当前位置:网站首页>Recursion: one dimensional linked lists and arrays
Recursion: one dimensional linked lists and arrays
2022-07-03 03:39:00 【My family Dabao is the cutest】
Reverse string
Write a function , Its function is to invert the input string . Input string as character array s Given in the form of .
Recursion is to transform a big problem into the same small problem , The original problem is the same as the minor problem , But the scale of the problem has been reduced . When reversing the string , In fact, it is the exchange of characters at both ends , Then go to the middle one by one .
| l —> | <— r | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | e | l | l | o |
| l —> | l | <— r | ||
| o | e | l | l | h |
You can see , Repeat the operation to exchange the strings on the left and right sides , Then the string keeps shrinking ( The scale of the problem has shrunk ), But the operation is always repeated .
When reversing a string, you do not need to operate after recursion , So before recursion
class Solution:
def reverseString(self, s: List[str]) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify s in-place instead. """
def dfs(arr, l, r):
if l >= r: # The termination condition of recursion
return
arr[l],arr[r] = arr[r],arr[l] # Repeat the operation section . Swap the left and right characters
dfs(arr,l+1,r-1) # Reduce the scale of the problem , Repeat
dfs(s,0,len(s)-1)
return s
Reverse a linked list
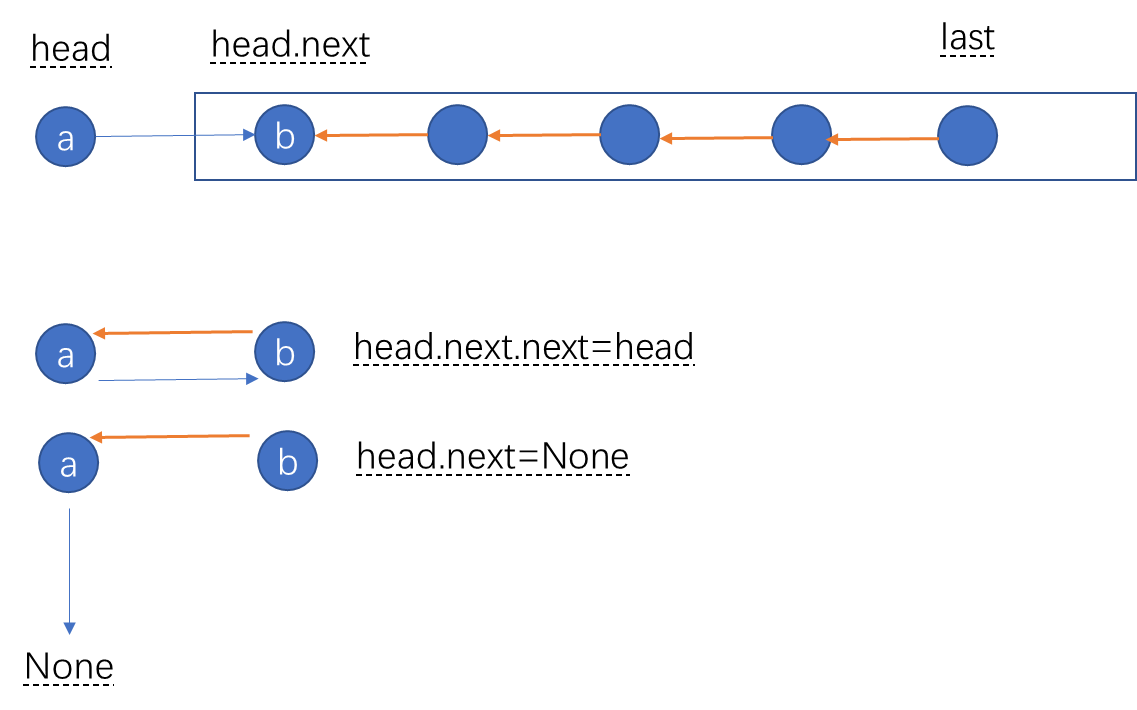
The inversion of the linked list can also be recursive , First, we need to find the last element , Then this element is the inverted head node , So we go back . Then we can reverse the elements , Suppose the follow-up has been reversed ( Recursion will be reversed one by one ), Now? a How should this node be reversed ?a Of next yes b, The aim now is to make b Of next Point to a, In fact, it's very simple
b=a.next # The goal is
b.next=a # The goal is to make b.next Point to a
a.next.next=a # because a.next=b, So it can be written directly as
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
last = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head
head.next = None
return last
Print linked list from end to end
Enter the head node of a linked list , Return the value of each node from the end to the end ( Return with array ).
There are operations after recursive functions , That is to say, this recursive function keeps looking back , Finally found the stop condition , It will return at this time , Do some operations after returning , Here is to save the data .
And found a problem , The parameter we input is head, Then there is another recursive function head.next, That is to say, at this time, we are actually led by cur and next Of .
At first, recursion doesn't go from top to bottom , No operation is required , Go until you finally find the stop condition , Then start to return step by step , This time is from bottom to top ( The reverse is true ), We take every step of head Just store it .
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | None | |
| head | ||||||
| head | ||||||
| head | ||||||
| here head yes 4 | head | |||||
| here head yes 5, Pass in head.next | head | |||||
| Stop conditions ,head is None | head |
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def reversePrint(self, head: ListNode) -> List[int]:
res = []
def dfs(head):
if head is None:
return
dfs(head.next) # head.next is None, At this time, the stop condition is found
res.append(head.val) # head The value of is not None, So add values , And at this time, it starts to return recursively head, That's the last step head
dfs(head)
return res
Delete the last of the linked list N Nodes
The recursion of the linked list is more like recursive traversal , Not through for Loop operation to traverse , Directly use the principle of recursion to traverse , Delete the penultimate N When there are nodes , Recursion will traverse to the tail in a forward direction , Then return from the bottom up , At this time, we can count , Record to No N+1 When it's time , We can operate .
There are two tips , One is to define a dummy Put the node of head In front of , So if you want to delete head The node of can still return dummy.next, The second is to use nonlocal This keyword , This keyword defines that internal functions can operate on variables other than functions .
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0,head)
def dfs(head):
nonlocal n
if head is None:
return
dfs(head.next)
n -= 1
if n == -1:
head.next = head.next.next
dfs(dummy)
return dummy.next
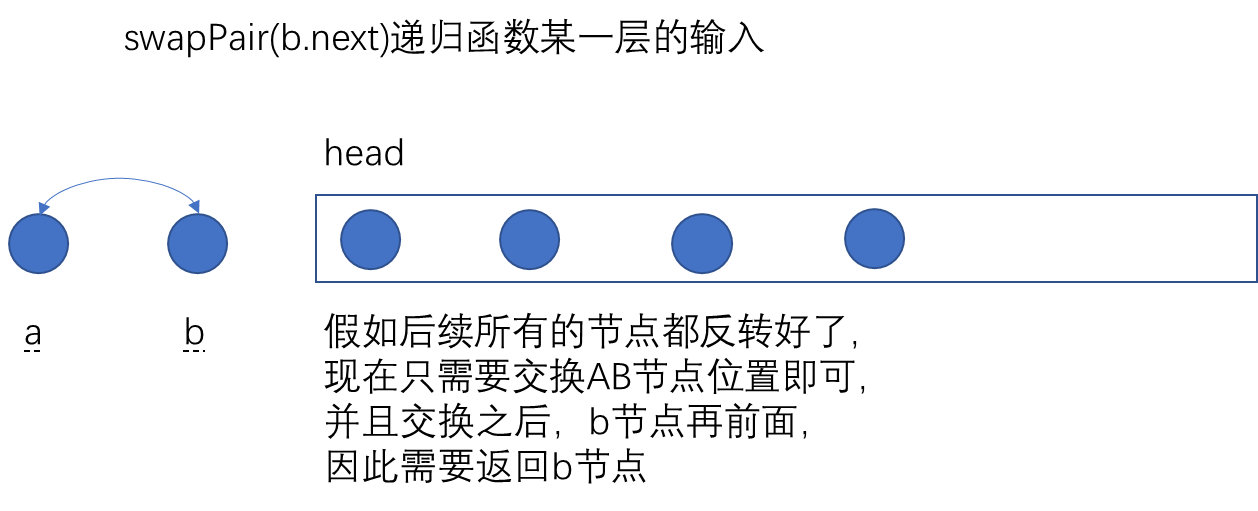
Two or two exchange nodes in a linked list

This can also consider recursion , We first swap two nodes , The following nodes are all repeated operations , therefore , This problem can be solved by cycling , You can also use recursion , But this question needs to think about what to return .
How do we know this iterative formula ? How to judge this problem is to use recursion ? What if a big problem can't be broken down into a small problem ?
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
a = head
b = head.next
a.next = self.swapPairs(b.next)
b.next = a
return b
2 The power of
Give you an integer n, Please judge whether the integer is 2 Power square
Recursion can also be considered for this problem , The big problem is to judge whether a number is 2 Power square , Divide this number by 2 The new number obtained later will also determine whether it is 2 Power square , That is, big problems can be broken down into small problems step by step , And every step is repeated , Repeat to judge whether it can be 2 to be divisible by
You can see that this problem directly returns the recursive function , And there is no other operation , This means that the result of recursion to the last layer is to return directly layer by layer , There is no middleman , So whether the last step can be divided directly is the final result .
I don't know n Whether it is 2 Power square , But if it can be solved n%2 To judge , If I know n%21, that n Definitely not 2 Power square , If n%20, I still don't know , But I can reduce the scale of the problem , If I know (n//2)%==1, that n Definitely not 2 Power square .
class Solution:
def isPowerOfTwo(self, n: int) -> bool:
if n == 1:
return True
elif n % 2 > 0 or n < 1:
return False
return self.isPowerOfTwo(n // 2)
Hanoi

Hanoi tower is also done in a recursive way . If we have N Disc , Let's go through C The former N-1 A disk moves to B above , And then put A The upper disc is moved to C above , And then we go through A, hold B On the top N-1 A disk moves to C above .
Why do you think of using recursion ? Because the original problem is the same as the reduced problem , We can N Turn it into N-1,N-1 Turn it into N-2, Until 2,1 wait . In the same way , Recursion is actually very much like a recursive formula for high school learning , First, Zengming N=1 It is in accordance with the law , Then prove N+1 Is also in line with the law . That is to say, no matter how big the problem is , All conform to the same law , So we can calculate it iteratively .
There is another interesting place in Hanoi Tower , Our input is move(n,A,B,C), To get this result , So we recurse one in our function move(n-1.A,C,B), The question is how do we put n-1 A disc to move ? I do not know! , So this is where recursion makes people confused , Can the problem be solved by recursion ? Yes , That's it . Anyway, I haven't figured it out yet , adopt move(n-1.A,C,B) after ,A There is only one disc on it , At this point, we move this disc directly to C Just above . The problem is , I don't even know now C Is there a disc on it , Ask what you can move directly , Amazing .
class Solution:
def hanota(self, A: List[int], B: List[int], C: List[int]) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify C in-place instead. """
def move(n,A,B,C):
if n == 1: # When there is one disc left , Direct will A The disc moves to C On
C.append(A.pop())
return
move(n-1, A, C, B) # take A above n-1 Two disks pass through C, Move to B above
C.append(A.pop()) # At this time A The last disc above moves to C Just above
move(n-1, B, A, C) # here B It has n-1 Disc ,B Re pass A hold n-1 A disk moves to C Just above
n = len(A)
move(n,A,B,C)
50. Pow(x, n)
This recursion is also very interesting , It's also a little hard to understand , We ask x n x^n xn In fact, recursion can be divided into two cases
x n = { ( x n 2 ) 2 n%2==0 x ∗ ( x n 2 ) 2 n%2==1 x^n= \begin{cases} (x^{\frac{n}{2}})^2 & \text{n\%2==0} \\ x*(x^{\frac{n}{2}})^2 & \text{n\%2==1} \\ \end{cases} xn={ (x2n)2x∗(x2n)2n%2==0n%2==1
The form of recursive function is
p o w ( x , n ) = { p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) 2 n%2==0 x ∗ p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) 2 n%2==1 pow(x,n)= \begin{cases} pow(x,n//2)^2& \text{n\%2==0} \\ x*pow(x,n//2)^2 & \text{n\%2==1} \\ \end{cases} pow(x,n)={ pow(x,n//2)2x∗pow(x,n//2)2n%2==0n%2==1
You ask me how to solve p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) pow(x,n//2) pow(x,n//2) I don't know either , Anyway, it can be solved by recursion according to this recursion formula . I don't know how to ask p o w ( x , n ) pow(x,n) pow(x,n), But if I find out p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) pow(x,n//2) pow(x,n//2) I can work out p o w ( x , n ) pow(x,n) pow(x,n) 了 , Such as sum solution p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) pow(x,n//2) pow(x,n//2) Well ? I just want to solve p o w ( x , n / / 4 ) pow(x,n//4) pow(x,n//4) That's all right. , In this way, the problem will eventually be reduced to n=1 That is, stop conditions , Then recursion returns , We can operate this to return the result .
This is very similar to the problem of Hanoi Tower , I don't know how to n A disk from A Move to C, But if I put n-1 A disc can move to B, Then it can be done .
class Solution:
def myPow(self, x: float, n: int) -> float:
def dfs(x,n):
if n == 0:
return 1
y = dfs(x, n//2)
if n % 2 == 0:
return y * y
else:
return x * y * y
if n < 0:
x = 1 / x
n = -n
r = dfs(x,n)
return r
边栏推荐
- For instruction, uploading pictures and display effect optimization of simple wechat applet development
- [algebraic structure] group (definition of group | basic properties of group | proof method of group | commutative group)
- QQ小程序开发之 一些前期准备:预约开发账号、下载安装开发者工具、创建qq小程序
- Null and undefined
- Introduction to mongodb
- 动态规划:最长回文子串和子序列
- TCP/IP模型中的重磅嘉宾TCP--尚文网络奎哥
- Ffmpeg download and installation tutorial and introduction
- MongoDB安装 & 部署
- Introduction à mongodb
猜你喜欢

Limit of one question per day
Ansible简介【暂未完成(半成品)】
MySQL MAC download and installation tutorial
Some preliminary preparations for QQ applet development: make an appointment for a development account, download and install developer tools, and create QQ applet
Téléchargement et installation du client Filezilla

MongoDB簡介

Error in compiled file: error: unmapped character encoding GBK

Captura下载安装及在Captura配置FFmpeg

编译文件时报错:错误: 编码GBK的不可映射字符
![[embedded module] OLED display module](/img/c4/474f5ee580d132654fbd1a4cd53bab.jpg)
[embedded module] OLED display module
随机推荐
For instruction, uploading pictures and display effect optimization of simple wechat applet development
[set theory] partial order relation (partial order relation definition | partial order set definition | greater than or equal to relation | less than or equal to relation | integer division relation |
PHP generates PDF tcpdf
Yolov5 project based on QT
Don't use the new Dede collection without the updated Dede plug-in
简易版 微信小程序开发之for指令、上传图片及展示效果优化
FileZilla Client下载安装
Hi3536c v100r001c02spc040 cross compiler installation
[mathematical logic] normal form (conjunctive normal form | disjunctive normal form | major item | minor item | maximal item | minor item | principal conjunctive normal form | principal disjunctive no
递归:深度优先搜索
[mathematical logic] propositional logic (propositional and connective review | propositional formula | connective priority | truth table satisfiable contradiction tautology)
Compare float with 0
Message queue addition failure
New programmers use the isXXX form to define Boolean types in the morning, and are discouraged in the afternoon?
Small guide for rapid formation of manipulator (VIII): kinematic modeling (standard DH method)
C programming learning notes [edited by Mr. Tan Haoqiang] (Chapter III sequence programming) 05 data input and output
监听对象中值变化及访问
释放数据力量的Ceph-尚文网络xUP楠哥
简易版 微信小程序开发之页面跳转、数据绑定、获取用户信息、获取用户位置信息
【全民编程】《软件编程-讲课视频》【零基础入门到实战应用】