当前位置:网站首页>PriorityQueue (large root heap / small root heap /topk problem)
PriorityQueue (large root heap / small root heap /topk problem)
2022-07-06 13:36:00 【Li bohuan】
PriorityQueue It's from JDK1.5 Start to provide new data structure interface , It's a very high priority queue based on priority heap . Priority queue is another kind of queue different from FIFO queue . Each time the element with the highest priority is removed from the queue .
By default ,PriorityQueue yes Small cap pile , As the code shows
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
queue.offer(5);
queue.offer(6);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(queue.poll() + " ");
}
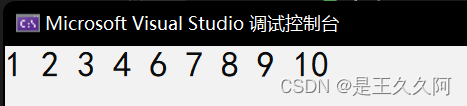
}Output results :

We can also construct it in the following ways Big pile top :
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2) -> o2 - o1);// Descending
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
queue.offer(5);
queue.offer(6);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(queue.poll() + " ");
}
}Output results :

Top K problem , Power button 347 Heli button 692:
Power button 347: Give you an array of integers nums And an integer k , Please return to the frequency before k High element . You can press In any order Return to the answer .
Example :
Input : nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 Output : [1,2]
The code is as follows : Pay attention to the construction of small top pile (o1,o2)-> o1.getValue() - o2.getValue() Don't omit .
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
//key Element value ,value For frequency of occurrence
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> queue
= new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)-> o1.getValue() - o2.getValue());
int[] res = new int[k];
for (int num : nums) {
map.put(num,map.getOrDefault(num,0) + 1);
}
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : entries) {
queue.offer(entry);
if(queue.size() > k){
queue.poll();
}
}
// What remains is the most frequent
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> poll = queue.poll();
res[i] = poll.getKey();
}
return res;Power button 692: Given a list of words words And an integer k , Return to the former k The most frequently used word . The answers returned should be sorted by word frequency from high to low . If different words have the same frequency , Sort in dictionary order .
Example :
Input : words = ["i", "love", "leetcode", "i", "love", "coding"], k = 2
Output : ["i", "love"]
analysis : "i" and "love" For the two words that appear most frequently , Are all 2 Time . Be careful , In alphabetical order "i" stay "love" Before .
This question is a little more difficult than the last one , Because when two words appear the same number of times, we should also consider sorting by dictionary , The second is that the answers need to be sorted from top to bottom , This is mainly reflected in the priority queue PriorityQueue On the structure of . The code is as follows :
public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
//key For the elements ,value For frequency of occurrence
HashMap<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
map.put(word,map.getOrDefault(word,0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(
((o1, o2) -> {
if(o1.getValue() == o2.getValue()){
return o2.getKey().compareTo(o1.getKey());
}
return o1.getValue() - o2.getValue();
})
);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
queue.offer(entry);
if(queue.size() > k){
queue.poll();
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
res.add(queue.poll().getKey());
}
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}Be careful o2.getKey().compareTo(o1.getKey()) Is in reverse order of the dictionary , Why do that , Because we use a small top pile here , So every time poll What comes out is the smallest frequency element , Last need reverse once , In order to cooperate with this , So when we construct the priority queue, we use the reverse order of the dictionary .
边栏推荐
- 9. Pointer (upper)
- 稻 城 亚 丁
- Redis的两种持久化机制RDB和AOF的原理和优缺点
- Tyut outline of 2022 database examination of Taiyuan University of Technology
- View UI Plus 發布 1.3.1 版本,增强 TypeScript 使用體驗
- MySQL事务及实现原理全面总结,再也不用担心面试
- (原创)制作一个采用 LCD1602 显示的电子钟,在 LCD 上显示当前的时间。显示格式为“时时:分分:秒秒”。设有 4 个功能键k1~k4,功能如下:(1)k1——进入时间修改。
- [面试时]——我如何讲清楚TCP实现可靠传输的机制
- 【话题终结者】
- There is always one of the eight computer operations that you can't learn programming
猜你喜欢
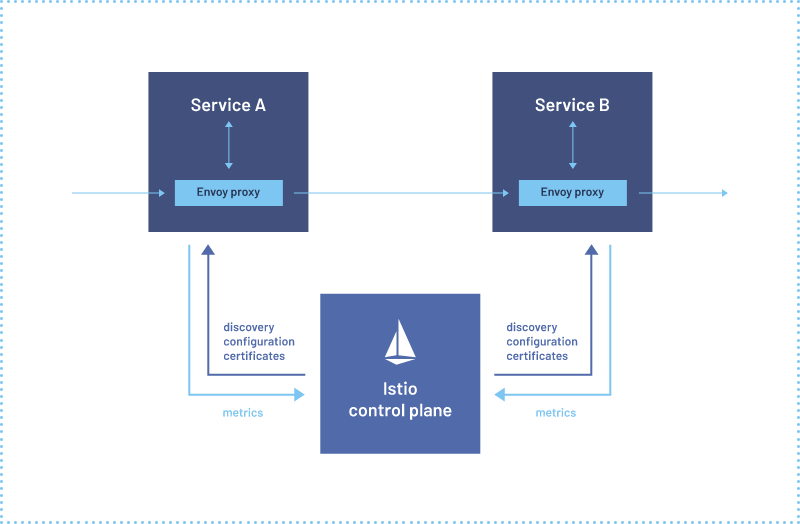
Alibaba cloud microservices (IV) service mesh overview and instance istio

5. Download and use of MSDN
20220211-CTF-MISC-006-pure_ Color (use of stegsolve tool) -007 Aesop_ Secret (AES decryption)
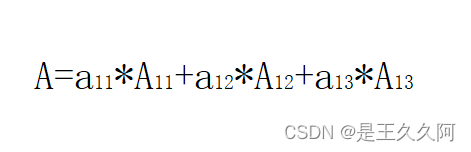
3. C language uses algebraic cofactor to calculate determinant
4.分支语句和循环语句
2.C语言矩阵乘法
13 power map
Application architecture of large live broadcast platform
魏牌:产品叫好声一片,但为何销量还是受挫
(ultra detailed onenet TCP protocol access) arduino+esp8266-01s access to the Internet of things platform, upload real-time data collection /tcp transparent transmission (and how to obtain and write L
随机推荐
编写程序,模拟现实生活中的交通信号灯。
最新坦克大战2022-全程开发笔记-1
8.C语言——位操作符与位移操作符
Cookie和Session的区别
IPv6 experiment
Mortal immortal cultivation pointer-2
仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(二)
C language Getting Started Guide
Implement queue with stack
Alibaba cloud microservices (I) service registry Nacos, rest template and feign client
6.函数的递归
ArrayList的自动扩容机制实现原理
C语言实现扫雷游戏(完整版)
Tyut Taiyuan University of technology 2022 "Mao Gai" must be recited
Design a key value cache to save the results of the most recent Web server queries
List set map queue deque stack
hashCode()与equals()之间的关系
西安电子科技大学22学年上学期《射频电路基础》试题及答案
5月14日杂谈
Aurora system model of learning database