int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
//int a[5] = {0}; // All initialized to 0
//int a[5] = {}; // Some compilers do not support this writing
//int a[5] = {1,2,3}; // Local initialization , Elements without assignment are automatically initialized to 0
int a[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}; // Do not specify array subscript , The system will set the array subscript according to the number of initialized data
printf("sizeof(a) = %ld\n",sizeof(a));
/* One dimensional array traversal */
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
//printf("a[%d] = %d\n",i,a[i]);
}
putchar(10);
return 0;
}
1.4 Bubble sort
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a[10] = {0};
printf(" Please enter 10 A digital :\n");
int i,j;
int length = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
for(i = 0 ; i < length;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
for(i = 0 ; i < length - 1;i++)
{
for(j = 0 ; j < length - 1 - i;j++)
{
if(a[j] < a[j+1])
{
#if 0
int t = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = t;
#endif
a[j] = a[j] + a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = a[j] - a[j + 1];
a[j] = a[j] - a[j + 1];
}
}
}
for(i = 0 ; i < length;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
putchar(10);
return 0;
}
Two 、 Two dimensional array
2.1 Definition and properties of two-dimensional array
Storage type data type Array name [ Row number ][ Number of columns ];
for example :int arr[3][4];
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a[2][3] = {
{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
//int a[2][3] = {
{1},{4,5}};
//int a[][3] = {
{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
//int a[][3] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
//int a[2][3] = {0};
int i,j;
for(i = 0;i < 3;i++)
{
for(j =0 ; j < 3;j++)
{
printf("a[%d][%d] = %d\n",i,j,a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("%p\n",&a[0][0]);
printf("%p\n",&a[0]);
printf("%p\n",a);
printf("%p\n",&a);
printf("%p\n",&a[0][0] + 1);
printf("%p\n",&a[0] + 1);
printf("%p\n",a + 1);
printf("%p\n",&a + 1);
return 0;
}
2.2 Initialization and traversal of two-dimensional array
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//int a[3][4];
//int a[2][3] = {
{4,5,6},{7,8,9}};// All initialization
//int a[2][3] = {1,2,3,4}; // Store by line , There is no set auto fill 0
//int a[2][3] = {
{1},{2}};
//int a[][3] = {
{10,20},{30}};
//int a[2][] = {1,2,3,4,5}; // Wrong writing
int i,j;
// The outer loop controls the number of lines
// The number of inner loop control columns
for(i = 0 ; i < 2;i++)
{
for(j = 0 ; j < 3;j++)
{
printf("%-5d",a[i][j]);
}
putchar(10);
}
return 0;
}
3、 ... and 、 Character arrays and strings
A character array : Every element stored in the array is a character
A string is essentially an array of characters
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char ch1[] = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
printf("sizeof(ch1) = %ld\n",sizeof(ch1));
// Traversal of character array
int i;
for(i = 0; i < sizeof(ch1)/sizeof(ch1[0]);i++)
{
printf("%c ",ch1[i]);
}
putchar(10);
char ch2[] = "world";
printf("sizeof(ch2) = %ld\n",sizeof(ch2));
printf("ch2 = %s\n",ch2);
char ch3[] = {'h','e','l','l','o','\0'};
printf("ch3 = %s\n",ch3);
char ch4[] = "hello\0world";
printf("sizeof(ch4) = %ld\n",sizeof(ch4));
for(i = 0 ; i < sizeof(ch4)/sizeof(ch4[0]);i++)
{
printf("[%c] %d\n",ch4[i],ch4[i]);
}
puts("---------------------------------------");
char str[4][32] = {"hello","nihao beijing","hello kitty","welcome to nanjing"};
int j;
for(i = 0 ; i < 4;i++)
{
for(j = 0 ; j < 32;j++)
{
printf("%c",str[i][j]);
}
putchar(10);
}
return 0;
}
3.1 Reverse string order
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char str[32] = {0};
printf(" Please enter a string : ");
scanf("%s",str);
int i = 0,length = 0;
while(str[i] != '\0')
{
length++;
i++;
}
int x = 0, y = length -1;
for(i = 0 ; i < length /2 ;i++)
{
char t = str[x];
str[x] = str[y];
str[y] = t;
x++;
y--;
}
printf("%s\n",str);
return 0;
}
3.2 insert data
Enter a string , Location , The elements inserted
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char str[32] = {0};
int num,i;
char ch;
printf(" Please enter the string , Location , The elements inserted :\n");
scanf("%s%d %c",str,&num,&ch);
int length = strlen(str);
for(i =0 ; i < length - num +1;i++)
{
str[length - i] = str[length -i - 1];
}
str[num - 1] = ch;
printf("%s\n",str);
return 0;
}
Four 、 String function
4.1 Why use string functions
Generally, strings are stored in an array , But after the array is defined , It cannot be operated as a whole , So we need to operate on strings with the help of string related functions
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char s1[] = "hello world";
char s2[] = "hello world";
if(s1 == s2)
{
printf("s1 = s2\n");
}
else
{
printf("s1 != s2\n");
}
// If the array is not initialized , Array subscript must be written
//char str[];
return 0;
}
4.2 Common string functions
4.2.1 strlen()
The header file :#include <string.h>
Prototype :size_t strlen(const char *s);
function : Get the length of a string
Parameters :s: To get a string of length
Pass in a string directly , Or character array names
Return value : Length of string
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//strlen Function to get the length of the string
// The length obtained is the first in this string \0 Length before position , barring \0
char s1[] = "hello world";
printf("strlen(s1) =%ld\n",strlen(s1));
printf("sizeof(s1) =%ld\n",sizeof(s1));
char s2[] = "hello wor\0ld";
printf("strlen(s2) =%ld\n",strlen(s2));
printf("sizeof(s2) =%ld\n",sizeof(s2));
// The following is not a string , No, \0, So it can't be used strlen To get the string length ,strlen I will always look for it from the first address \0
char s3[] = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
printf("strlen(s3) =%ld\n",strlen(s3));
printf("sizeof(s3) =%ld\n",sizeof(s3));
char s4[32] = "hello world";
printf("strlen(s4) =%ld\n",strlen(s4));
printf("sizeof(s4) =%ld\n",sizeof(s4));
return 0;
}
4.2.2 strcmp()
The header file :#include <string.h>
Prototype :int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2);
function : Compare the size of two strings
Parameters :s1,s2 Two strings
Return value :
0: s1 = s2
<0: s1 < s2
>0: s1 > s2
int strncmp(const char *s1, const char *s2, size_t n);
Used to compare two strings before n Whether the two bytes are the same
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//strcmp The comparison is \0 Previous content , It has nothing to do with the memory space of the string
//char s1[32] = "hello w\0orld";
//char s2[] = "hello w\0orld";
char s1[] = "h";
char s2[] = "hello abcdefgwhi";
int ret = strcmp(s1,s2);
if(ret == 0)
{
printf("s1 = s2\n");
}
else if(ret > 0)
{
printf("s1 > s2\n");
}
else
{
printf("s1 < s2\n");
}
int k = strncmp(s1,s2,2);
if(k == 0)
{
printf("s1 = s2\n");
}
else if(k > 0)
{
printf("s1 > s2\n");
}
else
{
printf("s1 < s2\n");
}
return 0;
}
4.2.3 strcpy()
The header file :#include <string.h>
Prototype :char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src);
function : take src The string is assigned to dest In a string
Parameters :
dest: Destination string
src: The source string
Return value :
Return the first address of the destination string
char *strncpy(char *dest, const char *src, size_t n);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char s1[32];
strcpy(s1,"hello world");
printf("s1 = %s\n",s1);
char s2[] = "hello world";
char s3[32] = "abcdefg";
//strcpy take s3 The first of \0 Copied to s2
strcpy(s2,s3);
printf("sizeof(s2) = %ld\n",sizeof(s2));
printf("s2 = %s\n",s2);
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < sizeof(s2)/sizeof(s2[0]);i++)
{
printf("[%c] %d\n",s2[i],s2[i]);
}
puts("------------------------");
char buf1[32] = "hello world";
char buf2[32] = "abcdefghijklmnopqrsst";
//strcpy(buf1,buf2);
// Is the first of the second parameter n Bytes are copied to the first parameter
strncpy(buf1,buf2,7);
printf("buf1 = %s\n",buf1);
return 0;
}
5.2.4 strcat()
The header file :#include <string.h>
Prototype :char *strcat(char *dest, const char *src);
function : take src Append to dest Behind
Parameters :
dest: Destination string
src: The source string
Return value :
The first address of the appended string
char *strncat(char *dest, const char *src, size_t n);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char s1[32] ="hello wo\0rldadadjajdalsdkjaskdj"; //hello woabcdefg\0
char s2[32] ="abcdefg\0higk";
strcat(s1,s2);
printf("s1 = %s\n",s1);
return 0;
}
5.2.5 Realize it by yourself strcpy Function functions
#include <stdio.h>
char *my_strcpy(char *s1,char *s2)
{
if(NULL == s1 || NULL == s2)
{
return NULL;
}
int i = 0;
while(s2[i] != '\0')
{
s1[i] = s2[i];
i++;
}
s1[i] = '\0';
return s1;
}
int main()
{
char s1[] = "hello world";
char s2[] = "world";
char *result = my_strcpy(s1,s2);
for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(s1)/sizeof(s1[0]); i++)
{
printf("[%c] %d\n",result[i],result[i]);
}
return 0;
}
6、 ... and 、 The pointer
6.1 The purpose of the pointer
The application procedure is simple , compact , Efficient
Effectively represent complex data structures
Dynamic memory allocation
Get the return value of more than one function
6.2 The concept of pointer
When a variable is defined in the program , The program will open up memory space in memory for this variable , Every byte of space in our memory has a number , Call this number address , Addresses are also called pointers
Without affecting understanding , Sometimes the address , The pointer , Pointer variables do not distinguish , Generic pointer
&: Fetch address
*:
1. Definition time , If the front is a type , Indicates that this is a definition statement , Define a pointer variable ,pa It's a pointer , Point to integer a
2. When using ,*pa = 100;* It means to take a value , Take the pointer pa The value of the memory pointed to
pa = Address
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//int a = 1;
//int *pa = &a;
printf("int* = %ld\n",sizeof(int *));
printf("char* = %ld\n",sizeof(char *));
printf("double* = %ld\n",sizeof(double *));
printf("float* = %ld\n",sizeof(float *));
printf("long* = %ld\n",sizeof(long *));
int a = 1;
char ch = 'a';
//int *pc = &ch; // incompatible types
char *pch = &ch;
//ch = 'x';
*pch = 'x'; // Equivalent to ch = 'x'
printf("ch = %c\n",ch);
printf("ch = %c\n",*pch);
int *pa = &a;
printf("%p\n",pch);
printf("%p\n",pa);
printf("%p\n",pch + 1); // Different types of pointers , Different steps
printf("%p\n",pa + 1);
return 0;
}
6.3 Operation of pointer variable
Pointer operation takes the address stored in pointer variables as the operation quantity .
therefore , The essence of pointer operation is the operation of address .
The types of pointer operations are limited , It can only perform arithmetic operations , Relation operation and assignment operation
6.3.1 Arithmetic operator
+: px + n The pointer moves in the direction of the larger address n Data
-: px - n The pointer moves in the direction of small address n Data
++: px++ The pointer moves in the direction of the larger address 1 Data
--: px++ The pointer moves in the direction of small address 1 Data
Pointer variable addition and subtraction , Indicates that the pointer variable moves in the direction of large or small address N Operation space , Subtract two pointer variables , Indicates how many operation spaces there are between two addresses ( How many elements )
Be careful , Two pointers do operations , Must be of the same type , Different types make no sense .
Adding and subtracting a pointer variable makes sense , Multiplication and division are meaningless
After ++ Priority is higher than the front ++
After ++ The law of union goes from left to right
In front of ++ and * Same priority , The law of union goes from right to left
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int arr[6] = {1,3,5,8,9,10};
int *p1 = arr;
printf("*p1 = %d\n",*p1);
p1++;
int *p2 = p1++;
printf("*p1 = %d,*p2 = %d\n",*p1,*p2);
printf("p1 - p2 = %ld\n",p1 - p2);
int y = *p1; // Value
printf("y = %d\n",y);
y = ++*p1;
printf("y = %d\n",y);
y = (*p1)++;
printf("y = %d\n",y);
y = *p1++; // When the assignment is complete , The pointer px Add 1
printf("y = %d\n",y);
printf("*p1 = %d\n",*p1);
/*y = ++*p1++; // When the assignment is complete , The pointer px Add 1
printf("y = %d\n",y);
printf("*p1 = %d\n",*p1);
*/
return 0;
}
6.3.2 Relational operator
> px > py
<
>=
<=
!=
==
Two pointer variables can determine the size of the save address through relational operators
The relational operator between two pointers represents the relationship between the address positions they point to , The pointer pointing to a large address is larger than the pointer pointing to a small address
The relation operation between pointers with different data types is meaningless , Between two pointers of data pointing to different data areas , Relational operators are meaningless .
The relation operation between pointer and general integer variable is also meaningless , But we can do equal or unequal relation operation with zero , Determine if the pointer is empty , Generally speaking, it is related to NULL
6.3.3 The assignment operation
Pointer variables can be assigned directly , But you cannot assign an integer to a pointer variable , Because there is no open space
Pointer assignment operation is to send an address value to pointer variable through assignment operator ,
6.2.4 practice : Enter a string , Flip the elements of the string
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char str[32] = {0};
gets(str);
printf(" Reverse the previous string :%s\n",str);
char *p = NULL,*q = NULL;
char tmp;
p = &str[0];
q = &str[strlen(str) - 1];
#if 0
while(p < q)
{
tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
p++;
q--;
}
#endif
for(;p < q;p++,q--)
{
tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
}
printf(" The inverted string :%s\n",str);
return 0;
}
7、 ... and 、 Pointers and one-dimensional arrays
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
int *p = a;
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < 5;i++)
{
//printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("%d ",*(p+i));
}
putchar(10);
char *s = "helloworld";
char str[32] ="hello nanjing";
s = str;
//printf("%s\n",s);
for(i = 0 ; i < 10;i++)
{
printf("%c",s[i]);
}
putchar(10);
return 0;
}
practice
practice 1: Realize by yourself through pointer strlen Function functions
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char buf[32] = {0};
printf(" Please enter a string :\n");
gets(buf);
char *p = buf;
int i;
while(*p != '\0')
{
p++;
i++;
}
printf("strlen(buf) = %d\n",i);
return 0;
}
practice 2: By pointer strcpy Function functions
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char s1[] = "helloworld!";
char s2[] = "abcdefghijk";
char *p = NULL,*q = NULL;
p = s1;
q = s2;
while(*q != '\0')
{
*p = *q;
p++;
q++;
}
*p = *q;
printf("s1 = %s\n",s1);
return 0;
}
Homework
Homework :
1. By pointer strcat function
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char s1[32] = "hello world";
char s2[] = "abcdefg";
char *p1 = &s1[strlen(s1)];
char *p2 = s2;
while(*p2 != '\0')
{
*p1 = *p2;
p1++;
p2++;
}
*p1 = '\0';
printf("%s\n",s1);
return 0;
}
2. Realization atoi Function functions
char str[] = '5891";
int num;
…
“5891” ----->5891
3. Enter a string , How many spaces are there in the output string
4. Enter two strings , Determine whether one string is a substring of another
s1 = hellloworld s2 = oworl
边栏推荐
- 詹姆斯·格雷克《信息简史》读后感记录
- RPA云电脑,让RPA开箱即用算力无限?
- Scrapy framework
- How can CSDN indent the first line of a paragraph by 2 characters?
- Data analysis series 3 σ Rule / eliminate outliers according to laida criterion
- Linkedblockingqueue source code analysis - add and delete
- Visual Studio Deployment Project - Create shortcut to deployed executable
- Flask learning record 000: error summary
- Tools for debugging makefiles - tool for debugging makefiles
- Basic learning of SQL Server -- creating databases and tables with the mouse
猜你喜欢
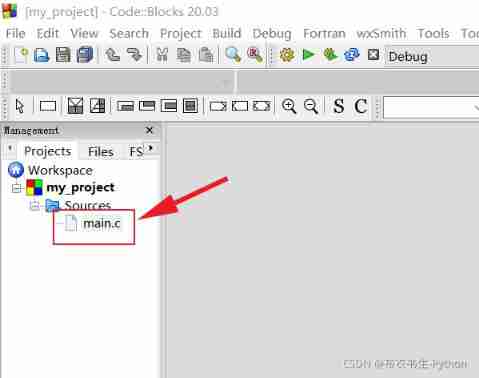
C language 001: download, install, create the first C project and execute the first C language program of CodeBlocks
Connect diodes in series to improve voltage withstand
QT creator add JSON based Wizard
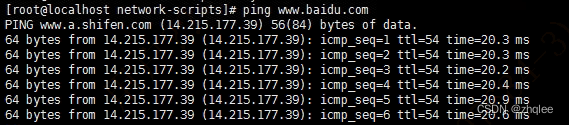
Ping error: unknown name or service

Coindesk comments on the decentralization process of the wave field: let people see the future of the Internet

Laser slam learning (2d/3d, partial practice)
![Binary sort tree [BST] - create, find, delete, output](/img/e4/a950607f8b76bc7f8d56063dd72126.png)
Binary sort tree [BST] - create, find, delete, output
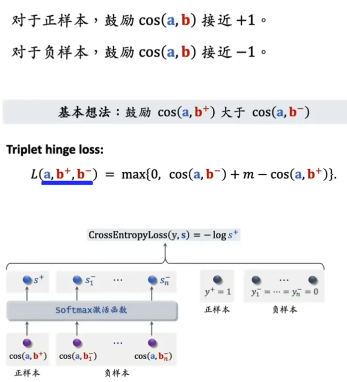
【推荐系统基础】正负样本采样和构造
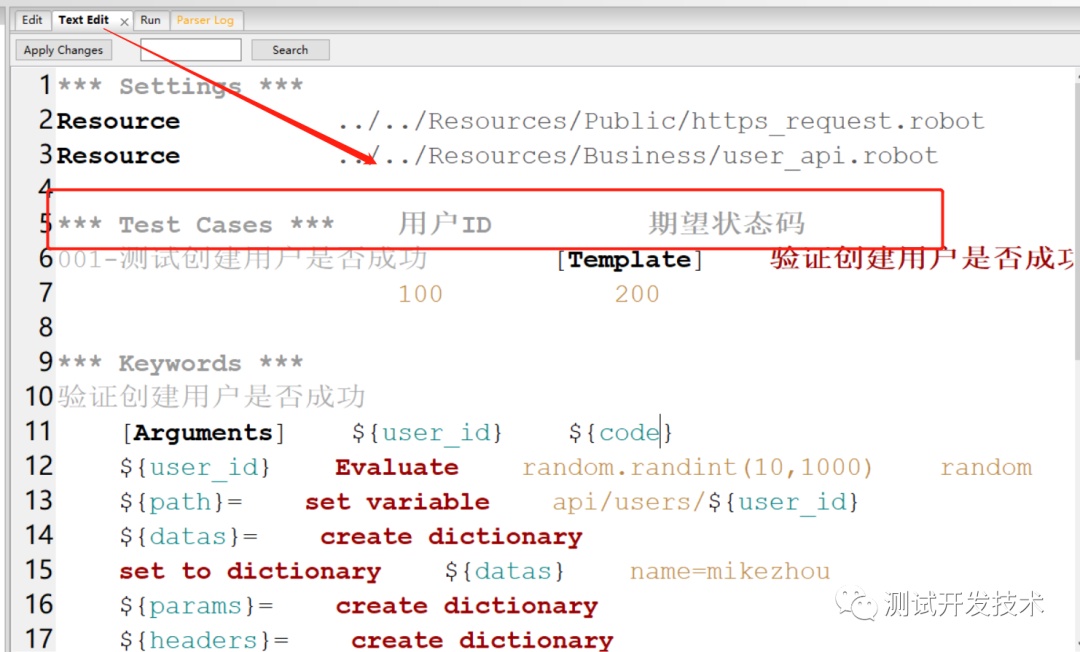
Automated testing: robot framework is a practical skill that 90% of people want to know
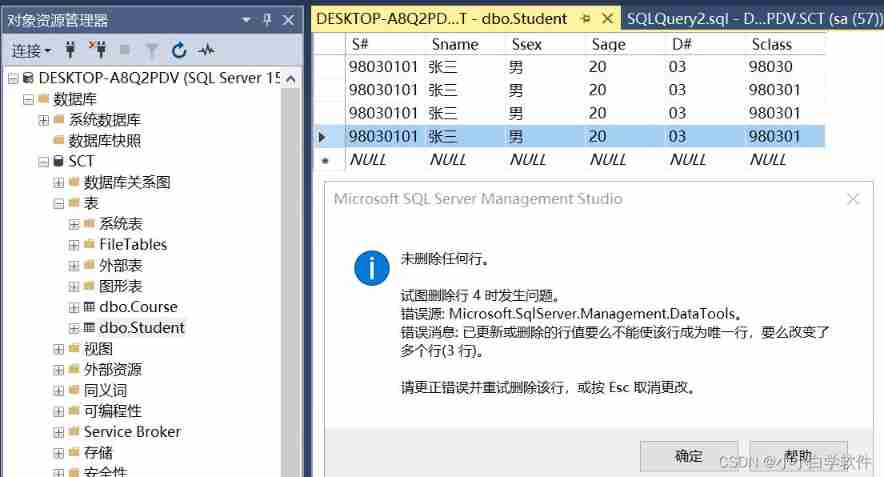
Solutions to problems in sqlserver deleting data in tables
随机推荐
Tools for debugging makefiles - tool for debugging makefiles
[programming problem] [scratch Level 2] 2019.09 make bat Challenge Game
Problems faced when connecting to sqlserver after downloading (I)
[programming questions] [scratch Level 2] March 2019 garbage classification
Trust orbtk development issues 2022
【编程题】【Scratch二级】2019.09 绘制雪花图案
测试流程不完善,又遇到不积极的开发怎么办?
ROS from entry to mastery (IX) initial experience of visual simulation: turtlebot3
Enterprise application demand-oriented development of human resources department, employee attendance records and paid wages business process cases
[leetcode] 20. Valid brackets
[path planning] use the vertical distance limit method and Bessel to optimize the path of a star
Stm32f1 and stm32cubeide programming example - rotary encoder drive
paddle一个由三个卷积层组成的网络完成cifar10数据集的图像分类任务
浪潮云溪分布式数据库 Tracing(二)—— 源码解析
One click free translation of more than 300 pages of PDF documents
Linkedblockingqueue source code analysis - add and delete
QT and OpenGL: loading 3D models using the open asset import library (assimp) - Part 2
Binary sort tree [BST] - create, find, delete, output
单机高并发模型设计
Emotional post station 010: things that contemporary college students should understand