当前位置:网站首页>[SQL] an article takes you to master the operations related to query and modification of SQL database
[SQL] an article takes you to master the operations related to query and modification of SQL database
2022-07-03 10:37:00 【Twilight drainage software】
This column will start with the basics , Step by step , Explain the basic concept and use of database , I hope everyone can gain something from it , Please also support .
Column address : Database must know and know
If there is something wrong with the knowledge of the article , Please correct me. ! Let's learn together , Progress together .
This article will explain in detail SQL Basic data types for 、SQL Basic schema definition 、SQL Query and modify statements 、SQL The basic structure of the query 、 Rename operation 、 String operations 、 Arrange the display order of tuples 、 Set operations 、 Aggregation function 、 Null value 、 nested subqueries 、 Null relation test 、with Clause 、 Database modification .
List of articles
SQL Language Overview
SQL At present, it has been widely used in the field of database , yes Structured Query Language( Structured query language ) Abbreviation ,SQL The earliest version was created by IBM Development .SQL Language consists of the following parts :
- DDL(Date Definition Language) Data definition language
- create table,alter table,drop table
- create index,drop index
- create view,drop view
- create trigger,drop trigger
- …
- DML(Data Manipulation Language) Data manipulation language
- select … from
- insert,delete,update
- DCL(Data Control Language) Data control language
- grant,revoke
SQL Data definition
The relational set in the database must be defined by the data definition language (DDL) Assigned to the system .
for example :
create table instructor(
ID char(5),
name varchar(20) not null,
dept_name varchar(20),
salary numeric(8,2),
primary key(ID)
);
SQL Of DDL Not only can you define a set of relationships , You can also define the information for each relationship , Include :
- Each relationship pattern
- The value type of each attribute
- Integrity constraints
- Index set maintained per relationship
- Security and permission information for each relationship
- The physical storage structure of each relationship on disk
SQL Basic data types for
- char(n): Fixed length string , User specified length n
- varchar(n): Variable length string , User specified maximum length n
- int: Integer types ( A subset of machine related integer types ), Equivalent to the whole process integer
- smallint: Small integer type ( A subset of machine related integer types )
- numeric(p, d): Fixed-point number , The accuracy is specified by the user . This number has p Digit number , among d To the right of the decimal point
- double: Double precision floating point
- float(n): The accuracy is at least n Floating point number of bits
- null: Each type can contain a special value , The value is null . You can declare that the attribute value is not empty , It is forbidden to add null values
- date: date , Including year 、 month 、 Japan , Such as ‘2015-3-20’
- time: Time , Including hours 、 minute 、 second , Such as ‘ 08:15:30’ or ‘ 08:15:30.75’
- timestamp: date + Time , Such as ‘2022-5-21 08:15:30.75’
SQL Basic schema definition
Create table statement create table

SQL Supports many different integrity constraints , Here we will only discuss a few commonly used :

Two about Create Example :

except Create sentence , There are also the following commonly used statements :
drop table command , Delete all information about the removed relationship from the database
example :
drop table r;
drop table instructor;
alter table command You can add attributes to existing relationships
example :
alter table r add A D
among ,A Is the name of the attribute to be added ,D Is the domain to be added , The values of all tuples in the relationship on the new attribute will be set to null.
Such as :
alter table instructor add birthday date;
alter table command You can also remove attributes from the relationship
alter table r DROP A;
We need to pay attention to : Many databases do not support this operation
We can also use alter table Modify the properties in the relationship :
alter table r modify ID char(10)
The complete case is as follows :
create table testCRUD(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY ,
str1 varchar(20),
str2 varchar(20),
str3 varchar(20)
);
alter table testCRUD drop str1;
alter table testCRUD add str4 varchar(20);
alter table testCRUD modify str2 int;
select * from testCRUD;
SQL Query and modify statements
SQL The basic structure of the query

example , Find out the names of all the teachers
select name
from instructor;
Expressed in relational algebra, the expression is : π n a m e i n s t r u c t o r pi_{name}{instructor} πnameinstructor, Be careful ,SQL The character... Is not allowed in attribute names ‘-’, For example dept_name Instead of dept-name.SQL Case insensitive , Therefore, you can use uppercase or lowercase letters to name the table 、 Properties, etc .
SQL Allow in relationships and SQL Duplicate tuple in expression result , To forcibly remove duplicates , Can be found in select Add keywords after distinct
example , Inquire about instructor All family names in the relationship , And remove duplicates
select distinct dept_name
from instructor;
SQL It also allows us to use keywords all To explicitly indicate that duplicates are not removed (SQL The default is all)
select all dept_name
from instructor;
asterisk “*” stay select clause , It can be used to express “ All attributes ”
example :
select *
from instructor;
meanwhile select Clause can also contain +、-、*、/ Arithmetic expressions for operators , Operands can be properties of constants or tuples
example :
select ID,name,salary*1.05 from instructor;
where Clause allows us to select only those in from A tuple that satisfies a particular predicate in the result relation of a clause , example , Find out what's going on in Computer Science And the salary exceeds 70000 The name of the teacher in dollars :
select name
from instructor
where dept_name='Computer_Science' and salary > 70000;
Above SQL The relational algebra expression corresponding to the query statement is :
π ( σ d e p t n a m e = ′ C o m p u t e r s c i e n c e ′ a n d s a l a r y > 7000 ( i n s t r u c t o r ) ) pi(sigma_{dept_name=‘Computer_science’ space andspace salary > 7000}(instructor)) π(σdeptname=′Computerscience′andsalary>7000(instructor))
SQL Allow in where Use logical conjunctions in clauses and,or and not, You can also use between Specified range query . The operation object of a logical conjunction can be a comparison operator <、 <=、>、>=、= and <> The expression of
example , Find out the salary in 90 000 The dollar and 100 000 The name of the teacher between dollars
select name
from instructor
where salary <= 100000 and salary >= 90000;
perhaps :
select name
from instructor
where salary between 90000 and 100000;
from Clause is a list of relationships that need to be accessed in query evaluation , adopt from Clause defines a Cartesian product on the relationships listed in the clause .
example 1: Find out the relationship instructor and teaches Cartesian product of
select * from instructor,teaches;
example 2: find Computer Science Teacher name and course logo of the Department
The corresponding table is as follows :


Rename operation
SQL Provides a mechanism for renaming relationships and attributes , That is to use as Clause :
old-name as new-name
as Clause can appear in select clause , It can also appear in from clause .
example 1: Consider the query just , Attribute name Rename it to instructor_name
select name as instructor_name,course_id
from instructor,teaches
where instructor.ID=teaches.ID and instructor.dept_name='Com. Sci'
example 2: Find out all the teachers , And the logo of the course they teach
select T.name, S.course_id
from instructor as T, teaches as S
where T.ID= S.ID;
Example 3 : Find out the names of all teachers , Their wages are at least higher than Biology The salary of a teacher in the Department is higher
select distinct T.name
from instructor as T,instructor as S
where T.salary > S.salary and S.dept_name='Biology';
String operations
The most common operation on a string is to use the operator like The pattern match , Use two special characters to describe the pattern :
- Percent sign (%): Match any substring
- Underline (_): Matches any character
example : Find the substring contained in the building name ‘Watson’ All family names
select dept_name
from department
where building like‘%Watson%
To enable the mode to contain special characters ( namely % and _),SQL It is allowed to define escape characters . We are like Use... In comparison escape Key words to define escape characters
example : Use backslashes () As escape character
like 'ab%cd%' # Match all to "ab%cd" Starting string
like 'ab\cd%' # Match all to "abcd" Starting string
Arrange the display order of tuples
SQL It provides users with some control over the display order of tuples in the relationship .order by Clause allows the tuples in the query results to be displayed in order
example , Listed alphabetically in Physics All the teachers in the Department
select name
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Physics'
order by name;
order by Clause uses ascending order by default . To explain the sort order , We can use desc Representation of descending order , Or use asc Expressing ascending order .
example : Press salary List the whole in descending order instructor Relationship , If there are several teachers with the same salary , Just sort them by name in ascending order
select *
from instructor
order by salary desc, name asc;
Set operations
SQL Acting on a relationship union、intersect and except Operation corresponds to... In mathematical set theory ∪ cup ∪、 ∩ cap ∩ and - operation .union、intersect and except Operation and select Different clauses , They will automatically remove heavy
complex , If you want to keep all the repetitions , Must use union all、intersect all and except all.
Be careful :
MySql Only union, and union all No, intersect and except.
stay Oracle in , Support union,union ALL,intersect and Minus; But does not support Intersect ALL and Minus ALL
example 1: Find out 2009 Classes begin in the autumn of , Or in 2010 All courses that start in the spring of or both courses
The corresponding table is as follows :

(select course_id
from section
where semester =‘Fall’and year = 2009)
union
(select course_id
from section
where semester =‘Spring’and year = 2010);
example 2: Find out 2009 Autumn and 2010 All courses begin at the same time in the spring of
(select course_id
from section
where semester =‘Fall’and year = 2009)
intersect
(select course_id
from section
where semester =‘Spring’and year = 2010);
example 3: Find out 2009 Classes begin in the autumn of , But not here. 2010 All courses that start in the spring of
(select course_id
from section
where semester =‘Fall’and year = 2009)
except
(select course_id
from section
where semester =‘Spring’and year = 2010);
Aggregation function
An aggregate function is a collection of values ( Set or multiset ) For input , A function that returns a single value . SQL Five intrinsic aggregation functions are provided :
- Average :avg
- minimum value :min
- Maximum :max
- The sum of the :sum
- Count :count
- among ,sum and avg The input must be a numeric set , But other operators can also act on non numeric data On a collection of types , Such as a string
In addition to the above five basic aggregation functions , And group aggregation (group by).group by Clause is used to construct the grouping , stay group by Tuples with the same values on all attributes in clause are grouped together .having Clause is similar to where Clause , However, it is a limiting condition for grouping , Instead of limiting tuples .having The predicates in a clause do not work until they are grouped , So you can use aggregation
function .
example 1, find Computer Science The average salary of Department Teachers
select avg (salary) as avg_salary
from instructor
where dept_name=‘Comp. Sci.’;
Above SQL Queries are equivalent to relational algebraic expressions :
g a v g ( s a l a r y ) ( σ d e p t n a m e = ′ C o m p . S c i ′ ( i n s t r u c t o r ) ) g_{avg(salary)}(sigma_{dept_name=‘Comp.Sci’}(instructor)) gavg(salary)(σdeptname=′Comp.Sci′(instructor))
example 2, Find out the average salary of each department
select dept_name avg (salary) as avg_salary
from instructor
group by dept_name ;
The legend is as follows :
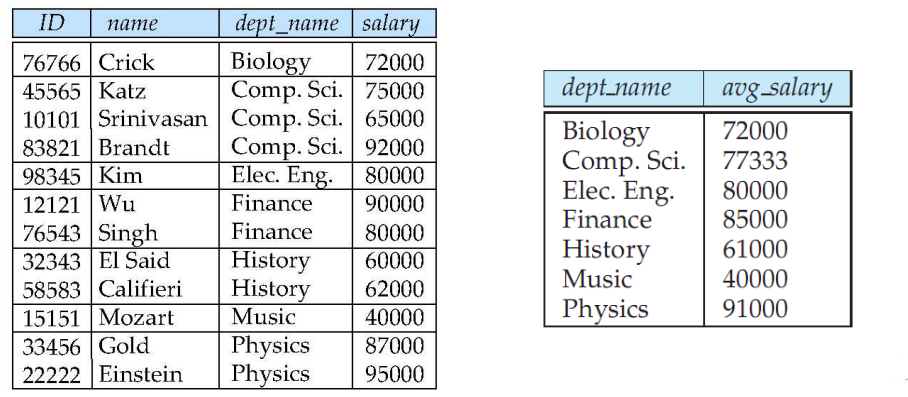
example 3, Find out that the average teacher's salary exceeds 42 000 The dollar is
select dept_name avg (salary) as avg_salary
from instructor
group by dept_name
having avg(salary)>42000;
Null value
We can use special keywords in predicates null Test null , You can also use is not null Test non null values .
example : find instructor Tuple in relation is in attribute salary The name of the teacher with a null value on
select name
from instructor where salary is null;
The existence of null value also brings trouble to the processing of aggregation operation . The aggregate function handles null values according to the following principles :
- except count(*) All aggregate functions except ignore null values in the input set
- Regulations : Empty set count The operation value is 0, All other aggregation operations return a null value when the input is an empty set
example : Calculate the sum of all teachers' salaries
select sum(salary)
from instructor;
sum The operator ignores all null values in the input , If instructor All tuples in the relationship are in salary All values on the are empty , be sum The result returned by the operator is null.
nested subqueries
SQL Provide nested sub query mechanism . Subqueries are nested in another query select-from-where expression . Subqueries are nested in where clause , Usually used for membership of a collection 、 The comparison of sets and the cardinality of sets are checked . It is mainly used for :
- Collective membership
- Comparison of sets
- Null relation test
- Repeated tuple existence test
- from Subquery in Clause
- with Clause
Collective membership
SQL Allows you to test the membership of tuples in relationships . Conjunctions in Test whether the tuple is in the collection Members of , Sets are created by select Clause consists of a set of values , The counterpart is not in.
example 1, Find out 2009 Autumn and 2010 All the courses that started at the same time in the spring semester of 2005
select distinct course_id
from section
where semester =‘Fall’and year= 2009 and
course_id in (select course_id
from section
where semester =‘Spring’and year= 2010);
Consider querying “ Find out the names of all teachers who meet the following conditions , Their wages are at least higher than Biology Department A teacher's salary is higher ”, in front , We will write this query :
select distinct T.name
from instructor as T,instructor as S
where T.salary > S.salary and S.dept_name =‘Biology’;
however SQL Provide another way to write the above query . The phrase “ At least bigger than one ” stay SQL of use >some Express , Then this query can also be written :
select name
from instructor
where salary > some (select salary
from instructor
where dept_name =‘Biology’);

Consider querying “ Find out the names of all teachers who meet the following conditions , Their wages are higher than Biology The salary of every teacher in the Department is high ” , stay SQL in , structure >all Corresponding to the phrase “ More than all Big ”, be
select name
from instructor
where salary > all(select salary
from instructor
where dept_name =‘Biology’);
example : Find the Department with the highest average salary
select dept_name
from instructor
group by dept_name
having avg (salary) >= all (select avg (salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name);
Null relation test
SQL There is also a feature to test whether there are tuples in the results of a subquery ,exists Structure returns... When the collection is not empty true value ,not exists Returns... When the collection is empty true value .
example , Find out what you're doing 2009 In the autumn semester of 2004 2010 All courses in the spring semester of , Use exists structure , Rewrite the query :
select course_id
from section as S
where semester =‘Fall’and year = 2009 and
exists (select *
from section as T
where semester =‘Spring’and year= 2010 and
S.course_id = T.course_id );
example , I found out Biology Students in all the courses offered by the Department
Use except structure , Write the query :

Add : If X Y = 0 ( empty Set ) X-Y=0( An empty set ) XY=0( An empty set ), be X Y Xsube Y XY
Add , Use mysql Test whether there are duplicate tuples in the result of a sub query .
example 1, Find out what's going on in 2009 Courses offered at most once a year
select T.course_id
from course as T
where 1 >= (select count(R.course_id)
from section as R
where T.course_id = R.course_id and
R.year = 2009)
example 2, Find out what's going on in 2009 Courses offered at least twice a year
select distinct T.course_id
from course as T
where 1 < (select count(R.course_id)
from section as R
where T.course_id = R.course_id and
R.year = 2009);
from Subquery in Clause
SQL Allow in from Clause using subquery expressions . whatever select-from-where The results returned by expressions are all relationships , So it can be inserted into another select-from-where Where any relationship can be found in .
example , Find out that the average salary of the Department exceeds 42000 The average salary of teachers in those departments of $ .
In the previous aggregation function , We used having Write this query . Now? , We use it in from Son Rewrite this query with a subquery in the sentence :

example , Find the Department with the largest total salary of all departments
Here it is ,having Clause is powerless . But we can use from The subquery of clause can be easily written Issue the following query :
select max(tot_salary)
from (select dept_name, sum(salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name) as dept_total(dept_name, tot_salary);
with Clause
with Clause provides a way to define a temporary relationship , This definition is only applicable to include with The query of clause is valid .
example 1, Find the system with the maximum budget value

example 2, Find the system where the total salary is greater than the average

Database modification
Delete
In addition to the extraction of database information ,SQL It is also defined to add 、 The operation of deleting and updating database information. The expression of deletion request is very similar to query , We can only delete the entire tuple , You can't just delete the values on some attributes ,SQL Delete with the following statement :
delete from r
where P;
among P Represents a predicate ,r Represents a relationship .
example 1, from instructor Delete from relationship dept_name by Finance All tuples of
delete from instructor
where dept_name =‘Finance’;
example 2, from instructor Delete all in the relationship Watson Working in the building
delete from instructor
where dept_name in (select dept_name
from department
where building =‘Watson’)
example 3, Delete the record of teachers whose salary is lower than the average university salary
delete from instructor
where salary < (select avg (salary)
from instructor);
Insert
SQL Allow to use insert sentence , Insert tuples into relationships , Form the following :
insert into r(c1,c2,...) values (e1,e2,...)
insert into r(c1,c2,...) select e1,e2,... from ...;
example 1, Suppose the information we want to insert is Computer Science The Department is called “Database Systems” Curriculum CS-437, It has 4 Credits
insert into course values (‘CS-437’, ‘Database Systems’, ‘Comp. Sci.’, 4);
SQL Allow in insert Statement , So the above statement can also be written as :
insert into course (course_id, title, dept_name, credits) values (‘CS-437’, ‘Database Systems’, ‘Comp. Sci.’, 4);
If in the example above , Database Systems” Course credits unknown , The insert statement can also be written as :
insert into course values (‘CS-437’, ‘Database Systems’, ‘Comp. Sci.’,null);
insert into course (course_id, title, dept_name) values (‘CS-437’, ‘Database Systems’, ‘Comp. Sci.’);
Suppose we want Music Every one of them has been repaired 144 Students with credits become Music The teachers of the Department , His salary is 18000 dollar
insert into instructor
select ID, name, dept_name, 18000
from student
where dept_name = ‘Music’ and tot_cred > 144;
to update
SQL Allow to use update sentence , Changing some attributes of a tuple without changing the whole tuple value , Form the following :
update r
set .....
where <condition>
example 1, Suppose the salary exceeds 100000 US $teachers rose 3% The salary of , The rest of the teachers went up 5% We can write two update sentence
update instructor
set salary = salary * 1.03
where salary > 100000;
update instructor
set salary = salary * 1.05
where salary <= 100000;
** Be careful :** These two update sentence The order of is very important . If the tune Change the order , May result in a slight increase in wages Less than 100 000 A teacher of dollars Will grow 8% The salary of
Query for the above example , We can also use SQL Provided case structure , Avoid the update order causing The problem of , Form the following :
case
when pred1 then result1
when pred2 then result2
. . .
when predn then resultn
else result0
end
Therefore, the query in the above example can be changed to :
update instructor
set salary = case
when salary <= 100000 then salary * 1.05
else salary * 1.03
end
summary
SQL The general form of query statement is as follows :

SQL Query statement execution order :

边栏推荐
- Leetcode skimming ---75
- Ut2014 supplementary learning notes
- Content type ‘application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8‘ not supported
- Simple real-time gesture recognition based on OpenCV (including code)
- 神经网络入门之模型选择(PyTorch)
- Rewrite Boston house price forecast task (using paddlepaddlepaddle)
- High imitation bosom friend manke comic app
- Preliminary knowledge of Neural Network Introduction (pytorch)
- Leetcode skimming ---278
- Boston house price forecast (tensorflow2.9 practice)
猜你喜欢
A super cool background permission management system
Hands on deep learning pytorch version exercise solution - 2.3 linear algebra

Leetcode - the k-th element in 703 data flow (design priority queue)
Rewrite Boston house price forecast task (using paddlepaddlepaddle)

Raspberry pie 4B deploys lnmp+tor and builds a website on dark web

LeetCode - 715. Range module (TreeSet)*****

EFFICIENT PROBABILISTIC LOGIC REASONING WITH GRAPH NEURAL NETWORKS

Drop out (pytoch)
Leetcode skimming ---367
Powshell's set location: unable to find a solution to the problem of accepting actual parameters
随机推荐
Model evaluation and selection
LeetCode - 715. Range module (TreeSet)*****
GAOFAN Weibo app
Hands on deep learning pytorch version exercise solution - 2.4 calculus
Drop out (pytoch)
Stroke prediction: Bayesian
【SQL】一篇带你掌握SQL数据库的查询与修改相关操作
Ind wks first week
6、 Data definition language of MySQL (1)
Ut2016 learning notes
Leetcode - 5 longest palindrome substring
Introduction to deep learning linear algebra (pytorch)
[graduation season] the picture is rich, and frugality is easy; Never forget chaos and danger in peace.
Leetcode skimming ---44
Leetcode刷题---202
Inverse code of string (Jilin University postgraduate entrance examination question)
Leetcode刷题---35
Data classification: support vector machine
C#项目-寝室管理系统(1)
High imitation Netease cloud music