当前位置:网站首页>数论函数及其求和 待更新
数论函数及其求和 待更新
2022-07-05 04:43:00 【Strezia】
主要记录一下相关的题目,略过知识讲解。
例题1 数论分块
题目描述
若 x x x 分解质因数结果为 x = p 1 k 1 p 2 k 2 ⋯ p n k n x=p_1^{k_1}p_2^{k_2}\cdots p_n^{k_n} x=p1k1p2k2⋯pnkn,令 f ( x ) = ( k 1 + 1 ) ( k 2 + 1 ) ⋯ ( k n + 1 ) f(x)=(k_1+1)(k_2+1)\cdots (k_n+1) f(x)=(k1+1)(k2+1)⋯(kn+1),求 ∑ i = l r f ( i ) \sum_{i=l}^rf(i) ∑i=lrf(i) 对 998 244 353 998\,244\,353 998244353 取模的结果。
时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n)。
思路
首先要知道 f ( x ) f(x) f(x) 其实就是 x x x 的约数个数。(每种素因子都有 k i k_i ki 个那么可以取 0 , 1 , . . . , k i 0,1,...,k_i 0,1,...,ki 一共 k i + 1 k_i+1 ki+1 种取法排列组合,由唯一分解定理显然乘积都是不同的)因为题目要求的是区间和,于是正常地转化为前缀和形式 a n s = ∑ i = 1 r f ( x ) − ∑ i = 1 l − 1 f ( x ) ans=\sum_{i=1}^rf(x)-\sum_{i=1}^{l-1}f(x) ans=∑i=1rf(x)−∑i=1l−1f(x) ,设 S ( n ) = ∑ i = 1 n f ( x ) S(n) = \sum_{i=1}^nf(x) S(n)=∑i=1nf(x),问题转化为了求 S ( n ) S(n) S(n) ,也就是求 1 − n 1-n 1−n 这 n n n 个数的因数个数之和。
1 − n 1-n 1−n 中含有因子 i i i 的数一共有 ⌊ n i ⌋ \lfloor\frac ni\rfloor ⌊in⌋ ,直接用数论分块即可。
代码
int ll, rr, n;
int cal(int l, int r) {
int ansr = 0, ansl = 0;
n = rr;
for(int l=1,r;l<=n;l=r+1){
r=n/(n/l);
ansr+=(n/l)*(r-l+1) % P;
ansr %= P;
}
n = ll;
for(int l=1,r;l<=n;l=r+1){
r=n/(n/l);
ansl+=(n/l)*(r-l+1) % P;
ansl %= P;
}
ansr = (ansr - ansl + P) % P;
return ansr;
}
void solve() {
cin >> ll >> rr;
ll--;
cout << cal(ll, rr) << endl;
}
例题2 数论分块
题目描述
给定一个整数 n n n,你需要求出 ∑ i = 1 n gcd ( i , n ) \sum\limits_{i=1}^n \gcd(i, n) i=1∑ngcd(i,n), n < 1 0 9 n<10^9 n<109
思路
注意到 g c d ( i , n ) gcd(i,n) gcd(i,n) 的取值最多只有 n n n 的约数个,所以考虑按取值分类,而且出现 g c d gcd gcd 的题往往都需要想办法凑出 g c d ( i , j ) = 1 gcd(i,j)=1 gcd(i,j)=1,于是我们把原式化为 ∑ d ∣ n d ∑ i = 1 n [ g c d ( i , n ) = d ] = ∑ d ∣ n d ∑ i = 1 n d [ g c d ( i , n d ) = 1 ] = ∑ d ∣ n d ϕ ( n d ) \sum_{d|n}d\sum_{i=1}^n[gcd(i,n)=d ]=\sum_{d|n}d\sum_{i=1}^{\frac nd}[gcd(i,\frac nd)=1]=\sum_{d|n}d\phi(\frac nd) d∣n∑di=1∑n[gcd(i,n)=d]=d∣n∑di=1∑dn[gcd(i,dn)=1]=d∣n∑dϕ(dn)
可以通过枚举 n n n 的约数直接求,时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n)。
代码
void solve() {
cin >> n;
ll ans = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i * i <= n; i++) {
if(n % i == 0) {
ans += i * phi(n/i);
if(n/i!=i) {
ans += (n/i) * phi(i);
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
莫比乌斯函数
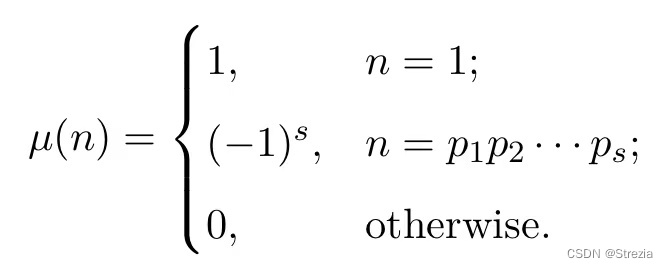
常用卷积
ϵ = μ ∗ 1 , I d = ϕ ∗ 1 \epsilon=\mu *1, Id=\phi*1 ϵ=μ∗1,Id=ϕ∗1 。
即 ϵ ( n ) = ∑ d ∣ n μ ( d ) \epsilon(n) = \sum_{d|n}\mu(d) ϵ(n)=∑d∣nμ(d) 。其中 ϵ ( n ) = 1 \epsilon(n)= 1 ϵ(n)=1 当且仅当 n = 1 n=1 n=1,否则 = 0 =0 =0 。
引例
给定 n , m n, m n,m,求二元组 ( x , y ) (x,y) (x,y) 的个数,满足 1 ≤ x ≤ n 1\leq x\leq n 1≤x≤n , 1 ≤ y ≤ m 1\leq y\leq m 1≤y≤m ,且 g c d ( x , y ) = 1 gcd(x,y)=1 gcd(x,y)=1 。 n , m ≤ 1 0 7 n,m\leq 10^7 n,m≤107 ,至多 1 0 4 10^4 104 组数据。
思路
∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m [ g c d ( x , y ) = 1 ] = ∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m ϵ ( g c d ( x , y ) ) = ∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m ∑ d ∣ g c d ( x , y ) μ ( d ) \sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m[gcd(x,y)=1]=\sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m\epsilon (gcd(x,y))=\sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m\sum_{d|gcd(x,y)}\mu(d) x=1∑ny=1∑m[gcd(x,y)=1]=x=1∑ny=1∑mϵ(gcd(x,y))=x=1∑ny=1∑md∣gcd(x,y)∑μ(d)
= ∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m ∑ d ∣ x , d ∣ y μ ( d ) = = ∑ d = 1 m i n ( n , m ) μ ( d ) ⌊ n d ⌋ ⌊ m d ⌋ =\sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m\sum_{d|x,d|y}\mu(d)==\sum_{d=1}^{min(n,m)}\mu(d)\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor\lfloor\frac md\rfloor =x=1∑ny=1∑md∣x,d∣y∑μ(d)==d=1∑min(n,m)μ(d)⌊dn⌋⌊dm⌋
对上式预处理 μ \mu μ 及其前缀和,按 ⌊ n d ⌋ ⌊ m d ⌋ \lfloor\frac nd\rfloor\lfloor\frac md\rfloor ⌊dn⌋⌊dm⌋ 的取值分段,就可以每组询问 O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n) 解决问题。
例题3 莫比乌斯反演
题目描述
设 d ( x ) d(x) d(x) 为 x x x 的约数个数,给定 n , m n,m n,m,求
∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 m d ( i j ) \sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^md(ij) i=1∑nj=1∑md(ij)
【数据范围】
对于 100 % 100\% 100% 的数据, 1 ≤ T , n , m ≤ 50000 1\le T,n,m \le 50000 1≤T,n,m≤50000。
思路
首先有结论:
d ( i j ) = ∑ x ∣ i ∑ y ∣ j [ g c d ( x , y ) = 1 ] d(ij)=\sum_{x|i}\sum_{y|j}[gcd(x,y)=1] d(ij)=x∣i∑y∣j∑[gcd(x,y)=1]
则原式:
∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 m d ( i j ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 m ∑ x ∣ i ∑ y ∣ j [ g c d ( x , y ) = 1 ] = ∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m [ g c d ( x , y ) = 1 ] ⌊ n x ⌋ ⌊ m y ⌋ \sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^md(ij)=\sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^m\sum_{x|i}\sum_{y|j}[gcd(x,y)=1]=\sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m[gcd(x,y)=1]\lfloor\frac nx\rfloor\lfloor\frac my\rfloor i=1∑nj=1∑md(ij)=i=1∑nj=1∑mx∣i∑y∣j∑[gcd(x,y)=1]=x=1∑ny=1∑m[gcd(x,y)=1]⌊xn⌋⌊ym⌋
将引例中结论带入:
= ∑ d = 1 m i n ( n , m ) μ ( d ) ∑ x = 1 ⌊ n d ⌋ ∑ y = 1 ⌊ m d ⌋ ⌊ n x d ⌋ ⌊ m y d ⌋ = ∑ d = 1 m i n ( n , m ) μ ( d ) ∑ x = 1 ⌊ n d ⌋ ∑ y = 1 ⌊ m d ⌋ ⌊ ⌊ n d ⌋ x ⌋ ⌊ ⌊ m d ⌋ y ⌋ =\sum_{d=1}^{min(n,m)}\mu(d)\sum_{x=1}^{\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor}\sum_{y=1}^{\lfloor\frac md \rfloor}\lfloor\frac n{xd}\rfloor\lfloor\frac m{yd}\rfloor=\sum_{d=1}^{min(n,m)}\mu(d)\sum_{x=1}^{\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor}\sum_{y=1}^{\lfloor\frac md \rfloor}\lfloor\frac{\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor}x\rfloor\lfloor\frac {\lfloor \frac md\rfloor}y\rfloor =d=1∑min(n,m)μ(d)x=1∑⌊dn⌋y=1∑⌊dm⌋⌊xdn⌋⌊ydm⌋=d=1∑min(n,m)μ(d)x=1∑⌊dn⌋y=1∑⌊dm⌋⌊x⌊dn⌋⌋⌊y⌊dm⌋⌋
令 f ( n ) = ∑ i = 1 n ⌊ n i ⌋ f(n)=\sum_{i=1}^n\lfloor\frac ni\rfloor f(n)=∑i=1n⌊in⌋ ,则
= ∑ d = 1 m i n ( n , m ) μ ( d ) f ( ⌊ n d ⌋ ) f ( ⌊ m d ⌋ ) =\sum_{d=1}^{min(n, m)}\mu(d)f(\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor)f(\lfloor\frac md\rfloor) =d=1∑min(n,m)μ(d)f(⌊dn⌋)f(⌊dm⌋)
又 f ( n ) = ∑ i = 1 n ⌊ n i ⌋ = ∑ k = 1 n d ( k ) f(n)=\sum_{i=1}^n\lfloor\frac ni\rfloor=\sum_{k=1}^nd(k) f(n)=∑i=1n⌊in⌋=∑k=1nd(k)
故可以通过欧拉筛 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 预处理出 d ( n ) d(n) d(n),通过前缀和得到 f ( n ) f(n) f(n),可以每次询问 O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n) 回答。
代码
int mu[maxn], prim[maxn], sum[maxn], cnt;
int g[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void get_mu(int n)
{
mu[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!vis[i]){
prim[++cnt]=i;mu[i]=-1;}
for(int j=1;j<=cnt&&prim[j]*i<=n;j++)
{
vis[prim[j]*i]=1;
if(i%prim[j]==0)break;
else mu[i*prim[j]]=-mu[i];
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)sum[i]=sum[i-1]+mu[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
long long ans=0;
for(int l=1,r;l<=i;l=r+1)
{
r=(i/(i/l));
ans+=1ll*(r-l+1)*1ll*(i/l);
}
g[i]=ans;
}
}
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int ans = 0;
int mn = min(n, m);
for(int l = 1, r; l <= mn; l = r + 1){
r = min(n/(n/l), m/(m/l));
ans += (sum[r] - sum[l-1]) * g[n/l] * g[m/l];
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
边栏推荐
- 3 minutes learn to create Google account and email detailed tutorial!
- Raki's notes on reading paper: soft gazetteers for low resource named entity recognition
- How should programmers learn mathematics
- Looking at Chinese science and technology from the Winter Olympics: what is the mystery of the high-speed camera that the whole people thank?
- Function template
- jmeter -- 分布式压测
- [crampon game] MC tutorial - first day of survival
- PHP reads the INI file and writes the modified content
- The difference between bundle, chunk and module
- Introduce Hamming distance and calculation examples
猜你喜欢
CSDN正文自动生成目录
Function (basic: parameter, return value)
【acwing】836. Merge sets
The 22nd Spring Festival Gala, an immersive stage for the yuan universe to shine into reality

2021 huashubei mathematical modeling idea + reference + paper

The remainder operation is a hash function
Wenet: E2E speech recognition tool for industrial implementation
Mxnet imports various libcudarts * so、 libcuda*. So not found
![[PCL self study: feature9] global aligned spatial distribution (GASD) descriptor (continuously updated)](/img/2b/933586b6feff1d48c5bee11cd734ba.jpg)
[PCL self study: feature9] global aligned spatial distribution (GASD) descriptor (continuously updated)
质量体系建设之路的分分合合
随机推荐
Is there a sudden failure on the line? How to make emergency diagnosis, troubleshooting and recovery
Key review route of probability theory and mathematical statistics examination
10 programming habits that web developers should develop
[groovy] closure (closure as function parameter | code example)
Raki's notes on reading paper: soft gazetteers for low resource named entity recognition
直播預告 | 容器服務 ACK 彈性預測最佳實踐
2021 huashubei mathematical modeling idea + reference + paper
[groovy] closure (closure parameter binding | curry function | rcurry function | ncurry function | code example)
函数(易错)
English topic assignment (27)
概率论与数理统计考试重点复习路线
JMeter -- distributed pressure measurement
Function (error prone)
Debug insights
Interface joint commissioning test script optimization V5.0 (end)
[groovy] closure (Introduction to closure class closure | closure parametertypes and maximumnumberofparameters member usage)
Variable category (automatic, static, register, external)
Construction d'un Cluster redis sous Windows
介绍汉明距离及计算示例
The principle of attention mechanism and its application in seq2seq (bahadanau attention)