当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode 314. Binary tree vertical order traversal - Binary Tree Series Question 6
LeetCode 314. Binary tree vertical order traversal - Binary Tree Series Question 6
2022-07-05 02:17:00 【CP Coding】
Given the root of a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from top to bottom, column by column).
If two nodes are in the same row and column, the order should be from left to right.
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Example 2:

Input: root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7] Output: [[4],[9],[3,0,1],[8],[7]]
Example 3:

Input: root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7,null,null,null,2,5] Output: [[4],[9,5],[3,0,1],[8,2],[7]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
The topic requires traversing the binary tree in vertical order , It's from the top to the bottom , Nodes in the same column are put into an array , The final result is a two-dimensional array composed of all column arrays . About the definition of columns : Suppose the column number of a node is col, Then its left child node is col-1, The column number of the right child node is col+1.
Because we are familiar with the horizontal sequence traversal algorithm , Therefore, this problem is based on horizontal sequence traversal , Assign a column number to each node , In this way, node values with the same column number can be put together . First, specify the column number of the root node as 0, Then traverse in horizontal order , In this way, the column number of the node on the left of the root node is negative , Starting from the root node, the column number decreases every time you move to the left 1; The column number of the node on the right of the root node is positive , Starting from the root node, the column number will be added at every position to the right 1; The column number of the node in the same column as the root node is 0. For ease of handling , You can use a two-dimensional array to store the root node and all the columns on its left , The index of an array is the opposite of the column number ( That is, the column number is 0, -1, -2, ... The corresponding array index is 0, 1, 2, ...), Then use a two-dimensional array to store all the columns on the right of the root node ( Because the column number is 0 To the left array , Therefore, the column number is 1, 2, 3, ... The corresponding array index is 0, 1, 2, ...). So when doing horizontal traversal , You can put the node in the corresponding position of the left or right array in real time according to the column number . For the left array , Whenever the absolute value of the column number is equal to the total number of arrays, a new column is added ; For the right array , Whenever the column number is greater than the total number of arrays, a new column is added .
def verticalOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
llist, rlist = [], []
lindex, rindex = 0, 1
q = deque([(root, 0)])
while q:
n = len(q)
for i in range(n):
node, index = q.popleft()
if index <= 0:
if len(llist) > -index:
llist[-index].append(node.val)
else:
llist.append([node.val])
else:
if len(rlist) > index - 1:
rlist[index - 1].append(node.val)
else:
rlist.append([node.val])
if node.left:
q.append((node.left, index - 1))
if node.right:
q.append((node.right, index + 1))
llist.reverse()
return llist + rlist
边栏推荐
- R语言用logistic逻辑回归和AFRIMA、ARIMA时间序列模型预测世界人口
- 85.4% mIOU! NVIDIA: using multi-scale attention for semantic segmentation, the code is open source!
- Action News
- Prometheus monitors the correct posture of redis cluster
- PHP Joseph Ring problem
- Es uses collapsebuilder to de duplicate and return only a certain field
- Abacus mental arithmetic test
- Write a thread pool by hand, and take you to learn the implementation principle of ThreadPoolExecutor thread pool
- Which common ports should the server open
- Process scheduling and termination
猜你喜欢
Visual explanation of Newton iteration method
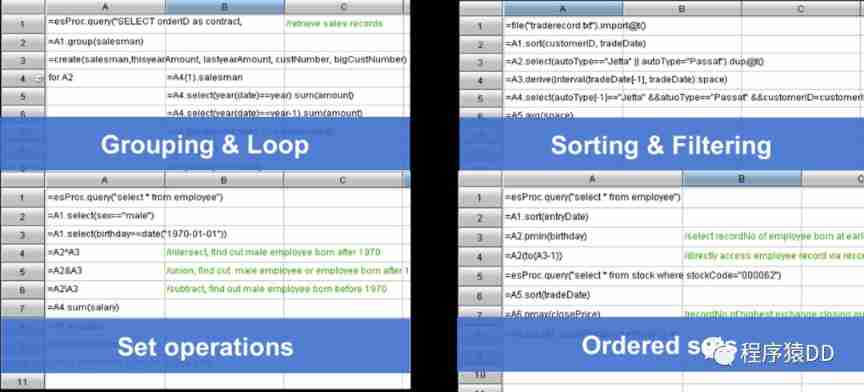
Open source SPL optimized report application coping endlessly
JVM's responsibility - load and run bytecode
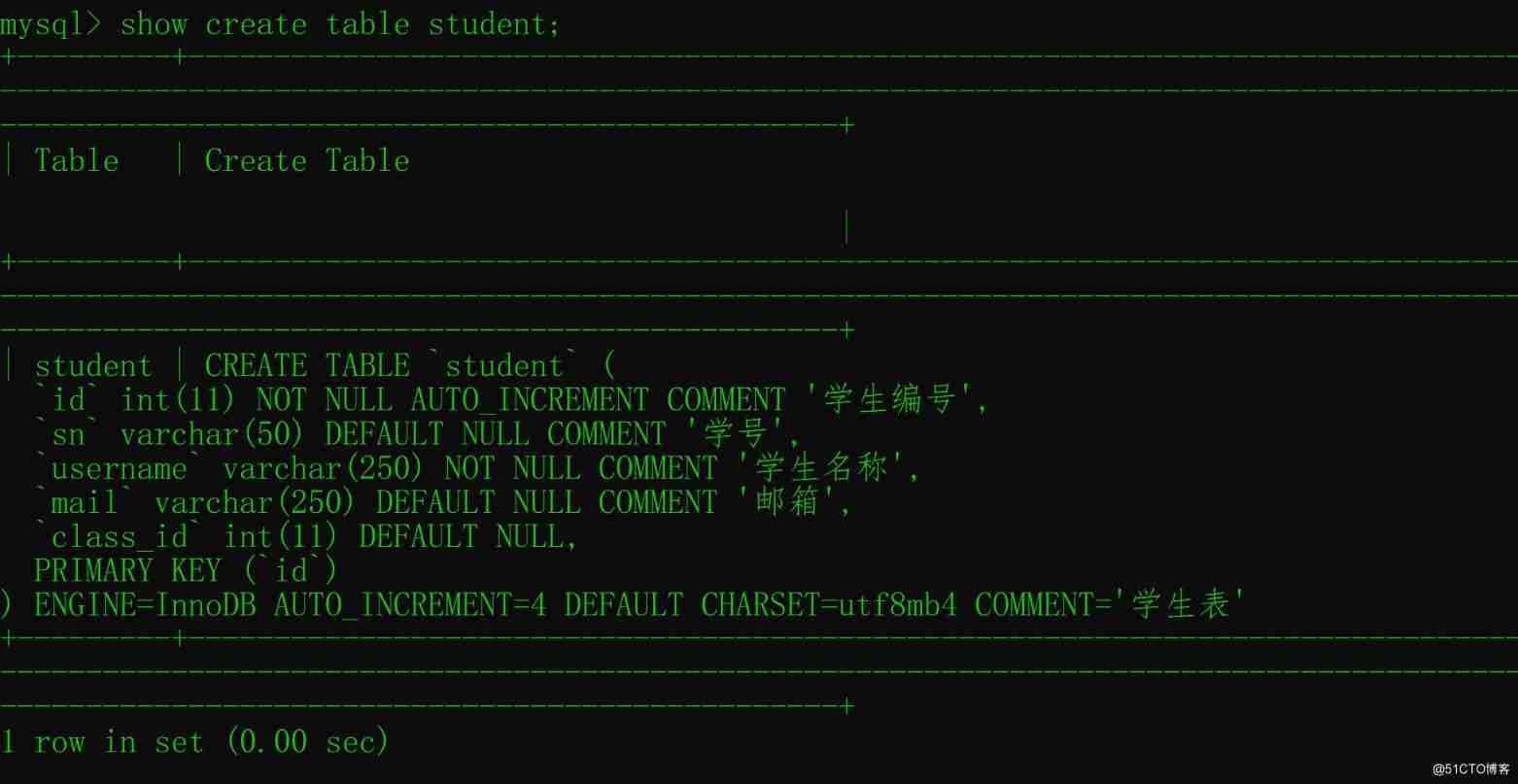
Five ways to query MySQL field comments!
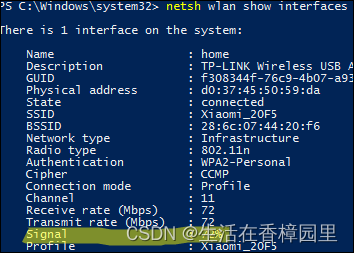
Win: use PowerShell to check the strength of wireless signal
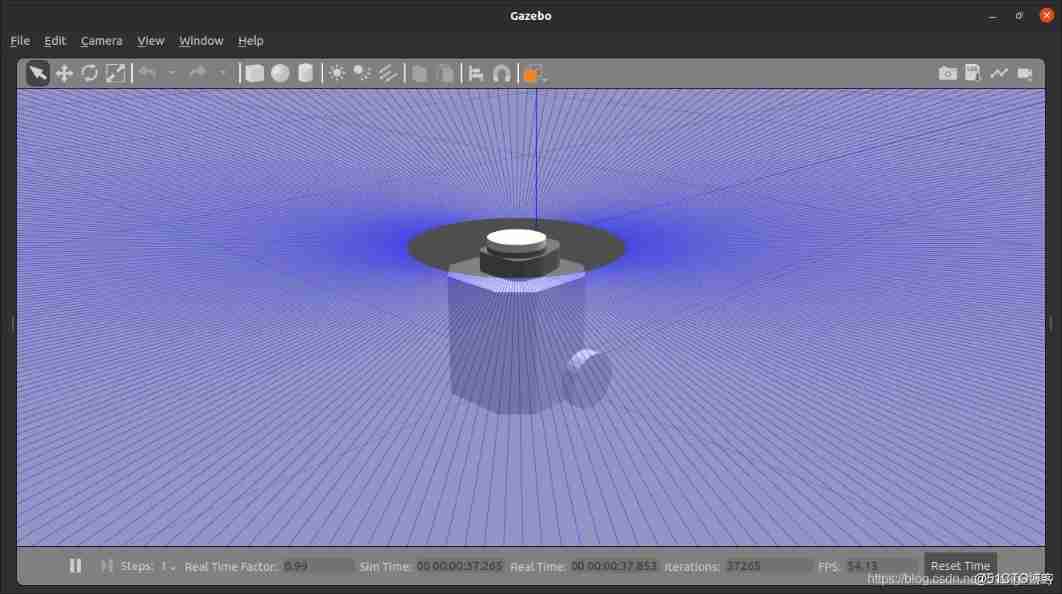
Interesting practice of robot programming 14 robot 3D simulation (gazebo+turtlebot3)

Android advanced interview question record in 2022

runc hang 导致 Kubernetes 节点 NotReady

Mysql database | build master-slave instances of mysql-8.0 or above based on docker
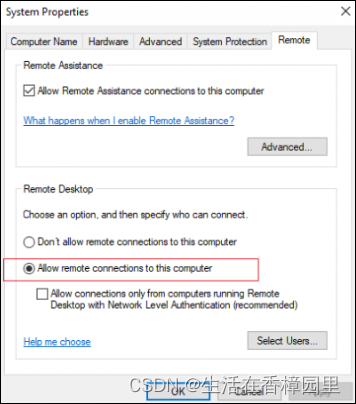
Win: use shadow mode to view the Desktop Session of a remote user
随机推荐
Tla+ through examples (XI) -- propositional logic and examples
Tucson will lose more than $400million in the next year
The perfect car for successful people: BMW X7! Superior performance, excellent comfort and safety
MATLB|多微电网及分布式能源交易
Win: use PowerShell to check the strength of wireless signal
The perfect car for successful people: BMW X7! Superior performance, excellent comfort and safety
Talk about the things that must be paid attention to when interviewing programmers
Limited query of common SQL operations
Grub 2.12 will be released this year to continue to improve boot security
A tab Sina navigation bar
Pytorch register_ Hook (operate on gradient grad)
WCF: expose unset read-only DataMember property- WCF: Exposing readonly DataMember properties without set?
PHP Joseph Ring problem
Icu4c 70 source code download and compilation (win10, vs2022)
"2022" is a must know web security interview question for job hopping
Huawei machine test question: longest continuous subsequence
He was laid off.. 39 year old Ali P9, saved 150million
Summary and practice of knowledge map construction technology
Win: enable and disable USB drives using group policy
PowerShell: use PowerShell behind the proxy server