当前位置:网站首页>机器学习笔记-Week02-卷积神经网络
机器学习笔记-Week02-卷积神经网络
2022-07-06 09:14:00 【爱吃章鱼的怪兽】
卷积神经网络
文章目录
深度学习三部曲
- Step1: 搭建神经网络结构
- Step2: 找到一个合适的损失函数
- Step3: 找到一个合适的优化函数,更新参数
损失函数
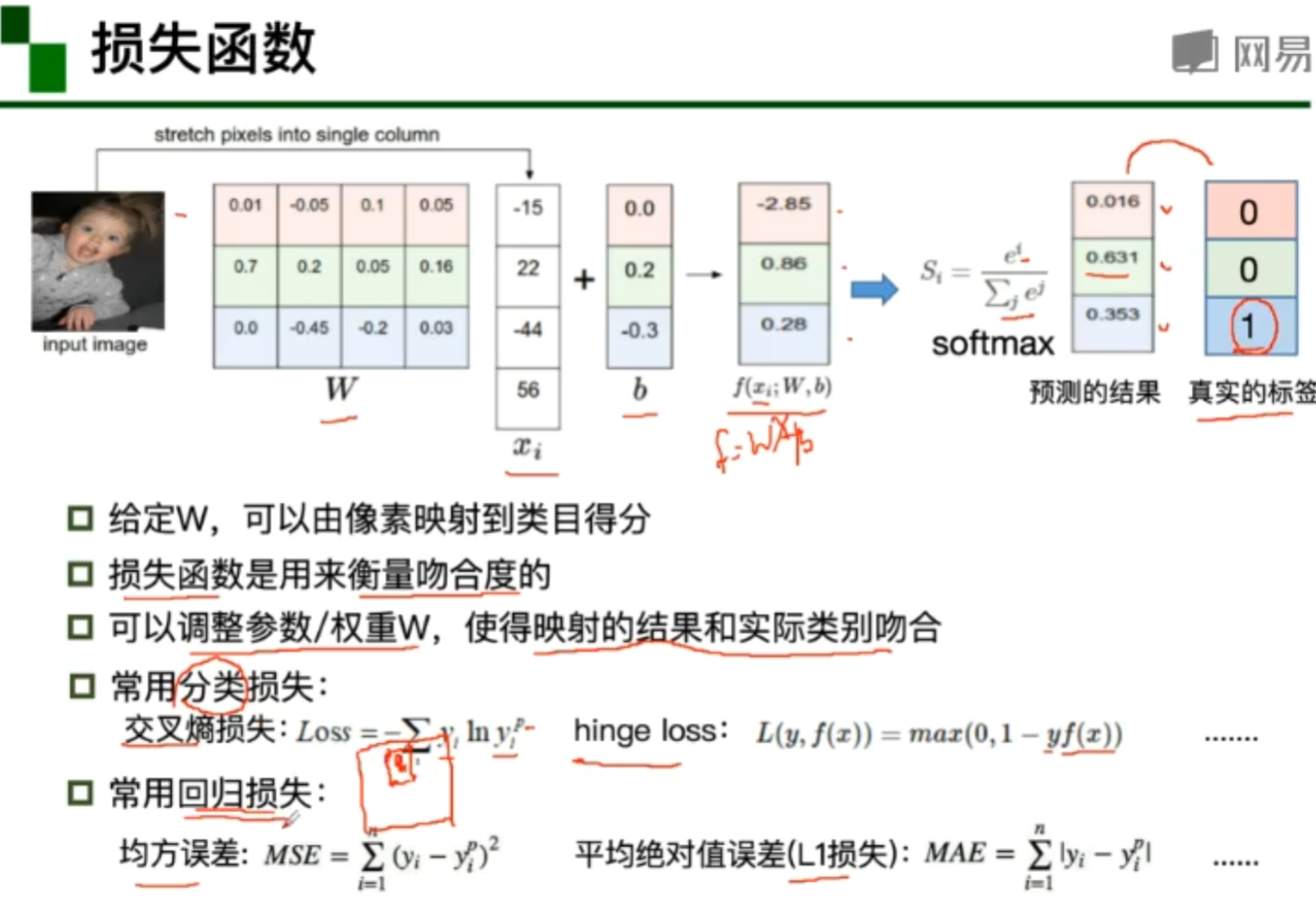
通过神经网络模型的预测。通过损失函数计算模型训练结果与真实结果的吻合度。
全连接网络处理图像
由于每个神经元与图像的像素点都有连接,导致参数过多的过拟合现象,使得过于强调训练集的某些特征,导致在功能上具有局限性
卷积神经网络
局部关联
参数共享
每个神经元只与部分图像连接,计算部分区域的卷积核。
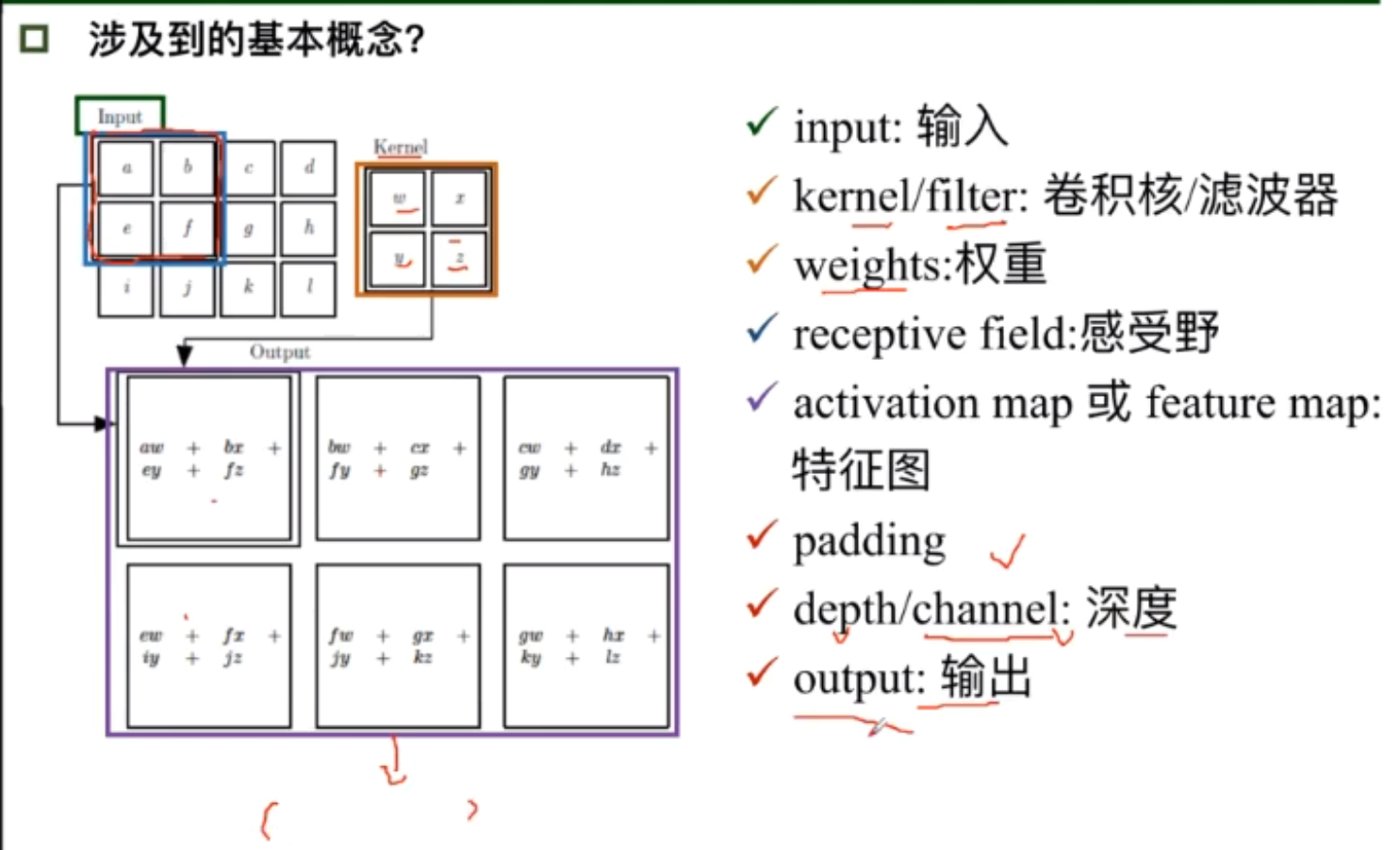
卷积

池化
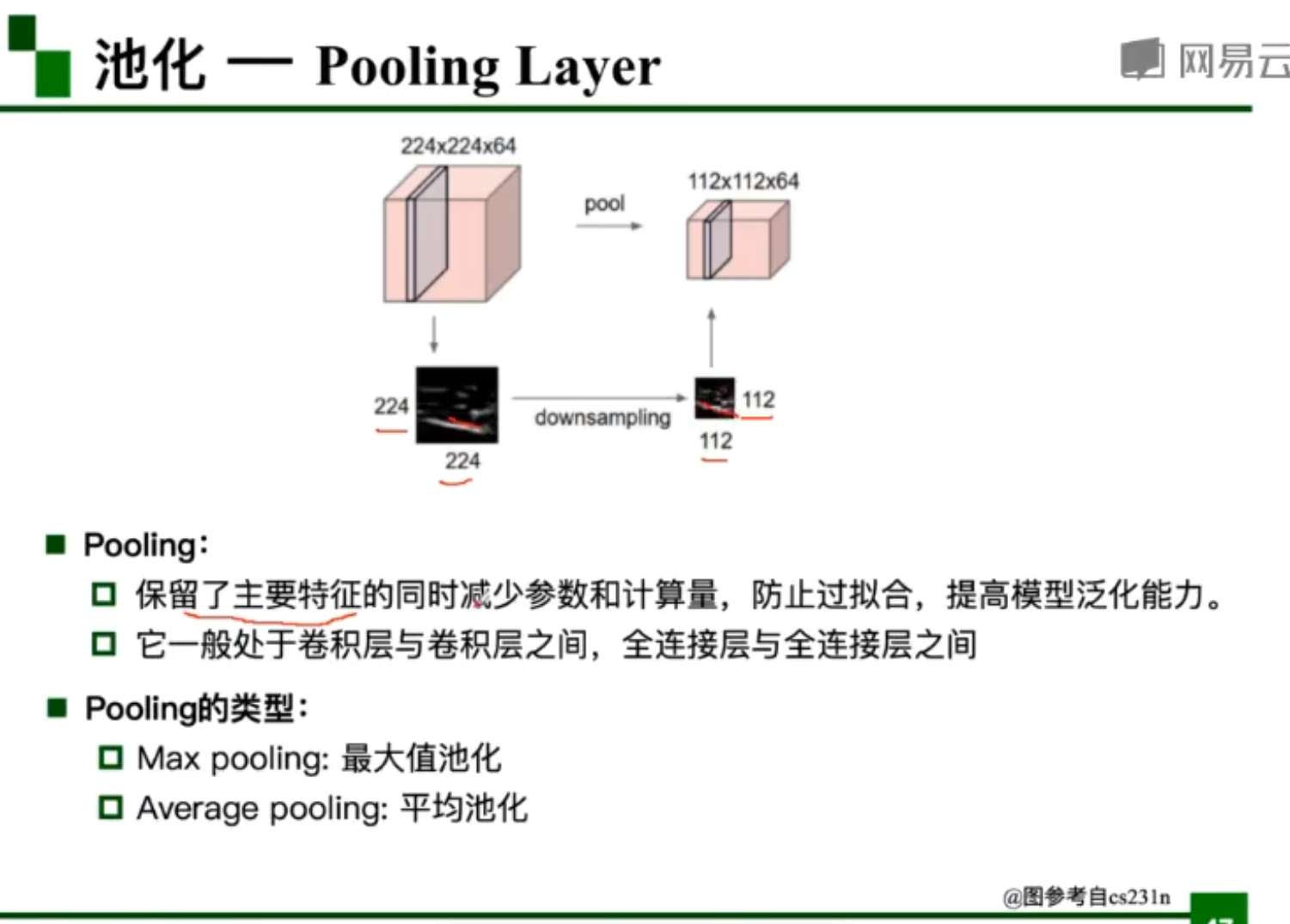
池化操作减少了参数量和计算量,池化层是一种数学操作,无参数
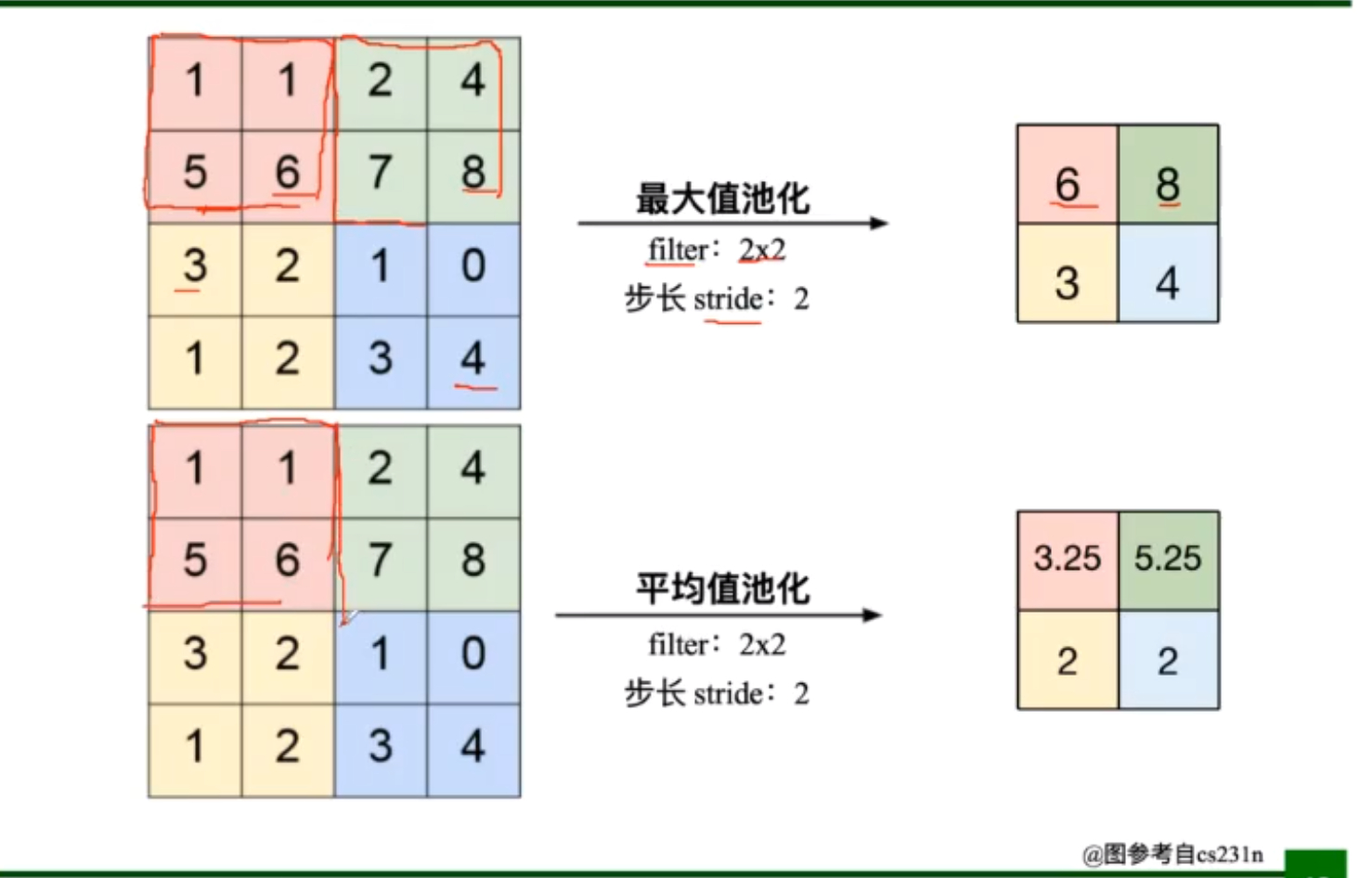
在分类识别任务中,更倾向于使用最大值池化
全连接
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-zIct7Mgt-1646810190645)(C:\Users\CrazyBin\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220307194013491.png)]
- 一个典型的卷积网络是由卷积层、池化层、全连接层交叉堆叠而成
- 卷积是对两个实变函数的一种数学操作
- 卷积具有局部关联,参数共享的特点
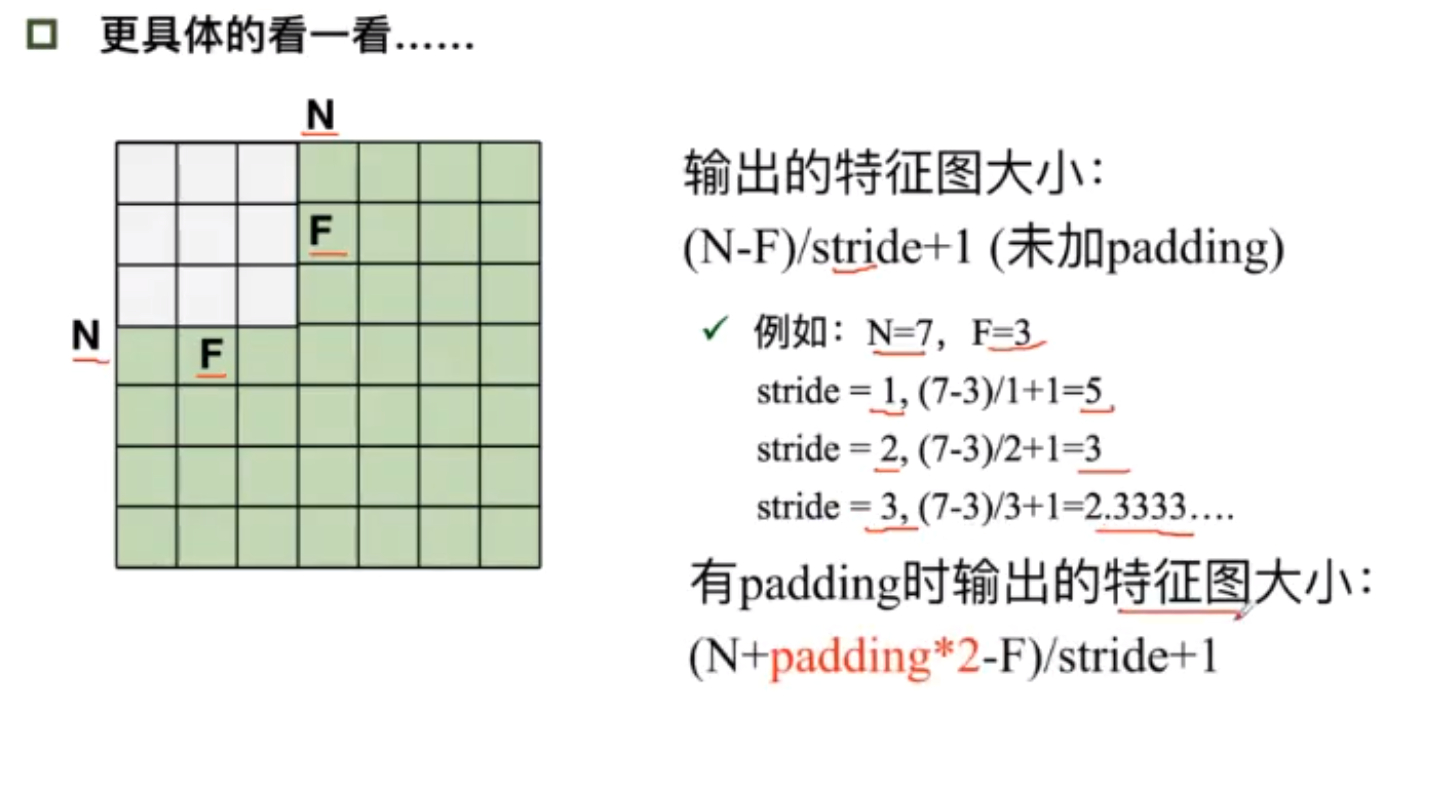
- 未加padding时输出的特征图大小: ( N − F ) / s t r i d e + 1 (N-F)/stride+1 (N−F)/stride+1 输入减去卷积除以步长加1
- 有padding时: ( N + p a d d i n g ∗ 2 − F ) / s t r i d e + 1 (N+padding*2-F)/stride+1 (N+padding∗2−F)/stride+1
- Pooling的类型:Max pooking:最大值池化,Average pooling:平均池化
- 全连接:通常全连接层在卷积神经网络尾部
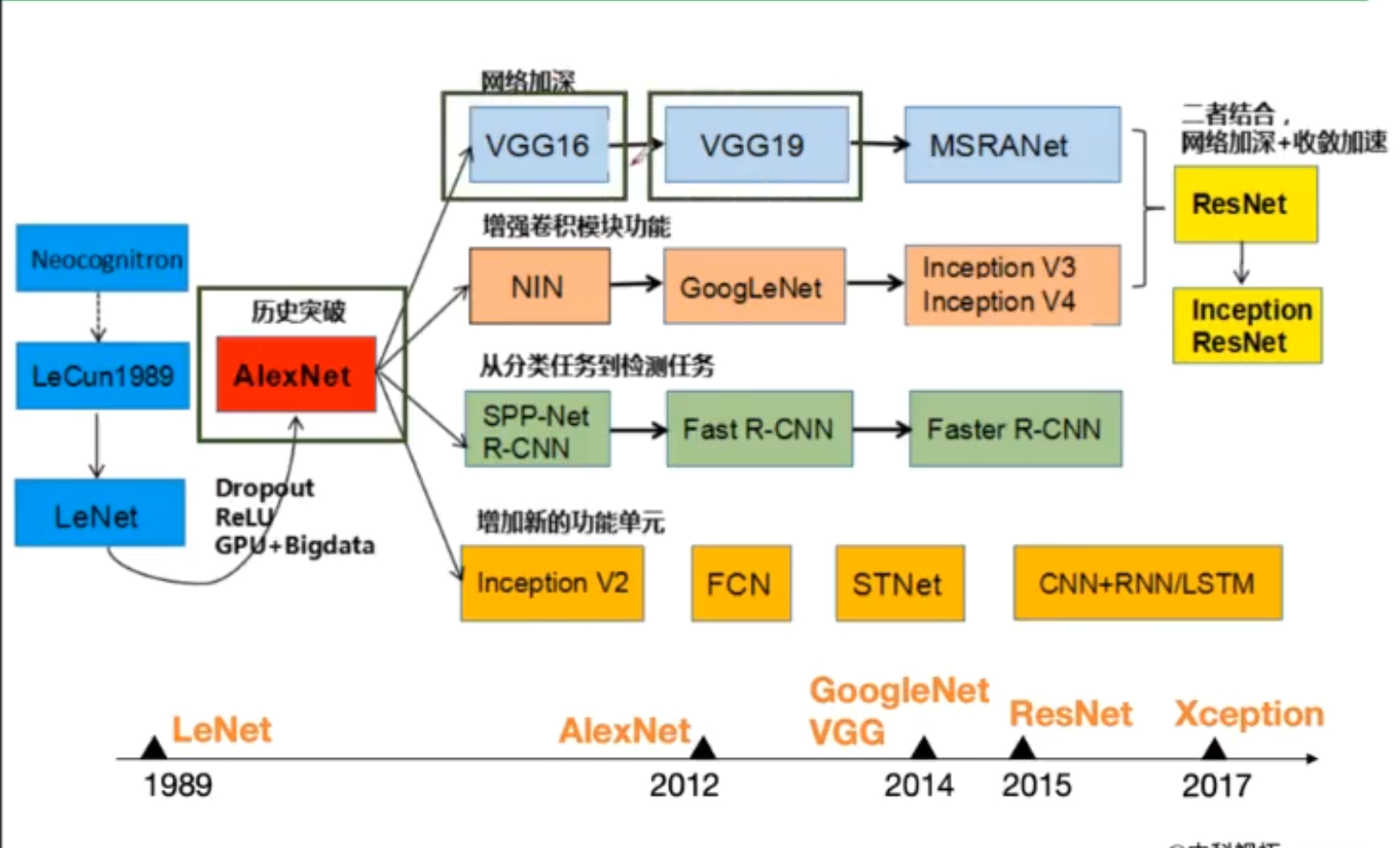
卷积神经网络典型结构
AlexNet
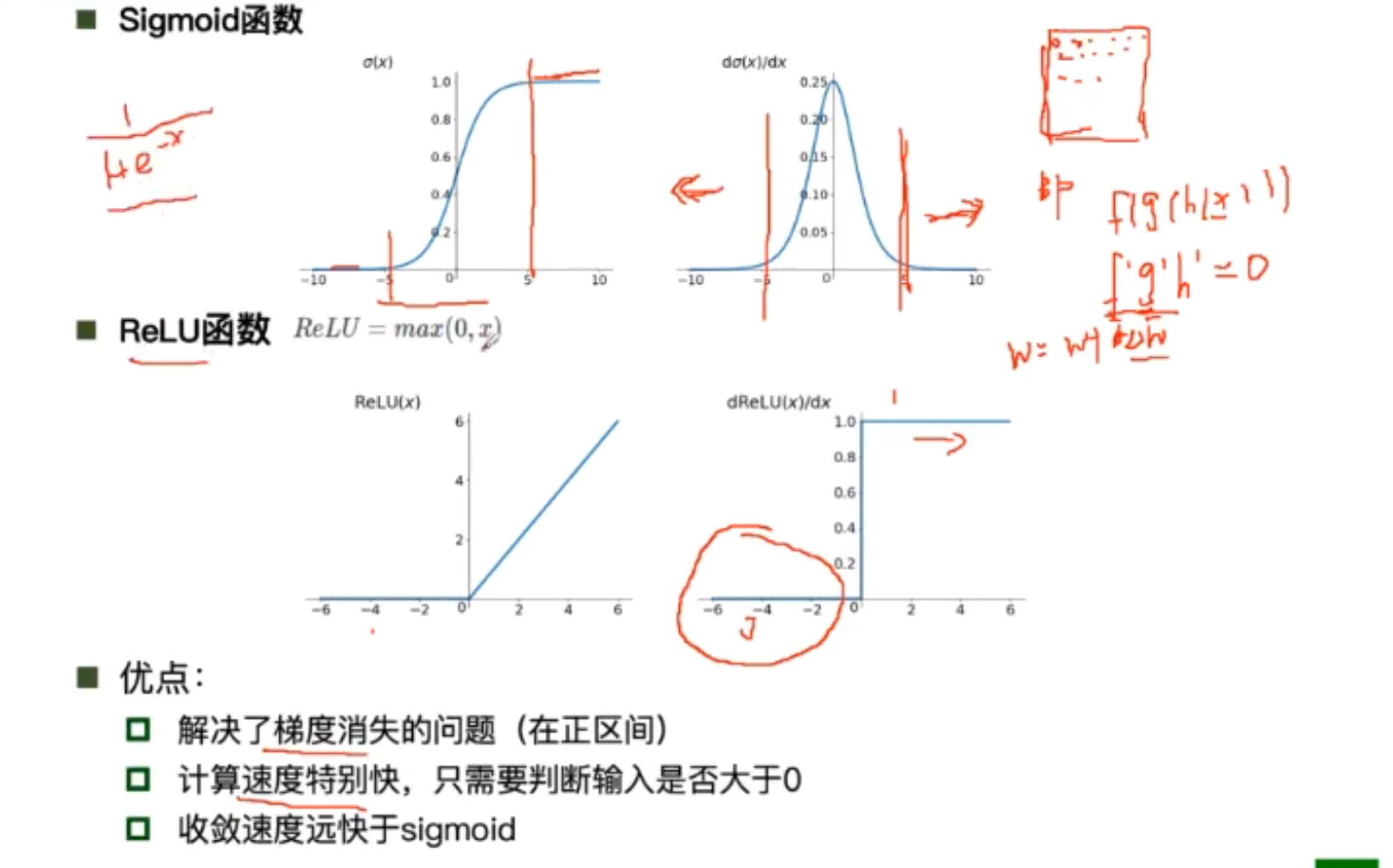 AlexNet使用Relu函数作为激活函数,使得BP算法反射调参数时的梯度消失问题得到了解决,Relu函数由于形式简单,梯度较大,使得函数的收敛速度快,使得模型训练反馈变快
AlexNet使用Relu函数作为激活函数,使得BP算法反射调参数时的梯度消失问题得到了解决,Relu函数由于形式简单,梯度较大,使得函数的收敛速度快,使得模型训练反馈变快
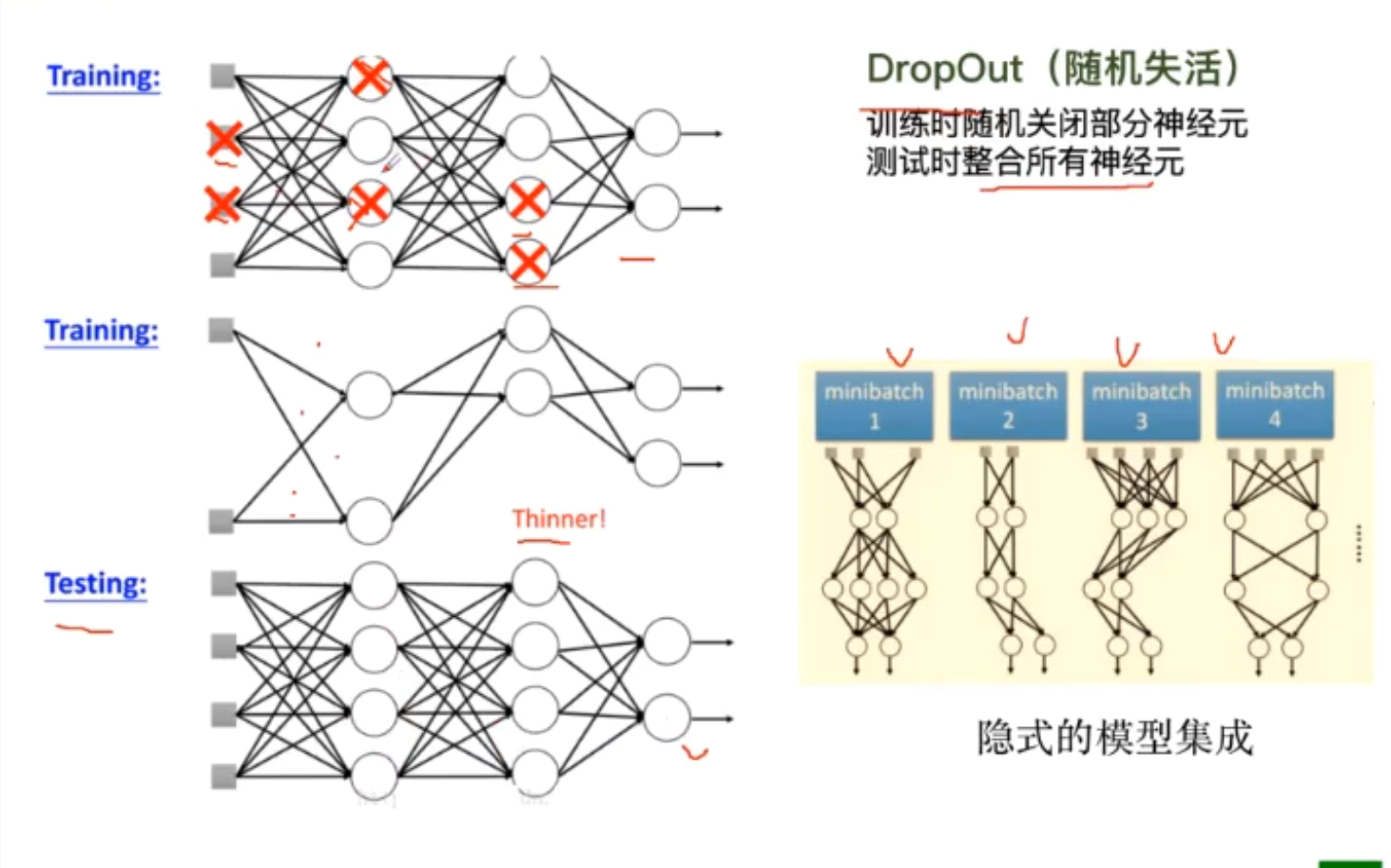
利用DropOut避免过拟合

增加训练集的数据
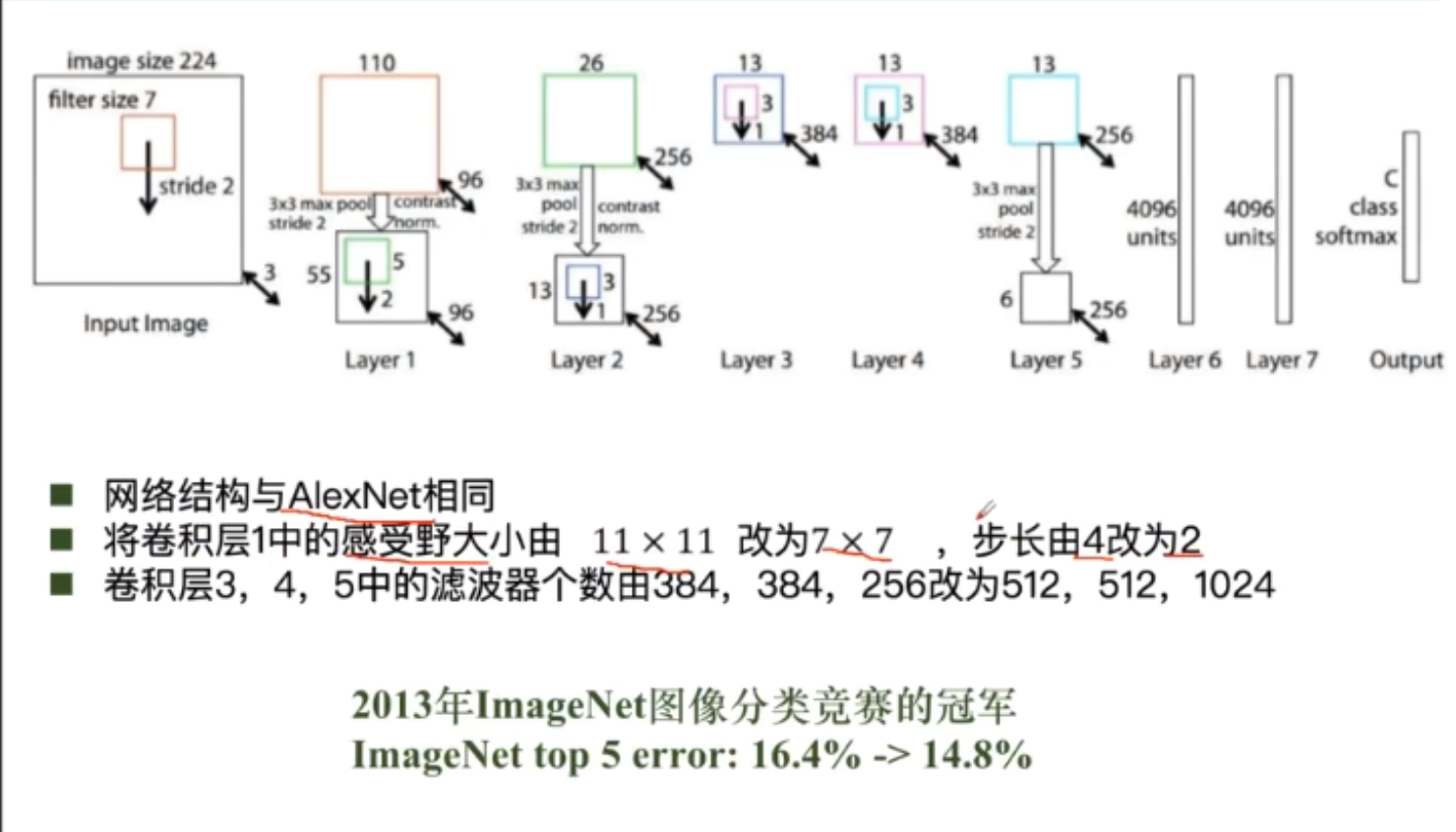
ZFNet
VGG

VGG是一个更深的网络,参数量很大
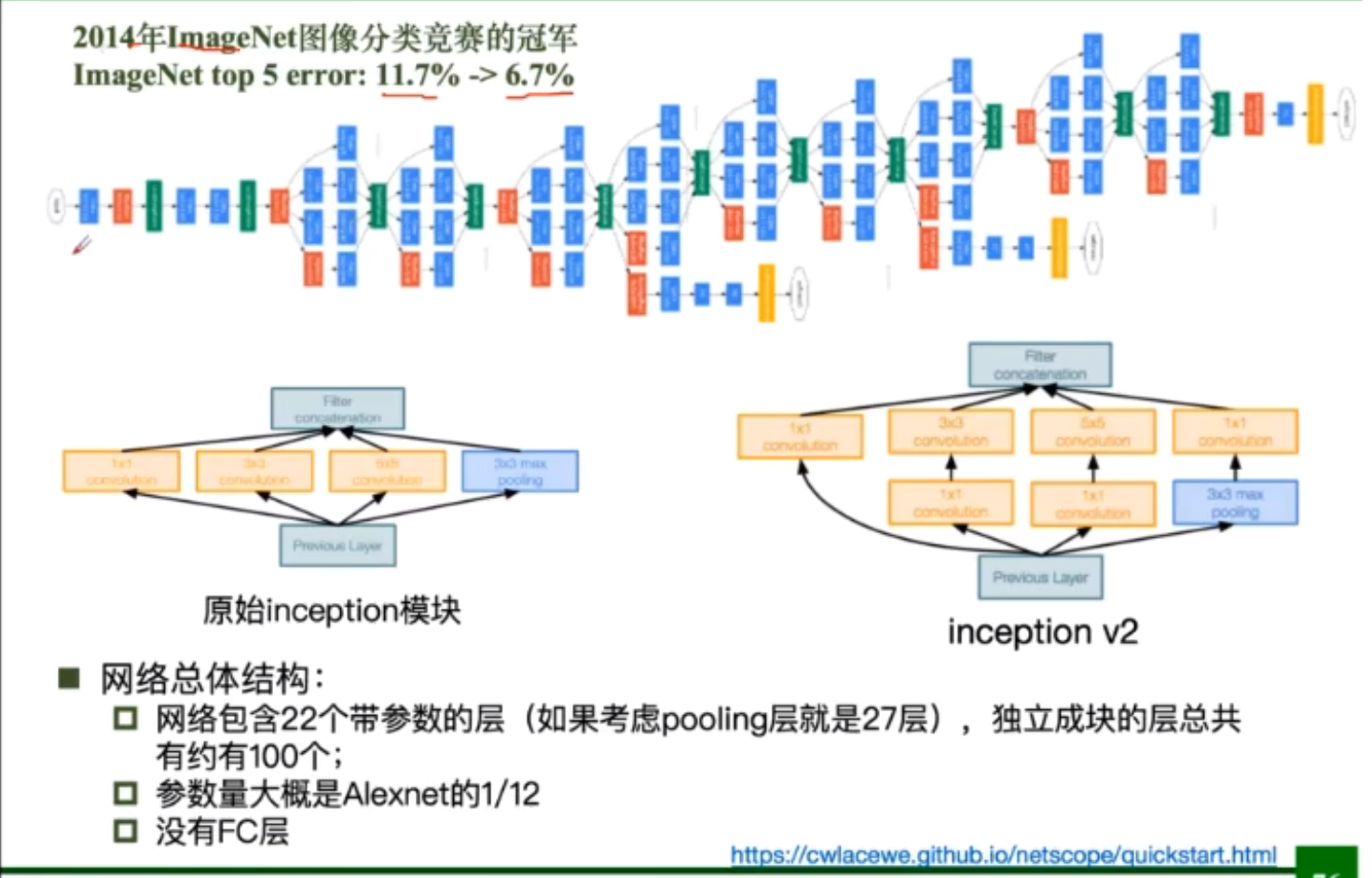
GoogleNet
ResNet
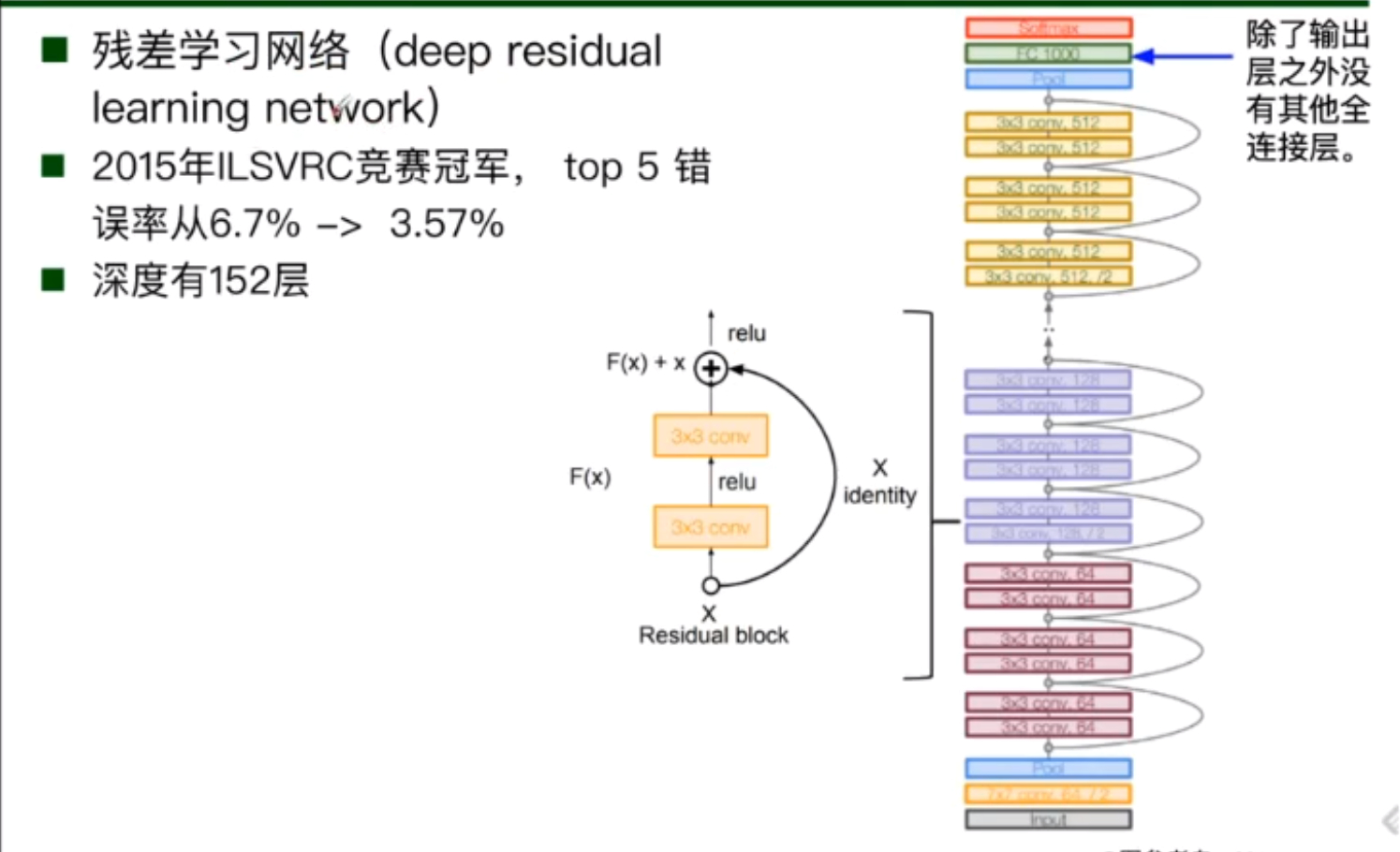
ResNet的重要思想是参差学习,由于网络在训练时随着层数的加深,容易出现退化现象。
使得我们很难模拟出希望的函数,但利用残差学习,将我们希望模拟出的函数转化为易于学习的形式,并在结果基础上加上我们的残差。
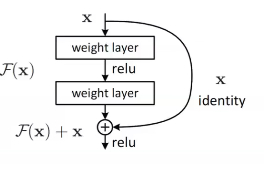
可以观察到ResNet是一个非常深的网络模型
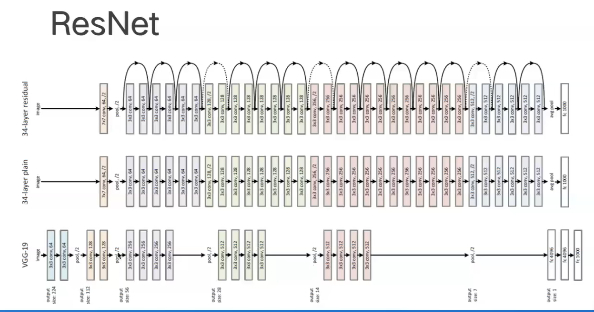
由于深度较深,容易出现退化现象,使得网络的训练效果差,利用ResNet的残差思想,在每两层的卷积层之间加上我们的恒等映射跨接层就能使得我们的模型效果得到很大提升。
对于不同深度的ResNet在结构上有一些差异
在50层以上的ResNet网络中有着BottleNeck瓶颈结构
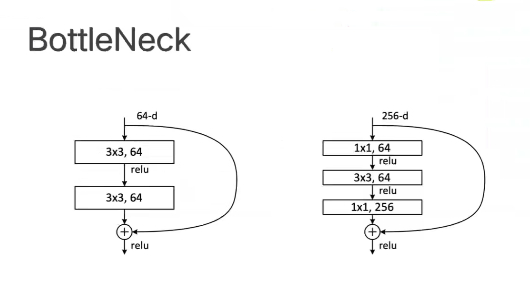
在较深的网络中进行了先降维再升维的操作,这是因为在网络模型较深时,所需要的参数量非常大。利用BottleNeck结构可以减少我们需要处理的参数量。
手动实现一个简单的ResNet网络
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.hub import load_state_dict_from url
model_urls = {
"resnet18": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-f37072fd.pth",
"resnet34": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-b627a593.pth",
"resnet50": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-0676ba61.pth",
"resnet101": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-63fe2227.pth",
"resnet152": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-394f9c45.pth",
"resnext50_32x4d": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth",
"resnext101_32x8d": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth",
"wide_resnet50_2": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet50_2-95faca4d.pth",
"wide_resnet101_2": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet101_2-32ee1156.pth",
}
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, padding=1):
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=padding, bias=False)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, norm_layer=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d
self.conv1 =conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 =norm_layer(planes)
self.relu = nn.Relu(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.downsample =downsample
self.strid =stride
def forward(self,x)
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class BottleNeck(nn.Module)
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, norm_layer=None):
super(BottleNeck, self).__init__()
if norm_;ayer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, planes)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, pkanes, stride)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(planes, planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride =stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None;
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, layer, num_class=1000, norm_layer=None):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
slef.inplanes =64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size = 7, stride=2,padding=3,bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplanes=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layer[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layer[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layer[3], stride=2)
self._avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512*block.expansion, num_class)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out'. nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def _make_layer(self,block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
norm_layer = self.norm_layer
downsample = None
if stride !=1 or self.inplanes != planes*block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes*block.expansion, stride),
norm_layer(planes*block,expansion)
)
layers=[]
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, norm_layer))
self.inplanes = planes * slef.expansion
for _ in range(1,blocks):
layers.append(block(slef.inplanes, planes, norm_layer=norm_layer))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = slef.layer2(x)
x = slef.layer3(x)
x = slef.layer4(x)
x = slef.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flattern(x,1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def _resnet(arch, block, layers, pretrained, progress, **kwargs):
model = ResNet(block, layers, **kwargs)
if pretrianed:
state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(model_urls[arch], progress=progress)
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
return model
def resnet152(pretrained=Falsem progress=True, **kwargs):
return _resnet('resnet152', BottleNeck. [3, 8, 36, 3],pretrained, progress, **kwargs)
model = resnet152(pretrianed =True)
model.eval()
MNIST数据集分类
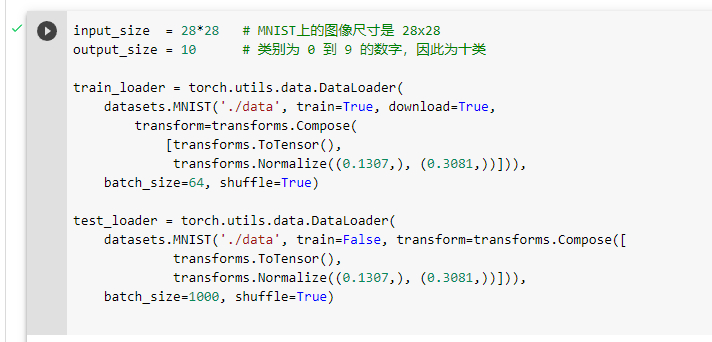
加载MNIST数据集
利用matplotlib加载数据可视化
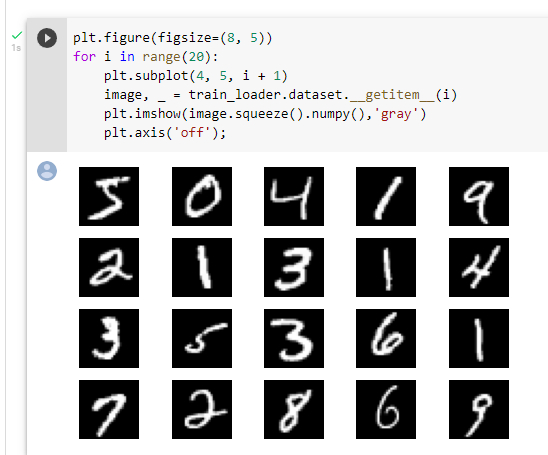
创建全连接网络和卷积神经网络

可以看到,当我们创建一个神经网络时,需要定义每个网络的每一个layer,而forward函数则是调用我们神经网络的函数,在foward函数总,我们可以定义池化操作与激活函数
定义训练测试函数
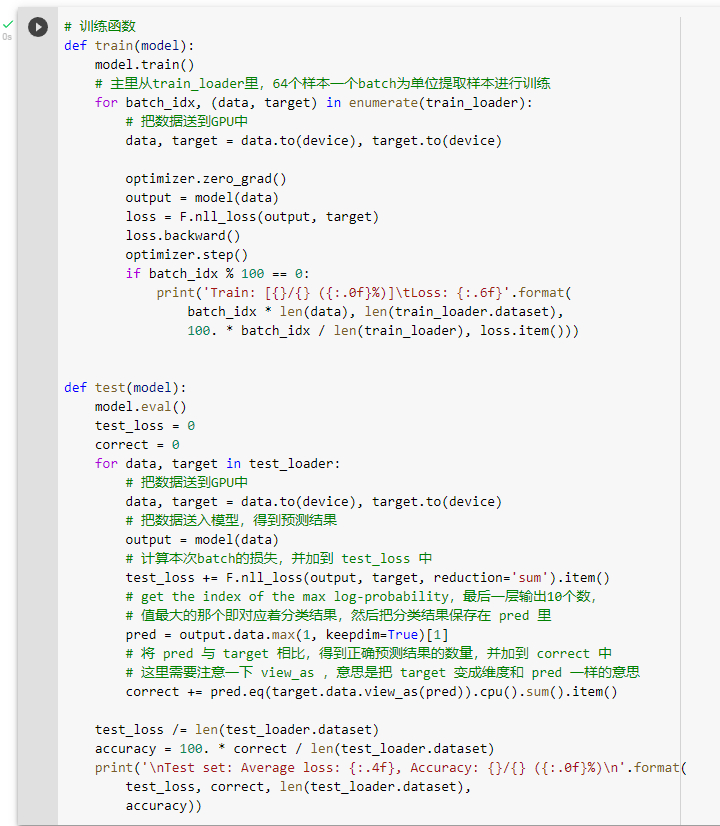
利用全连接网络训练
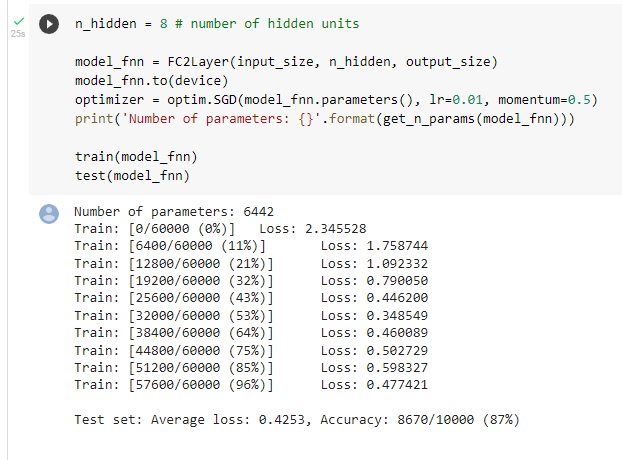
观察到训练之后经过测试,模型的准确率在87%
利用卷积神经网络训练
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-WtoTeV9B-1646810190663)(C:\Users\CrazyBin\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220309130953394.png)]
可以观察到在参数数量上,两个模型都是一样的,但是训练的结果卷积神经网络准确率更高,这说明通过卷积和池化操作使得提取的特征更为准确
打乱训练图像的像素

定义打乱数据之后的训练和测试函数
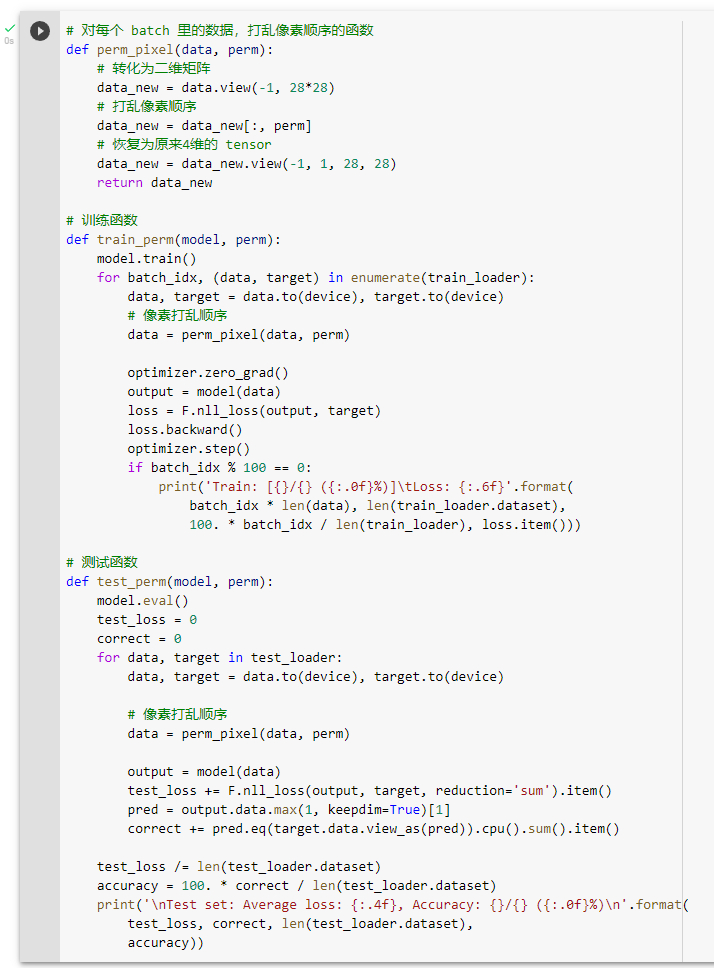
观察打乱后训练结果
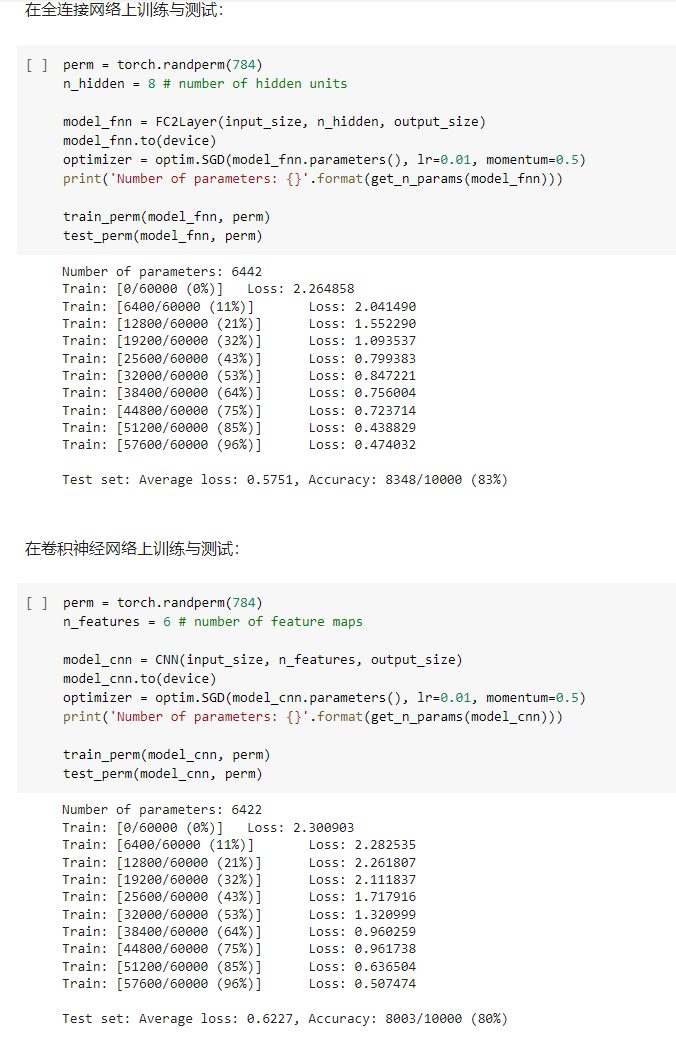
观察打乱数据后的两个模型,发现性能接近。卷积神经网络的性能较之前有着明显的下贱。这是因为卷积和池化操作都是利用局部图片的像素关系得到的结果,能够很好的提取局部特征而避免过拟合现象。但是打乱顺序后,使得局部的像素关系特征变弱,导致性能的下降。
CIFAR10数据集分类
CIFAR10数据集包含十个类别,有着RGB3层颜色通道

加载训练集
查看训练集的部分图像与标签
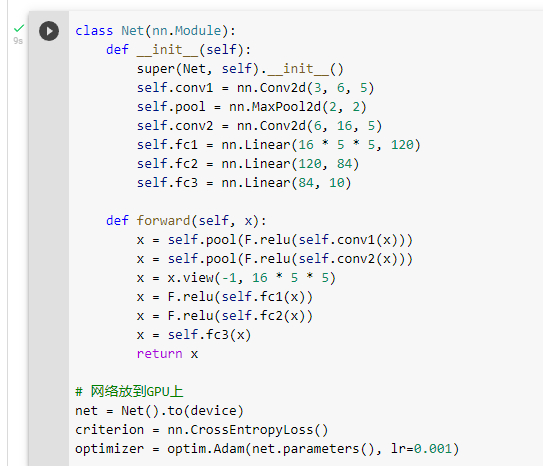
构建网络与forward函数
训练网络
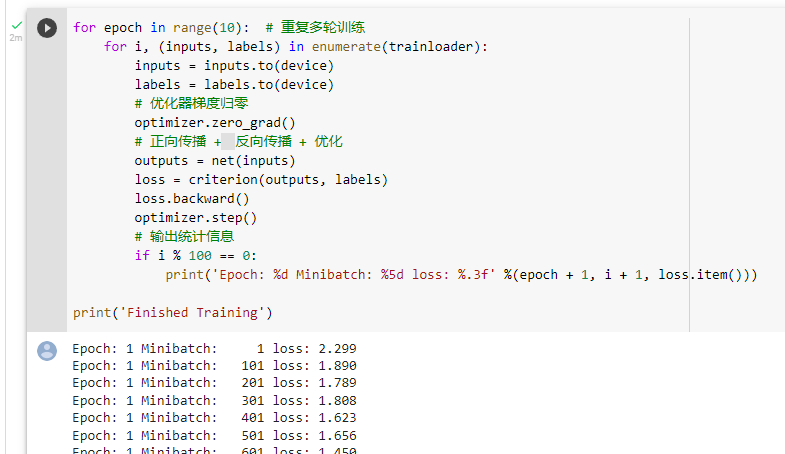
测试模型
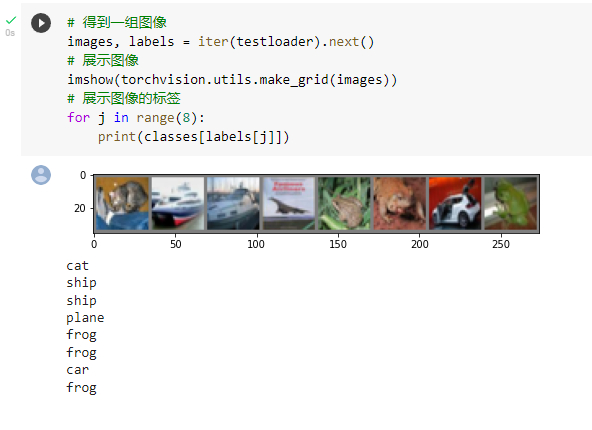
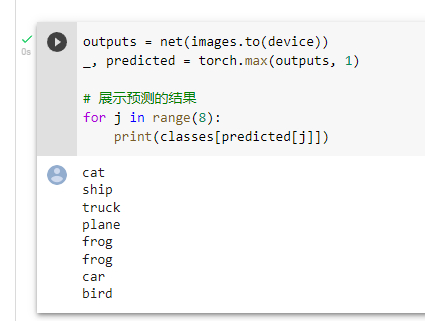
发现只对了5个
测试整个数据集
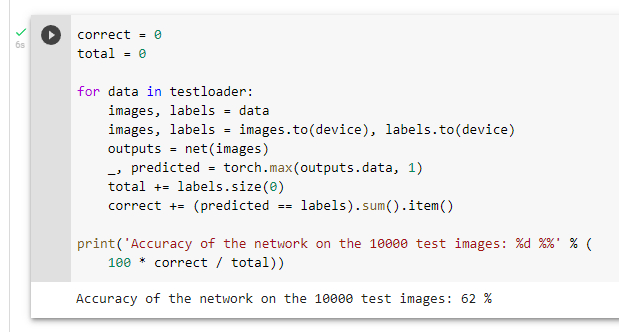
准确率为62%,所用的模型为一个普通的卷积神经网络
参考资料:
边栏推荐
- CSDN问答模块标题推荐任务(二) —— 效果优化
- AcWing 1298.曹冲养猪 题解
- Windows下安装MongDB教程、Redis教程
- Copie maître - esclave MySQL, séparation lecture - écriture
- MySQL主从复制、读写分离
- Introduction and use of automatic machine learning framework (flaml, H2O)
- A brief introduction to the microservice technology stack, the introduction and use of Eureka and ribbon
- QT creator design user interface
- JDBC principle
- 打开浏览器的同时会在主页外同时打开芒果TV,抖音等网站
猜你喜欢
解决安装Failed building wheel for pillow

csdn-Markdown编辑器
软件测试与质量学习笔记3--白盒测试
学习问题1:127.0.0.1拒绝了我们的访问
Copie maître - esclave MySQL, séparation lecture - écriture
Introduction and use of automatic machine learning framework (flaml, H2O)
Error connecting to MySQL database: 2059 - authentication plugin 'caching_ sha2_ The solution of 'password'
windows下同时安装mysql5.5和mysql8.0
CSDN question and answer tag skill tree (I) -- Construction of basic framework
![[free setup] asp Net online course selection system design and Implementation (source code +lunwen)](/img/ac/b518796a92d00615cd374c0c835f38.jpg)
[free setup] asp Net online course selection system design and Implementation (source code +lunwen)
随机推荐
Error connecting to MySQL database: 2059 - authentication plugin 'caching_ sha2_ The solution of 'password'
Tcp/ip protocol (UDP)
SSM整合笔记通俗易懂版
Test objects involved in safety test
Kubernetes - problems and Solutions
Ansible实战系列二 _ Playbook入门
自动机器学习框架介绍与使用(flaml、h2o)
JDBC principle
數據庫高級學習筆記--SQL語句
windows下同时安装mysql5.5和mysql8.0
SSM integrated notes easy to understand version
01 project demand analysis (ordering system)
Armv8-a programming guide MMU (2)
Development of C language standard
Learning question 1:127.0.0.1 refused our visit
npm一个错误 npm ERR code ENOENT npm ERR syscall open
Postman environment variable settings
Mysql 其他主机无法连接本地数据库
[BMZCTF-pwn] 12-csaw-ctf-2016-quals hungman
Invalid default value for 'create appears when importing SQL_ Time 'error reporting solution