当前位置:网站首页>Group counting notes (1) - check code, original complement multiplication and division calculation, floating point calculation
Group counting notes (1) - check code, original complement multiplication and division calculation, floating point calculation
2022-07-05 04:38:00 【May there be no wa after this】
The knowledge points of this article are learned from B standing @ Wang Dao Forum , Support genuine . Click here to enter -> Wangdao computer postgraduate entrance examination The principle of computer organization
The original purpose of writing this note is to show yourself , If you forget some knowledge points in the future, you can review . Of course , There's no problem if you want to see it , But I suggest you watch videos to learn .
Check code
Parity code
Parity code , stay N Add a check bit to the valid information bits to detect whether there is an error in the data transmission process .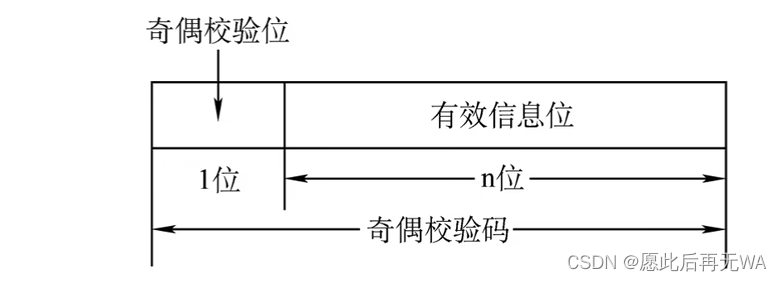 The definition of parity is to look at the whole check code ( Check bit + Information bits ) in 1 Number of occurrences , If odd check code is used , Then the check code is 1 The number of occurrences is odd , And vice versa .
The definition of parity is to look at the whole check code ( Check bit + Information bits ) in 1 Number of occurrences , If odd check code is used , Then the check code is 1 The number of occurrences is odd , And vice versa .
example : Seek coding 10110101 Parity check code .
Set the highest bit as the check bit , Then we can write it in this form :_10110101, among _ Is the check digit to be filled , There are an odd number 1(5 individual ), In order to have an odd number in the check code 1, Then the check digit of odd check code should be 0, namely 010110101, There are even numbers in the check code 1, Then the parity check digit of the parity check code should be 1( At this time, there is 6 individual 1).
According to the above check code, we can know , When there is 1 Or an odd number of bits by 0 Turn into 1 Or by the 1 Turn into 0 when , Errors can be detected ; But when even bits jump , This method cannot detect exceptions .
Parity codes have another drawback , Even if errors can be detected , It's impossible to judge which one has a problem , You can only ask the other party to retransmit data .
Note that this is just a summary of some knowledge points of the video , It is recommended that you read this article after watching the video .
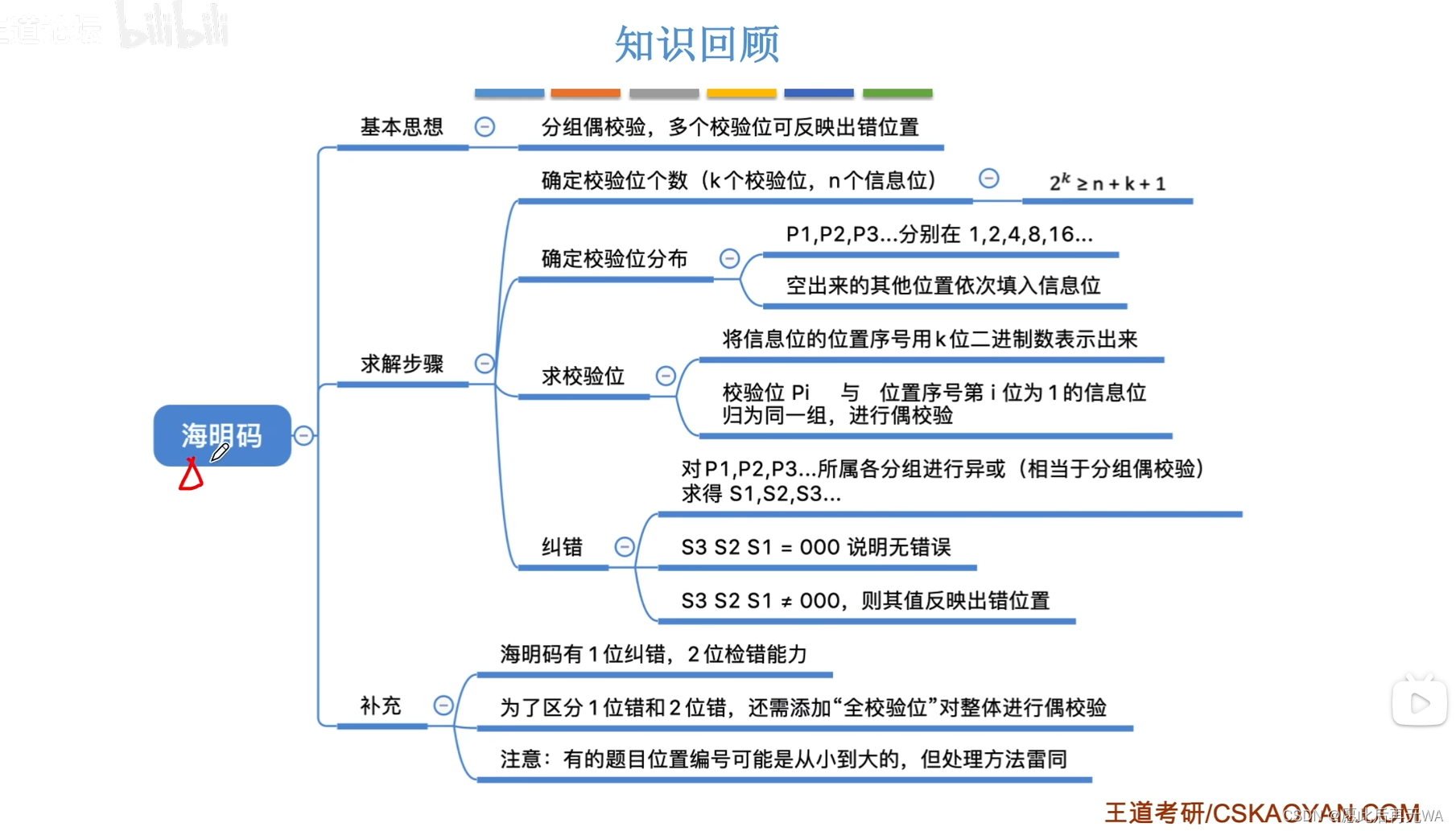
To solve the problem of undetectable errors , Heming found a Hamming code that can detect errors .
The general idea of Hamming code is : Divide the information bits into k Group , Then, each group was tested separately accidentally check , Mark the error position through multiple check bits and correct it skillfully .
Then how many parity bits are needed ? Suppose the information bit has n position , Check bit yes k position , Then the check code has n+k position , And a check code can indicate two states , that k A check code can indicate 2 ^ k States . A state can indicate an error ( Here we only talk about detecting and correcting one bit Hamming code ), Then there is n+k Errors may occur at positions , In addition, a status is required to indicate the correct situation . Combined with the above description , There is such a formula :2 ^ k >= n+k+1.(k Indicates the check digit ,n The sign bit ). Explain the solution steps of Hamming code with examples .
Suppose the information bit is 1010.
- According to the formula 2^k >= n+k+1 Determine the number of check bits , Because the information bit length is 4, namely n=4, To make the inequality hold ,k The minimum value of is 3, That is, the length of the check bit is 3.
- Markup elements distinguish States . Set the information bit to D4,D3,D2,D1, Check bit is P3,P2,P1, The corresponding Hamming code is H7H6H5H4H3H2H1.
- Determine the position of the check bit . The check digit can not be placed casually ,Pi Must be on 2^(i-1) position , After determining the check digit , Fill in the information code from high to low from left to right , Note that the order cannot be changed . such as 1010, It is also in this order when filling , If it is 1011, Also fill in 1011 This order , There may be check bits between each information bit , But the relative position of information bits will not change . Finally, fill in the value corresponding to the information bit .
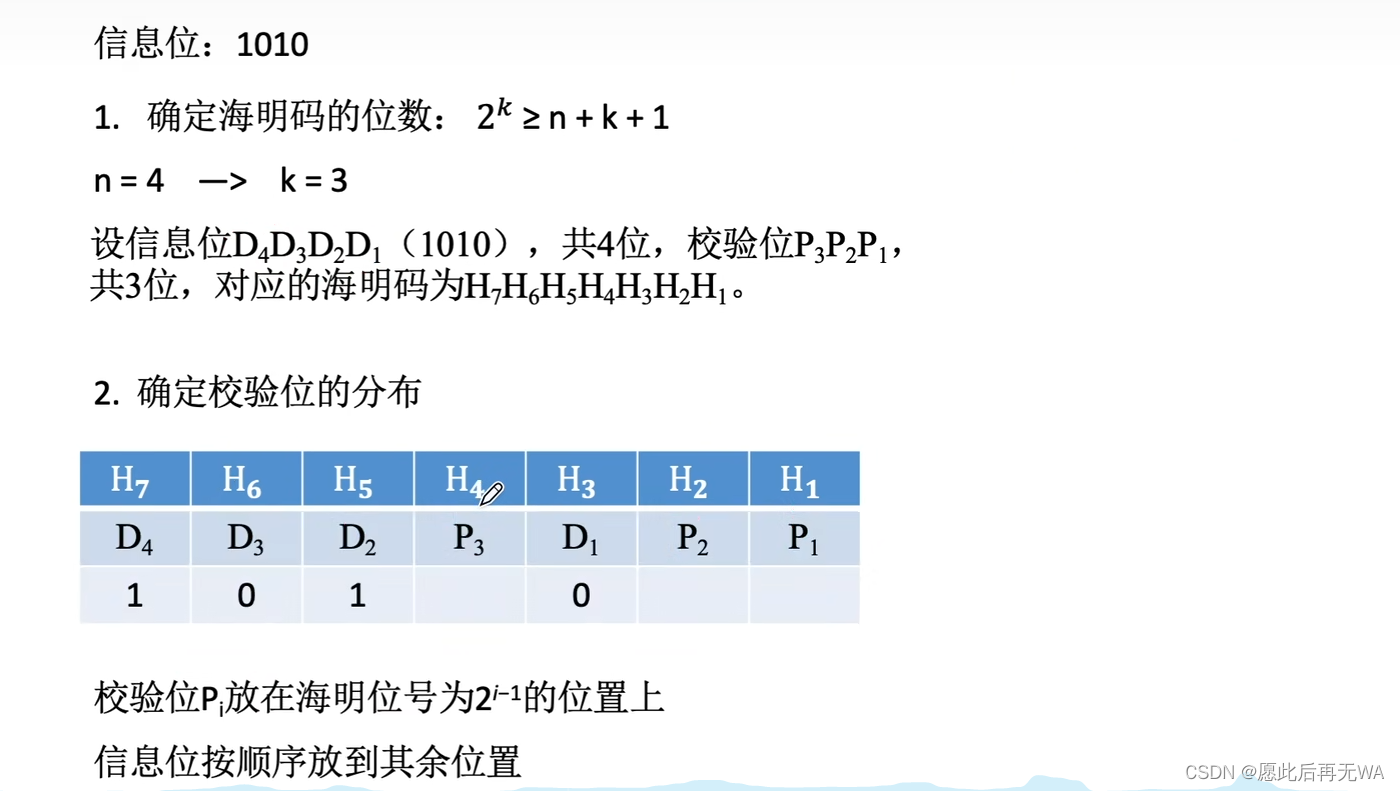
- Get the value of the check digit . Simply put, the subscript of the Hamming bit where the information bit is located needs to be composed of several 2 Of k Power constitute . Like D1 The location of Hamming code is H3,3=2+1, therefore 3 from 2 Of 1 Power plus 2 Of 0 Power composition , So you can use H1 and H2 Express , That is, the corresponding p1,p2, alike ,5=4+1, therefore H5 It can be used H4+H1 To express , namely P3+P1… And so on , You can know how to express each information bit , as well as You can know which information bits each check bit can represent . Let each check bit represent the information bit Exclusive or operation , You can get the value corresponding to the check digit .
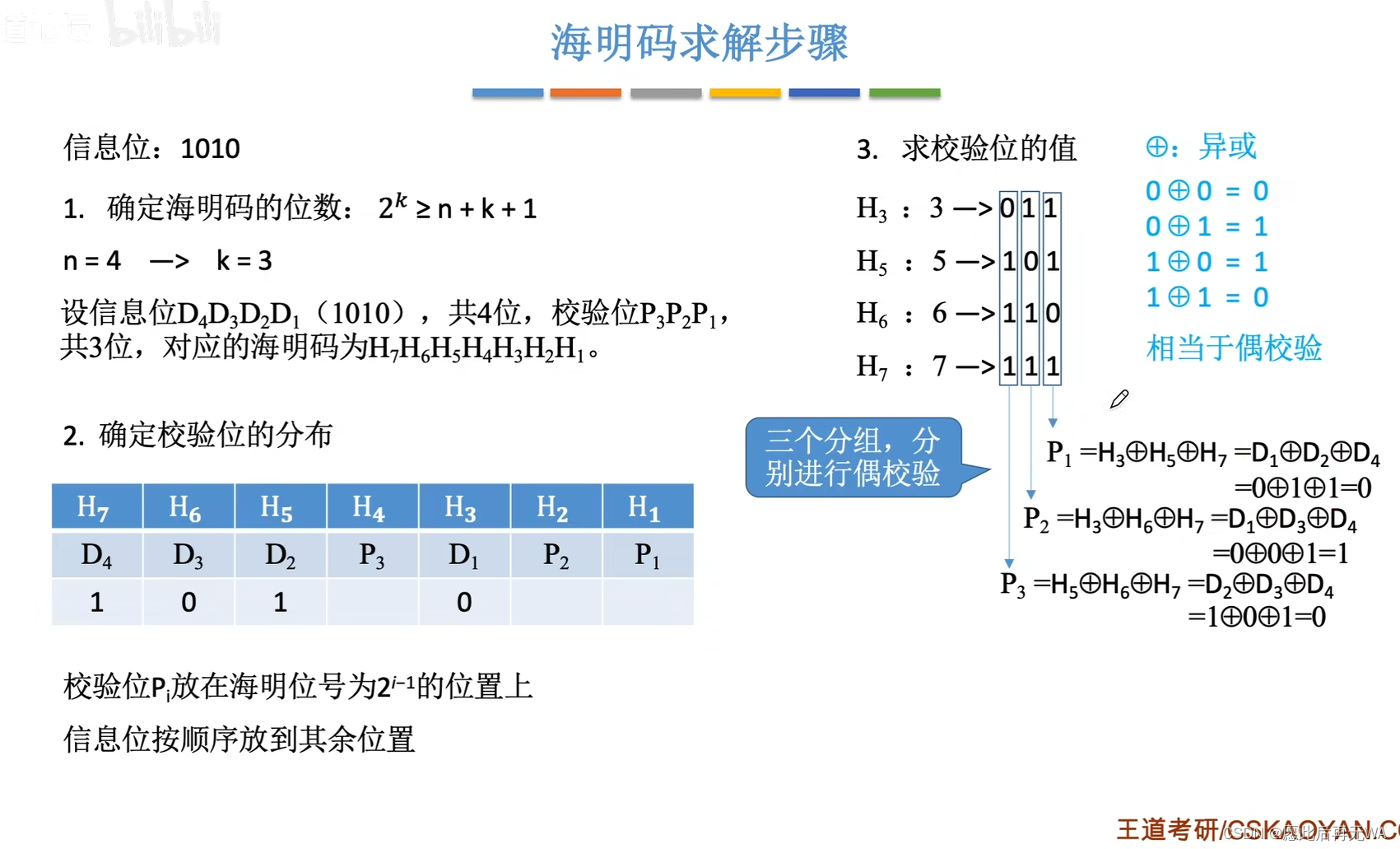
- error correction . Finally, in the obtained data , XOR the check bit with the information bit it can represent , If the result is 0, Then the data is correct . If there is an error , According to the relationship between check codes , You can always find the location of the error .
 Take a look back. , Remember how to calculate the value of the check digit ? The value of the parity bit is the result of XOR with the values of all the information bits it can represent .
Take a look back. , Remember how to calculate the value of the check digit ? The value of the parity bit is the result of XOR with the values of all the information bits it can represent .
We have known the relationship between information bits and check bits , Now suppose D4 This information bit is wrong , by 1 Jump to 0, See the fourth check equation on the picture , Combined with the distribution of check bits of the second point, we can get ,S1S2S3=111( Count back to front ), and 111 Converting from binary to decimal is 7, and H7 The corresponding is D4 The location of ? Don't you think it's incredible ? I just think , Have a good understanding of .
Hamming code has 1 Bit error correction capability and 2 Bit error detection capability . When there are two jumps in the check code at the same time, only errors in the check code can be found , And cannot correctly judge the specific location of the error . Take the error correction equation in the above figure as an example , hypothesis P1P2 Jump occurs , that S1S2S3 The result is 011( Count back to front ), If judged according to the normal process , It means H3 There is an error in this position , It's not .
In order to correctly identify the situation where two data jump , You can add more full check bits on the basis of the check code , Its value is the result of exclusive or of all values in the previous check code , Finally, perform a parity check as a whole , Combined with the previous error correction equation , Then we can figure out whether it is one mistake or two mistakes , Understand it in combination with the diagram .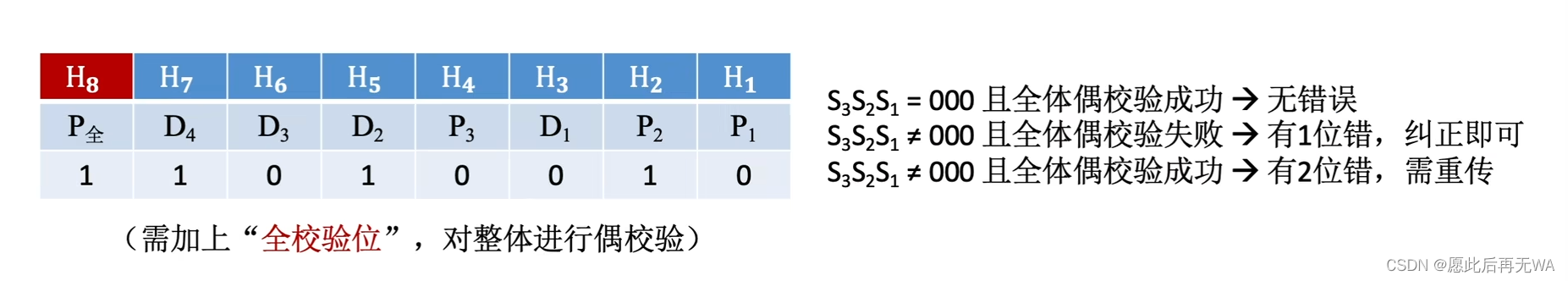
Cyclic redundancy check code
It is still recommended to watch the video first and then the summary .
To put it simply , It takes the transmitted data as the dividend , And the sender and receiver of the data agree on a polynomial , Determine the divisor according to the coefficients of the polynomial , And according to the highest term of the polynomial, it is necessary to add several after the divisor 0, Finally, divide the divisor by the divisor and the remainder with the original 0 Replace , Then the newly generated divisor and divisor must have a remainder of 0, If during data transmission , Jump occurs , As a result, the remainder is not 0, Then the data is incorrect , Need to retransmit .
Let's understand with examples .
Let the generating polynomial be G(x)=x3+x2+1, The information code is 101001, Find the corresponding CRC code .
- Determine the divisor . Polynomials can be written as 1 · x3 + 1 · x2 + 0 · x1 + 1 · x0, Then take out their coefficients , So that is 1101, And this is the divisor we need .
- determine 0 The number of . We need to know how many words should be added after the information code 0. Because the highest term of a polynomial is 3, Therefore, it is necessary to add 3 individual 0, Fill up 0 The information code after is the dividend we need .
- Mod . Let's use divisor and divisor model 2 division 、 model 2 Subtraction Divide and subtract , Get the remainder . Be careful , The remainder may not be divisible , We just need to divide 3 individual 0 You can do it without continuing to fill in later 0.
- Get the remainder with the same length as the highest term of the polynomial ( If the remainder length is small , Then fill in the front 0), In addition, it replaces the beginning 3 individual 0, Get a new information code , This is the code Cyclic redundancy code , The sender can send this code to the receiver , And check according to the polynomial agreed in advance , If the division is 0, Then the data is correct , Otherwise, the data is abnormal , Need to retransmit .
About the mould 2 Division and module 2 reduce : It is suggested that you watch videos to understand more easily . Click here .(5 branch 50 Second starts )
Cyclic redundancy code is very important , You must master .
Because of time , I wanted to take notes well , Now it seems impossible to achieve , We should seize the time to prepare the network , Let's put it here first .
Original code multiplication
Complement multiplication
Original code division
Complement division
Floating point operation
边栏推荐
- 如何优雅的获取每个分组的前几条数据
- Raki's notes on reading paper: code and named entity recognition in stackoverflow
- A survey of automatic speech recognition (ASR) research
- Introduction to RT thread kernel (5) -- memory management
- Interface joint commissioning test script optimization V5.0 (end)
- MySQL in-depth learning - index creation and deletion, index design principles, index failure scenarios, query optimization, index push down ICP
- Hexadecimal to decimal
- 电源管理总线 (PMBus)
- 这是一个不确定的时代
- Cookie learning diary 1
猜你喜欢
![[popular science] basic knowledge of thermal design: heat dissipation analysis of 5g optical devices](/img/45/380e739f5eed33626c363756f814d3.png)
[popular science] basic knowledge of thermal design: heat dissipation analysis of 5g optical devices

American 5g open ran suffered another major setback, and its attempt to counter China's 5g technology has failed

TPG x AIDU | AI leading talent recruitment plan in progress!
![[AI bulletin 20220211] the hard core up owner has built a lidar and detailed AI accelerator](/img/cc/06580ce7b553182968d273841a78b4.jpg)
[AI bulletin 20220211] the hard core up owner has built a lidar and detailed AI accelerator

How can CIOs use business analysis to build business value?
Setting up redis cluster cluster under Windows
Moco is not suitable for target detection? MsrA proposes object level comparative learning target detection pre training method SOCO! Performance SOTA! (NeurIPS 2021)...
电源管理总线 (PMBus)

直播預告 | 容器服務 ACK 彈性預測最佳實踐
Network security - record web vulnerability fixes
随机推荐
Machine learning decision tree
Neural network and deep learning Chapter 1: introduction reading questions
Ffmepg usage guide
Hexadecimal to decimal
[illusory engine UE] method to realize close-range rotation of operating objects under fuzzy background and pit recording
Interview related high-frequency algorithm test site 3
Basic analysis of IIC SPI protocol
CSDN body auto generate directory
Fonction (sujette aux erreurs)
Function (error prone)
Wenet: E2E speech recognition tool for industrial implementation
Decryption function calculates "task state and lifecycle management" of asynchronous task capability
Key review route of probability theory and mathematical statistics examination
函数(基本:参数,返回值)
Solution of circular dependency
Is there a sudden failure on the line? How to make emergency diagnosis, troubleshooting and recovery
The 22nd Spring Festival Gala, an immersive stage for the yuan universe to shine into reality
You Li takes you to talk about C language 7 (define constants and macros)
About the prompt loading after appscan is opened: guilogic, it keeps loading and gets stuck. My personal solution. (it may be the first solution available in the whole network at present)
Moco is not suitable for target detection? MsrA proposes object level comparative learning target detection pre training method SOCO! Performance SOTA! (NeurIPS 2021)...