当前位置:网站首页>Deep analysis of C language data storage in memory
Deep analysis of C language data storage in memory
2022-07-06 08:32:00 【Finally - null】
author : In the end —NULL
motto : Make a little progress every day , Persistence makes a big difference !
Article content : C Storage of language data in memory .
Preface :
After a period of study, we have learned that in C Language contains various data , But do we really understand the meaning of type , And how different data types are stored in memory . Next, we will dissect one by one .
Catalog
1. A detailed description of data types :
3. Storage of different data types in memory
2. The storage form of data in memory :
3. Storage order of data in memory :
2. Judge the big and small ends :
4.char Type of data stored in memory
1. A signed char Store data range in memory :
2. Unsigned char Store data range in memory :
5. Storage rules of floating point numbers in memory
1. Floating point storage rules :
2. Rules for storing floating-point numbers in memory
1. A detailed description of data types :
1. Plastic surgery Family
char
unsigned char
signed char
short
unsigned short [int]
signed short [int]
int
unsigned int
signed int
long
unsigned long [int]
signed long [int]
2. Floating point family
float
double
3. Construction type
> An array type
> Type of structure struct
> Enumeration type enum
> Joint type union
4. Pointer types
int *pi;
char *pc;
float* pf;
void* pv;
5. Empty type
void
2. The meaning of type
1. Different data types determine how much memory space we apply for in memory when defining variables .
2. Different data types determine the form in which we store data in the open space
3. Storage of different data types in memory
1. Concept introduction :
Data is stored in binary form in the computer : There are three representations , namely Original code , Inverse code , Complement code .
The three representations have corresponding sign bits : highest ‘0’ It means a positive number , highest ‘1’ A negative number
Three different representation rules :
Original code : Write it directly according to the corresponding binary bit
Inverse code : The sign bits remain the same , The other bits are reversed bit by bitComplement code : Add one to the inverse code to get the complement
2. The storage form of data in memory :
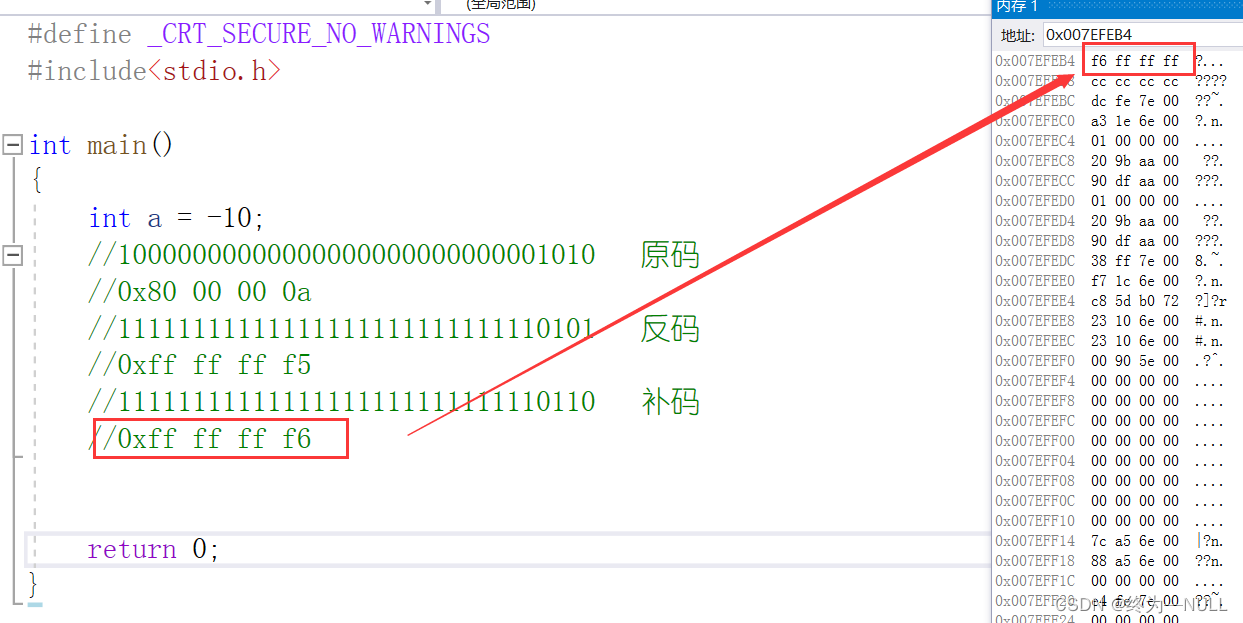
int a= - 10;
summary : Through debugging, it is found that the data is stored in the form of complement in memory .
3. Storage order of data in memory :
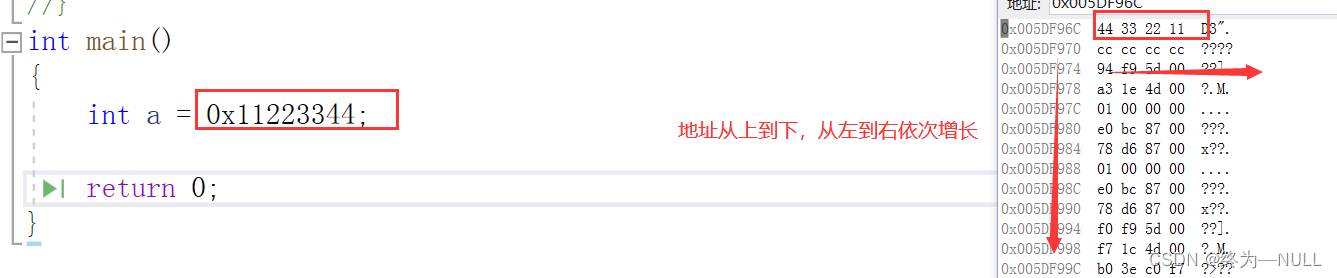
1. Large and small end :
The phenomenon :
Why is the data we define opposite to the data stored in memory ?
Big end storage : Low byte order ( Low weight bit ) The data of is stored at a high address , High byte order ( High weight bit ) The data of is stored at the low address .
Small end storage : Low byte order ( Low weight bit ) The data of is stored at the low address , High byte order ( High weight bit ) The data of is stored at a high address .
Whether to use big end storage or small end storage for storing data depends on the compiler . stay VS Small end storage .
2. Judge the big and small ends :
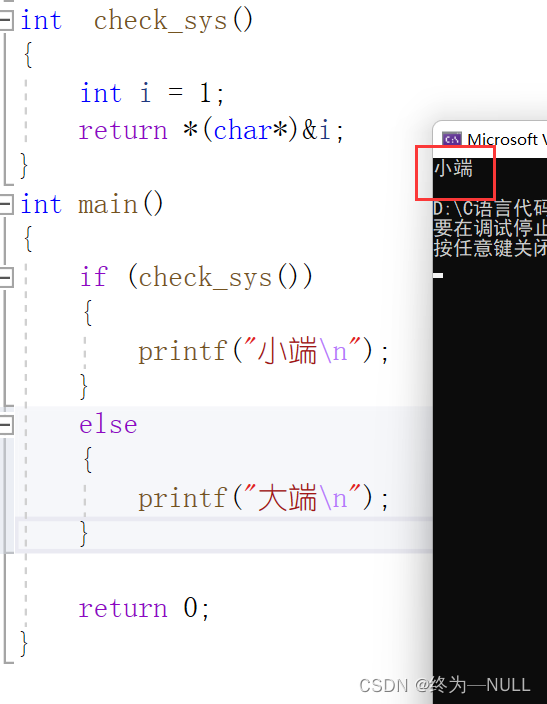
Title Description : Write a piece of code , Determine whether the compiler used is small end storage or large end storage .
Ideas : Shaping data 1 Forced to char type , Then apply the solution
#include<stdio.h> int check_sys() { int i = 1; return *(char*)&i; } int main() { if (check_sys()) { printf(" The small end \n"); } else { printf(" Big end \n"); } return 0; }
4.char Type of data stored in memory
char
signed char ; // The signed
unsigned char;// Unsigned
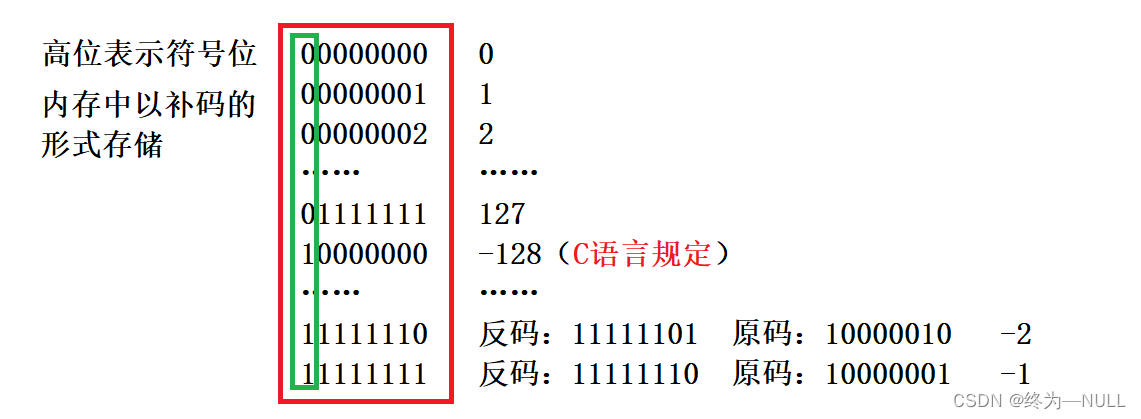
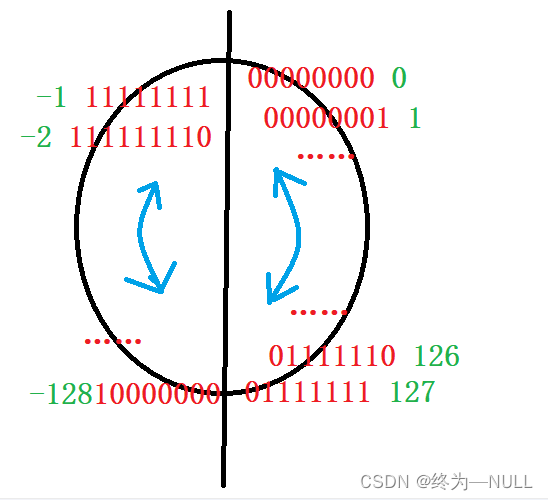
1. A signed char Store data range in memory :
summary : The signed char The data storage range of type is -128~127
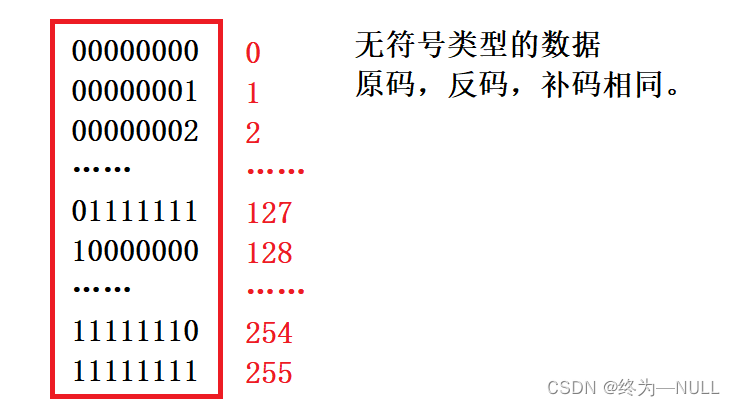
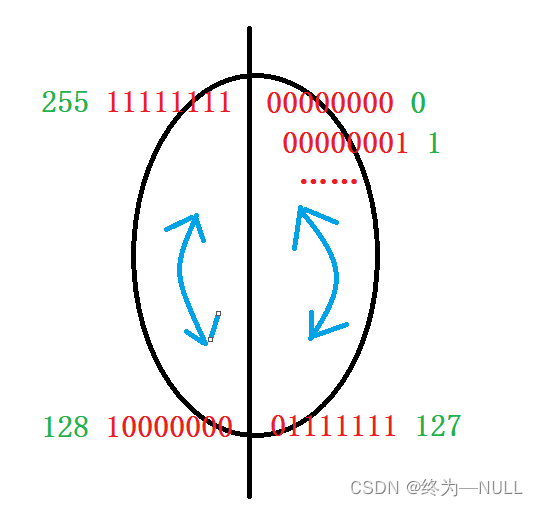
2. nothing Symbol char Store data range in memory :
summary : The storage range of unsigned data in memory is 0~255
5. Storage rules of floating point numbers in memory
1. Floating point storage rules :
According to international standards IEEE( Institute of electrical and Electronic Engineering ) 754, Any binary floating point number V It can be expressed in the following form :
(-1)^S * M * 2^E
(-1)^S The sign bit , When S=0,V Is a positive number ; When S=1,V It's a negative number .
M Represents a significant number , Greater than or equal to 1, Less than 2.
2^E Indicates the index bit .
give an example :
5.5
Binary form :101.1
Scientific enumeration :1.011*2^2
Add sign bits :(-1)^0*1.011*2^2
0==S M==1.001 E==2
2. Rules for storing floating-point numbers in memory
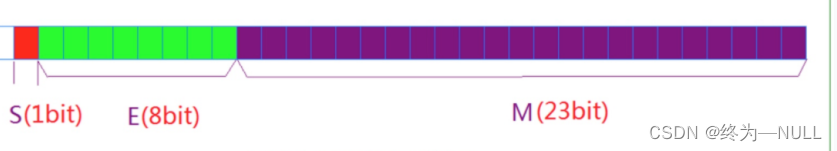
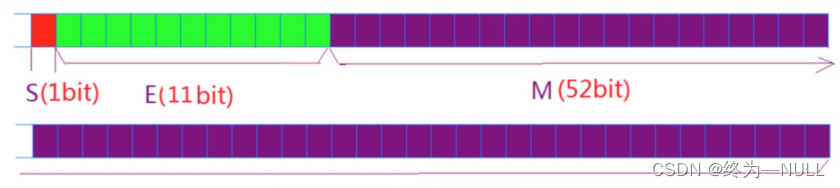
1.32 Bit single precision floating point number :
highest 1 Bits are sign bits S, And then there was 8 Bit index E, The rest M yes 23 Significant digits ( Does not include 1, In order to improve the accuracy ).
2.64 Bit double progress floating-point number :
highest 1 Bits are sign bits S, And then there was 11 Bit index E, The rest M yes 52 Significant digits ( Does not include 1, In order to improve the accuracy ).
Index E Storage rules for :
E Is an unsigned number , therefore E by 8 position , The scope is 0~255, If E by 11 position , The scope is 0~2047.
But because floating-point numbers are negative , So when storing single precision floating-point numbers, add 127, Double precision floating-point number plus 1023
3. Rules for fetching floating-point numbers from memory
1.E Not all for 0 Or not all of them 1:
Index E The value of minus 127(1023), Add 1.
2.E All for 0:
Floating point E be equal to 1-127 perhaps (1-1023) That's the true value .
The significant number is not preceded by 1, It's reduced to 0.xxxxx Decimals of , This is to indicate positive and negative 0, And close to 0 A very small number of .
3.E All for 1:
At this time , If the significant number M All for 0, Express ± infinity ( It depends on the sign bit s);
4. give an example :
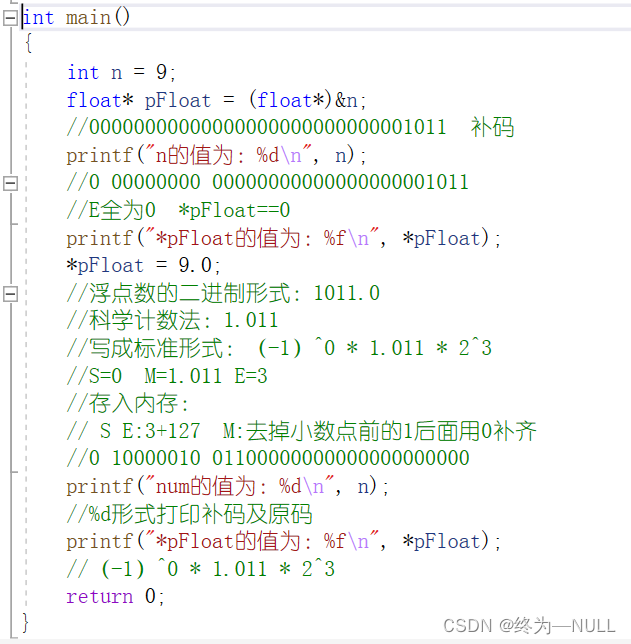
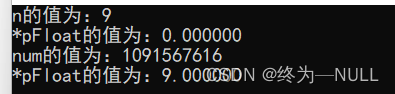
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int n = 9; float *pFloat = (float *)&n; printf("n The value of is :%d\n",n); printf("*pFloat The value of is :%f\n",*pFloat); *pFloat = 9.0; printf("num The value of is :%d\n",n); printf("*pFloat The value of is :%f\n",*pFloat); return 0; }Code interpretation :
6. summary
The above is about the storage rules of integer data and floating-point numbers in memory . I hope it helped you , If there are errors and deficiencies in the middle content, please leave a comment .
边栏推荐
- [2022 Guangdong saim] Lagrange interpolation (multivariate function extreme value divide and conquer NTT)
- Zhong Xuegao, who cannot be melted, cannot escape the life cycle of online celebrity products
- sublime text没关闭其他运行就使用CTRL+b运行另外的程序问题
- Synchronized solves problems caused by sharing
- Rviz仿真时遇到机器人瞬间回到世界坐标原点的问题及可能原因
- China high purity silver nitrate Market Research and investment strategy report (2022 Edition)
- 延迟初始化和密封类
- egg. JS getting started navigation: installation, use and learning
- 2022.02.13 - NC001. Reverse linked list
- 从表中名称映射关系修改视频名称
猜你喜欢

2022.02.13 - NC003. Design LRU cache structure
JVM performance tuning and practical basic theory - Part 1

Analysis of pointer and array written test questions
pytorch训练好的模型在加载和保存过程中的问题
win10系统中的截图,win+prtSc保存位置
个人电脑好用必备软件(使用过)
![[research materials] 2022 enterprise wechat Ecosystem Research Report - Download attached](/img/35/898a8086bc35462b0fcb9e6b58b86b.jpg)
[research materials] 2022 enterprise wechat Ecosystem Research Report - Download attached
leetcode刷题 (5.28) 哈希表

Leetcode question brushing (5.28) hash table
Synchronized solves problems caused by sharing
随机推荐
tree树的精准查询
[MySQL] database stored procedure and storage function clearance tutorial (full version)
Hungry for 4 years + Ali for 2 years: some conclusions and Thoughts on the road of research and development
同一局域网的手机和电脑相互访问,IIS设置
Upgrade tidb with tiup
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
如何进行接口测试测?有哪些注意事项?保姆级解读
Online yaml to CSV tool
Browser thread
MySQL learning record 07 index (simple understanding)
Circular reference of ES6 module
LDAP application (4) Jenkins access
被破解毁掉的国产游戏之光
Sort according to a number in a string in a column of CSV file
Use dumping to back up tidb cluster data to S3 compatible storage
电脑F1-F12用途
On the day of resignation, jd.com deleted the database and ran away, and the programmer was sentenced
Golang force buckle leetcode 1020 Number of enclaves
Research Report on Market Research and investment strategy of microcrystalline graphite materials in China (2022 Edition)
Deep learning: derivation of shallow neural networks and deep neural networks