当前位置:网站首页>Game theory matlab
Game theory matlab
2022-07-06 02:50:00 【Foreign rookie】
Catalog
1. Initialization of each parameter
2. Calculated expectation and actual expectation
1. brief introduction
Game theory It's also called game theory (Game Theory) both Modern mathematics A new branch of , It's also Operations research An important subject of .
Game theory mainly studies the interaction between formulated incentive structures . It is to study phenomena with the nature of struggle or competition Mathematical theory And methods . Game theory considers the prediction behavior and actual behavior of individuals in the game , And study their optimization strategies . Biologists use game theory to understand and predict some results of evolution .
Game theory has become economics One of the standard analysis tools . In Biology 、 economics 、 international relation 、 Computer science 、 political science 、 Military strategy and many other disciplines are widely used .
The basic concept includes players 、 action 、 Information 、 Strategy 、 earnings 、 Equilibrium and results . among People in the game 、 Strategy and revenue are the most basic elements . People in the game 、 Actions and results are collectively referred to as The rules of the game .
Game theory is simply ,A Take measures to affect B act ,B Behavior influence A The decision , The two play back and forth , Finally, a dynamic balance is achieved . Strictly speaking, game theory is just a way to solve problems .
2. Algorithm principle
Take electric taxis and power stations for example , Suppose that the electric taxi and the power station belong to the same company , The company wants to control the number of taxis in the target area to achieve the expected distribution through the price pricing measures of power station replacement .
For drivers , There are two costs , One is distance cost d, One is to pay the cost p, The payment cost is the electricity price paid for replacing the battery , We can set up weighting factors a Combine the two to build a utility function , The driver will choose the smallest replacement station of this function to replace the battery , After replacing the battery, the driver usually starts to receive orders around
![]()
For the company , The objective function is the actual distribution of taxis in different regions e And expectation distribution E The sum of absolute differences of , The company influences the driver's choice by adjusting the price , So as to adjust the distribution of drivers in different areas
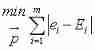
Model analysis of two-tier game theory
① The first stage , After the charging station calculates the power change request of each electric taxi , According to the optimization objective , Formulate price strategy
② The second stage , The electric taxi selects the target replacement station from all the replacement stations according to its own utility function to replace the battery
③ The first stage and the second stage are carried out alternately , Until equilibrium is reached
Algorithm design steps

3. The example analysis
1. Initialization of each parameter
n=900;% Power exchange demand
min_price=170;% The price range of electricity exchange
max_price=230;
A=normrnd(36,5,1,25);% Initial expectations , The average value is 36, The variance of 5 Gaussian distribution of
E=fix(A); % the 0 Round the direction , Such as ,4.1,4.5,4.8 Round it all 4
% The following is the adjustment according to the demand E Size
a=sum(E)-n;
A=A-a/25;
E=fix(A);
b=sum(E)-n;
A=A-b/25;
E=fix(A);
a1=0.05;a2=0.95;% Distance cost and change point price weight
x=rand(n,1).*20000;% Initialize the required vehicle location
y=rand(n,1).*20000;
H=[2,2;2,6;2,10;2,14;2,18% Initialize the power station location
6,2;6,6;6,10;6,14;6,18
10,2;10,6;10,10;10,14;10,18
14,2;14,6;14,10;14,14;14,18
18,2;18,6;18,10;18,14;18,18].*1000;
% Draw the location map of the initialized driver and the power station
figure
plot(x,y,'r*')
hold on
plot(H(:,1),H(:,2),'bo')
legend(' The driver ',' Change station ')
title(' Initial location map ')return :
2. Calculated expectation and actual expectation
%% Calculated expectation and actual expectation
D=[];% The proportion of demand vehicles to each replacement station
price=200.*ones(1,25);
for i=1:length(H)
for j=1:length(x)
D(i,j)=a1*sqrt((H(i,1)-x(j))^2+(H(i,2)-y(j))^2)+a2*price(i);% The total cost
end
end
[d1,d2]=min(D);% Select the nearest replacement station
C=tabulate(d2(:));% Count the number of power station replacement
e=C(:,2);
err=sum(abs(E-e')) % Sum of expectation differences , That is, the game object return : Because of the random , All of them may be different every time

3. The game process
%% game
J=[]; % The difference between price changes
ER(1)=err;
for k=2:100
j=0;
for i=1:25
if e(i)<E(i) && price(i)>=min_price
price(i)=price(i)-1;
j=j+1;
end
if e(i)>E(i) && price(i)<=max_price
price(i)=price(i)+1;
j=j+1;
end
end
J=[J,j];
DD=[];
for i=1:length(H)
for j=1:length(x)
DD(i,j)=a1*sqrt((H(i,1)-x(j))^2+(H(i,2)-y(j))^2)+a2*price(i);
end
end
[dd1,dd2]=min(DD);
CC=tabulate(dd2(:));
e=CC(:,2);
err=sum(abs(E-e'));
ER=[ER,err];
end4. mapping
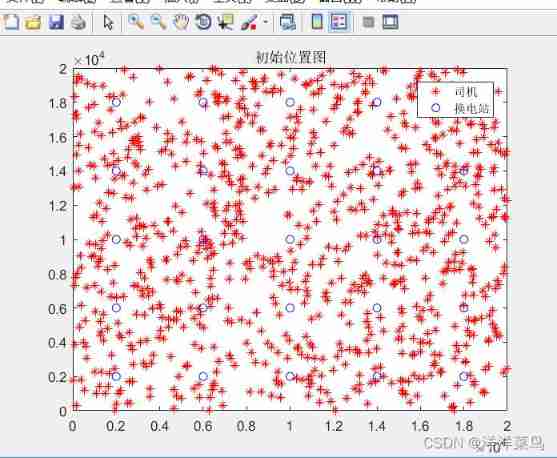
% mapping
figure
plot(ER,'-o')
title('E-e The difference of ')
set(gcf,'unit','normalized','position',[0.2,0.2,0.64,0.32])
legend('E-e')
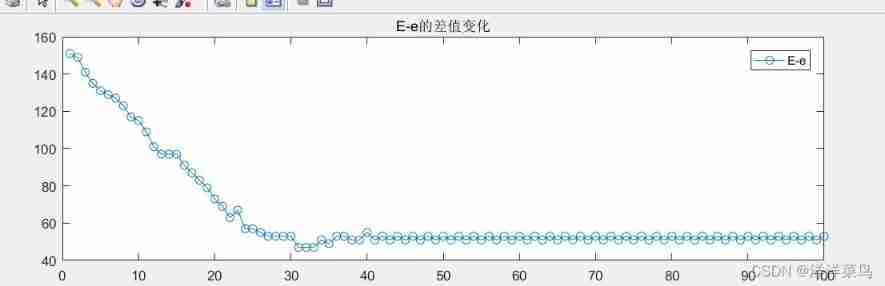
figure
plot(J,'r-o')
title(' The difference in price changes ')
xlabel('Iterations(t)')
set(gcf,'unit','normalized','position',[0.2,0.2,0.64,0.32])
legend('sum of Price(t)-Price(t-1)')
figure
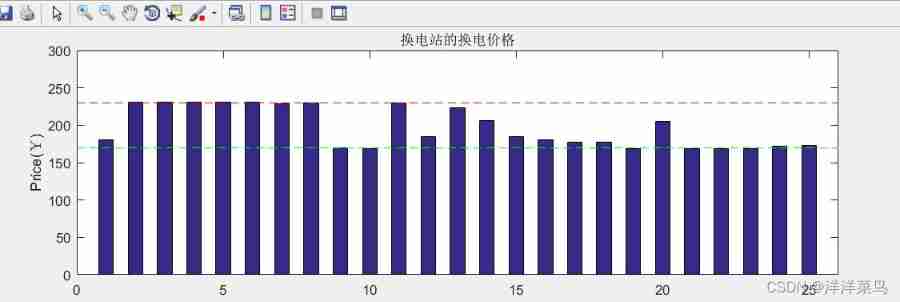
bar(price,0.5)
hold on
plot([0,26],[min_price,min_price],'g--')
plot([0,26],[max_price,max_price],'r--')
title(' The replacement price of the power station ')
ylabel('Price(¥)')
axis([0,26,0,300])
set(gcf,'unit','normalized','position',[0.2,0.2,0.64,0.32]);
figure
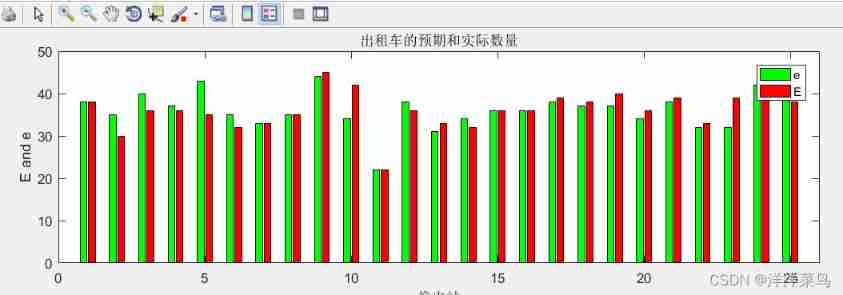
h=bar([e,E'],'gr');
set(h(1),'FaceColor','g'); set(h(2),'FaceColor','r');
axis([0,26,0,50])
title(' Expected and actual number of taxis ')
ylabel('E and e')
set(gcf,'unit','normalized','position',[0.2,0.2,0.64,0.32]);
xlabel(' Change station ')
legend('e','E')return :
Complete code
clear;clc;
setenv('BLAS_VERSION','') % Make error correction
n=900;% Power exchange demand
min_price=170;% The price range of electricity exchange
max_price=230;
A=normrnd(36,5,1,25);% Initial expectations , The average value is 36, The variance of 5 Gaussian distribution of
E=fix(A); % the 0 Round the direction , Such as ,4.1,4.5,4.8 Round it all 4
% The following is the adjustment according to the demand E Size
a=sum(E)-n;
A=A-a/25;
E=fix(A);
b=sum(E)-n;
A=A-b/25;
E=fix(A);
a1=0.05;a2=0.95;% Distance cost and change point price weight
x=rand(n,1).*20000;% Initialize the required vehicle location
y=rand(n,1).*20000;
H=[2,2;2,6;2,10;2,14;2,18% Initialize the power station location
6,2;6,6;6,10;6,14;6,18
10,2;10,6;10,10;10,14;10,18
14,2;14,6;14,10;14,14;14,18
18,2;18,6;18,10;18,14;18,18].*1000;
% Draw the location map of the initialized driver and the power station
figure
plot(x,y,'r*')
hold on
plot(H(:,1),H(:,2),'bo')
legend(' The driver ',' Change station ')
title(' Initial location map ')
%% Calculated expectation and actual expectation
D=[];% The proportion of demand vehicles to each replacement station
price=200.*ones(1,25);
for i=1:length(H)
for j=1:length(x)
D(i,j)=a1*sqrt((H(i,1)-x(j))^2+(H(i,2)-y(j))^2)+a2*price(i);% The total cost
end
end
[d1,d2]=min(D);% Select the nearest replacement station
C=tabulate(d2(:));% Count the number of power station replacement
e=C(:,2);
err=sum(abs(E-e')); % Sum of expectation differences , That is, the game object
% ER(1)=err
%% game
J=[]; % The difference between price changes
ER(1)=err;
for k=2:100
j=0;
for i=1:25
if e(i)<E(i) && price(i)>=min_price
price(i)=price(i)-1;
j=j+1;
end
if e(i)>E(i) && price(i)<=max_price
price(i)=price(i)+1;
j=j+1;
end
end
J=[J,j];
DD=[];
for i=1:length(H)
for j=1:length(x)
DD(i,j)=a1*sqrt((H(i,1)-x(j))^2+(H(i,2)-y(j))^2)+a2*price(i);
end
end
[dd1,dd2]=min(DD);
CC=tabulate(dd2(:));
e=CC(:,2);
err=sum(abs(E-e'));
ER=[ER,err];
end
% mapping
figure
plot(ER,'-o')
title('E-e The difference of ')
set(gcf,'unit','normalized','position',[0.2,0.2,0.64,0.32])
legend('E-e')
figure
plot(J,'r-o')
title(' The difference in price changes ')
xlabel('Iterations(t)')
set(gcf,'unit','normalized','position',[0.2,0.2,0.64,0.32])
legend('sum of Price(t)-Price(t-1)')
figure
bar(price,0.5)
hold on
plot([0,26],[min_price,min_price],'g--')
plot([0,26],[max_price,max_price],'r--')
title(' The replacement price of the power station ')
ylabel('Price(¥)')
axis([0,26,0,300])
set(gcf,'unit','normalized','position',[0.2,0.2,0.64,0.32]);
figure
h=bar([e,E'],'gr');
set(h(1),'FaceColor','g'); set(h(2),'FaceColor','r');
axis([0,26,0,50])
title(' Expected and actual number of taxis ')
ylabel('E and e')
set(gcf,'unit','normalized','position',[0.2,0.2,0.64,0.32]);
xlabel(' Change station ')
legend('e','E')边栏推荐
- tcpdump: no suitable device found
- 【Kubernetes 系列】一文学会Kubernetes Service安全的暴露应用
- [ruoyi] ztree custom icon (iconskin attribute)
- [ruoyi] set theme style
- Httprunnermanager installation (III) - configuring myql Database & initialization data under Linux
- QT release exe software and modify exe application icon
- Force buckle 146 LRU cache
- "Hands on learning in depth" Chapter 2 - preparatory knowledge_ 2.5 automatic differentiation_ Learning thinking and exercise answers
- MySQL advanced notes
- 米家、涂鸦、Hilink、智汀等生态哪家强?5大主流智能品牌分析
猜你喜欢
微服务间通信
Solution: attributeerror: 'STR' object has no attribute 'decode‘

2022.02.13
Taobao focus map layout practice

codeforces每日5題(均1700)-第六天

ERA5再分析资料下载攻略
微软语音合成助手 v1.3 文本转语音工具,真实语音AI生成器
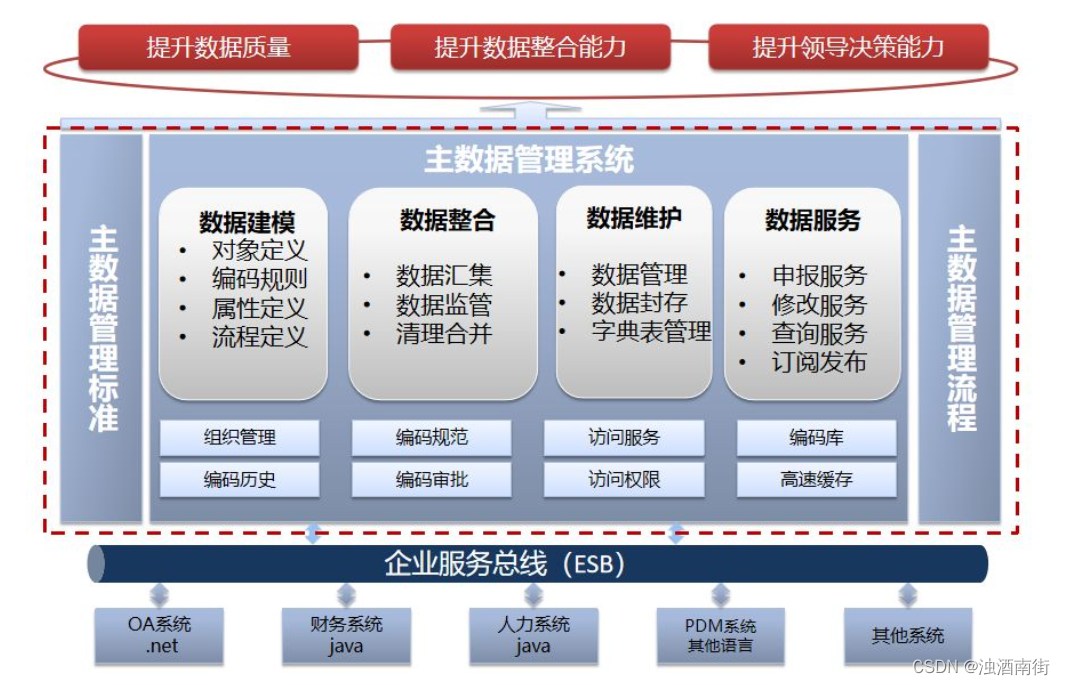
Master data management theory and Practice
Httprunnermanager installation (III) - configuring myql Database & initialization data under Linux

codeforces每日5题(均1700)-第六天
随机推荐
Patch NTP server at the beginning of DDoS counterattack
Referenceerror: primordials is not defined error resolution
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 23
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 8
Function knowledge points
Force buckle 146 LRU cache
2345文件粉碎,文件强力删除工具无捆绑纯净提取版
C # create self host webservice
2345 file shredding, powerful file deletion tool, unbound pure extract version
JS events (add, delete) and delegates
Single instance mode of encapsulating PDO with PHP in spare time
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 10
Deeply analyze the chain 2+1 mode, and subvert the traditional thinking of selling goods?
Li Kou today's question -729 My schedule I
Yyds dry inventory comparison of several database storage engines
DDoS attacks - are we really at war?
Introduction to robotframework (I) brief introduction and use
Spherical lens and cylindrical lens
2.11 simulation summary
【指针训练——八道题】