当前位置:网站首页>Concurrent network modular reading notes transfer
Concurrent network modular reading notes transfer
2022-07-04 22:14:00 【51CTO】
At present, there are many network libraries , among libevent Is based on Reactor Realized , and boost.asio Is based on Proactor Realized .Reactor and Proactor The main difference between modes is the real operation ( As read / Write ) Who did it ,Reactor The application needs to read or write data by itself , And in the Proactor In the pattern , The application does not need to actually read / Writing process , The operating system will read the buffer or write the buffer to the real IO equipment , The application only needs to read from the buffer ( The operating system has been read for us ) Or write to the buffer ( The operating system will help us write ) that will do . stay Proactor In the pattern , After the user initiates the asynchronous operation, it returns , Let the operating system handle the request , Then wait for the callback to the completion event function to process the results of the asynchronous operation .
2.3 The driver (Proactor)
1. problem
Processing multiple service requests asynchronously can usually improve the performance of event driven applications in distributed systems . After asynchronous service processing , The program must handle the corresponding completion event sent by the operating system to indicate the end of asynchronous calculation . To effectively support this asynchronous computing model , The following four mandatory conditions need to be solved :
1) To improve scalability and latency , An application must process multiple completion events at the same time while prohibiting time-consuming operations from excessively delaying the processing of other operations .
2) To maximize throughput , It should be avoided CPU Any unnecessary context switching between , Synchronization and data mobility .
3) Integrating new or improved services with existing completion event multiplexing and allocation mechanisms costs the least .
4) Application code should try not to be affected by the complexity of multithreading and synchronization mechanism .
2. Solution
Divide the application service into two parts : Time consuming operations executed asynchronously and completion handlers that process the results after these operations are completed . Integrate the multiplex decomposition of completion events when asynchronous operations are completed and allocate them to the corresponding completion handlers that handle them . Separate the completion event multiplexing and allocation mechanism from the application related processing of completion events in the completion handler .
Specifically, it means : Introduce an asynchronous operation for each service provided by the application . These asynchronous operations actively initialize the processing of service requests through a handle and completion handler , The completion handler handles completion events that contain the results of these asynchronous operations . for example , Asynchronous operation can be called by the initiator in the application to accept the connection request sent from the remote application . Asynchronous operations are performed by asynchronous operation processors . After the operation is completed , The asynchronous operation processor inserts a completion event containing the operation result in the completion event queue .
An asynchronous event demultiplexer called the initiator waits for the queue . After the asynchronous event demultiplexer deletes a completion event from the queue , The driver demultiplexes and allocates the event to the application related completion handler corresponding to the asynchronous operation , The completion handler then processes the results of the asynchronous operation , You may need to call other asynchronous operations , These asynchronous operations follow the above chain of activities .
3. structure
The operating system provides a handle (handle) To identify entities ( Such as network connection ) Or open the file ( Can generate completion events ), Can respond to external service requests ( Such as connection or data request from remote application ) And produce completion events , It can also respond to operations generated within the application ( Such as timeout or asynchrony I/O system call ) And produce completion events .
Asynchronous operations (asynchronou operation) Indicates that in the implementation, such as through socket Handle the time-consuming operation to be used when reading and writing data asynchronously . After calling an asynchronous operation , Perform the asynchronous operation without blocking the caller's control thread . In this way, the caller can perform other operations . If an operation has to wait for another event to happen , Such as a connection request generated by a remote application , Then it will be delayed until the event arrives .
Finish processing (Completion handler) Defines an interface consisting of one or more hook methods , You can use these methods to process the information returned in the completion event related to the application . The completion event is generated after the asynchronous operation is executed .

After implementing the inherited hook method , Complete the processing procedure (concrete completion handler) A completion handler is specialized to define a specific application service . When the asynchronous operation related to the completion handler is completed , The hook method receives and processes the result information contained in the completion event . A concrete completion handler corresponds to a handle that can be used to call asynchronous operations .

Asynchronous operation processor (asychronous operation processor) Call an asynchronous operation of a handle and run to the end , The asynchronous operation processor is usually implemented by the operating system kernel . After the asynchronous operation is completed , The asynchronous operation processor generates the corresponding completion event . According to the handle targeted by the operation , The asynchronous operation processor inserts the completion event into the completion event queue corresponding to the handle (completion event queue) in , The queue holds completion events to be multiplexed to the corresponding completion handler .

Asynchronous event demultiplexer (asynchronous event demultiplexer) It's a function , It waits for the completion event that will be inserted into the completion event queue after the asynchronous operation is completed . Then the asynchronous event resolver function deletes one or more completion events from the queue , And return it to the caller .
The driver (proactor) Provide event loops for application processes or threads . In this event cycle , The driver invokes an asynchronous event demultiplexer , Wait for the completion event to happen . When the event arrives , The asynchronous event resolver returns . Then the driver multiplexes the event to the corresponding completion program , And assign the appropriate hook method to the handler , To handle the results of the completion event .

Start the program (initiator) It is an entity inside the application , It calls the asynchronous operation of the asynchronous operation processor . Usually, the startup program processes the result of the asynchronous operation called , under these circumstances , It plays the role of completing the handler .

4. Realization
The participants in the active mode can be divided into two layers :
· Multichannel decomposition / Allocate infrastructure layer components . This layer follows the general , Application independent policies perform asynchronous operations . It also demultiplexes and assigns completion events of asynchronous operations to corresponding completion handlers .
· Components of the application layer . This layer defines asynchronous operations and specific completion handlers that execute service processing related to applications .
1) Divide application services into asynchronous operations and completion handlers . In order to realize the driver mode , The activation of asynchronous operations through handles in application services must be separated from the processing of the results of these operations . The result of this activity is a set of asynchronous operations , A set of completion handlers , And the association between a set of asynchronous operations and completion handlers .
2) Define the completion handler interface . The interface in the completion handler consists of one or more hook methods . These hook methods represent the completion processing of application related completion events , These completion events are generated after the asynchronous operation is completed .
2.1) Define a type that passes the results of asynchronous operations . When the asynchronous operation is completed or cancelled , The result of the completion event must be passed to the completion handler . These results indicate whether the asynchronous operation succeeded or failed , And the number of bytes successfully transferred .
2.2) Determine the type of assignment target . There are two types of completion handlers that can be associated with handles , And as the target of the driver allocation mechanism : Object and function pointers .
2.3) Define the completion handler allocation interface policy . Single method allocation interface strategy and multi method allocation interface strategy .
3) Implement asynchronous operation processor .
3.1) Define asynchronous operation interface . Different parameters can be passed to asynchronous operations , Such as handle 、 Data buffer 、 Buffer length and information required to perform completion processing after the operation is completed . When designing the program interface of the starter to call the asynchronous operation of the asynchronous operation processor , There are two problems to be solved :
· Try to increase portability and flexibility .
· Effectively , Simply handle multiple completion handlers , Driver and completion event queue .
3.2) Select the asynchronous operation processing mechanism . When the initiator calls an asynchronous operation , The asynchronous operation processor performs the operation without blocking the control thread of the initiator . An asynchronous operation processor provides a mechanism for managing asynchronous completion identification and asynchronous execution of operations . When the operation ends, it also generates a completion event , And insert the event into the appropriate completion event queue .
Some asynchronous operation processors allow the initiator to cancel the asynchronous operation , But the completion of the event still needs to happen . such , The completion handler can correctly reuse asynchronous completion tags and other resources .
4) Define the driver interface . The application uses the driver interface to call an event loop , Delete the completion event from the completion event queue , Demultiplex the completion event to the corresponding completion handler and assign the corresponding hook method .
5) Implement the driver interface .
5.1) Develop the driver implementation layer .
5.2) Select the completion event queue and asynchronous event demultiplexer mechanism .
·FIFO Multichannel decomposition . This type of asynchronous event resolver function waits for the completion event corresponding to any asynchronous operation associated with the completion event queue , Delete these events according to the insertion order of these completion events .
· Selective multiplexing . This type of asynchronous event multiplexer function selectively waits for a specific subset of events to complete , These completion events must be explicitly passed when the function is called .
5.3) Determine how to multiplex completion events to completion handlers . An effective way to multiplex completion events to completion handlers , The concise strategy is to use the asynchronous completion tag pattern . Using this strategy , Once the program is started, it calls the asynchronous operation , The asynchronous operation processor will receive information to guide the subsequent completion of processing .
When the asynchronous operation is completed , The asynchronous operation processor generates the corresponding completion event , Associate completion events with asynchronous completion tags , And insert the modified completion event into the corresponding completion event queue . After the asynchronous event demultiplexer removes the completion event from its completion event queue , The driver implementation can be used as an asynchronous completion marker for completion events in constant time O(1) Inner multiplexed to the specified completion handler .
5.4) Determine how to assign hook methods to the specified completion handler .
5.5) Define the specific driver implementation .
6) Determine the number of drivers in the application .
7) Implement the specific completion handler .
7.1) Determine the strategy for maintaining the state of the specific completion handler .
7.2) Select the mechanism to configure the specific completion handler with the handle .
7.3) Realize the function of completing the handler .
8) Realize the startup program .
5. Conclusion
advantage :
1) Transaction separation .
2) Portability .
3) Encapsulation of concurrency mechanism . One advantage of separating the driver from the asynchronous operation processor is that the application can configure the driver with different concurrency strategies , Without affecting other application components and services .
4) Separate threading from concurrency control .
5) performance .
6) Simplify application synchronization .
Insufficient :
1) The scope of application is limited .
2) Programming 、 Debugging and testing complexity .
3) Asynchronously scheduled 、 Control and cancel the operation being performed
Receiver - The connector (Acceptor - Connector)
1. problem
In connection oriented networked systems , Applications usually contain a considerable number of configuration agents for establishing connections and initializing Services . Most of these configuration codes are independent of the processing of data exchanged between connection transmission endpoints by the service . Therefore, close coupling between configuration code and service processing code is not ideal , Because this cannot solve the following four mandatory conditions :
1) It should be easy to change the connection role , To support different application features .
2) It should be easy to add services , Types of service implementations and communication protocols , It does not affect the existing connection establishment and service initialization configuration code .
3) The change of connection establishment and service initialization strategy is less frequent than that of the communication protocol and service implemented by the application .
4) For large-scale networked systems , It should be possible to use advanced operating system features , Such as asynchronous connection mechanism to reduce the connection establishment delay .
2. Solution
Connect and initialize peer services in networked applications , Separate from the processing performed by these services after connection and initialization .
To be specific : Encapsulate application services in peer service handlers . Each service handler implements half of the end-to-end services in networked applications . Use two factories to connect and initialize peer services : Receptors and connectors . The two factories cooperate with each other , Create a full association between two peer service handlers and their two connected transport endpoints , Each transport endpoint is encapsulated in a transport handle .
The receiver factory represents the relevant peer service handler , Passively establish a connection after the connection request event sent by the remote peer service handler arrives . In turn, , The connector factory actively establishes a connection with the specified remote peer service handler on behalf of the peer service handler .
After the connection is established , The receiver and connector factory initialize the corresponding peer service handler , Send them their respective transfer handles . The peer service handler then uses the transport handle to exchange data through the connected transport endpoint , Conduct application related processing . Generally speaking , After connection and initialization , The service handler does not interact with the receiver and sender .
3. structure
The transmission endpoint of passive mode is a factory , It listens for connection requests , Accept connection requests and establish transfer handles , The transport endpoint of the new connection is encapsulated in the transport handle . You can exchange data by reading and writing the corresponding transmission handle through the connected transmission endpoint .
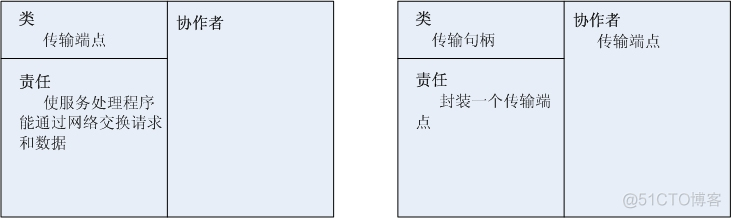
The service handler defines half of the end-to-end services in the network system . In this end-to-end service, a specific service handler usually has both the client role and the server role . In the case of peer-to-peer use , It can play these two roles at the same time . A service handler provides an activation hook method , Used to initialize after connecting to the service handler of its peer . in addition , The service handler also includes a transport handle that encloses the transport endpoint , Such as data mode socket handle . Once connected , The service handler uses the transport handle to exchange data with the peer service handler through their connection to the transport endpoint .

The receiver is a factory , Its functions include passively establishing the connected transmission endpoint , Create and initialize related transport handles and service handlers . One receiver provides two methods : Connection initialization and connection completion , These two methods realize the above functions with the help of passive mode transmission endpoint .
When calling the initialization method , The receiver binds the passive mode transmission endpoint to a transmission address , Like a TCP The port number and IP The host address , It passively listens for connection requests .
When the connection request arrives , The connection completion method of the receiver is as follows 3 A step :
· First , It uses the passive mode transport endpoint to create a connected transport endpoint , And encapsulate the endpoint in the transport handle .
· second , It creates a service handler , Used to process data requests made by peer service handlers through connected transport endpoints .
· Third , It stores the transfer handle in the corresponding service handler , Then call the activation hook method of the service handler , This method lets the service handler complete initialization by itself .
The connector is also a factory , The functions it realizes include the transmission endpoint that actively establishes the connection , Initialize its corresponding transport handle and service handler . It provides 2 A way : Connection start and connection completion methods .
Pass the connection start method to an existing service handler , This method establishes a transmission endpoint for it and the receiver . As introduced earlier , The receiver must be listening for connection requests on a transport address .
Separate the connection start method and completion method of the connector , This enables the connector to support transparent synchronous and asynchronous connection establishment .
· For synchronization , The connector that activates the connection request blocks its caller , Until the transmission endpoint is connected . in the future , The connector directly calls the activation hook method of the service handler .
· For asynchronous cases , Run connection requests asynchronously , The activation method of the connector returns immediately . Only after the connector is notified that the transport endpoint has completed the connection asynchronously , The connection completion method activates the service handler .

Whether connecting the transmission endpoint synchronously or asynchronously , Upload and input the endpoint in the connection , Both the receiver and the connector initialize a service handler by calling its activation hook method . in the future , Service handlers generally do not need to interact with connector and receiver factories .
The allocator is responsible for demultiplexing different types of service requests ( Such as connection request and data request ) Indication event of .

· For receptors , The allocator demultiplexes connection indication events received from one or more transport handles that encapsulate the transport endpoint . Multiple receivers can register the same allocator , The allocator listens for them for connection requests from peer connectors .
· For connectors , The allocator demultiplexes completion events that arrive in response to asynchronously activated connections . To deal with this situation , The connector registers itself with an allocator , To receive these connection completion events , Then the allocator runs its event loop . When the completion event arrives , It notifies the corresponding connector . Then the connector calls the activation hook method of the specified service handler , Let the service handler initialize itself . therefore , An allocator and connector can activate and complete connections asynchronously on behalf of multiple service handlers .
Be careful , Asynchronous connection establishment does not require the use of allocators , Because the thread that starts the connection will be blocked by waiting for the connection completion event . therefore , This thread can directly activate the service handler .
Specific service handlers define some end-to-end services related to applications , This part of the service is activated by a specific receiver or connector . The specific receiver uses the specific service handler . Transport endpoints and transport handles used by these service handlers to instantiate generic receivers . Similarly , Specific connectors also instantiate generic connectors .
4. Realization
Receiver - The components in the connector pattern can be decomposed into the following three layers :
· Multichannel decomposition / Allocate infrastructure layer components . This layer implements a general application independent event allocation strategy .
· Connect management components . This layer implements general application independent connection and initialization Services .
· Application layer components . This layer customizes the general strategies of the upper two layers , It uses subclass derivation , Object composition and / Or instantiation of parameterized types , To create concrete components that are used to establish connections , Exchange data and perform service related processing .
1) Realize multiplexing / Allocate infrastructure component layer .
1.1) Select the transmission mechanism , These mechanisms include :
· Passive mode transport endpoint component .
· Connected transport endpoint components .
· Transmission address component .
· Transfer handle component .
1.2) Implement the allocation mechanism . These mechanisms consist of allocators and event handler components . The dispatcher is responsible for matching the request to the corresponding receiver , Connectors are associated with service handlers . The event handler defines the event handling interface provided by the service in the event driven application .
2) Implement the connection management component layer . This layer is responsible for creating service handlers , Actively or passively connect the service handler to the remote service handler , And activate the service handler after connecting . All components in this layer are common , And depends on specific IPC Mechanism , Specific service handlers , Specific receptors and specific connectors . There are three main components in the connection management layer : Service Handler , Receptors and connectors .
2.1) Define a common service handler interface . The service handler provides a common interface , It is by the client , Server or both in end-to-end services ( Client and server ) Jointly defined Services . This interface includes initializing the service handler , Execute the services it defines and maintain the IPC Mechanism and other methods .
2.2) Define a general receiver interface . Implement a common strategy in the receiver component , This strategy is used to passively establish connections , The established initialization specific service handler , These specific service handlers use these connections to exchange data with peer service handlers . An initialization method is also defined in the receiver , For applications to call this method , It is used to notify other applications in the network of its passive mode transmission endpoint .
2.3) Implement a general receiver method . The application initializes the receiver by calling its initialization method . When calling the initialization method, there should be a specified transmission address ( Such as local host IP Name and TCP Port number ) Parameters of . The receiver uses this address parameter to listen for connection requests initiated by the peer connector . It passes this address through the concrete receiver subclass of the receiver or through typed parameters to the concrete configured in the general receiver IPC Connection mechanism . then IPC The connection mechanism initializes the passive mode transmission endpoint of the receiver , Tell its address to the remote application that wants to establish a connection with the receiver .
2.4) Define common connector interfaces . The connector component implements a common strategy for actively establishing connections and initializing service handlers , These service handlers are responsible for handling request and response events on the connection .
2.5) Implement the general connector method . Connectors for applications connect() Method to start a connection , Specific connectors can use this template method , Modify the active connection strategy transparently without changing the connector interface and implementation . therefore ,connect() Leave the specific steps in the connection strategy to the hook method , Specific connectors can overload these hook methods for personalized operations .
3) Implement the components of the application layer . This layer implements specific service handlers , Specific receptors and specific connectors .
5. Conclusion
advantage :
1) Reusability , Portability and scalability . Receiver - The connector pattern separates the mechanism of connecting and initializing service handlers from the service processing that follows . Application independent mechanisms in receivers and connectors are reusable components .
2) Robustness, . Receiver - The connector pattern separates the service handler from the receiver . This separation ensures that passive mode transmission endpoints cannot be used for reading / Writing data . This increases type safety , It can eliminate a kind of error that often occurs when using weak type network programming interface .
3) Efficiency . Receiver - Connector mode can actively establish connections with a large number of hosts asynchronously and efficiently in a wide area network with great delay .
Insufficient :
1) Increased indirection . Compared with directly using the underlying network programming interface , Receiver - Connector mode is not direct .
2) Added complexity . For connecting to only one server , A simple client application that uses a single network programming interface to execute a service , Receiver - Connector patterns add unnecessary complexity . However, using a common receiver and connector wrapper appearance can keep developers from thinking about boring , Error prone and non portable low-level network programming mechanism , This simplifies the design of the application .
http proxy server (3-4-7 Layer of the agent )- Network event library common component 、 kernel kernel drive Camera drive tcpip Network protocol stack 、netfilter、bridge Seems to have seen !!!! But he that doeth good Don't ask future -- Height and weight 180 Fat man
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Bookmark
做BI开发,为什么一定要熟悉行业和企业业务?

抖音实战~评论数量同步更新
close系统调用分析-性能优化
What is business intelligence (BI), just look at this article is enough
Machine learning notes mutual information

Why do you have to be familiar with industry and enterprise business when doing Bi development?
Sorting and sharing of selected papers, systems and applications related to the most comprehensive mixed expert (MOE) model in history

B站大量虚拟主播被集体强制退款:收入蒸发,还倒欠B站;乔布斯被追授美国总统自由勋章;Grafana 9 发布|极客头条
From repvgg to mobileone, including mobileone code
随机推荐
QT—绘制其他问题
283. Moving zero-c and language assisted array method
El tree combined with El table, tree adding and modifying operations
New intersectionobserver usage notes
Cloudcompare & open3d DBSCAN clustering (non plug-in)
HDU - 2859 Phalanx(DP)
抖音实战~评论数量同步更新
Enabling digital economy Fuxin software attends the BRICs high level Forum on Sustainable Development
制作条形码的手机App推荐
HUAWEI nova 10系列发布 华为应用市场筑牢应用安全防火墙
迷失在Mysql的锁世界
Solve the problem of data disorder caused by slow asynchronous interface
gtest从一无所知到熟练使用(4)如何用gtest写单元测试
VS2019 C# release下断点调试
el-tree结合el-table,树形添加修改操作
The drawing method of side-by-side diagram, multi row and multi column
sqlserver对数据进行加密、解密
Why should garment enterprises talk about informatization?
面试题 01.01. 判定字符是否唯一
MongoDB中的索引操作总结