当前位置:网站首页>List set data removal (list.sublist.clear)
List set data removal (list.sublist.clear)
2022-07-06 17:18:00 【Xiaobai said (๑• ๑)】
List Set data removal (List.subList.clear)
I have encountered such a problem these two days : A set of data is passed in as a parameter , Now? piecewise Use the data of this set , The used data needs to be removed from this set , It is convenient to obtain the data of the second paragraph .
hypothesis : The data length of a set is 11 individual , Now use this set in two paragraphs , The first paragraph uses 5 Data , Use of the second paragraph 6 Data , Achieve segmented use of set data . In order to get the data correctly , After obtaining the first data , Take the first five data from list Remove... From collection , Then get the second data , This also facilitates circulation .
At first I did this remove(), Remove data :
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("g");
list.add("k");
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
list.add("g");
list.add("h");
list.add("i");
// Simulate to get the first five numbers in the first paragraph
List<String> oneList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
oneList.add(list.get(i));
list.remove(i);
}
// After the simulation obtains the second paragraph 6 Number
List<String> twoList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
twoList.add(list.get(i));
list.remove(i);
}
}
because ArrayList It's not thread safe , It is obviously not appropriate to do this in the cycle , Problems are likely to occur in concurrency .
So I changed another way ,removeAll(), remove List Data in :
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("g");
list.add("k");
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
list.add("a");
list.add("a");
list.add("a");
// Simulate to get the first five numbers in the first paragraph
List<String> oneList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
oneList.add(list.get(i));
}
list.removeAll(oneList);
// After the simulation obtains the second paragraph 6 Number
List<String> twoList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
twoList.add(list.get(i));
}
list.removeAll(twoList);
}
Notice that the data in the set has changed , This is also the change I found later :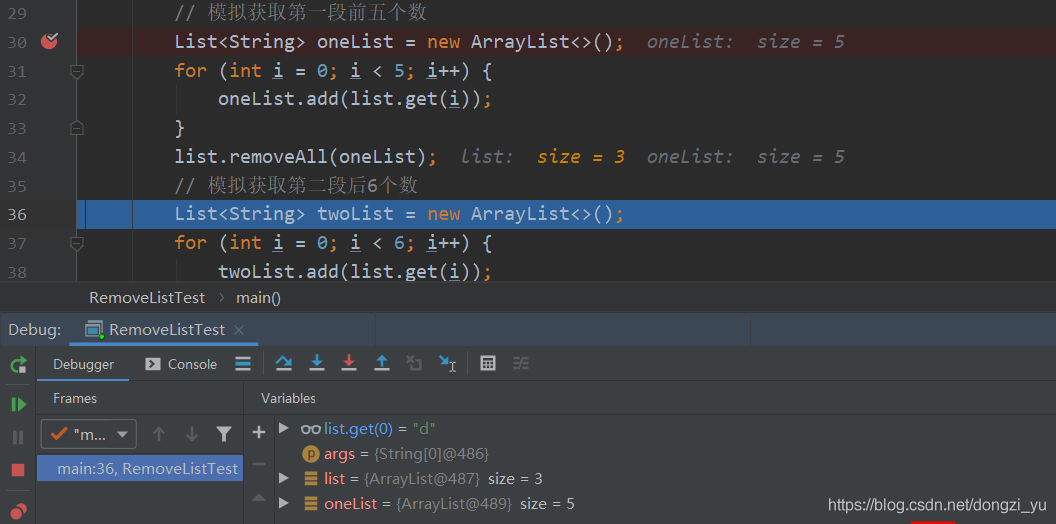
list Originally 11 Data , Take out 5 After that, there should be still 6 Data , however removeAll After that, there is still 3 Data , This must be wrong , Because this will make the array subscript out of bounds exception when obtaining the second segment of data .
Later, I found out by looking at the source code ,removeAll The same elements are removed .
Looking up the data, we found that using iterators will not remove duplicate elements , But the iterator is not the way I want to remove data , It can't achieve the effect I want .
Finally, we found that using subList() It is reliable to get a subset of the current set to remove , And there are no above two problems .
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("g");
list.add("k");
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
list.add("a");
list.add("a");
list.add("a");
// Simulate to get the first five numbers in the first paragraph
List<String> oneList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
oneList.add(list.get(i));
}
// Get subset clear data
List<String> subList_1 = list.subList(0, 5);
subList_1.clear();
// After the simulation obtains the second paragraph 6 Number
List<String> twoList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
twoList.add(list.get(i));
}
list.subList(0, 6).clear();
}
At the end of the article, I want to explain subList Actions and parameters :
subList Is the method to get a subset of the current set
Parameters fromIndex: Specify the starting point of the new list ( Include this point )
Parameters toIndex: Specify the end point of the new list ( This point is not included )
Personally, it means subscript fromIndex Start taking value , take toIndex It's worth .
Refer to the connection
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
TCP的三次握手和四次挥手
汇编语言段定义
JVM garbage collector part 1
复盘网鼎杯Re-Signal Writeup
字节跳动海外技术团队再夺冠:高清视频编码已获17项第一

学习投资大师的智慧

ByteDance overseas technical team won the championship again: HD video coding has won the first place in 17 items
Idea breakpoint debugging skills, multiple dynamic diagram package teaching package meeting.
手把手带你做强化学习实验--敲级详细
EasyRE WriteUp
随机推荐
【逆向中级】跃跃欲试
Program counter of JVM runtime data area
mysql的合计/统计函数
SQL调优小记
Wu Jun's trilogy experience (VII) the essence of Commerce
Yum install XXX reports an error
JVM garbage collector part 2
【逆向】脱壳后修复IAT并关闭ASLR
In the command mode in the VI editor, delete the character usage at the current cursor__ Command.
关于Stream和Map的巧用
CentOS7上Redis安装
原型链继承
8086 segmentation technology
Instructions for Redux
Only learning C can live up to expectations TOP4 S1E6: data type
Logical operation instruction
After the subscript is used to assign a value to the string type, the cout output variable is empty.
PostgreSQL 14.2, 13.6, 12.10, 11.15 and 10.20 releases
汇编语言基础知识
arithmetic operation