当前位置:网站首页>7-6 矩阵的局部极小值(PTA程序设计)
7-6 矩阵的局部极小值(PTA程序设计)
2022-07-06 09:22:00 【编程林黛玉】
给定M行N列的整数矩阵A,其中3≤M,N≤10,如果A的非边界元素A[i][j]小于相邻的上下左右4个元素,那么就称元素A[i][j]是矩阵的局部极小值。要求编写程序输出给定矩阵的全部局部极小值及其所在的位置。每行按照“元素值 行号 列号”的格式输出一个局部极小值,其中行、列编号从1开始。要求按照行号递增输出;若同行有超过1个局部极小值,则该行按列号递增输出。若没有局部极小值,则输出“None”。
输入格式:
先在第一行输入矩阵的行数M和列数N,再从第二行开始输入整数矩阵A的所有元素。
输出格式:
按题目要求输出给定矩阵的全部局部极小值及其所在的位置。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4 5
9 9 9 9 9
9 3 9 5 9
9 5 3 5 9
9 9 9 9 9
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
3 2 2
3 3 3
代码(Python):
m,n=map(int,input().split()) #输入行数m和列数n
list1=[] #list1用来存放矩阵
count=0 #用来记录有几个符合条件的值
for i in range(m): #注意二维数组的输入方式
s = input() #一行一行的输入
list1.append([int(n) for n in s.split()]) #对每一行的数用空格分开,split()函数的返回值是一个列表,即将每一行作为一个元素,进行强制类型转换后,加入到list1中
for i in range(1,m-1): #遍历矩阵的每一个内部元素
for j in range(1,n-1):
if list1[i][j]<list1[i-1][j] and list1[i][j]<list1[i][j-1] and list1[i][j]<list1[i+1][j] and list1[i][j]<list1[i][j+1]: #判断其是否小于其上下左右的4个元素
print(list1[i][j],i+1,j+1) #如果小于上下左右4个元素的话,就是矩阵的局部极小值,疏忽局部极小值和它的位置,因为列表从0开始,矩阵的行和列从1开始,所以要加1
count=1 #为了方便判断有没有符合条件的值
if count==0: #count=0表示没有符合条件的值
print("None") #没有的话输出None上面的程序给出了比较详细的注释,以便新手小白参考。程序的思路设计或者代码实现并不是最优的,欢迎各位大佬指正错误或者给出更优质的思路。
我是一只想成为鲲鹏的菜鸟,大家的鼓励是我前进的动力,欢迎大家点赞收藏评论哦!
边栏推荐
- Arduino+ water level sensor +led display + buzzer alarm
- The difference between abstract classes and interfaces
- 最新坦克大战2022-全程开发笔记-2
- 简单理解ES6的Promise
- Leetcode.3 无重复字符的最长子串——超过100%的解法
- canvas基础2 - arc - 画弧线
- String abc = new String(“abc“),到底创建了几个对象
- 【九阳神功】2021复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
- Questions and answers of "signal and system" in the first semester of the 22nd academic year of Xi'an University of Electronic Science and technology
- C language to achieve mine sweeping game (full version)
猜你喜欢

透彻理解LRU算法——详解力扣146题及Redis中LRU缓存淘汰
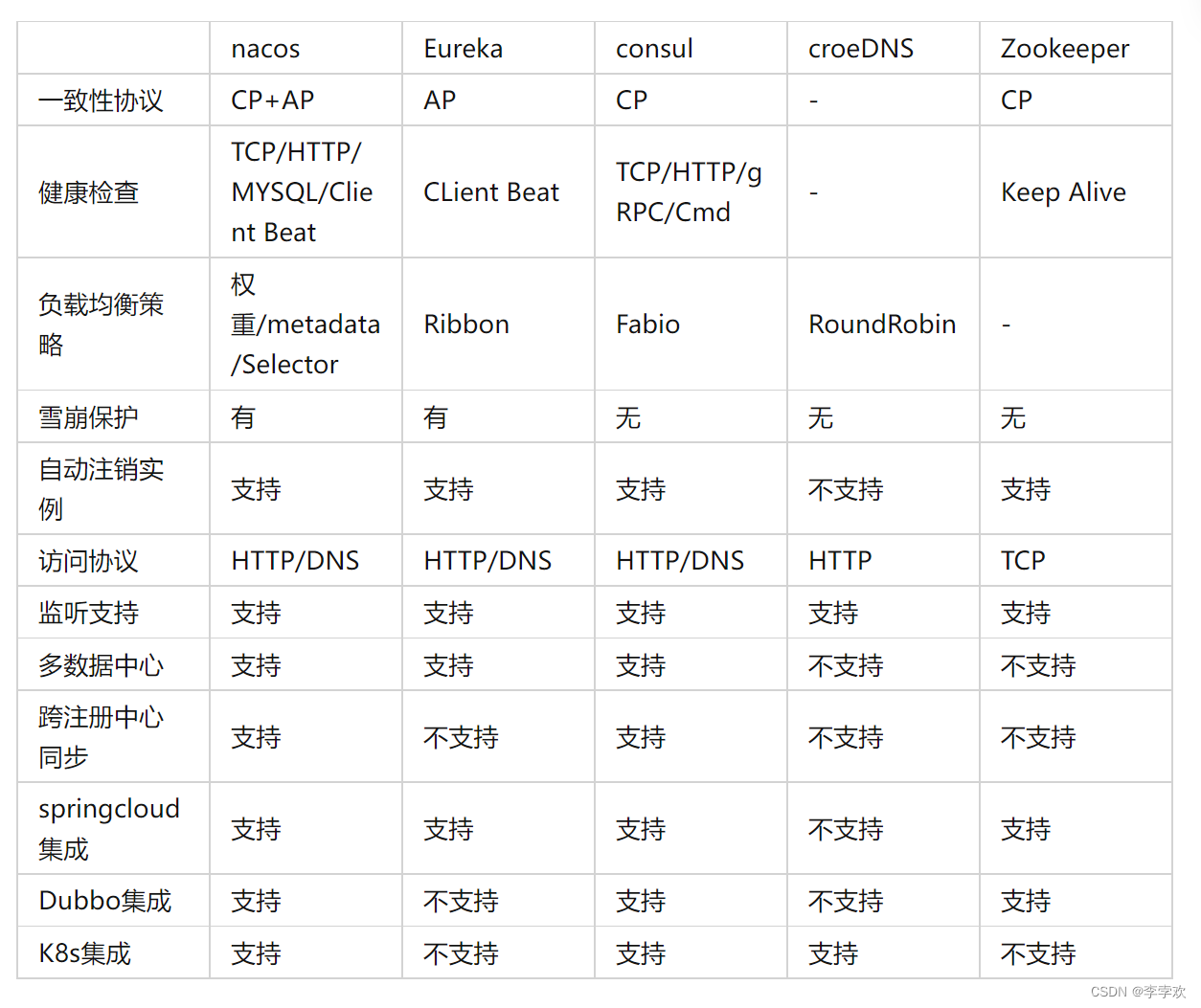
Custom RPC project - frequently asked questions and explanations (Registration Center)
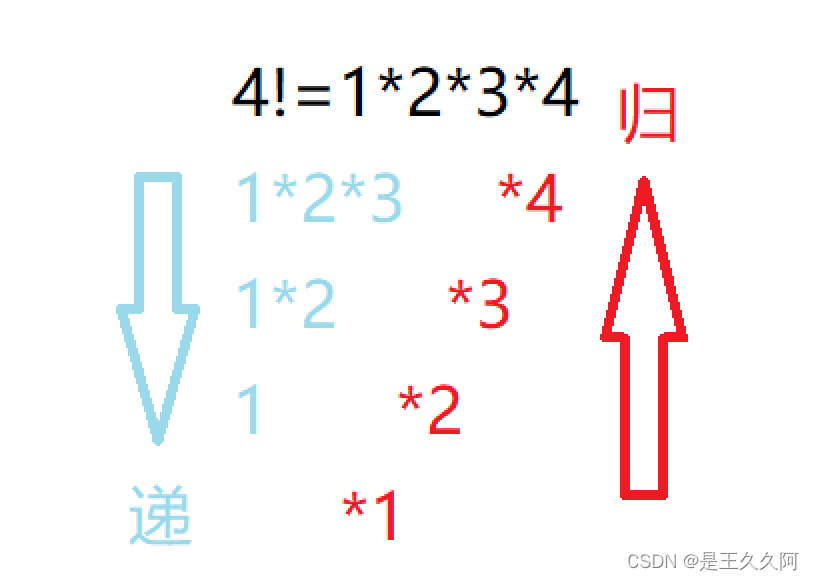
5.函数递归练习
fianl、finally、finalize三者的区别
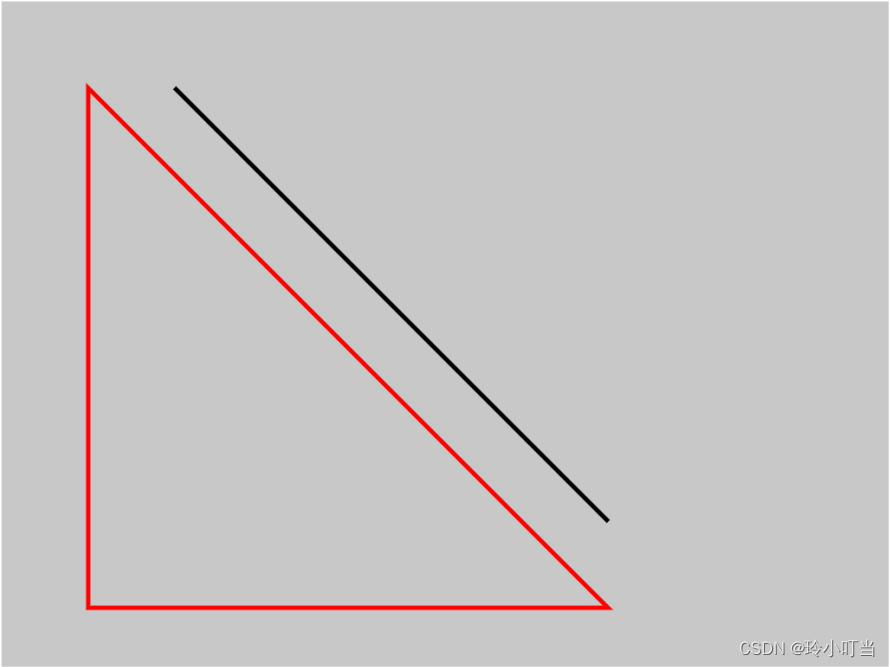
canvas基础1 - 画直线(通俗易懂)
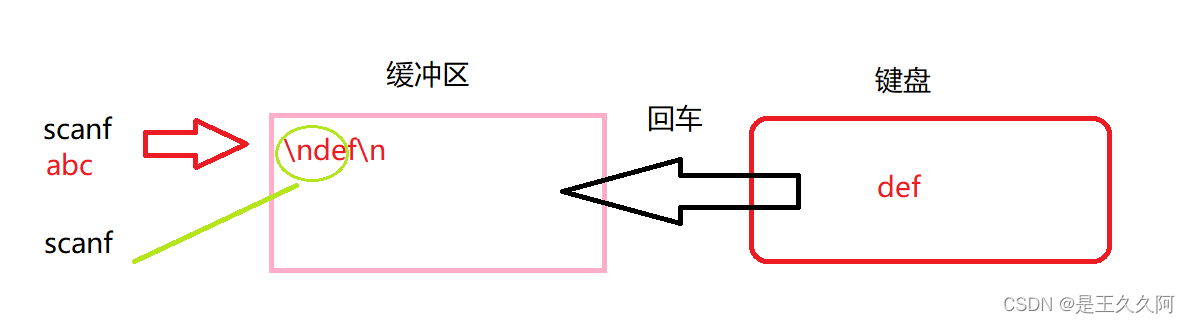
3.输入和输出函数(printf、scanf、getchar和putchar)
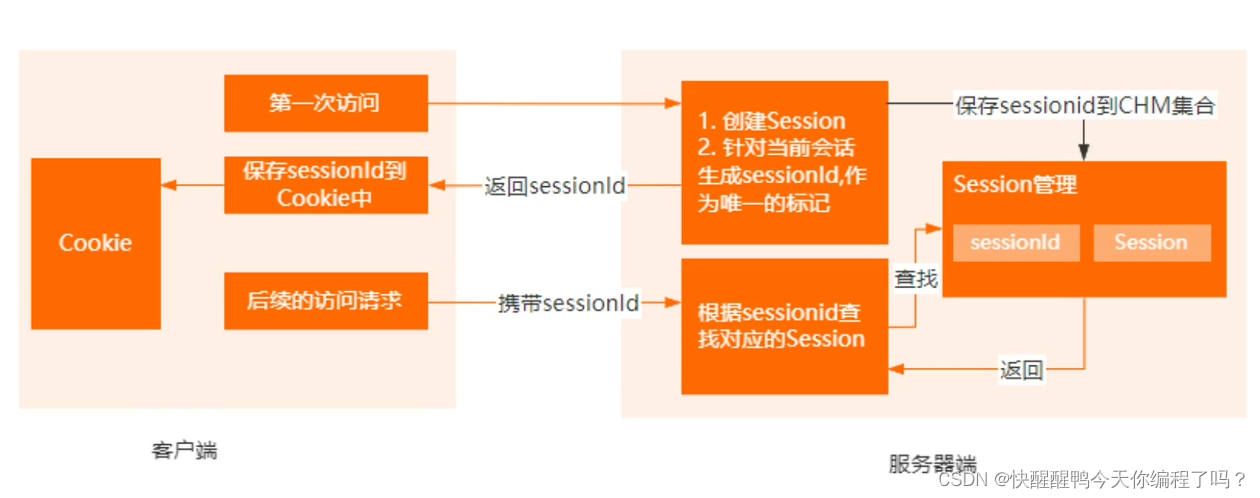
The difference between cookies and sessions
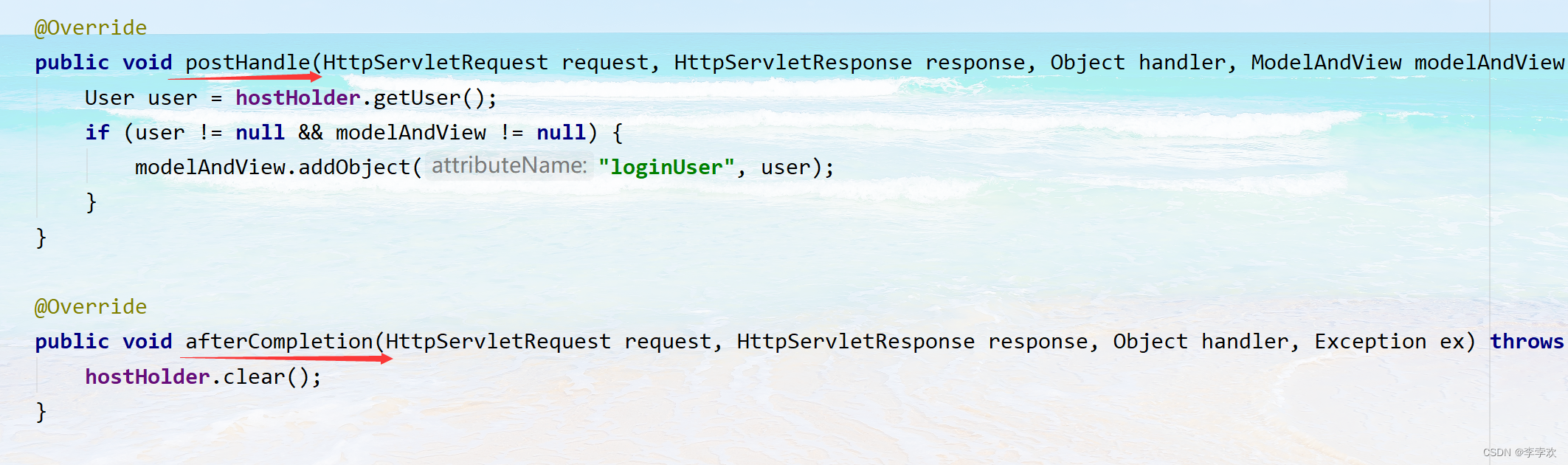
FAQs and answers to the imitation Niuke technology blog project (I)
C语言入门指南

Differences among fianl, finally, and finalize
随机推荐
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2020 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
MySQL lock summary (comprehensive and concise + graphic explanation)
这次,彻底搞清楚MySQL索引
[modern Chinese history] Chapter V test
CorelDRAW plug-in -- GMS plug-in development -- Introduction to VBA -- GMS plug-in installation -- Security -- macro Manager -- CDR plug-in (I)
Miscellaneous talk on May 27
MySQL中count(*)的实现方式
1. C language matrix addition and subtraction method
编写程序,模拟现实生活中的交通信号灯。
C语言实现扫雷游戏(完整版)
Set container
ArrayList的自动扩容机制实现原理
受检异常和非受检异常的区别和理解
(原创)制作一个采用 LCD1602 显示的电子钟,在 LCD 上显示当前的时间。显示格式为“时时:分分:秒秒”。设有 4 个功能键k1~k4,功能如下:(1)k1——进入时间修改。
自定义RPC项目——常见问题及详解(注册中心)
【九阳神功】2016复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
The difference between overloading and rewriting
Redis cache obsolescence strategy
【九阳神功】2018复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
[面試時]——我如何講清楚TCP實現可靠傳輸的機制