当前位置:网站首页>2. C language matrix multiplication
2. C language matrix multiplication
2022-07-06 13:26:00 【It's Wang Jiujiu】
Catalog
Multiply left and multiply right
2.C Programming matrix multiplication function with language
Write function ( Array form and pointer form )
1. principle
Multiply left and multiply right
In linear algebra , Matrix left multiplication is different from matrix right multiplication .
for example : The existing matrix A:  , matrix B:
, matrix B: .
.
AB For matrix B Left multiplication matrix A:
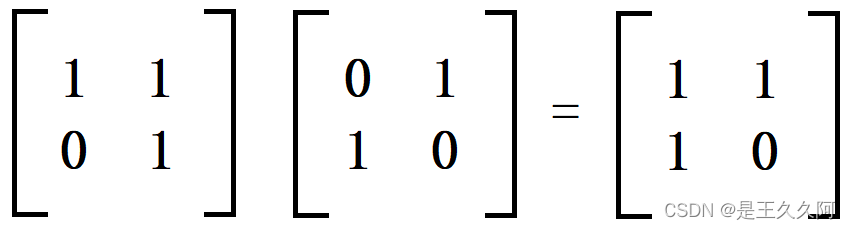
BA For matrix B Right multiply matrix A:
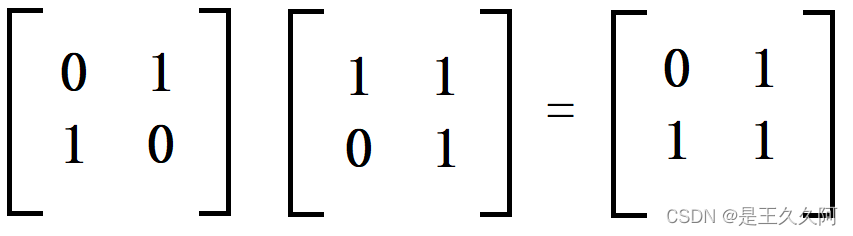
It is found by calculation that : The result of left multiplication and right multiplication is completely different , So in matrix multiplication , It is necessary to distinguish between left and right multiplication .
Multiplication principle
The conditions that matrix multiplication needs to meet : The number of columns of the matrix on the left = The number of rows of the matrix on the right .
Rows and columns of the result matrix : Row number = The number of rows of the matrix on the left , Number of columns = The number of columns in the right matrix .


Matrix multiplication process :
With AB For example :
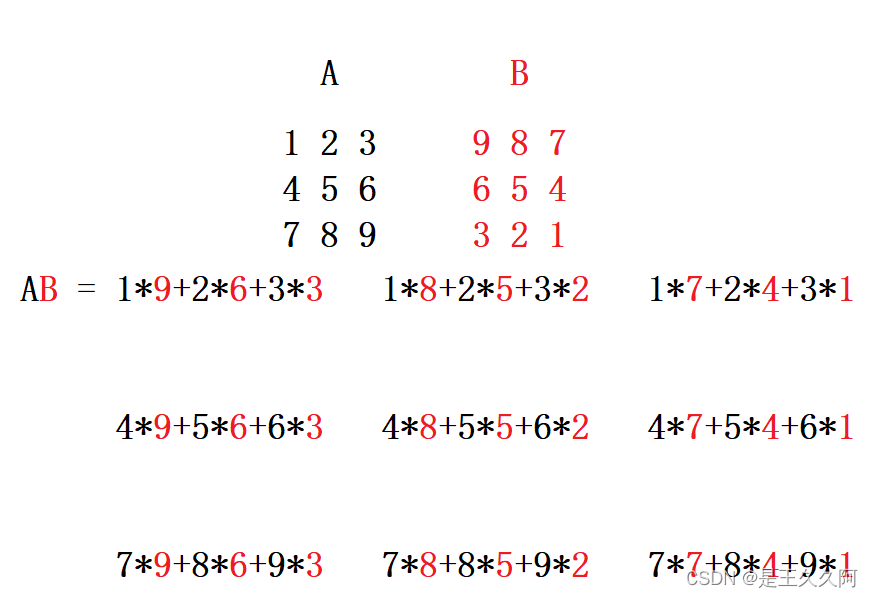
- A The order of the matrix One The elements in the row and B Matrix No One Elements in columns Corresponding Multiply again Add up , The results are placed in the first row and the first column ;
- A The order of the matrix One The elements in the row and B Matrix No Two Elements in columns Corresponding Multiply again Add up , The results are placed in the first row and the second column ;
- A The order of the matrix One The elements in the row and B Matrix No 3、 ... and Elements in columns Corresponding Multiply again Add up , The results are placed in the first row and the third column ;
- ......
- A The order of the matrix 3、 ... and The elements in the row and B Matrix No 3、 ... and Elements in columns Corresponding Multiply again Add up , The results are placed in the third row and the third column ;
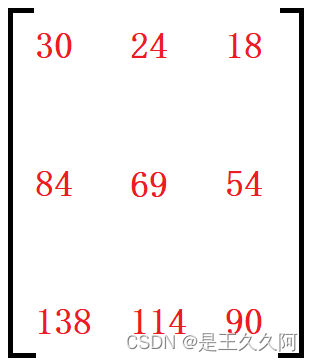
The final result is :
2.C Programming matrix multiplication function with language
Write function ( Array form and pointer form )
Although matrix can be divided into left multiplication and right multiplication , But just change the position of the incoming parameter , You can realize left multiplication and right multiplication .
The core idea :
- Use a two-dimensional array to store the numbers in the matrix , use define Define row and column values , Facilitate code changes .
- Define a matrix left multiplication function Matrix_left_mul, Pass the matrix and its row and column length to the function .
- utilize 3 individual for Loop traversal completes the calculation .
Parameters can be passed in the form of an array , It can also be passed in the form of a pointer , Both are essentially the same . Both methods will be introduced .
1、 Let's create two arrays arr1 and arr2 To store two matrices
( When creating a two-dimensional array , You can't omit Columns , You can omit lines ; But in matrix multiplication , Both row and column information should be )
// Rows and columns of the left matrix
#define COL1 4
#define ROW1 3
// Rows and columns of the right matrix
#define ROW2 4
#define COL2 3
double arr1[ROW1][COL1] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};
double arr2[ROW2][COL2] = { 12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};2、 Pass parameters and judge whether the condition of matrix matching is true
utilize assert Assert whether the condition holds , If not, the system will prompt an error ,assert Need to include header file <assert.h>.
Because the array parameter passes the address , So the type of the function is set to void that will do .
If there is no judgment , After passing in the wrong parameter , The access of two-dimensional array will overflow , Returns a random number .
Array form :
void Matrix_left_mul(double arr1[][COL1], double arr2[][COL2], double arr3[][COL2],int row1,int row2,int col1,int col2)
{
assert(col1 == row2);// Determine whether the left column is equal to the right row , Need to include header file
}Pointer form :
void Matrix_left_mul(double(*arr1)[COL1], double (*arr2)[COL2], double(*arr3)[COL2], int row1, int row2, int col1, int col2)
{
assert(col1 == row2);// Determine whether the left column is equal to the right row ,assert Need to include header file
}3、for Loop traversal calculation
Create three for loop :
- first for loop (i): Circulant left matrix i That's ok
- the second for loop (j): Circular right matrix j Column
- Third for loop (k): Cycle left rows one by one k Elements × Right column k Elements , Add up the results
Array form :
int i = 0;// That's ok
int j = 0;// Column
int k = 0;// In the ranks , The first k Multiply elements
for (i = 0; i < row1; i++)// From i OK, let's start
{
for (j = 0; j < col2; j++)// From j Column start
{
for (k = 0; k < col1; k++)//i Line elements and j Multiply column elements , The results add up
{
arr3[i][j] += arr1[i][k] * arr2[k][j];
}
}
}Pointer form :
void Matrix_left_mul(double(*arr1)[COL1], double (*arr2)[COL2], double(*arr3)[COL2], int row1, int row2, int col1, int col2)
{
assert(col1 == row2);// Determine whether the left column is equal to the right row ,assert Need to include header file
int i = 0;// That's ok
int j = 0;// Column
int k = 0;// In the ranks , The first k Multiply elements
for (i = 0; i < row1; i++)// From i OK, let's start
{
for (j = 0; j < col2; j++)// From j Column start
{
for (k = 0; k < col1; k++)//i Line elements and j Multiply column elements , The results add up
{
*(* (arr3 + i)+j) += *(*(arr1 + i) + k) * *(*(arr2 +k) + j);
}
}
}
}use define The advantage of defining constants is flexibility , Easy to use , Subsequently, you only need to change the relevant parameters of the input matrix to perform the operation .
test
stay VS in ,F10 Enter debugging mode , monitor arr1,arr2,arr3 Array . For the convenience of monitoring , We temporarily change the array to integer , The parameters in the array are integers .
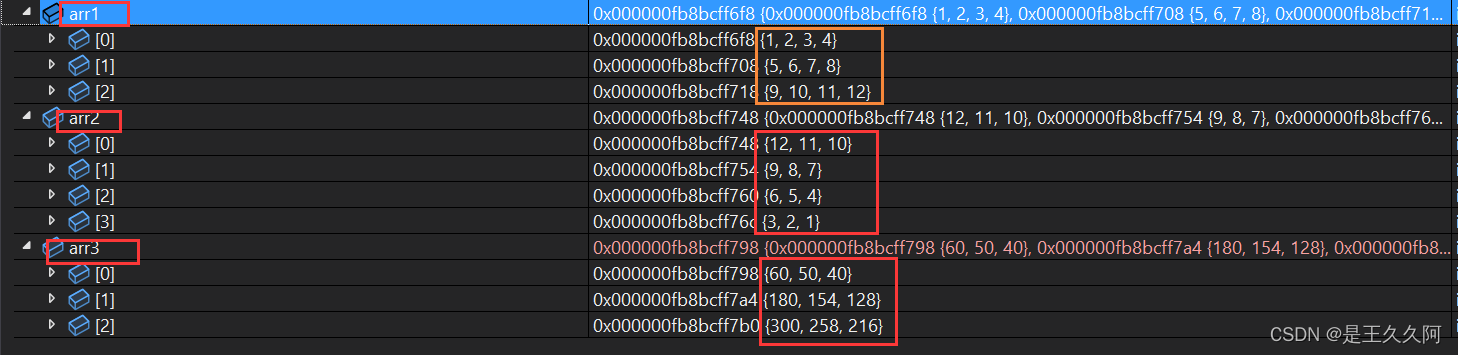
The result is absolutely right , If you don't trust, you can also test several groups of data .
3. Complete code
Array form :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
// Rows and columns of the left matrix
#define COL1 4
#define ROW1 3
// Rows and columns of the right matrix
#define ROW2 4
#define COL2 3
void Matrix_left_mul(double arr1[][COL1], double arr2[][COL2], double arr3[][COL2],int row1,int row2,int col1,int col2)
{
assert(col1 == row2);// Determine whether the left column is equal to the right row ,assert Need to include header file
int i = 0;// That's ok
int j = 0;// Column
int k = 0;// In the ranks , The first k Multiply elements
for (i = 0; i < row1; i++)// From i OK, let's start
{
for (j = 0; j < col2; j++)// From j Column start
{
for (k = 0; k < col1; k++)//i Line elements and j Multiply column elements , The results add up
{
arr3[i][j] += arr1[i][k] * arr2[k][j];
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
double arr1[ROW1][COL1] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};
double arr2[ROW2][COL2] = { 12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1 };
double arr3[ROW1][COL2]={0};// The row of the resulting matrix is equal to the row of the left matrix , The column is equal to the column of the right matrix
Matrix_left_mul(arr1, arr2, arr3,ROW1,ROW2,COL1,COL2);
return 0;
}Pointer form
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
// Rows and columns of the left matrix
#define COL1 4
#define ROW1 3
// Rows and columns of the right matrix
#define ROW2 4
#define COL2 3
void Matrix_left_mul(double(*arr1)[COL1], double (*arr2)[COL2], double(*arr3)[COL2], int row1, int row2, int col1, int col2)
{
assert(col1 == row2);// Determine whether the left column is equal to the right row ,assert Need to include header file
int i = 0;// That's ok
int j = 0;// Column
int k = 0;// In the ranks , The first k Multiply elements
for (i = 0; i < row1; i++)// From i OK, let's start
{
for (j = 0; j < col2; j++)// From j Column start
{
for (k = 0; k < col1; k++)//i Line elements and j Multiply column elements , The results add up
{
*(* (arr3 + i)+j) += *(*(arr1 + i) + k) * *(*(arr2 +k) + j);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
double arr1[ROW1][COL1] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 };
double arr2[ROW2][COL2] = { 12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1 };
double arr3[ROW1][COL2] = { 0 };// The row of the resulting matrix is equal to the row of the left matrix , The column is equal to the column of the right matrix
Matrix_left_mul(arr1, arr2, arr3, ROW1, ROW2, COL1, COL2);
return 0;
}边栏推荐
- Pit avoidance Guide: Thirteen characteristics of garbage NFT project
- MPLS experiment
- E-R graph to relational model of the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
- Differences and application scenarios between MySQL index clock B-tree, b+tree and hash indexes
- JS interview questions (I)
- 3.猜数字游戏
- 凡人修仙学指针-1
- Record: newinstance() obsolete replacement method
- 162. Find peak - binary search
- String class
猜你喜欢
图书管理系统小练习

TYUT太原理工大学2022“mao gai”必背

Rich Shenzhen people and renting Shenzhen people
12 excel charts and arrays

Quickly generate illustrations
Alibaba cloud side: underlying details in concurrent scenarios - pseudo sharing
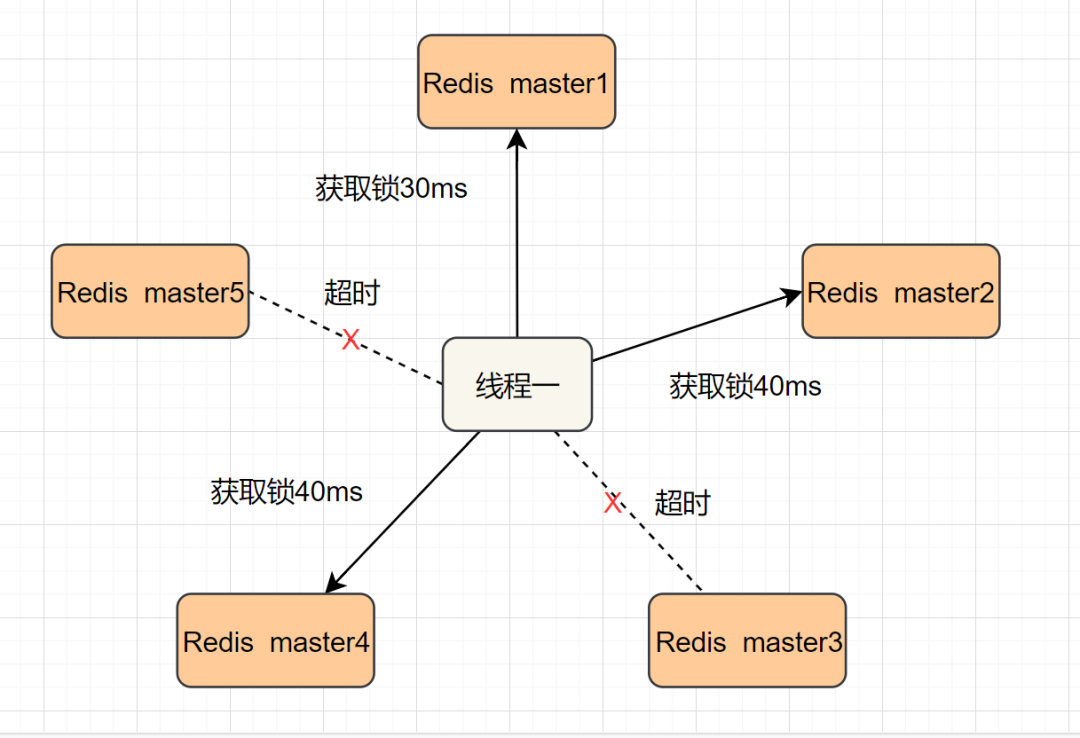
Interview Essentials: talk about the various implementations of distributed locks!

Smart classroom solution and mobile teaching concept description
TYUT太原理工大学2022软工导论大题汇总

1.C语言初阶练习题(1)
随机推荐
How to ensure data consistency between MySQL and redis?
4.30动态内存分配笔记
167. Sum of two numbers II - input ordered array - Double pointers
TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库考试题型大纲
西安电子科技大学22学年上学期《射频电路基础》试题及答案
FileInputStream和BufferedInputStream的比较
Decomposition relation model of the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
阿里云微服务(四) Service Mesh综述以及实例Istio
TYUT太原理工大学2022软工导论考试题型大纲
View UI Plus 发布 1.3.1 版本,增强 TypeScript 使用体验
4.二分查找
Introduction and use of redis
TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库大题之分解关系模式
(ultra detailed onenet TCP protocol access) arduino+esp8266-01s access to the Internet of things platform, upload real-time data collection /tcp transparent transmission (and how to obtain and write L
最新坦克大战2022-全程开发笔记-1
1.C语言矩阵加减法
E-R graph to relational model of the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
8.C语言——位操作符与位移操作符
面渣逆袭:Redis连环五十二问,三万字+八十图详解。
Record: I accidentally wrote a recursion next time