当前位置:网站首页>[beauty of algebra] singular value decomposition (SVD) and its application to linear least squares solution ax=b
[beauty of algebra] singular value decomposition (SVD) and its application to linear least squares solution ax=b
2022-07-05 08:55:00 【Li Yingsong~】
Singular value decomposition (Singular Value Decomposition,SVD) Is an important matrix decomposition in linear algebra , Is the generalization of eigen decomposition on any matrix , In stereo vision 、 3D reconstruction is widely used . Because it can be used to solve the least square solution of linear equations , So in solving the essential matrix 、 Homography matrix 、 Point cloud rigid transformation matrix , Can use SVD. This article will give you a brief introduction to singular value decomposition , And through formula derivation to explain its application in linear least square solution A x = b Ax=b Ax=b Application on .
List of articles
Singular value decomposition (SVD Decomposition) Definition
For any matrix A ∈ R m × n A\in R^{m\times n} A∈Rm×n, There are orthogonal matrices U ∈ R m × m U\in R^{m\times m} U∈Rm×m, V ∈ R n × n V\in R^{n\times n} V∈Rn×n, And diagonal matrix Σ ∈ R m × n \Sigma \in R^{m\times n} Σ∈Rm×n:
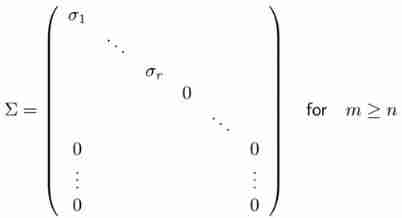
among , Diagonal elements meet :
σ 1 ≥ ⋯ ≥ σ r ≥ σ r + 1 = ⋯ = σ min ( m , n ) = 0 \sigma_1\geq\cdots\geq\sigma_r\geq\sigma_{r+1}=\cdots=\sigma_{\min(m,n)}=0 σ1≥⋯≥σr≥σr+1=⋯=σmin(m,n)=0
bring , A = U Σ V T A=U\Sigma V^T A=UΣVT.
This decomposition is called matrix A A A Singular value decomposition of (Singular Value Decomposition), Is a very important matrix decomposition , Diagonal matrix Σ \Sigma Σ Diagonal elements of σ i \sigma_i σi Called matrix A A A The singular value of . matrix U U U The column vector of becomes a left singular vector , matrix V V V The column vector of becomes a right singular vector .
Use orthogonal matrix V V V, The following formula can be obtained :
A V = U Σ AV=U\Sigma AV=UΣ
This can be explained as , There is a special set of orthogonal vectors ( for example V V V Column vector set of ), Through the matrix A A A Map to another set of orthogonal vectors ( for example U U U Column vector set of ).
SVD Some characteristics of
Given matrix A A A A group of SVD decompose
A = U Σ V T A=U\Sigma V^T A=UΣVT
among , σ 1 ≥ ⋯ ≥ σ r ≥ σ r + 1 = ⋯ = σ min ( m , n ) = 0 \sigma_1\geq\cdots\geq\sigma_r\geq\sigma_{r+1}=\cdots=\sigma_{\min(m,n)}=0 σ1≥⋯≥σr≥σr+1=⋯=σmin(m,n)=0
There is a corollary ( R ( A ) R(A) R(A) and N ( A ) N(A) N(A) They are matrices A A A Range space and zero space ):
- r a n k ( A ) = r rank(A)=r rank(A)=r
- R ( A ) = R ( [ u 1 , . . . u r ] ) R(A)=R([u_1,...u_r]) R(A)=R([u1,...ur])
- N ( A ) = R ( [ u r + 1 , . . . , u n ] ) N(A)=R([u_{r+1},...,u_n]) N(A)=R([ur+1,...,un])
- R ( A T ) = R ( [ v 1 , . . . v r ] ) R(A^T)=R([v_1,...v_r]) R(AT)=R([v1,...vr])
- N ( A T ) = R ( [ v r + 1 , . . . , v m ] ) N(A^T)=R([v_{r+1},...,v_m]) N(AT)=R([vr+1,...,vm])
If we introduce
U r = [ u 1 , . . . , u r ] , Σ = d i a g ( σ 1 , . . . , σ r ) , V r = [ v 1 , . . . , v r ] U_r=[u_1,...,u_r],\Sigma=diag(\sigma_1,...,\sigma_r),V_r=[v_1,...,v_r] Ur=[u1,...,ur],Σ=diag(σ1,...,σr),Vr=[v1,...,vr]
Then there are
A = U r Σ r V r T = ∑ i = 1 r σ i u i v i T A=U_r\Sigma_rV_r^T=\sum_{i=1}^r\sigma_iu_iv_i^T A=UrΣrVrT=i=1∑rσiuiviT
This is called a matrix A A A Binary decomposition of (dyadic decomposition), About to rank as r r r Matrix A A A Decompose into r r r One rank is 1 Sum of matrices .
meanwhile , You can get
A T A = V Σ T Σ V T a n d A A T = U Σ Σ T U T A^TA=V\Sigma^T\Sigma V^T and AA^T=U\Sigma\Sigma^TU^T ATA=VΣTΣVTandAAT=UΣΣTUT
You know , Square of singular value σ i 2 , i = 1 , . . . , p \sigma_i^2,i=1,...,p σi2,i=1,...,p It's a symmetric matrix A T A A^TA ATA and A A T AA^T AAT The eigenvalues of the , v i v_i vi and u i u_i ui They are the corresponding eigenvectors . The proof is as follows :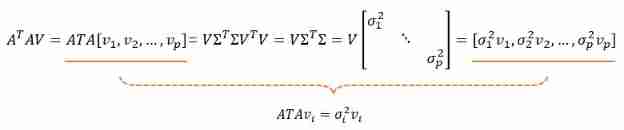
This conclusion is very useful , We are trying to understand A x = 0 Ax=0 Ax=0 when , Requirements A T A A^TA ATA The eigenvector corresponding to the minimum eigenvalue of , That is to say SVD Decomposed matrix V V V The last column of . Another application scenario is the covariance matrix PCA When analyzing , You can use SVD Decomposed matrix V V V Each column is a vector in each direction .
Through this conclusion , We can easily calculate the matrix A A A Of 2- Norm sum Frobenius norm :
∣ ∣ A ∣ ∣ 2 = max x ≠ 0 ∣ ∣ A x ∣ ∣ 2 ∣ ∣ x ∣ ∣ 2 = max x ≠ 0 x T A T A x x T x = max x ≠ 0 x T λ A T A x x T x = max x ≠ 0 λ A T A = σ 1 ∣ ∣ A ∣ ∣ F = ∑ i = 1 m ∑ j = 1 n a i j 2 = t r a c e ( A T A ) = σ 1 2 + ⋯ + σ p 2 , p = min ( m , n ) \begin{aligned} ||A||_2&=\sqrt{\max_{x\neq0}\frac{||Ax||_2}{||x||_2}}=\sqrt{\max_{x\neq0}\frac{x^TA^TAx}{x^Tx}}=\sqrt{\max_{x\neq0}\frac{x^T\lambda_{A^TA}x}{x^Tx}}=\sqrt{\max_{x\neq0}\lambda_{A^TA}}=\sigma_1\\ ||A||_F&=\sqrt{\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^m\sum_{j=1}^na_{ij}^2}=\sqrt{trace(A^TA)}=\sqrt{\sigma_1^2+\cdots+\sigma_p^2},p=\min(m,n) \end{aligned} ∣∣A∣∣2∣∣A∣∣F=x=0max∣∣x∣∣2∣∣Ax∣∣2=x=0maxxTxxTATAx=x=0maxxTxxTλATAx=x=0maxλATA=σ1=i=1∑mj=1∑naij2=trace(ATA)=σ12+⋯+σp2,p=min(m,n)
SVD Solve the linear least square problem Ax=b
Let's see SVD The classic application of : Solve the least square solution of linear equation .
Consider a linear least squares problem A x = b Ax=b Ax=b:
min x ∣ ∣ A x − b ∣ ∣ 2 2 \min_x||Ax-b||_2^2 xmin∣∣Ax−b∣∣22
Given matrix A ∈ R m × n A\in R^{m\times n} A∈Rm×n A group of SVD decompose : A = U Σ V T A=U\Sigma V^T A=UΣVT
According to the matrix U U U and V V V The orthogonality of , Yes
∣ ∣ A x − b ∣ ∣ 2 2 = ∣ ∣ U T ( A x − b ) ∣ ∣ 2 2 = ∣ ∣ U T A x − U T b ∣ ∣ 2 2 = ∣ ∣ Σ V T x − U T b ∣ ∣ 2 2 ||Ax-b||_2^2=||U^T(Ax-b)||_2^2=||U^TAx-U^Tb||_2^2=||\Sigma V^Tx-U^Tb||_2^2 ∣∣Ax−b∣∣22=∣∣UT(Ax−b)∣∣22=∣∣UTAx−UTb∣∣22=∣∣ΣVTx−UTb∣∣22
another z = V T x z=V^Tx z=VTx, Then there are
∣ ∣ A x − b ∣ ∣ 2 2 = ∣ ∣ Σ V T x − U T b ∣ ∣ 2 2 = ∑ i = 1 r ( σ i z i − u i T b ) 2 + ∑ i = r + 1 m ( u i T b ) 2 ||Ax-b||_2^2=||\Sigma V^Tx-U^Tb||_2^2=\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^r(\sigma_iz_i-u_i^Tb)^2+\sum_{i=r+1}^m(u_i^Tb)^2 ∣∣Ax−b∣∣22=∣∣ΣVTx−UTb∣∣22=i=1∑r(σizi−uiTb)2+i=r+1∑m(uiTb)2
therefore ,
min x ∣ ∣ A x − b ∣ ∣ 2 2 = min x ( ∑ i = 1 r ( σ i z i − u i T b ) 2 + ∑ i = r + 1 m ( u i T b ) 2 ) \min_x||Ax-b||_2^2=\min_x(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^r(\sigma_iz_i-u_i^Tb)^2+\sum_{i=r+1}^m(u_i^Tb)^2) xmin∣∣Ax−b∣∣22=xmin(i=1∑r(σizi−uiTb)2+i=r+1∑m(uiTb)2)
obviously , When σ i z i = u i T b \sigma_iz_i=u_i^Tb σizi=uiTb when , Take the minimum , Then the least square solution is :
z i = u i T b σ i , i = 1 , . . . , r z i = a r b i t r a r y , i = r + 1 , . . . , n \begin{aligned} z_i&=\frac{u_i^Tb}{\sigma_i},i=1,...,r\\ z_i&=arbitrary,i=r+1,...,n \end{aligned} zizi=σiuiTb,i=1,...,r=arbitrary,i=r+1,...,n
The minimum value is
min x ∣ ∣ A x − b ∣ ∣ 2 2 = ∑ i = r + 1 m ( u i T b ) 2 \min_x||Ax-b||_2^2=\sum_{i=r+1}^m(u_i^Tb)^2 xmin∣∣Ax−b∣∣22=i=r+1∑m(uiTb)2
from z = V T x z=V^Tx z=VTx, Available x = V z x=Vz x=Vz, therefore , adopt SVD The formula for finding the linear least square solution is
x = V z z i = u i T b σ i , i = 1 , . . . , r z i = a r b i t r a r y , i = r + 1 , . . . , n \begin{aligned} x&=Vz\\ z_i&=\frac{u_i^Tb}{\sigma_i},i=1,...,r\\ z_i&=arbitrary,i=r+1,...,n \end{aligned} xzizi=Vz=σiuiTb,i=1,...,r=arbitrary,i=r+1,...,n
In the above formula, we find , When r = n r=n r=n when , There is a unique least square solution , When r < n r<n r<n when , There are countless least squares solutions , At this point, we can find the minimum norm solution :
x † = V z † z i † = u i T b σ i , i = 1 , . . . , r z i † = 0 , i = r + 1 , . . . , n \begin{aligned} x_\dagger&=Vz_\dagger\\ z_i^\dagger&=\frac{u_i^Tb}{\sigma_i},i=1,...,r\\ z_i^\dagger&=0,i=r+1,...,n \end{aligned} x†zi†zi†=Vz†=σiuiTb,i=1,...,r=0,i=r+1,...,n
We know that the least square solution can also pass ( A T A ) − 1 ( A T b ) (A^TA)^{-1}(A^Tb) (ATA)−1(ATb) To solve , And by SVD The advantage of the solution is that it does not need complex inverse operation , And can handle A T A A^TA ATA It is the case that the singular matrix is irreversible .
About bloggers :
Ethan Li Li Yingsong ( You know : Li Yingsong )
Wuhan University Doctor of photogrammetry and remote sensing
Main direction Stereo matching 、 Three dimensional reconstruction
2019 Won the first prize of scientific and technological progress in surveying and mapping in ( Provincial and ministerial level )
Love 3D , Love sharing , Love open source
GitHub: https://github.com/ethan-li-coding
mailbox :[email protected]
Personal wechat :
Welcome to exchange !
Pay attention to bloggers and don't get lost , thank !
Blog home page :https://ethanli.blog.csdn.net
边栏推荐
- Codeworks round 681 (Div. 2) supplement
- Return of missing persons
- Halcon shape_ trans
- kubeadm系列-02-kubelet的配置和启动
- Understanding rotation matrix R from the perspective of base transformation
- Dynamic dimensions required for input: input, but no shapes were provided. Automatically overriding
- js异步错误处理
- Guess riddles (7)
- 【日常训练--腾讯精选50】557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
- AdaBoost use
猜你喜欢

My university
Summary and Reflection on issues related to seq2seq, attention and transformer in hands-on deep learning
Use and programming method of ros-8 parameters
Mathematical modeling: factor analysis
混淆矩阵(Confusion Matrix)
Add discount recharge and discount shadow ticket plug-ins to the resource realization applet

Halcon clolor_ pieces. Hedv: classifier_ Color recognition
Introduction Guide to stereo vision (2): key matrix (essential matrix, basic matrix, homography matrix)
EA introduction notes
Count of C # LINQ source code analysis
随机推荐
Pytorch entry record
Halcon wood texture recognition
One dimensional vector transpose point multiplication np dot
Jenkins Pipeline 方法(函数)定义及调用
ECMAScript6介绍及环境搭建
ORACLE进阶(三)数据字典详解
Mengxin summary of LIS (longest ascending subsequence) topics
kubeadm系列-00-overview
Guess riddles (7)
Codeforces round 684 (Div. 2) e - green shopping (line segment tree)
[daily training] 1200 Minimum absolute difference
Codeforces Round #648 (Div. 2) E.Maximum Subsequence Value
Introduction Guide to stereo vision (2): key matrix (essential matrix, basic matrix, homography matrix)
【日常训练--腾讯精选50】557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
Guess riddles (9)
Guess riddles (8)
[Niuke brush questions day4] jz55 depth of binary tree
微信H5公众号获取openid爬坑记
什么是防火墙?防火墙基础知识讲解
嗨 FUN 一夏,与 StarRocks 一起玩转 SQL Planner!
