当前位置:网站首页>L2-013 red alarm (C language) and relevant knowledge of parallel search
L2-013 red alarm (C language) and relevant knowledge of parallel search
2022-07-04 07:29:00 【Yun Cheng】
#include <stdio.h>
int arr[501], cha[501];
struct shuru
{
int x, y;
}; struct shuru shuru[5100];
void join(int x, int y)
{
int t1 = Find(x);
int t2 = Find(y);
if (t1 != t2)
{
arr[t2] = t1;
}
return;
}
int Find(int x)
{
if (x == arr[x])
{
return arr[x];
}
else
{
arr[x] = Find(arr[x]);
return arr[x];
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
shuru[i].x = x;
shuru[i].y = y;
join(x, y);
}
int num = 0, num1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == i)
{
num++;
}
}
int k;
scanf("%d", &k);
while (k--)
{
num1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
}
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
cha[x] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (cha[shuru[i].x] == 1 || cha[shuru[i].y] == 1)
{
continue;
}
else
{
join(shuru[i].x, shuru[i].y);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == i)
{
num1++;
}
}
if (num == num1 || num + 1 == num1)
{
printf("City %d is lost.\n", x);
}
else
{
printf("Red Alert: City %d is lost!\n", x);
}
num = num1;
}
num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (cha[i] == 1)
{
num++;
}
}
if (num == n)
{
printf("Game Over.\n");
}
return 0;
}The above is the code of the problem , Let's briefly describe the relevant knowledge about the union search set
The following is about arrays arr The explanation of , About arr The array of stores numbers for reasons

When the array does not store any connectivity , Each address is an independent root node , When there is a connection input , Set two addresses as x,y. Can make arr[x] The corresponding value changes to y, At this time x No longer exists as an independent root node , At this time x yes y A child node of , Thus establishing connectivity .
And look up the two most critical functions ,Find() and join()
int Find(int x)
{
if (x == arr[x])
{
return arr[x];
}
else
{
arr[x] = Find(arr[x]);
return arr[x];
}
}
As shown in the code snippet
arr[x] Medium x It's one of the two cities , and arr[x] The corresponding value is the other of the two cities Find The function aims to find its corresponding root node , As shown in the above figure, the root node of the binary tree is 1, And if a binary tree does not establish a connected relationship , It is itself a root node , So the point is arr The corresponding value in should have been initialized to itself , When x=arr[x] Prove that he is the root node , The value returned at this time is himself , And every address that exists as a child node , Can be pointed to the most fundamental root node through the pointing relationship of the array , When the root node is not reached Find The function will continue to look , Until you find satisfaction x=arr[x] Of x, Only then will we continue to return x Value
void join(int x, int y)
{
int t1 = Find(x);
int t2 = Find(y);
if (t1 != t2)
{
arr[t2] = t1;
}
return;
}
join function First use of Find Function to find t1 And t2 The root node , If they are equal, they are actually connected , It is connected through the same root node , If it's not equal , Just make y As x The child node of exists , The principle is as shown in the figure
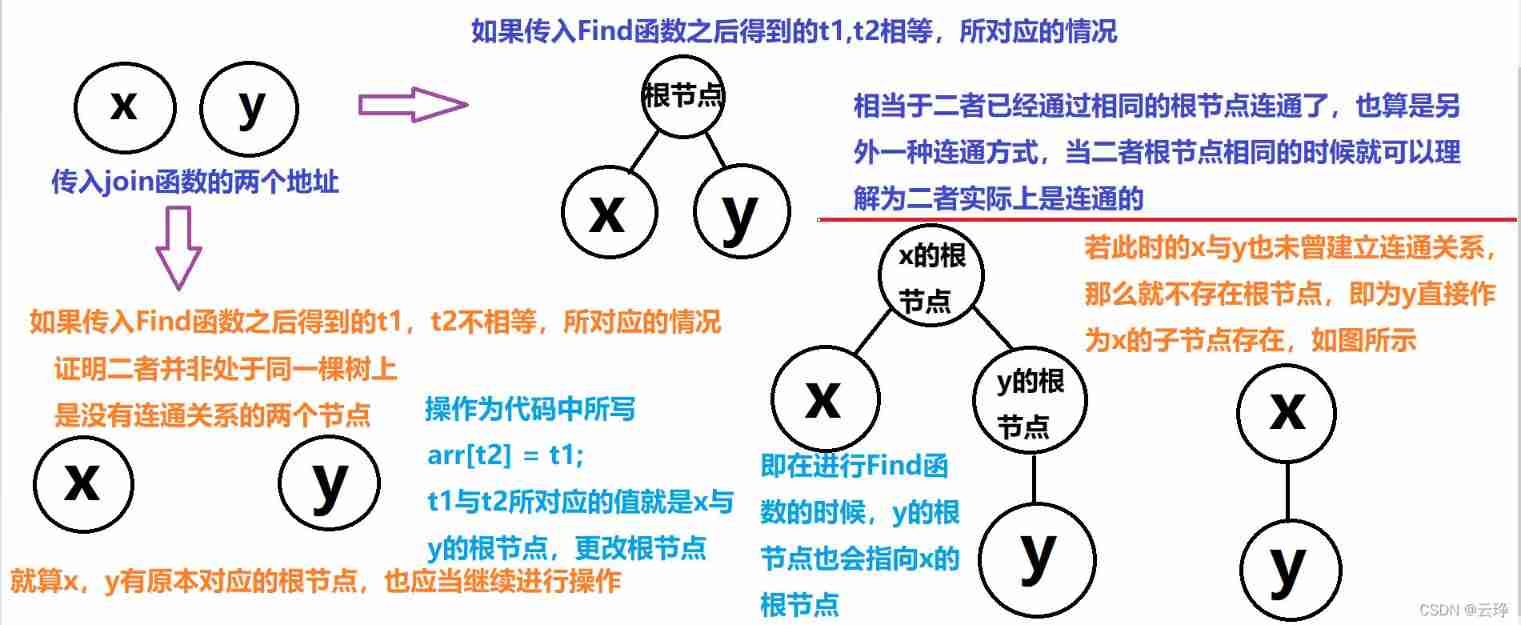
In essence, it is to build one binary tree after another in the array of arrays , Use the data stored in it to judge whether each node is a node on the same tree , If it is a node on a tree , Then it proves that the two are connected , If it is not a node on the same tree , Then it proves that the two are not connected .
The next code segment is the specific search process
int main()
{
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
}
// Make each city an independent node
// Wait for the input of connectivity , Once you enter connectivity, enter , Start connecting them into a tree
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
shuru[i].x = x;
shuru[i].y = y;
join(x, y);
}
// Use the structure array to record each input City address , That is to say x,y
// Simultaneous utilization join Function to connect these two nodes
// At the end of the cycle , Data entry is over , All nodes that need to be connected have completed the connection
int num = 0, num1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == i)
{
num++;
}
}
// Count the number of trees
// Exist alone , A node without any connectivity is also a tree
int k;
scanf("%d", &k);
while (k--)
{
num1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
}
// Clear all the connected data
// All the trees become original individual nodes
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
cha[x] = 1;
// Will find the point of cha[x] Change it to 1
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (cha[shuru[i].x] == 1 || cha[shuru[i].y] == 1)
{
continue;
}
else
{
join(shuru[i].x, shuru[i].y);
}
}
// Traverse the entered data , In addition to cha[x] The value of or cha[y] To change the value of 1 Outside the address of
// Continue to build tree relationships
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == i)
{
num1++;
}
}
// Count the number of trees again , Write it down as num1
if (num == num1 || num + 1 == num1)
{
printf("City %d is lost.\n", x);
}
else
{
printf("Red Alert: City %d is lost!\n", x);
}
num=num1
// If num == num1 || num + 1 == num1, It proves that the disappearance of the occupied city has not
// Fundamentally affect the connectivity of the city , Because the number of trees has not changed
// The conditions here will be explained later with a diagram
}
num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (cha[i] == 1)
{
num++;
}
// Look for cities that have been captured here , If the city has been occupied
//num The number of will increase
}
if (num == n)
{
printf("Game Over.\n");
}
// If num And n It's all equal , It proves that all cities have been occupied
// The game ends
return 0;
}Explain the conditions in the code segment num == num1 || num + 1 == num1

边栏推荐
- Chain ide -- the infrastructure of the metauniverse
- SQL foundation 9 [grouping data]
- The frost peel off the purple dragon scale, and the xiariba people will talk about database SQL optimization and the principle of indexing (primary / secondary / clustered / non clustered)
- Text processing function sorting in mysql, quick search of collection
- The important role of host reinforcement concept in medical industry
- [real case] how to deal with the failure of message consumption?
- Jianmu continuous integration platform v2.2.2 release
- Handwritten easy version flexible JS and source code analysis
- Node foundation ~ node operation
- Two years ago, the United States was reluctant to sell chips, but now there are mountains of chips begging China for help
猜你喜欢

University stage summary
Flink memory model, network buffer, memory tuning, troubleshooting
Bottom problem of figure
Adaptive spatiotemporal fusion of multi-target networks for compressed video perception enhancement

Unity 从Inspector界面打开资源管理器选择并记录文件路径
![[Flink] temporal semantics and watermark](/img/4d/cf9c7e80ea416155cee62cdec8a5bb.jpg)
[Flink] temporal semantics and watermark
Experience installing VMware esxi 6.7 under VMware Workstation 16
Status of the thread
大厂技术专家:架构设计中常用的思维模型
《剑指Offer》第2版——力扣刷题
随机推荐
2022-021ARTS:下半年开始
[network security] what is emergency response? What indicators should you pay attention to in emergency response?
jdbc连接es查询的时候,有遇到下面这种情况的大神嘛?
Paddleocr prompt error: can not import AVX core while this file exists: xxx\paddle\fluid\core_ avx
Status of the thread
MYCAT middleware installation and use
神经网络入门(下)
2022 - 021arts: début du deuxième semestre
Technical experts from large factories: common thinking models in architecture design
What is the use of cloud redis? How to use cloud redis?
Blog stop statement
Su Weijie, a member of Qingyuan Association and an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania, won the first Siam Youth Award for data science, focusing on privacy data protection, etc
Boosting the Performance of Video Compression Artifact Reduction with Reference Frame Proposals and
Rhcsa day 3
Comparison between applet framework and platform compilation
Docker install MySQL
flask-sqlalchemy 循环引用
Used on windows Bat file startup project
Crawler (III) crawling house prices in Tianjin
Recursive Fusion and Deformable Spatiotemporal Attention for Video Compression Artifact Reduction