当前位置:网站首页>98. Verify the binary search tree ●●
98. Verify the binary search tree ●●
2022-07-05 23:24:00 【chenyfan_】
98. Verify binary search tree ●●
describe
Give you the root node of a binary tree root , Determine whether it is an effective binary search tree .
It works The binary search tree is defined as follows :
- The left subtree of the node contains only Less than Number of current nodes .
- The right subtree of the node contains only Greater than Number of current nodes .
- All left and right subtrees themselves must also be binary search trees .
Example
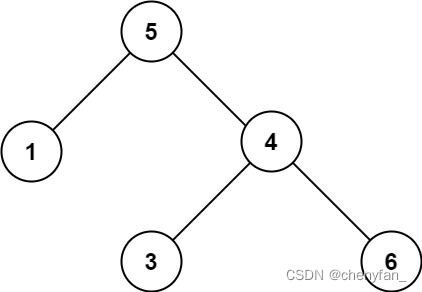
Input :root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
Output :false
explain : The value of the root node is 5 , But the value of the right child node is 4 .
Answer key
nature : Middle order traversal , The value of the output binary search tree node is an ordered sequence .
Therefore, you can traverse in order and record all elements with an array , Then traverse the array to judge .
But it can also overall situation Define a Value to be compared , Directly in the middle order traversal process Comparative judgment And constantly update the value to be compared , It should be noted that :
You cannot simply compare that the left node is smaller than the middle node , The right node is larger than the middle node , What we want to compare is All nodes of the left subtree Smaller than the intermediate node , All nodes in the right subtree Larger than the intermediate node , Therefore, compare with the previous nodes .
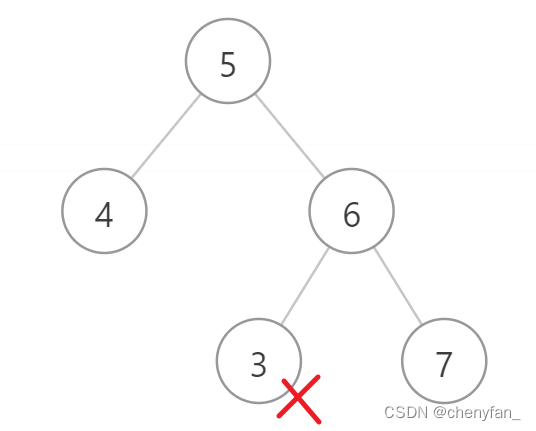
1. In the sequence traversal recursive
- Initialize the value to be compared to long long Type min , Deal with the situation that there is an integer minimum in the question ;
class Solution {
public:
long long preValue = LONG_MIN; // The previous number before initialization is the long minimum
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return true;
bool left = isValidBST(root->left); // Left
if(root->val <= preValue){
// in
return false; // When traversing the middle order, compare with the previous number to judge the order
}else{
preValue = root->val;
}
bool right = isValidBST(root->right); // Right
return left && right; // Effectiveness of left and right subtrees
}
};
- Or define the value to be compared as the node type
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* preNode = nullptr; // Nodes to be compared
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return true;
bool left = isValidBST(root->left); // Left
if(preNode != nullptr && root->val <= preNode->val){
// in
return false; // Invalid , sign out
}else{
preNode = root; // When traversing the middle order, compare with the previous number to judge the order
}
bool right = isValidBST(root->right); // Right
return left && right; // Effectiveness of left and right subtrees
}
};
2. In the sequence traversal iteration
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* preNode = nullptr; // Nodes to be compared
TreeNode* curr = root;
while(curr != nullptr || !st.empty()){
if(curr){
st.push(curr); // Nodes on the stack
curr = curr->left; // The node pointer points to the left child
}else{
// Traverse all left children
curr = st.top();
st.pop(); // in
if(preNode && curr->val <= preNode->val) return false;
preNode = curr;
curr = curr->right; // The node pointer points to the right child
}
}
return true;
}
};
- utilize Null pointer marker Unified iterative writing of
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* curr = nullptr;
TreeNode* preNode = nullptr; // The former element , Nodes to be compared
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()){
curr = st.top();
st.pop(); // Visit children who are not at the top of the empty stack
if(curr != nullptr){
// The stack order is : Right - in -null- Left ; The stack order is : Left -null- in - Right
if(curr->right) st.push(curr->right);
st.push(curr);
st.push(nullptr);
if(curr->left) st.push(curr->left);
}else{
curr = st.top(); // null The following elements indicate that you have visited , At this point, you need to pop up and take out the element value
st.pop();
if(preNode != nullptr && curr->val <= preNode->val) return false;
preNode = curr;
}
}
return true;
}
};
边栏推荐
- openresty ngx_ Lua regular expression
- PLC编程基础之数据类型、变量声明、全局变量和I/O映射(CODESYS篇 )
- 2.13 summary
- Openresty ngx Lua regular expression
- LeetCode——Add Binary
- How to quickly understand complex businesses and systematically think about problems?
- 并查集实践
- Practice of concurrent search
- 2022 G3 boiler water treatment simulation examination and G3 boiler water treatment simulation examination question bank
- 代码农民提高生产力
猜你喜欢
Realize reverse proxy client IP transparent transmission
第十七周作业

Mathematical formula screenshot recognition artifact mathpix unlimited use tutorial
Detailed explanation of pointer and array written test of C language
LabVIEW打开PNG 图像正常而 Photoshop打开得到全黑的图像
Pyqt control part (I)

The PNG image is normal when LabVIEW is opened, and the full black image is obtained when Photoshop is opened

2: Chapter 1: understanding JVM specification 1: introduction to JVM;
98. 验证二叉搜索树 ●●

Registration and skills of hoisting machinery command examination in 2022
随机推荐
From the perspective of quantitative genetics, why do you get the bride price when you get married
Thoroughly understand JVM class loading subsystem
idea 连接mysql ,直接贴配置文件的url 比较方便
LeetCode102. Sequence traversal of binary tree (output by layer and unified output)
媒体查询:引入资源
二叉树递归套路总结
2.13 summary
Krypton Factor purple book chapter 7 violent solution
TVS管和ESD管的技術指標和選型指南-嘉立創推薦
Dynamic memory management (malloc/calloc/realloc)
Selenium+pytest automated test framework practice
Alibaba Tianchi SQL training camp task4 learning notes
grafana工具界面显示报错influxDB Error
Summary of binary tree recursive routines
Commonly used probability distributions: Bernoulli distribution, binomial distribution, polynomial distribution, Gaussian distribution, exponential distribution, Laplace distribution and Dirac delta d
What is the process of building a website
Selenium+Pytest自动化测试框架实战
无刷驱动设计——浅谈MOS驱动电路
poj 2762 Going from u to v or from v to u? (推断它是否是一个薄弱环节图)
3D point cloud slam