当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Global Round 19 ABC
Codeforces Global Round 19 ABC
2022-07-05 01:37:00 【Vijurria】
The main idea of the topic : Given a length of n Array of a, We can subscript 1~n-1 Select a number from flag So it can be divided into two sections , And for this [1,flag] [flag,n] The values of the two intervals are sorted in non descending order ( Not strictly ascending ).
If the whole sequence is not sorted in ascending order, it will be output YES, Otherwise NO.
input
3 3 2 2 1 4 3 1 2 1 5 1 2 2 4 4output
YES YES NO
It is found that as long as a number exists, it is not in its place , It cannot be transformed into a non descending sequence .( Because its operability is extremely strong , Subscript exists in 1~n-1 In the range of )
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[200200],b[200200];
int main()
{
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
b[i]=a[i];
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
bool flag=false;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i]!=b[i]) flag=true;// Non descending order
}
if(flag==false) cout<<"NO"<<endl;
else cout<<"YES"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}The main idea of the topic : Given a size of n Array of a, Find the sum of the values of all its sub segments .
Its value is defined as the number of segments + Of all segments MEX The sum of the .(mex: The smallest natural number that has never appeared )
If you can delete a few from the beginning ( Maybe zero or all ) Elements and delete a few from the end ( Maybe zero or all ) Elements come from y get x, The array x It's an array y Subsegment .
input
4 2 1 2 3 2 0 1 4 2 0 5 1 5 0 1 1 0 1output
4 14 26 48
The first one involved in the calculation in the code for loop , Obviously, what is easy to see is the sum of interval lengths ! Such as [1 3 5 4 2], Divided into multiple sub segments, that is, a single length has 5 individual , Double length ones have 4 individual , There are three 3 individual , Four have 2 individual , There are five 1 individual ··· By analogy, the length of other intervals .
If you know the length of the interval, you should find the length of each interval mex 了 . It's amazing , Look at the picture get

In fact, why are you looking for 0 Just do it ? Because if not 0 When the number of , It may not be able to find smaller numbers or need larger numbers to fill in the range it participates in , So it doesn't make much sense , But individually, they are 0, It doesn't matter whether you add it or not . So we just need to see 0 And the number of intervals it participates in .
The number of intervals is equal to the number !!!
【 Why was it the same idea when I wrote last night, but I didn't see these figures 0 How to find the way ???( Autistic )】
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[200200];
int main()
{
//cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
sum+=i*(n-i+1);
//cout<<sum<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i]==0) sum+=i*(n-i+1);
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}The main idea of the topic : Given a length of n Sequence a, Let's subscript 2~n-1 All the numbers of are moved to the subscript 1 Or subscript n The place of . The rules of moving are :Select(i,j,k): choice 3 An index 1≤i<j<k≤n, Make No j Piles contain at least 2 A stone , Then he started from the pile j Remove from 2 A stone , And put a stone into i In the pile , Put a stone in k In the pile .
Ask us : Move all the stones to the pile 1 And heaps n What is the minimum number of operations required ? Or determine whether it is impossible .
It is impossible to output -1.
input
4 5 1 2 2 3 6 3 1 3 1 3 1 2 1 4 3 1 1 2output
4 -1 1 -1
Quite apart from the a1 and an, see 2~n-1 In order to know the number of operation steps , If it's an even number, just 2, Odd numbers 2 Round up again . Here we can get the minimum number of steps .
that -1 What do you think of the situation ? Even numbers can be divided, so don't think , If the number is odd, the title is given j Must be in >=2 To participate in mobile , So it is certain that when the middle row is all 1 He couldn't move when he was ; From the example given, we can see that when there is n==3 And when the middle is an odd number, it is actually equivalent to having one in the middle 1 He can't move .
The rest of the numbers can be moved to both sides by more or less moving times .
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[200200];
int main()
{
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
long long int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
long long int n,sum=0;
cin>>n;
for(long long int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
if(i>=2&&i<=n-1)
{
if(a[i]%2==1) sum+=(a[i]+1)/2;
else sum+=a[i]/2;
}
}
long long int sum1=0;
for(long long int i=2;i<=n-1;i++)
{
if(a[i]==1) sum1++;
}
if((n==3&&a[2]%2==1)||sum1==n-2) cout<<"-1"<<endl;
else cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}There is a hole here that it needs to be opened LL, Otherwise wa hey
————————————
D ah !dp ah , Come back another day ...
边栏推荐
- Mysql database | build master-slave instances of mysql-8.0 or above based on docker
- [FPGA tutorial case 10] design and implementation of complex multiplier based on Verilog
- Global and Chinese market of network connected IC card smart water meters 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Win: use shadow mode to view the Desktop Session of a remote user
- Five ways to query MySQL field comments!
- Armv8-a programming guide MMU (3)
- Basic operation of database and table ----- the concept of index
- Exploration and practice of integration of streaming and wholesale in jd.com
- PHP wechat official account development
- ROS command line tool
猜你喜欢

小程序容器技术与物联网 IoT 可以碰撞出什么样的火花
![[CTF] AWDP summary (WEB)](/img/4c/574742666bd8461c6f9263fd6c5dbb.png)
[CTF] AWDP summary (WEB)

PHP wechat official account development
Yyds dry inventory jetpack hit dependency injection framework Getting Started Guide
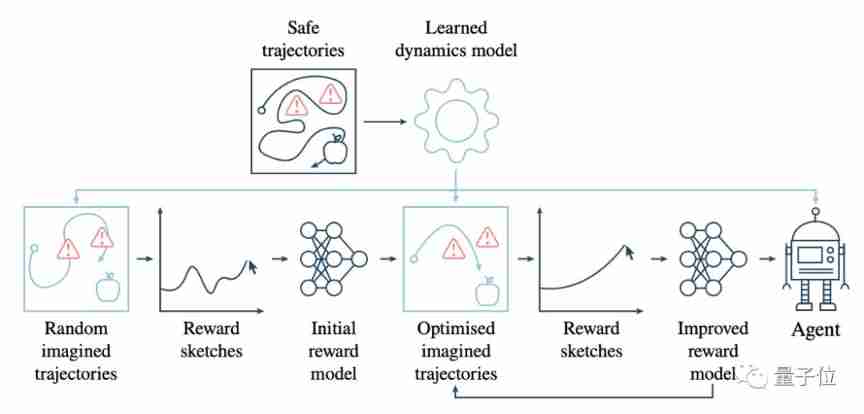
How to safely eat apples on the edge of a cliff? Deepmind & openai gives the answer of 3D security reinforcement learning
Application and Optimization Practice of redis in vivo push platform
【大型电商项目开发】性能压测-优化-中间件对性能的影响-40
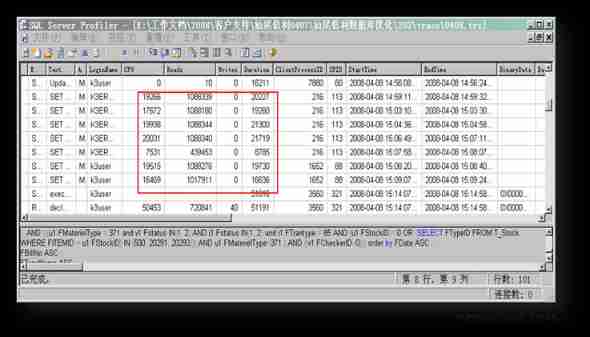
Database performance optimization tool
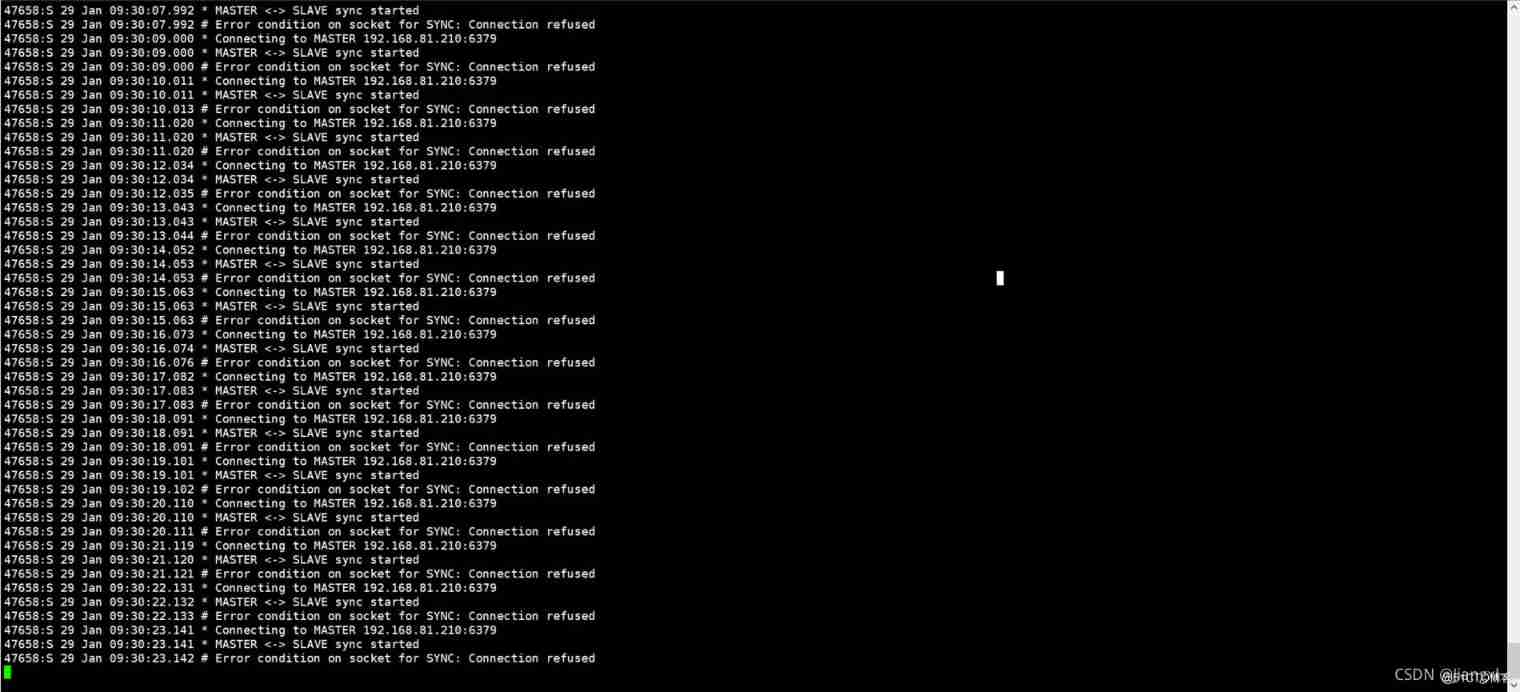
Redis master-slave replication cluster and recovery ideas for abnormal data loss # yyds dry goods inventory #
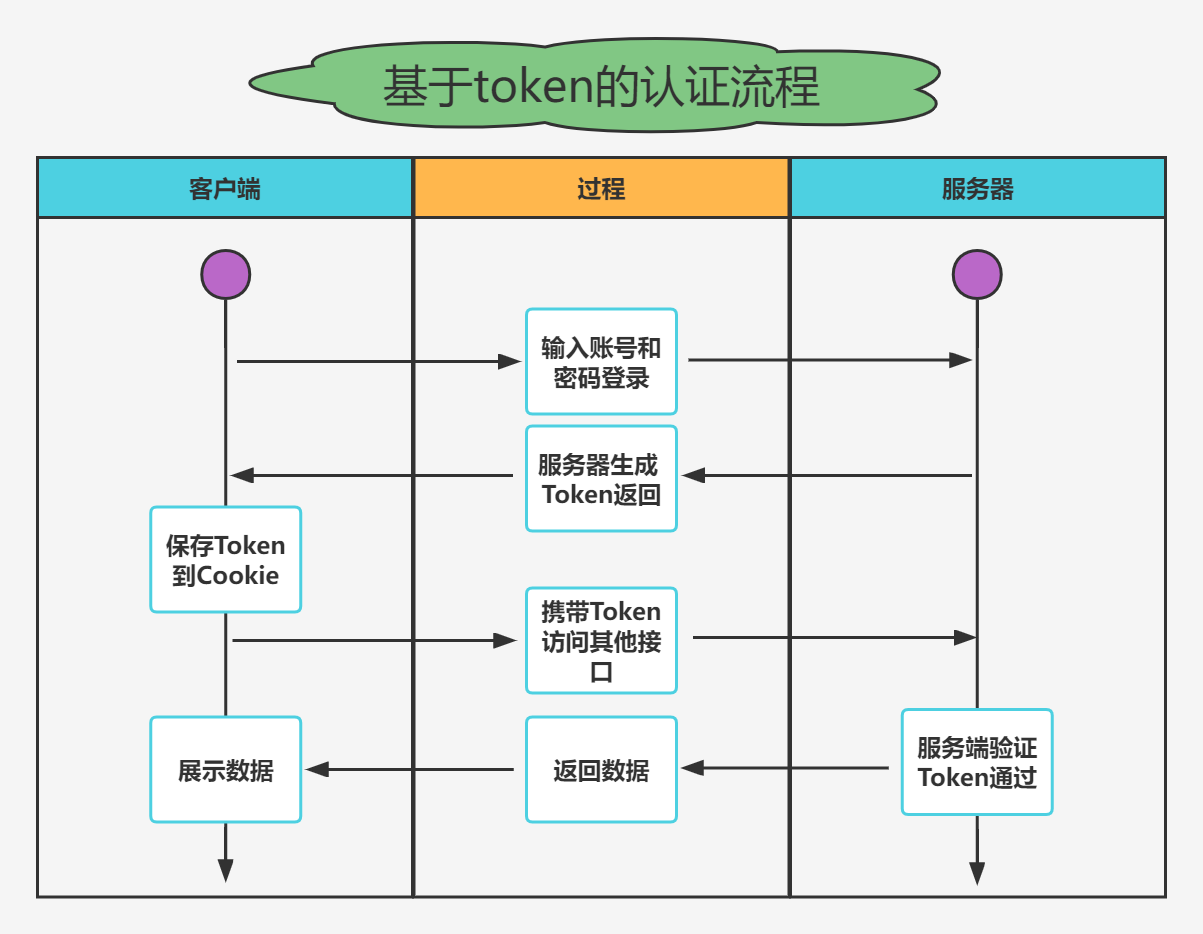
实战模拟│JWT 登录认证
随机推荐
Kibana installation and configuration
Incremental backup? db full
The perfect car for successful people: BMW X7! Superior performance, excellent comfort and safety
Nebula importer data import practice
What is the length of SHA512 hash string- What is the length of a hashed string with SHA512?
Express routing, express middleware, using express write interface
19. Delete the penultimate node of the linked list
Redis(1)之Redis简介
[Chongqing Guangdong education] National Open University spring 2019 1042 international economic law reference questions
JS implementation determines whether the point is within the polygon range
Basic operations of database and table ----- delete index
es使用collapseBuilder去重和只返回某个字段
Great God developed the new H5 version of arXiv, saying goodbye to formula typography errors in one step, and mobile phones can also easily read literature
微信小程序:星宿UI V1.5 wordpress系统资讯资源博客下载小程序微信QQ双端源码支持wordpress二级分类 加载动画优化
Lsblk command - check the disk of the system. I don't often use this command, but it's still very easy to use. Onion duck, like, collect, pay attention, wait for your arrival!
流批一体在京东的探索与实践
Database postragesq role membership
C语音常用的位运算技巧
WCF: expose unset read-only DataMember property- WCF: Exposing readonly DataMember properties without set?
Wechat applet: exclusive applet version of the whole network, independent wechat community contacts