当前位置:网站首页>Poker game program - man machine confrontation
Poker game program - man machine confrontation
2022-07-06 13:48:00 【Programming Lindaiyu】
Write poker game program , It is preliminarily set that the player is man-machine confrontation , Everyone catches 12 card , The rule of the game is that you can only play one card at a time , Roll the dice to decide who plays first . Those with large points should control those with small points . If you can't control each other, don't play cards , Let the other party play cards . The party who finishes first wins . The weight size is specified as follows ( From big to small ):13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1. Design and color : Square piece , Heart , Spade , The plum blossom .
The overall flow chart is as follows :

The flow chart of playing cards in turn is as follows :
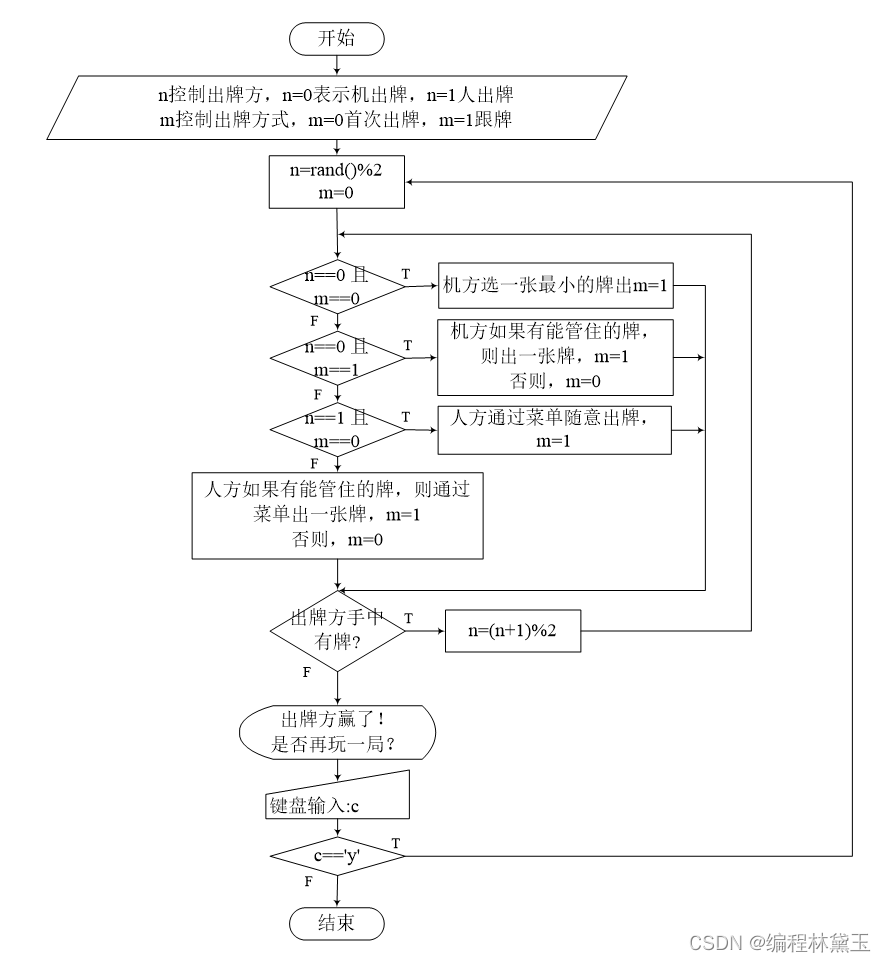
The global variables are as follows :
jk=[] # A deck of cards
cp=[] # The card in the computer hand
ps=[] # The cards in people's hands
dt=[] # The cards that have been played on the table
n=random.randint(0,1) # Who should play cards ,0: Computer licensing ,1: People play cards
m=0 # How to play cards ,0 For the first time ,1: Follow the card
The function module is defined as follows :
The name of the function | Function description | Parameters | Return value | Other instructions |
createjk() | Produce a deck of playing cards and shuffle , Put the generated cards on the list jk in | nothing | nothing | |
dest() | Deal function , Each party sends 12 card , Send it to the list cp( Machine side ) and ps( Human side ) in . | nothing | nothing | |
psplay() | The function of playing cards once | nothing | nothing | |
cpplay() | The function of the computer playing cards once | nothing | nothing | |
play() | The overall function of playing cards , Win or lose | nothing | nothing | |
The main function | Call the above function to complete the game | nothing | nothing |
Code (Python):
Code before improvement :
import random
# Global variables cannot be set too many , If necessary , Otherwise it's hard to maintain
jk=[] # A deck of cards
cp=[] # The card in the computer hand
ps=[] # The cards in people's hands
dt=[] # Cards that have been played on the table
n=random.randint(0,1) # Who should play cards ,0: Computer licensing 1: People play cards
m=0 # How to play cards ,0 For the first time ,1 Follow the card
def createjk(): # Produce a deck of playing cards and shuffle
color=[' Red hearts ',' Square piece ',' Spade ',' The plum blossom ']
for c in color: # Produce a deck of cards , Use a double-layer cycle , Each Decor produces 1-13 The number of
for j in range(1,14):
jk.append((c,j)) # Add the generated cards to the list
for i in range(10000): # Shuffle
x1=random.randint(0,51) # produce 0-51 altogether 52 A random number
x2=random.randint(0,51)
while (x1==x2): # First judge x1 and x2 Whether it is equal or not , If equal, then give x2 Assign another value , Until they are not equal
x2=random.randint(0,51)
jk[x1],jk[x2]=jk[x2],jk[x1] # take x1 and x2 In exchange for , Shuffle
def dest(): # Deal function ,destribute distribution
for i in range(12): # Although there are 52 card , But only 24 Zhang
x=jk.pop() #pop() Method is used to remove an element from the list ( Default to last element ), And returns the value of that element
y=jk.pop() # Notice to remove , Back again
if len(cp)==0: # Licensing computers
cp.append(x)
else: # Sequential insertion , Insert list , And insert it into the appropriate position in sequence
k=len(cp)-1 # Length reduction 1 It is the subscript of the last element in the list
while(k>=0 and cp[k][1]>x[1]): #cp[k][1] and x[1] Medium [1] You can't save , Because each tuple in the list contains two more elements , The first 0 Elements are decors , The first 1 The first element is the number on the card
k=k-1
cp.insert(k+1,x) # Exit loop , namely k<0 or cp[k][1]<=x[1], if k<0, namely -1, explain x Is the smallest , Then insert cp[0] It's about ; if cp[k][1]<=x[1], because k=k-1, Then add it back
if len(ps)==0: # Deal cards for people , The same algorithm as licensing computers
ps.append(y)
else:
k=len(ps)-1
while(k>=0 and ps[k][1]>y[1]):
k=k-1
ps.insert(k+1,y)
def psplay(): # People play cards
global m # Be sure to declare global variables , Otherwise the following m and n Are considered local variables
global n
print("*****************************************")
print(" Cards played :")
print(dt) # Output the cards on the desktop
print(" The card in your hand :")
L=len(ps)
s=''
for i in range(L): # Add the cards in people's hands in a cycle s In a string
s+='%d:%s%d,'%(i+1,ps[i][0],ps[i][1]) # In fact, it can also be output directly ps, But then there will be no label
s+='0: You can't afford to '
print(s) # take s Output
while(True):
k=int(input(' Please play cards '))
if k==0: # If input 0, I can't afford , Then order m=0, For the first time , And exit the loop
m=0
break
elif (k>0 and k<=L) and (m==0 or (m==1 and ps[k-1][1]>dt[-1][1])):
# otherwise , if k The input is within a reasonable range , And it is the first time to play cards or follow cards and k The corresponding card is larger than the corresponding last card on the table , Do the following
# Be careful , Must judge m Value , Because it is necessary to judge whether to follow or play for the first time , For the first time , Will not add “ Bigger than the last card on the table ”
dt.append(ps[k-1]) # If the conditions are met, the card will be played , Then add this card to the desktop list
del(ps[k-1]) # And delete this card in people's hands
m=1 # And change m= Value , Make the next step follow
break
def cpplay():
global m
global n
k=0
if m==0: # Judge m Value , For the first time
print(" Computer out ") # Then tell people
print(cp[0]) # And put the first card in the hands of the computer , That is, the smallest card output , Inform people immediately
dt.append(cp[0]) # Add the hand to the table list
del(cp[0]) # And delete this card in the computer hand
m=1 # And change m= Value , Make the next step follow
else: # If it is a follow card
k=0 # Make k=0, Start with the first card and look for a card larger than the card on the table
while(k<len(cp) and dt[-1][1]>=cp[k][1]): # determine k Look for a card larger than the last card on the table
k+=1
if k==len(cp): # Judge whether the condition for exiting the cycle is that no qualified card is found
print(" Computers can't afford ")
m=0
else: # The condition for judging to exit the cycle is to find a card that meets the conditions
print(" The computer is out ")
print(cp[k])
dt.append(cp[k])
m=1
def play(): # Start playing
global m
global n
n=random.randint(0,1) # Decide who plays first
m=0 # For the first time
while(True):
if n==0: # If n==0, Computer first
cpplay()
if len(cp)==0: # If the computer finishes playing cards , The length is 0, It means that the computer finishes playing cards first , That is, the computer wins
print(" The computer won ")
break
else: # otherwise n==1, People play cards
psplay()
if len(ps)==0: # If the computer finishes playing cards , The length is 0, It means that the computer finishes playing cards first , That is, the computer wins
print(" The man won ")
break
n=(n+1)%2 # After each card , take n Replace the value of , Change the other side to play cards
# If you exit the loop , It means that one party won , Play cards 、 Computer 、 people 、 All cards on the table are empty
jk.clear() # At the end of each game, clear all the lists of the program , So as not to affect the next game
cp.clear()
ps.clear()
dt.clear()
# The main program
c='y' # initialization c, Start the first round by entering the following cycle
while c=='y':
createjk() # Generate cards and shuffle
dest() # Licensing
play() # Start playing
c=input(' Whether to have another round ?(y/n)')
print(" Game over , bye !")Running results :

Improved code :
import random
jk=[] # A deck of cards
cp=[] # The card in the computer hand
ps=[] # The cards in people's hands
dt=[] # The cards that have been played on the table
n=0 # Who should play cards ,0: Computer licensing ,1: People play cards
m=0 # How to play cards ,0 For the first time ,1: Follow the card
def showjk(x): # Display list x All playing cards in
s=''
for i in x:
s+=i[0]+str(i[1])+' '
return s
def createjk(): # Produce a deck of playing cards , And shuffle
color=['','','','']
for c in color: # Generate a deck of playing cards
for j in range(1,14):
jk.append((c,j))
for i in range(10000): # Shuffle
x1=random.randint(0,51) # Draw two cards at random
x2=random.randint(0,51)
while(x1==x2): # If these two cards are the same , Then re extract , Until these two cards are different
x2=random.randint(0,51)
jk[x1],jk[x2]=jk[x2],jk[x1] # Swap these two cards
def dest(): # Deal function ,destribution distribution , That is, the meaning of licensing
for i in range(12):
x=jk.pop() # Draw a card to the variable x, The card in the hand of the machine will be issued —— list cp in
y=jk.pop() # Draw a card to the variable y, The card in the hand of the machine will be issued —— list ps in
# The following is a sequence preserving insert , Insert each card in descending order
if len(cp)==0: # If the list cp It's empty. , And just insert
cp.append(x)
else:
k=len(cp)-1 # Find the list cp The maximum subscript position of
while(k>=0 and cp[k][1]>x[1]):# Find... From back to front , Find the first point less than x Subscript of the number of points , If not, then k The value of is -1
k=k-1
cp.insert(k+1, x) # take x Insert into k+1 That position
# Here is what will be y Cards inserted into people's hands , The algorithm is the same as above
if len(ps)==0:
ps.append(y)
else:
k=len(ps)-1
while(k>=0 and ps[k][1]>y[1]):
k=k-1
ps.insert(k+1, y)
def psplay(): # People play a card
global m
global n
print()
print(' desktop :'+showjk(dt))
print(' The card in your hand :')
L=len(ps)
s=''
for i in range(L):
s=s+'%d:%s%d, '%(i+1,ps[i][0],ps[i][1]) # Show all the cards in one's hand , There is a serial number in front of each card
s+='0: You can't afford to '
print(s) # Show menu
while(True): # This cycle controls the licensing and ensures the legitimacy of licensing
k=int(input(' Please play cards ')) # Receive user input
if k==0: # Indicates that the user does not play cards
m=0 #m=0 Is for the next cycle , Let the next computer side play cards in the way of first playing
break
# The following sentence determines whether the card played is legal ,0<k<=L Control user input k Must be in the optional range
# if m==0 You can play cards at will , If m==1 Then the card must be larger than the last card on the table
elif (0<k<=L) and (m==0 or (m==1 and ps[k-1][1]>dt[-1][1])):
dt.append(ps[k-1]) # Add legally played cards to the list of played cards dt in
del(ps[k-1]) # stay ps Delete the cards played
m=1 # Prepare for the next cycle , Let the computer follow the card
break
def cpplay(): # The computer plays a card
global m
global n
k=0
if m==0: # For the first time , You can play cards at will , Generally, the smallest card in the hand
# The cards played are shown below , Because it is the first time to play cards , So the smallest card is played
print(' Computer out :'+showjk([cp[0]]))
dt.append(cp[0])# Add the cards played to the list of cards played dt in
del(cp[0]) # from cp The list will play cards to delete
m=1 # Set the way of playing cards in the next round to follow
else: # This branch is m==1 The situation of , The computer should follow the card
k=0
# The following cycle is to find the smallest card in the computer's hand that is larger than the card in the previous round
while(k<len(cp) and dt[-1][1]>=cp[k][1]): #k from 0 Start looking backwards in turn
k+=1
if k==len(cp): # If it is out of range, it means that no card larger than the one just played in the last round is found
print(' Computers can't afford ')
m=0
else:
print(' The computer is out '+showjk([cp[k]]))
#print(cp[k]) # Play the cards you find
dt.append(cp[k]) # Add to the list of cards played dt in
del(cp[k]) # from cp List delete
m=1 # Set up m For the 1, Let the next round of people press “ Follow the card ” The way of playing cards
def play():
global n
global m
n=random.randint(0, 1) #n use 0 To 1 Between random numbers , Randomly decide who plays first
m=0
print('***************************')
print(' Game begins ') # Set the initial playing method to “ For the first time ”
if n==0:
print(' This time, the game computer will play cards first ')
else:
print(' People play cards first ')
while(True):
if n==0: # Computer licensing
cpplay() # The computer plays a card
if len(cp)==0: # If the card in the computer hand is 0, Then the computer wins
print(' The computer won !!!')
break
else:
psplay() # here n==1, People play a card
if len(ps)==0: # If the card in one's hand is 0, Then people win
print(' The man won !!!')
break
n=(n+1)%2 # Flip n Value , Turned out to be 1 Then it turns to 0, The original value is 0 Then it turns to 1
jk.clear()
cp.clear()
ps.clear()
dt.clear()
# The main program
c='y'
while c=='y':
createjk()
dest()
play()
c=input(' Whether to have another round ?(y/n)')
print(' Game over , bye !') This is an interesting program , People and computers take turns playing cards , The one who finishes first wins , But it's still relatively simple , It's just that both sides play cards to compare the size , There are not many rules in the poker games we usually play, such as fighting landlords . and , In the above procedure , Computers don't know how to play cards “ tactical ”, It only knows that if it has a bigger card in its hand, it will keep playing .
But everyone must know the famous man-machine confrontation ——2017 year 5 month , stay China Wuzhen go Summit On , It's with the world's number one go champion Kerjie Against the , With 3 Than 0 The total score of . It is generally acknowledged that the power of alpha go has exceeded the top level of human professional go , stay GoRatings In the world professional go ranking published on the website , It once surpassed Ke Jie, the No.1 chess player in the world .

Alpha go (AlphaGo) Previous versions , Combined with the chess score of millions of human go experts , As well as intensive learning for self-training .AlphaGoZero On this basis, our ability has been qualitatively improved . The big difference , It no longer requires human data . in other words , It didn't touch human chess at the beginning . The R & D team just let it play chess freely on the chessboard , Then play a game with yourself . According to alpha go team leader David · Silva (Dave Sliver) Introduce ,AlphaGoZero Use new reinforcement learning methods , Let yourself become a teacher . The system didn't even know what go was at first , Just start with a single neural network , Through the powerful search algorithm of neural network , Played self chess . With the increase of self game , The neural network gradually adjusts , Improve the ability to predict the next step , Finally win the game . What's more powerful is , With the deepening of training , Alpha go team found ,AlphaGoZero Also found the rules of the game independently , And out of a new strategy , It brings new insights into the ancient game of go .
More Than This ,6 month 1 Japan , China's first original virtual student “ Hua Zhibing ” Officially appeared in Beijing and entered the Knowledge Engineering Laboratory of the Department of computer science and technology of Tsinghua University , And one after another 《 The boy 》 And the Internet . Different from ordinary virtual digital people , Hua Zhibing has continuous learning ability , Can gradually “ Grow up ”, constantly “ Study ” Patterns implied in data , Including text 、 Vision 、 Images , Video etc. , Just as human beings can constantly learn behavior patterns from what they experience around them . as time goes on , Hua Zhibing learned new abilities for new scenes , Integrate organically into your own model , And become smarter and smarter .

Man machine confrontation is the frontier direction of artificial intelligence research , It has become a hotspot in the field of intelligence at home and abroad , In the future, the demand for AI professionals in the industry will gradually increase , Interested students can learn more about human-computer confrontation or artificial intelligence !
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
7-5 走楼梯升级版(PTA程序设计)

仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(二)
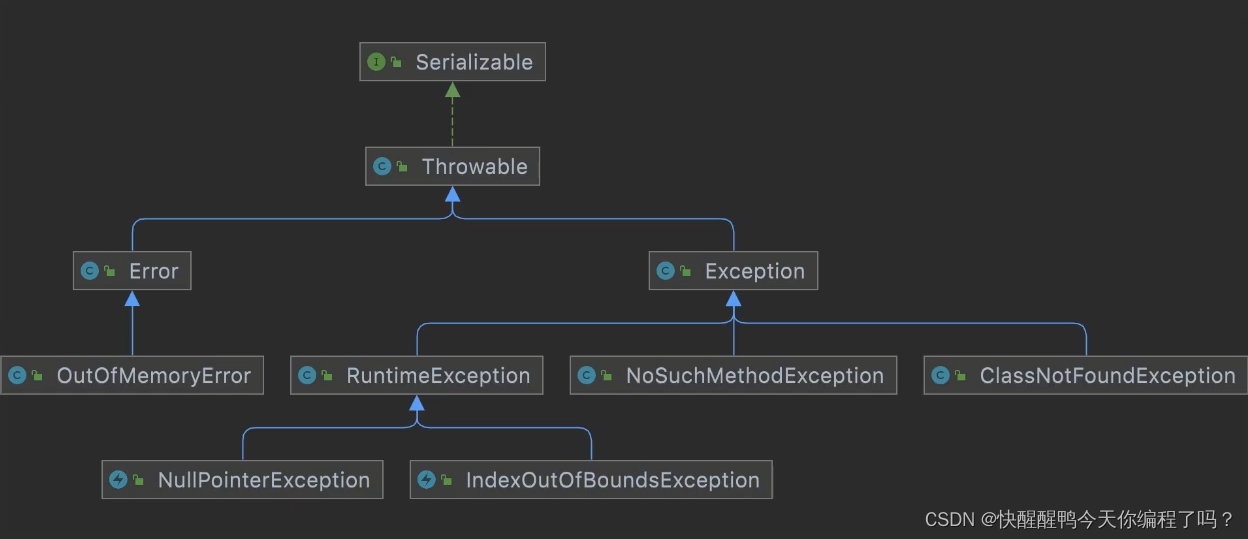
受检异常和非受检异常的区别和理解
自定义RPC项目——常见问题及详解(注册中心)
C language Getting Started Guide
实验六 继承和多态
.Xmind文件如何上传金山文档共享在线编辑?
![[面试时]——我如何讲清楚TCP实现可靠传输的机制](/img/d6/109042b77de2f3cfbf866b24e89a45.png)
[面试时]——我如何讲清楚TCP实现可靠传输的机制
Leetcode. 3. Longest substring without repeated characters - more than 100% solution
Write a program to simulate the traffic lights in real life.
随机推荐
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2021 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
Using qcommonstyle to draw custom form parts
6. Function recursion
Implementation principle of automatic capacity expansion mechanism of ArrayList
7-14 错误票据(PTA程序设计)
实验六 继承和多态
甲、乙机之间采用方式 1 双向串行通信,具体要求如下: (1)甲机的 k1 按键可通过串行口控制乙机的 LEDI 点亮、LED2 灭,甲机的 k2 按键控制 乙机的 LED1
Mortal immortal cultivation pointer-1
Safe driving skills on ice and snow roads
7-1 输出2到n之间的全部素数(PTA程序设计)
About the parental delegation mechanism and the process of class loading
3. Input and output functions (printf, scanf, getchar and putchar)
Wechat applet
记一次猫舍由外到内的渗透撞库操作提取-flag
[modern Chinese history] Chapter V test
2. First knowledge of C language (2)
【九阳神功】2020复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
抽象类和接口的区别
Difference and understanding between detected and non detected anomalies
[modern Chinese history] Chapter 9 test