当前位置:网站首页>链式二叉树的基本操作(C语言实现)
链式二叉树的基本操作(C语言实现)
2022-07-07 16:50:00 【Brant_zero】
目录
本篇博客学习的是最普通的链式二叉树,这个结构在实际应用的中的作用并不是很大,但是我们仍要学习这个结构。学习这个结构的目的是为了以后我们研究更复杂的树型结构打下基础。废话不多说,直接开始。
目录
一、链式二叉树的创建
首先我们来创建一颗树,创建一棵树分为以下三个步骤:①定义树中结点的结构②创建新结点③将结点链接起来;这样就可以一个树就被建立了起来。
1.1 定义节点结构
//节点的创建
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;1.2 节点的创建
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}1.3 节点的链接
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
//链接
node1->left = node2; // 1
node1->right = node4;// 2 4
node2->left = node3;// 3 # 5 6
node4->left = node5;// # # # # # #
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}二、树的深度遍历
树我们是创建好了,接下来我们来观察一下我们树的链接情况,此时就要遍历一遍树。但是树的结构特殊,不同于我们之前学的数组,遍历起来很方便。于是引申出以下几种遍历方式。
1. 前序、中序、后序遍历
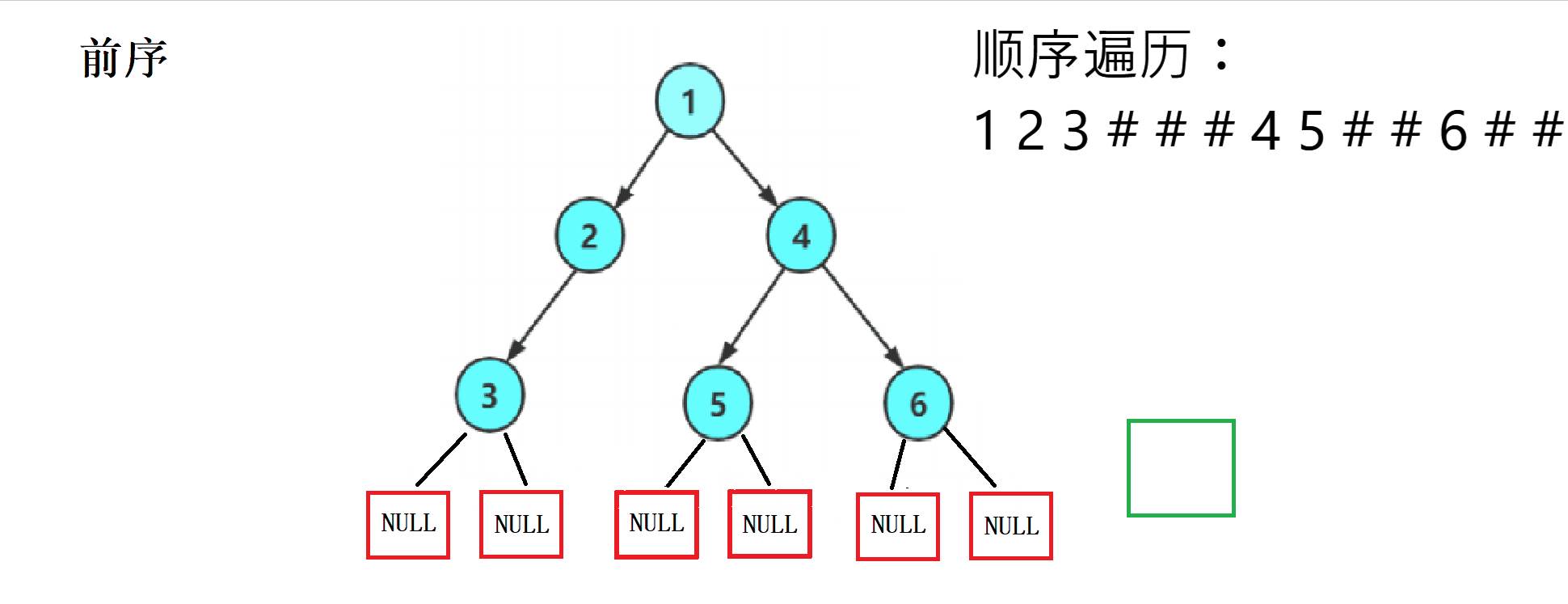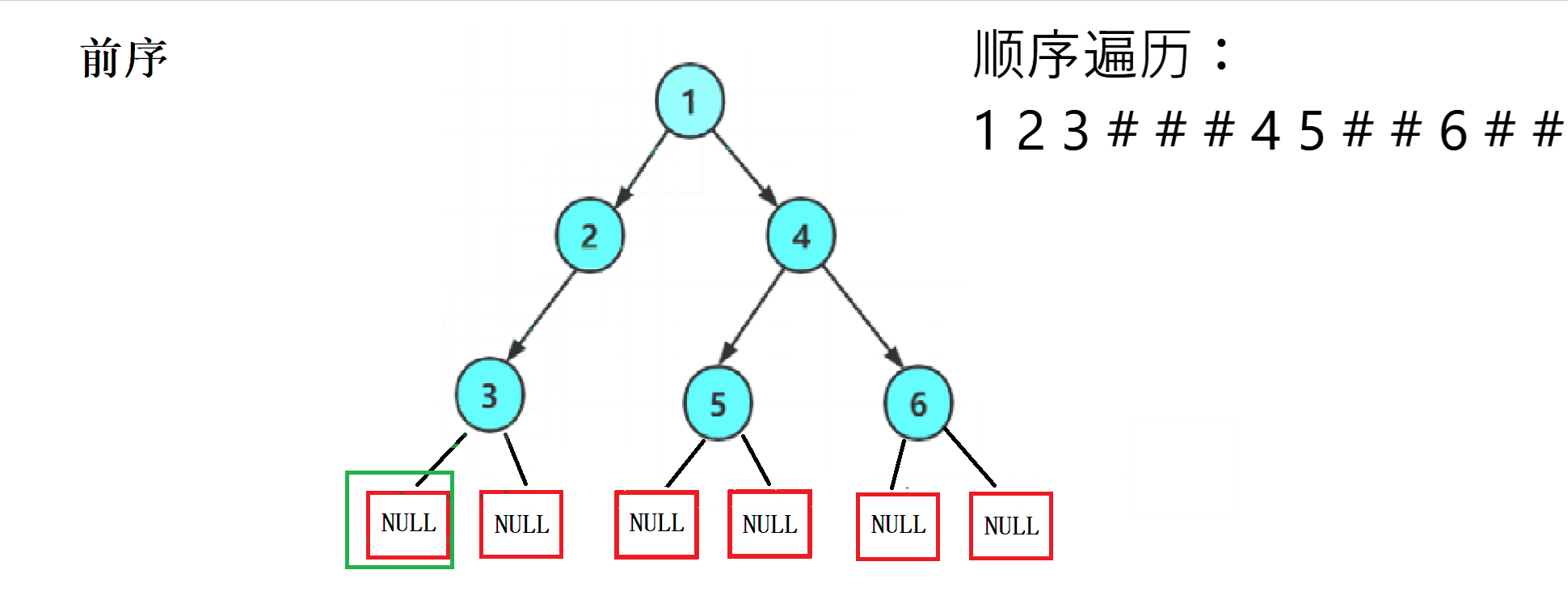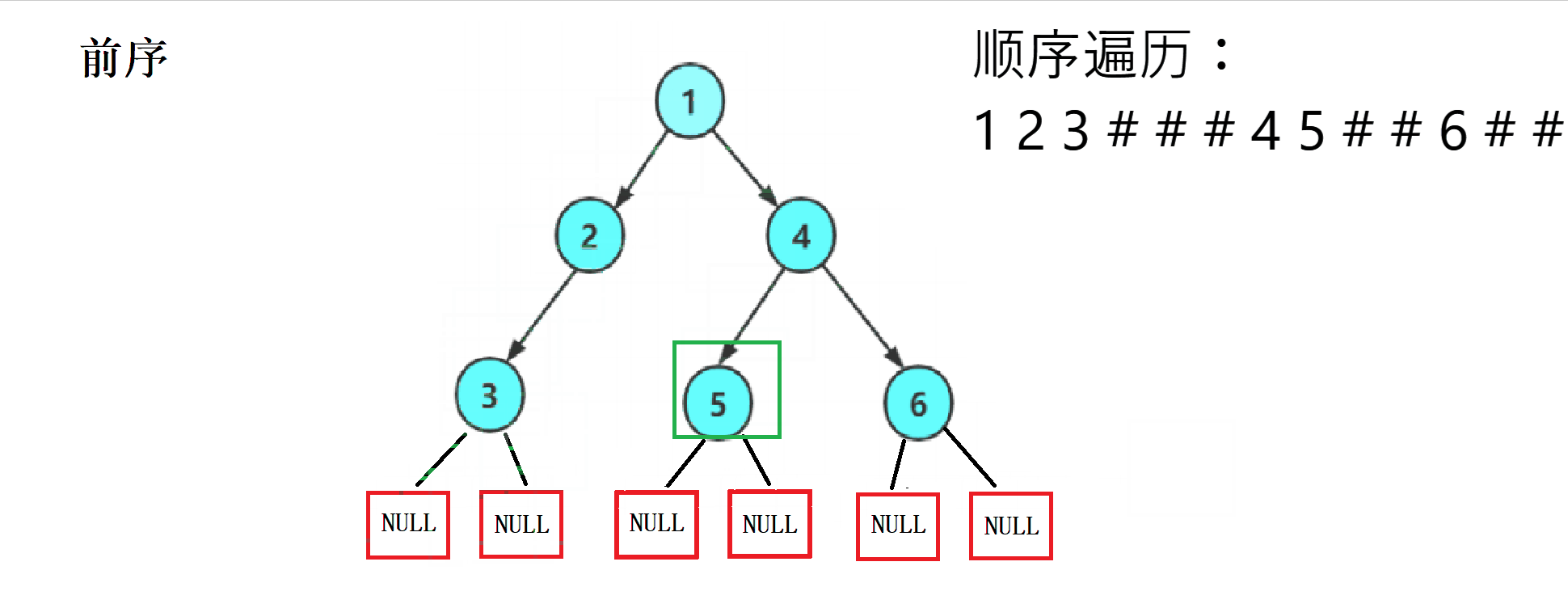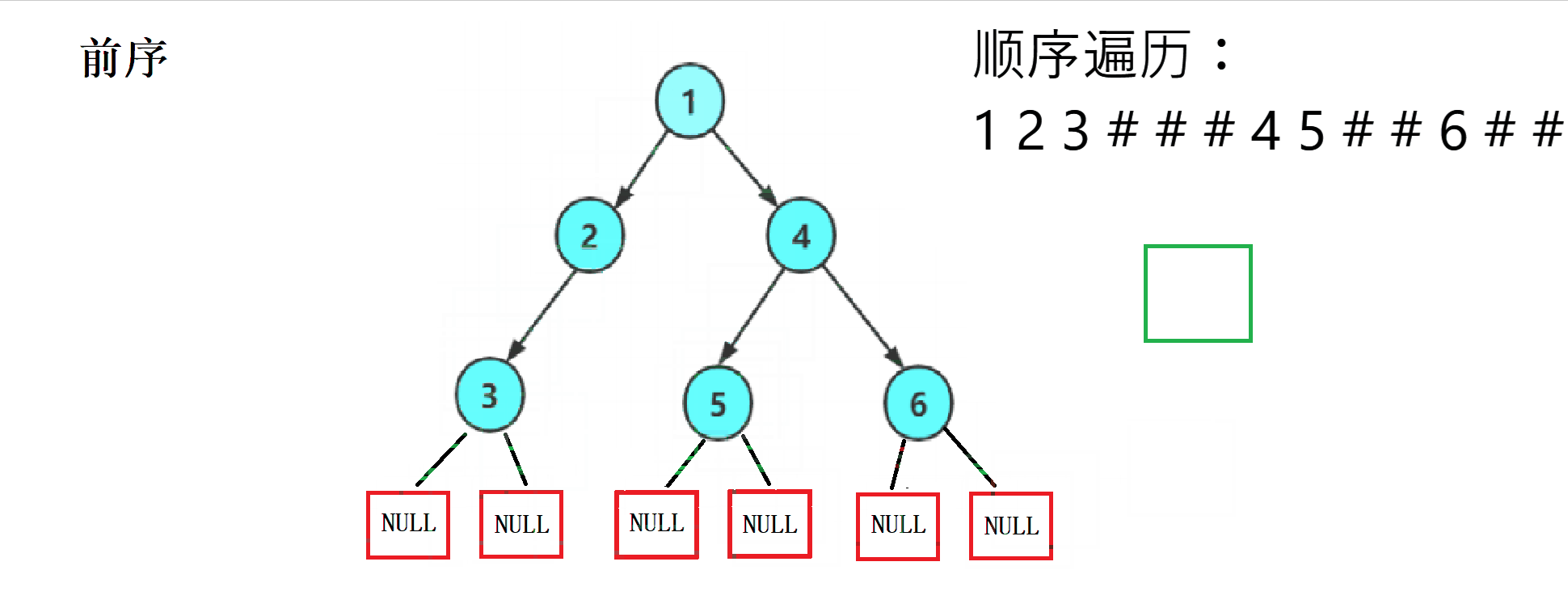
三种方式的访问顺序
前序——( 根 --> 左子树 --> 右子树)
中序——( 左子树 --> 根 --> 右子树)
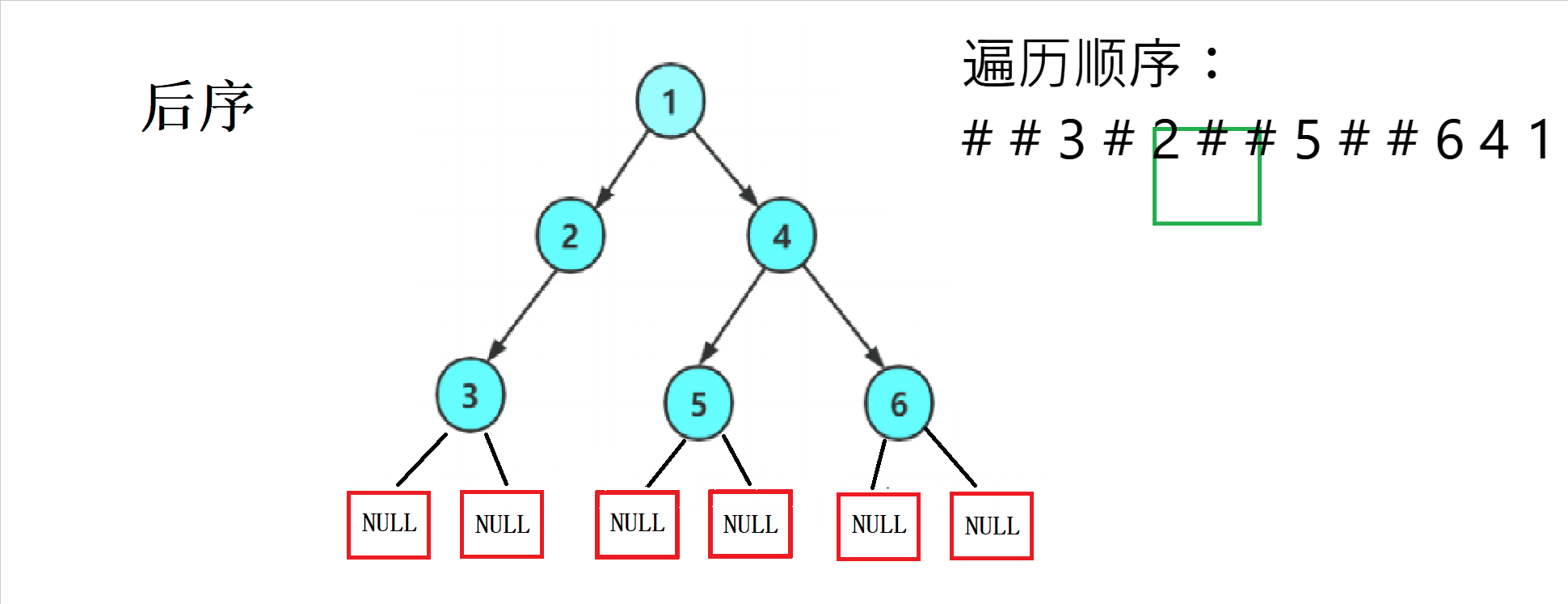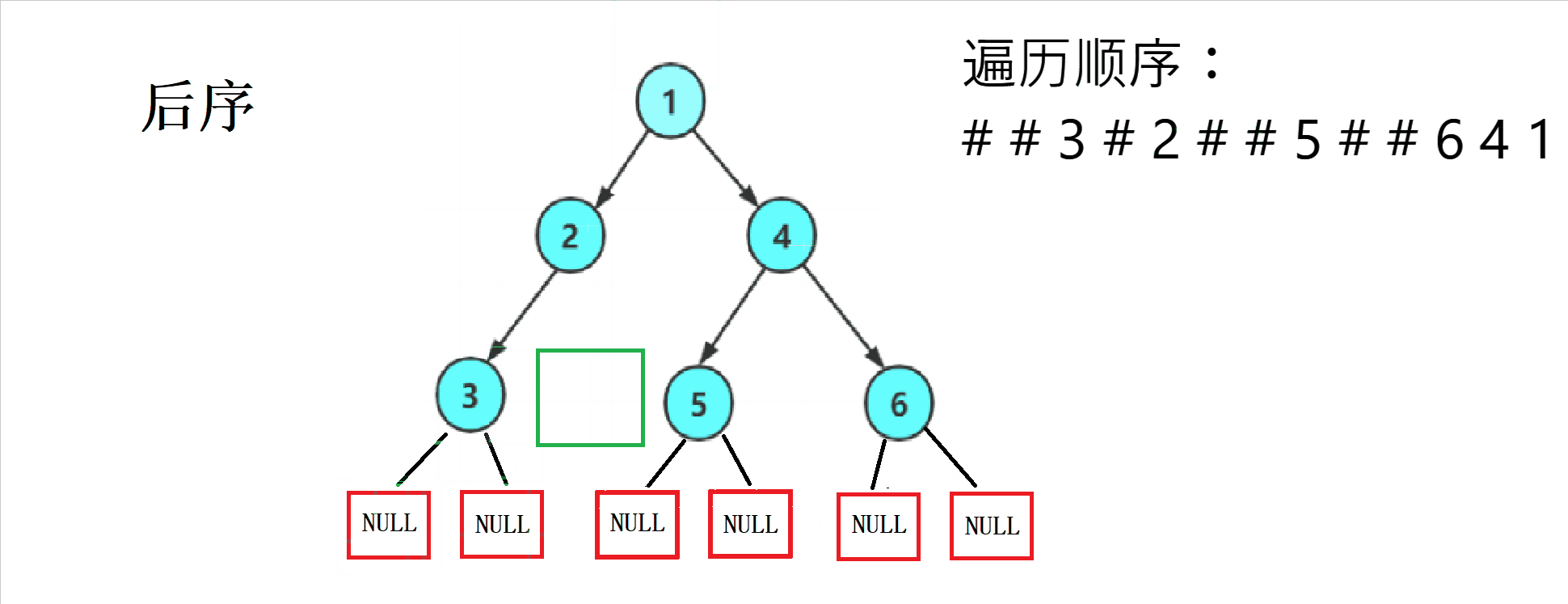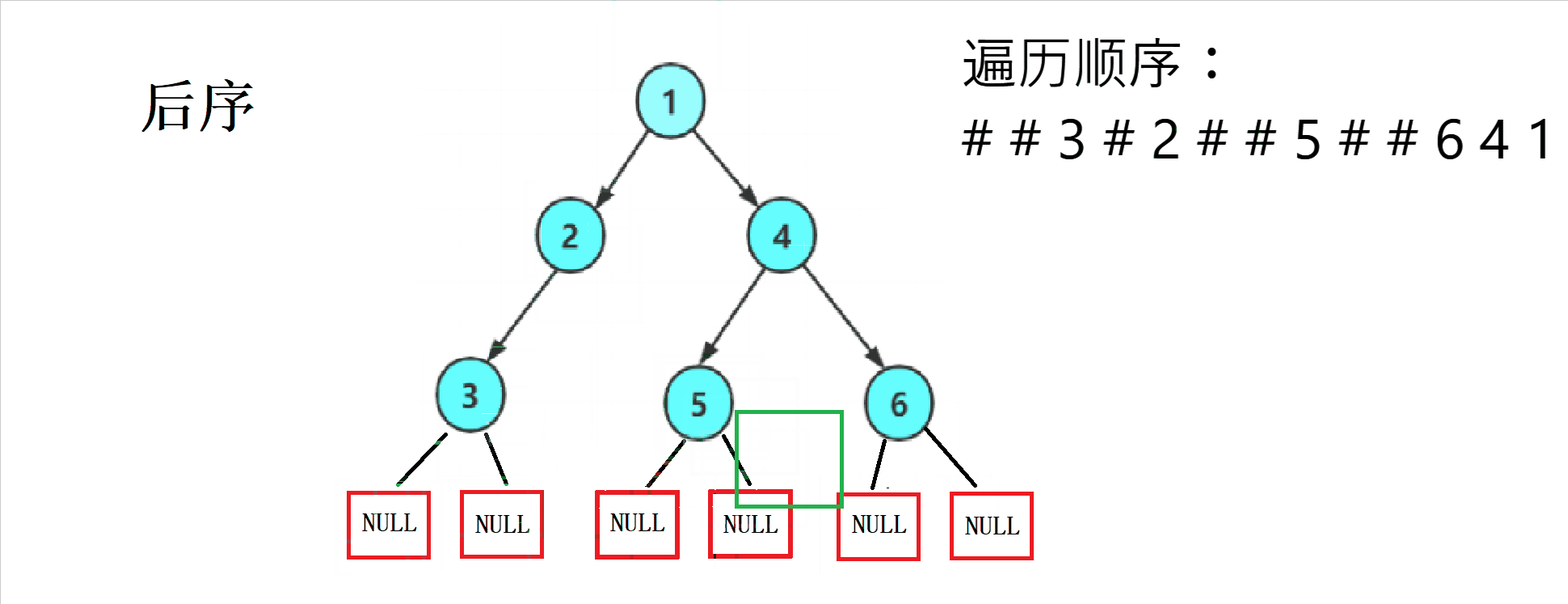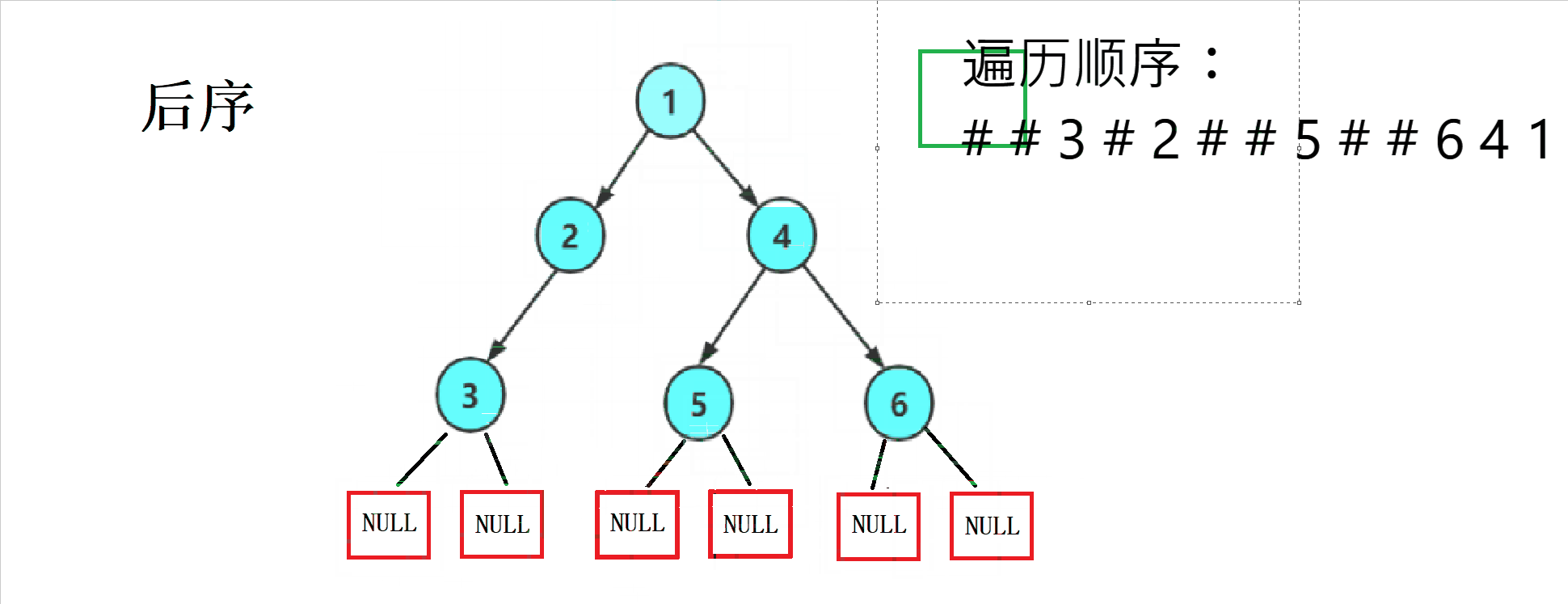
后序——( 左子树 --> 右子树 --> 根)
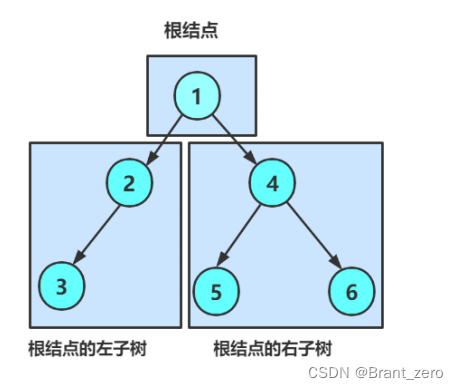
1.2 三种方式的遍历顺序图

2. 代码实现
这遍历规律性强,我们使用递归可以很容易的写出来,并将每个为NULL的位置打印一个#作为代替。
前序遍历
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}中序遍历
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}后序遍历
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}3. 遍历检测
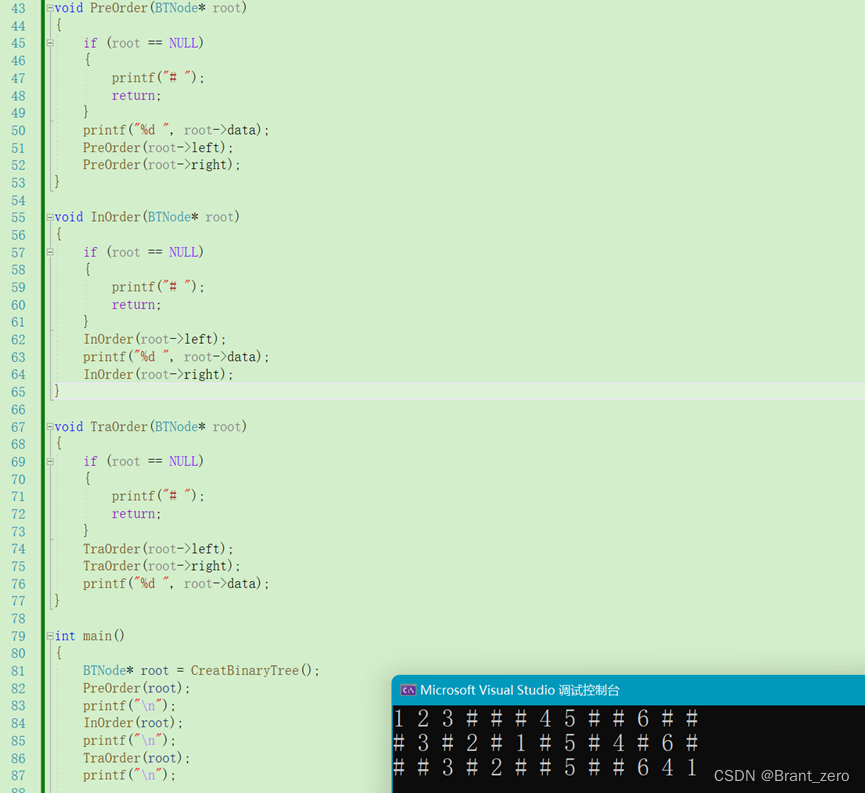
三、树的层序遍历
完成了以上三种深度遍历后,肯定有人想问了,如果我像按照一层一层的顺序来遍历怎么实现呢?
层序遍历的实现需要在队列的辅助下才能实现,具体怎么实现我们往下看。
3.1 层序遍历
思想:
①将根结点放入队列中。
②弹出队头元素并打印,然后将队头元素的左结点和右节点依次放入队列
③重复以上操作直到队列为空,即可一层一层地遍历完整个树。
因为,如果左子树或右子树为空,就不会往队列里放了,这样前面的结点会按照前进先出的规律依次出队列,既可达到我们层序遍历的目的。
//层序遍历
//思想 放一个根节点 弹出一个根节点 连着存放左节点和右节点,
//队列为空的时候为空就不放了
void LevelOrder (BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
//队列不为空就继续以上操作
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//出对头的数据
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestroy (&q);
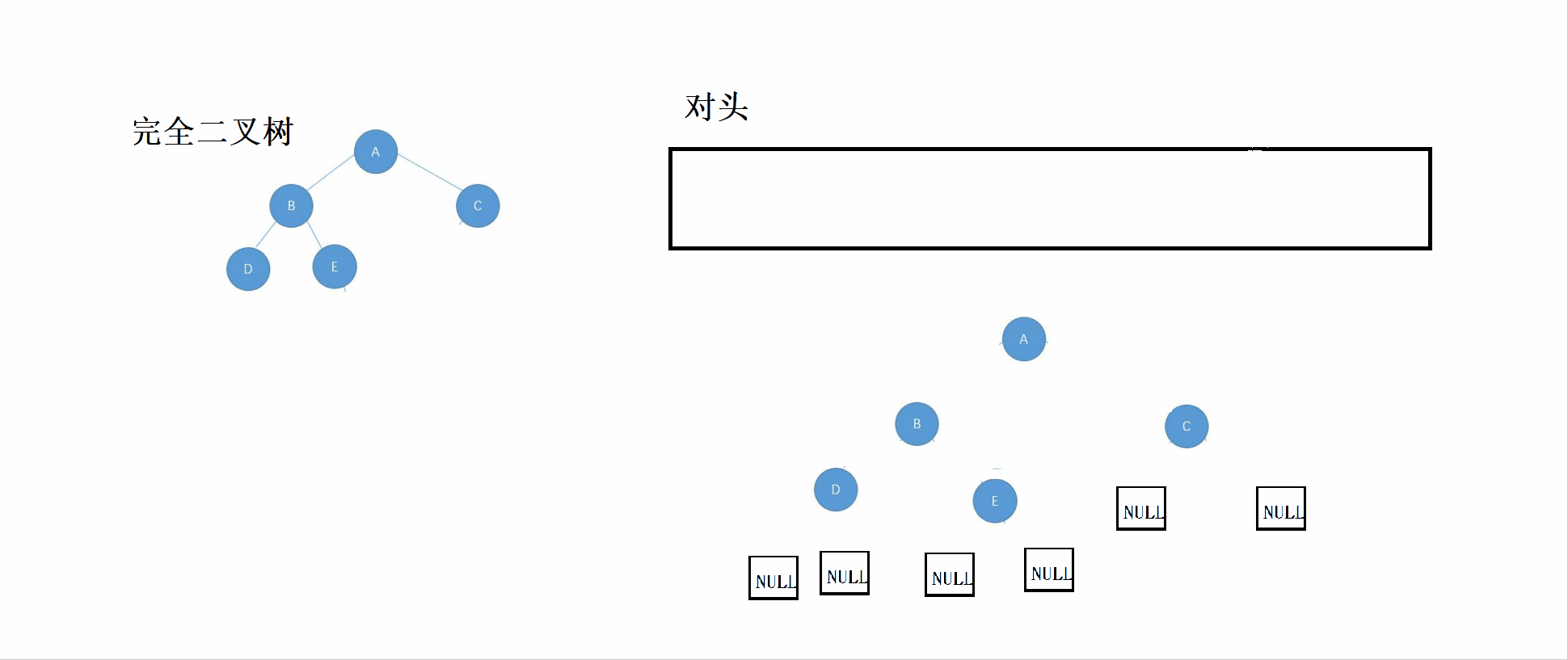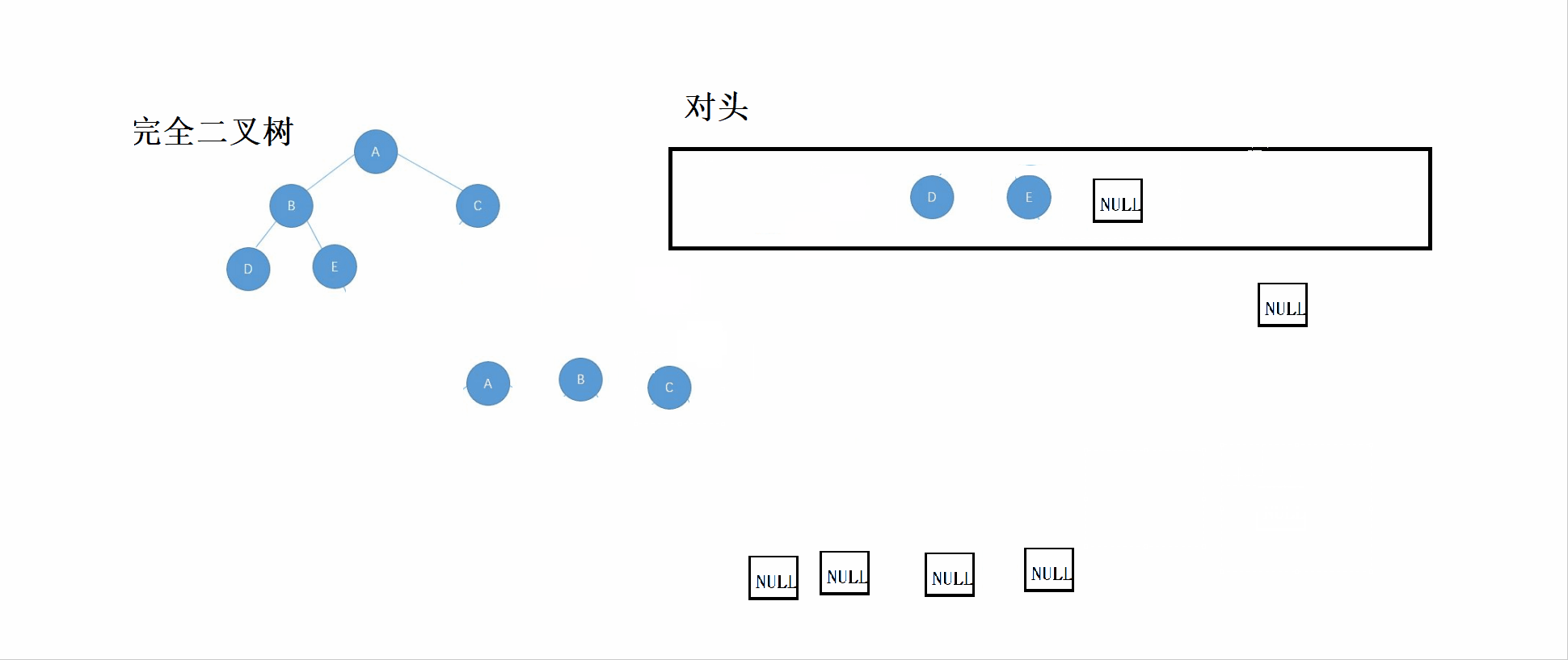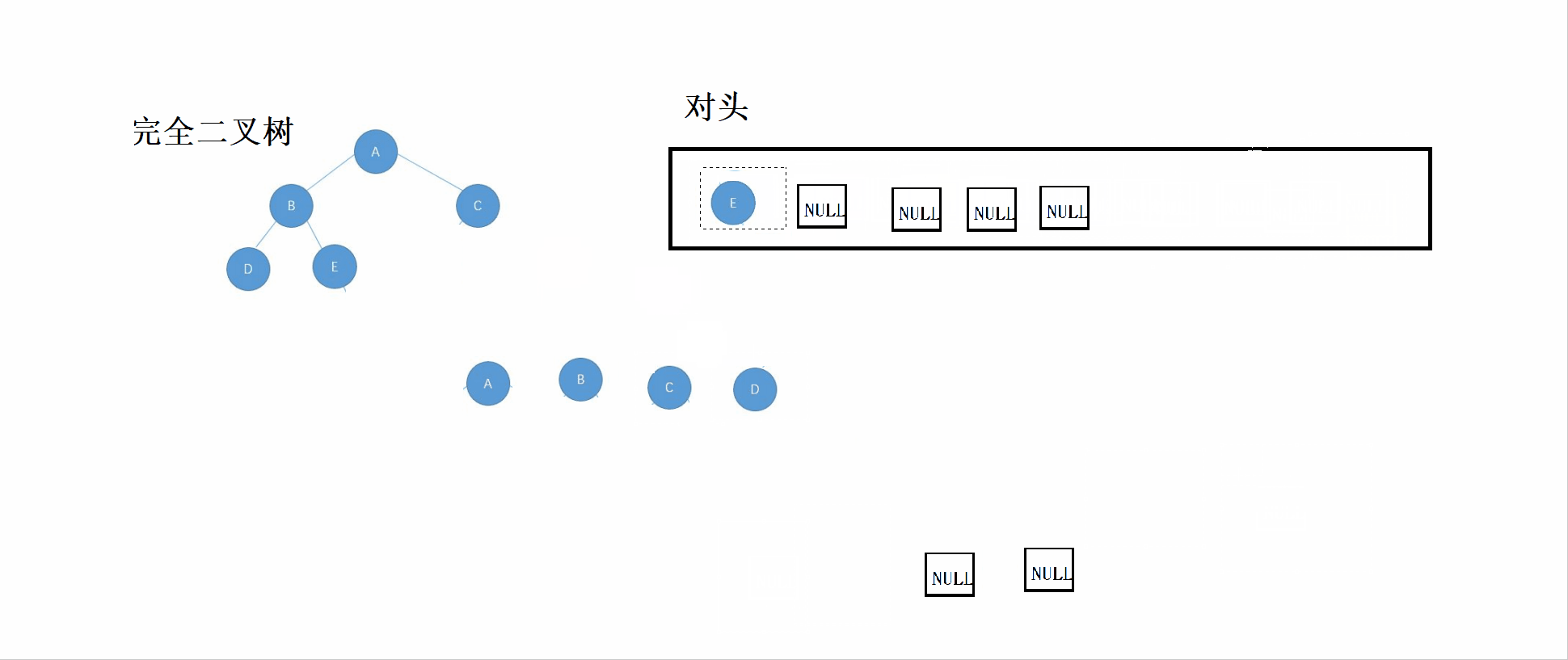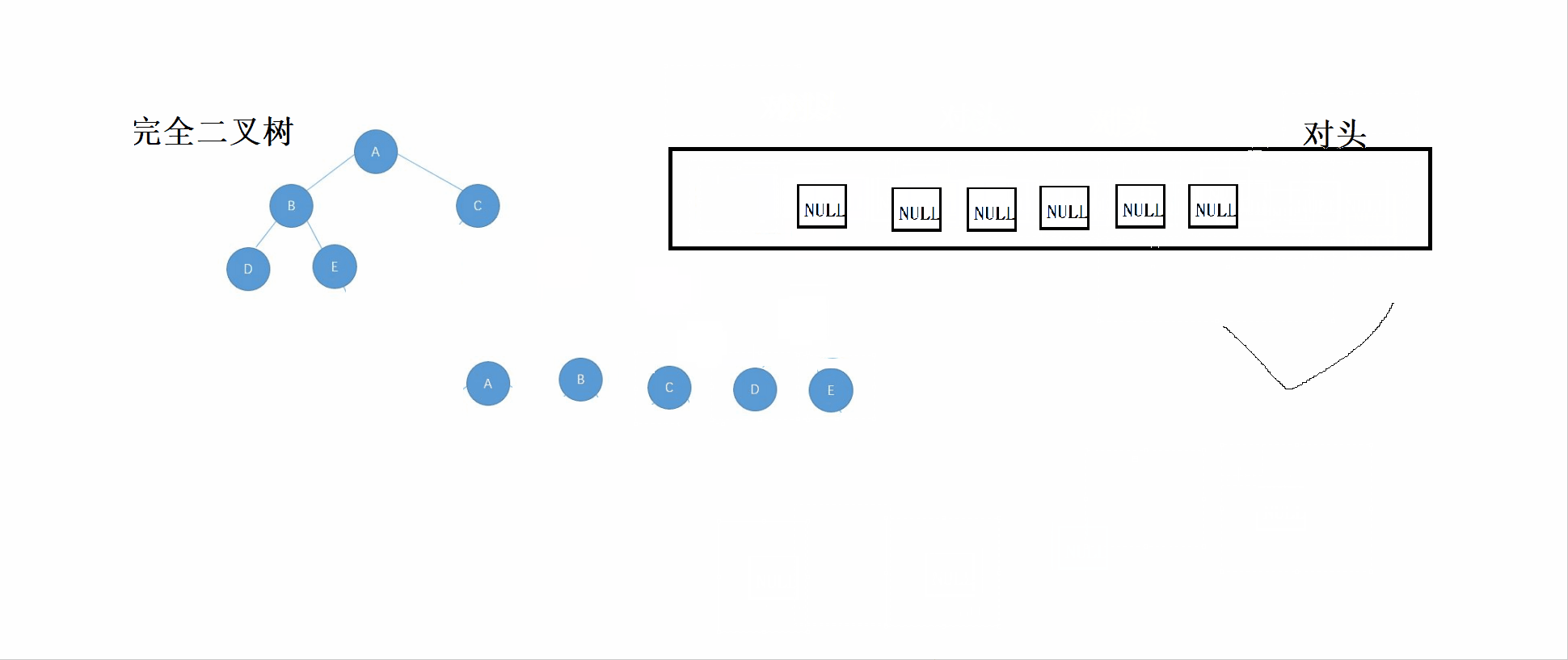
}3.2 完全二叉树的鉴定
完全二叉树:n-1层为满,最后一层不满,而满二叉树是一种特别的完全二叉树。
思想:
①根据层序遍历的规则,依次将根结点、左子树、右子树放入队列
②如果对头数据为NULL,则停止插入队列。
③对该队列进行检查,如果NULL的后面有非NULL结点,则表示该树不是完全二叉树,直到队列为空(即完全二叉树最后一个结点过后全为NULL结点)。
先看这个GIF图,然后可以结合代码看理解。

//判断当前树是否是完全二叉树
//如果空后面还有非空,就不是完全二叉树
bool TreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
else
{
//遇到空则跳出层序遍历
break;
}
//1.如果后面全是完全二叉树
//2.如果空后面还有非空,则不是完全二叉树
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
return false;
}
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}四、树的基本功能
实现了树的遍历还远远不够,我们这里来实现一下更常见的功能。
4.1 树中节点的个数
//求节点的个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}4.2 树中叶子节点的数量
//求叶子节点的数量的两种写法
int TreeLeafSize1(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return ((root->left == NULL) && (root->right == NULL)) ? 1 :
TreeLeafSize1(root->left) + TreeLeafSize1(root->right) ;
}4.3 第k层节点的数量
//求第k层节点的数量
//1.转化为求左子树的k-1层,右子树的k-1层
int KLeveSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return KLeveSize(root->left, k - 1) + KLeveSize(root->right, k - 1);
}4.4 查找树的节点
//查找树的节点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
/*if (TreeFind(root->left, x) )
return TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (TreeFind(root->right, x))
return TreeFind(root->right, x);*/
//以上方法会深部遍历两次 不推荐
BTNode* LeftNode = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (LeftNode)
return LeftNode;
BTNode* RightNode = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (RightNode)
return RightNode;
return NULL;
}4.5 树的深度
//求二叉树的深度
int TreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int left = TreeDepth(root->left);
int right = TreeDepth(root->right);
return left > right ? left+1 : right+1;
}4.6 树的销毁
//二叉树的销毁
//后序遍历销毁
void TreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
TreeDestory(root->left);
TreeDestory(root->right);
//本不应在 检查使用
//free之前打印一下释放的情况
printf("\n%p : %d ", root,root->data);
free(root);
}二叉树相对于前面的栈和队列难度有所提升,要对递归比较熟悉,大家可以结合画图慢慢消化。递归类的代码不好调试,大家可以结合深度遍历以打印的方式来观察,或者在电脑画图板上走读代码理解。
本篇博客到此就结束了,二叉树还是很有难度的,接下来会做一些练习然后开始学习堆,希望大家持续关注。
边栏推荐
- 单臂路由和三层交换的简单配置
- 线程池和单例模式以及文件操作
- [trusted computing] Lesson 10: TPM password resource management (II)
- [principles and technologies of network attack and Defense] Chapter 5: denial of service attack
- 用存储过程、定时器、触发器来解决数据分析问题
- PHP面试题 foreach($arr as &$value)与foreach($arr as $value)的用法
- [C language] string function
- Introduction of common API for socket programming and code implementation of socket, select, poll, epoll high concurrency server model
- socket编程之常用api介绍与socket、select、poll、epoll高并发服务器模型代码实现
- 2022年理财有哪些产品?哪些适合新手?
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
[principle and technology of network attack and Defense] Chapter 6: Trojan horse
Tips for this week 140: constants: safety idioms
Static routing configuration
手撕Nacos源码(先撕客户端源码)
Three forms of multimedia technology commonly used in enterprise exhibition hall design
Unlike the relatively short-lived industrial chain of consumer Internet, the industrial chain of industrial Internet is quite long
持续测试(CT)实战经验分享
【软件测试】从企业版BOSS直聘,看求职简历,你没被面上是有原因的
Tips of this week 141: pay attention to implicit conversion to bool
Skills of embedded C language program debugging and macro use
[trusted computing] Lesson 10: TPM password resource management (II)
强化学习-学习笔记8 | Q-learning
静态路由配置
Tips for short-term operation of spot silver that cannot be ignored
Differences between rip and OSPF and configuration commands
6.关于jwt
【塔望方法论】塔望3W消费战略 - U&A研究法
Thread pool and singleton mode and file operation
回归测试的分类
Summary of debian10 system problems



![学习open62541 --- [67] 添加自定义Enum并显示名字](/img/98/e5e25af90b3f98c2be11d7d21e5ea6.png)
![[论文分享] Where’s Crypto?](/img/27/9b47bfcdff8307e63f2699d6a4e1b4.png)