当前位置:网站首页>Handling hardfault in RT thread
Handling hardfault in RT thread
2022-07-07 06:19:00 【TangZhenye】
1. background
When the system goes into abnormal , Usually, it will enter the handler corresponding to the exception , When there are illegal operations in the system , Such as division 0、 Non aligned access 、 Burst the stack , This triggers hardfault abnormal , In general ,hardfault Middle is a while(1), At this time, there are illegal operations in the system , It's going to be while(1) Hang forever , But at this time, we need to find out why the system crashed , How ? Where to check ? Usually enter hardfault The post call stack is also gone , Novice players will have a headache , I don't know where to start . therefore , When the system goes down , We must have enough information to help us analyze the cause of downtime
2. Basic knowledge of
- cm framework , The first action in response to an exception , It is to automatically save the necessary register information on site , In turn psp、pc、lr、r12、r3-r0 The hardware automatically pushes it into the appropriate stack
- cm The architecture is a dual stack pointer design , When the context environment is a threaded environment , The stack pointer is psp, When the context is an interrupt environment , Stack pointer is msp, The dual stack pointer design is naturally os And come , This ensures that the thread environment is isolated from the interrupt environment
- cm The stack of architecture grows downward
- Anytime , There is only one sp The pointer , Or psp, Or msp
3. rt-thread Construct stack frame
stay rt-thread Each thread in has its own stack space , Stack space can be static , It can also be applied dynamically , A stack is a continuous piece of memory .
struct exception_stack_frame { rt_uint32_t r0; rt_uint32_t r1; rt_uint32_t r2; rt_uint32_t r3; rt_uint32_t r12; rt_uint32_t lr; rt_uint32_t pc; rt_uint32_t psr; }; struct stack_frame // Different architectures , The size of stack frames is also different { /* r4 ~ r11 register */ rt_uint32_t r4; rt_uint32_t r5; rt_uint32_t r6; rt_uint32_t r7; rt_uint32_t r8; rt_uint32_t r9; rt_uint32_t r10; rt_uint32_t r11; struct exception_stack_frame exception_stack_frame; }; /* Initialize the thread stack , Construct stack frame */ rt_uint8_t *rt_hw_stack_init(void *tentry, void *parameter, rt_uint8_t *stack_addr, void *texit) { struct stack_frame *stack_frame; rt_uint8_t *stk; unsigned long i; stk = stack_addr + sizeof(rt_uint32_t);// To the top of the stack , The highest address in a continuous space stk = (rt_uint8_t *)RT_ALIGN_DOWN((rt_uint32_t)stk, 8); stk -= sizeof(struct stack_frame);// Offset down sizeof(struct stack_frame) A size stack_frame = (struct stack_frame *)stk; /* init all register */ for (i = 0; i < sizeof(struct stack_frame) / sizeof(rt_uint32_t); i ++) { ((rt_uint32_t *)stack_frame)[i] = 0xdeadbeef; } stack_frame->exception_stack_frame.r0 = (unsigned long)parameter; /* r0 : argument */ stack_frame->exception_stack_frame.r1 = 0; /* r1 */ stack_frame->exception_stack_frame.r2 = 0; /* r2 */ stack_frame->exception_stack_frame.r3 = 0; /* r3 */ stack_frame->exception_stack_frame.r12 = 0; /* r12 */ stack_frame->exception_stack_frame.lr = (unsigned long)texit; /* lr When the thread exits , Will execute thread */ stack_frame->exception_stack_frame.pc = (unsigned long)tentry; /* entry point, pc, Thread switching , Enter the user thread function */ stack_frame->exception_stack_frame.psr = 0x01000000L; /* PSR */ /* return task's current stack address */ return stk; }Why construct a stack frame ?
After a thread is initialized , How to enter the thread processing function ? It is decided by the scheduler , The scheduler chooses to switch to the highest priority thread that is ready at the current time , Will manually trigger a Pendsv abnormal , Get into Pendsv When abnormal , The context of the thread being cut will be saved , Restore the context of the thread to be executed to the register . Through the backward method , Without the initial stack context of the above construct , How to restore to the register ? therefore , After constructing a stack frame , Stack the contents of the above stack frame into the register ,pc The register is assigned as tentry This function pointer , The stack pointer of the thread to be executed at this time sp( Point to the top of the stack , Because this thread executes for the first time , It's done again push operation ) Update to psp, When the exception ends and returns , It jumps to the processing function of the thread . If the thread returns , The thread will never be executed , therefore , You also need to collect the corpse of the thread , That is to release the resources occupied by this thread , When constructing stack frames texit function , The address of this function is Pendsv In the exception handler push here we are lr In the register , When the function returns , The function must be executed . Corpse collection , It happened in idle In the thread , When the system is idle , Release these zombie threads .
rt-thread Switch thread details
rt-thread When switching threads , Get into PendSv Before the exception ,psp This is the top of the stack of the thread being cut , At this time, the hardware is automatically pressed 8 Value of registers , You also need to manually push the remaining registers into the stack corresponding to this thread , Because the thread needs to give up the right to use the processor , Therefore, the context of this thread needs to be saved in the stack .
There is another key step , The context of the thread being cut has been saved in the stack , At this time, in the thread control block sp No updates , Thread cutting is based on sp To cut , therefore , You still need to psp The value of is updated back to sp . At this time, the context of the thread is saved in the stack , At the same time, the top of the stack is also saved in the thread control block , Next time the context is restored , You will be able to recover .
4. rt-thread in HardFault_Handler
rt-thread take HardFault_Handler Rewrote , Delete the meaningless while(1), Added more information
IMPORT rt_hw_hard_fault_exception EXPORT HardFault_Handler HardFault_Handler PROC ; get current context TST lr, #0x04 ; if(!EXC_RETURN[2]) ITE EQ MRSEQ r0, msp ; [2]=0 ==> Z=1, get fault context from handler. MRSNE r0, psp ; [2]=1 ==> Z=0, get fault context from thread. STMFD r0!, {r4 - r11} ; push r4 - r11 register STMFD r0!, {lr} ; push exec_return register TST lr, #0x04 ; if(!EXC_RETURN[2]) ITE EQ MSREQ msp, r0 ; [2]=0 ==> Z=1, update stack pointer to MSP. MSRNE psp, r0 ; [2]=1 ==> Z=0, update stack pointer to PSP. PUSH {lr} # Push the lr To determine whether the exception occurred in the thread or in the interrupt BL rt_hw_hard_fault_exception POP {lr} ORR lr, lr, #0x04 BX lr ENDP ALIGN 4 ENDBefore entering the exception , The hardware automatically pushes some registers onto the stack , At this time lr The value in the register represents the environment before entering the exception ( Thread or interrupt ), This environment determines that the stack pointer is psp still msp. therefore , Judge this lr The register of bit2 yes 0 still 1 To get the stack used before entering the exception . Then press the registers that will not be pressed by the hardware into the corresponding stack (psp or msp) in , Then update the top of the stack to r0 In the register , Jump into C Function to print relevant information , The input parameter is the top address
/* The position of members shall be placed in strict accordance with the stack pressing order */ struct exception_info { rt_uint32_t exc_return; // Enter the environment before the exception struct stack_frame stack_frame; // Constructed stack frame data structure }; void rt_hw_hard_fault_exception(struct exception_info * exception_info) { #if defined(RT_USING_FINSH) && defined(MSH_USING_BUILT_IN_COMMANDS) extern long list_thread(void); #endif struct stack_frame* context = &exception_info->stack_frame; if (rt_exception_hook != RT_NULL) // Hook function { rt_err_t result; result = rt_exception_hook(exception_info); // Execute other exception analysis functions if (result == RT_EOK) return; } rt_kprintf("psr: 0x%08x\n", context->exception_stack_frame.psr); rt_kprintf("r00: 0x%08x\n", context->exception_stack_frame.r0); rt_kprintf("r01: 0x%08x\n", context->exception_stack_frame.r1); rt_kprintf("r02: 0x%08x\n", context->exception_stack_frame.r2); rt_kprintf("r03: 0x%08x\n", context->exception_stack_frame.r3); rt_kprintf("r04: 0x%08x\n", context->r4); rt_kprintf("r05: 0x%08x\n", context->r5); rt_kprintf("r06: 0x%08x\n", context->r6); rt_kprintf("r07: 0x%08x\n", context->r7); rt_kprintf("r08: 0x%08x\n", context->r8); rt_kprintf("r09: 0x%08x\n", context->r9); rt_kprintf("r10: 0x%08x\n", context->r10); rt_kprintf("r11: 0x%08x\n", context->r11); rt_kprintf("r12: 0x%08x\n", context->exception_stack_frame.r12); rt_kprintf(" lr: 0x%08x\n", context->exception_stack_frame.lr); rt_kprintf(" pc: 0x%08x\n", context->exception_stack_frame.pc); if(exception_info->exc_return & (1 << 2) ) // bit2 by 1, Represents the threading environment { rt_kprintf("hard fault on thread: %s\r\n\r\n", rt_thread_self()->name); #if defined(RT_USING_FINSH) && defined(MSH_USING_BUILT_IN_COMMANDS) list_thread(); #endif } else { rt_kprintf("hard fault on handler\r\n\r\n"); } #ifdef RT_USING_FINSH hard_fault_track(); #endif /* RT_USING_FINSH */ while (1); }According to the above print information and corresponding disassembly , You can find it hardfault The code being executed before , meanwhile , When a function is called , The return address is also pushed into the corresponding stack , therefore , According to these basic information , There is still some processing space , It can be written by the great God cmbacktrace The software package automatically analyzes the function call stack .
The key point is to master the handling ideas when the system is down , Need to be right cm The processor of the architecture has a certain understanding
5. Manual analysis
First, according to the environment before entering the exception , Make sure it's that sp, Then the sp Copy the value of to the memory lookup window , lookup sp Points to in memory pc value ( Because the hardware will automatically press the stack ), Then in disassembly according to this pc You can find the assembly instruction executed before the exception occurs 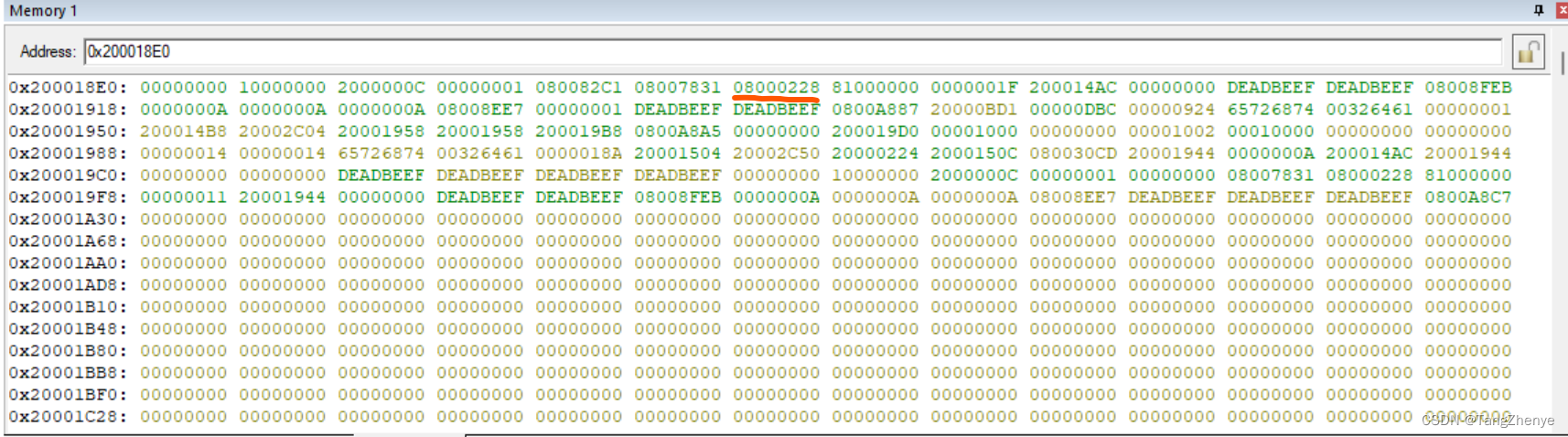
Why is the red underline in the above figure pc Well ? It needs to be determined according to the number and order of registers automatically pressed by hardware , Different processors are different
边栏推荐
- Bypass open_ basedir
- 字符串常量与字符串对象分配内存时的区别
- Rk3399 platform development series explanation (WiFi) 5.52. Introduction to WiFi framework composition
- VMware安装后打开就蓝屏
- k8s运行oracle
- JVM命令之 jstat:查看JVM統計信息
- Three updates to build applications for different types of devices | 2022 i/o key review
- 一名普通学生的大一总结【不知我等是愚是狂,唯知一路向前奔驰】
- Rk3399 platform development series explanation (WiFi) 5.53, hostapd (WiFi AP mode) configuration file description
- Software testing knowledge reserve: how much do you know about the basic knowledge of "login security"?
猜你喜欢
@Detailed differences between pathvariable and @requestparam
JVM命令之 jinfo:实时查看和修改JVM配置参数
![[FPGA] EEPROM based on I2C](/img/28/f4f2efda4b5feb973c9cf07d9d908f.jpg)
[FPGA] EEPROM based on I2C

Career experience feedback to novice programmers
Implementation of VGA protocol based on FPGA
Financial risk control practice - decision tree rule mining template
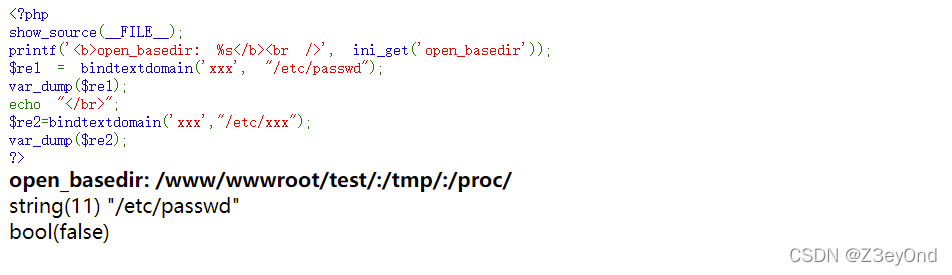
Bypass open_ basedir
Sequential storage of stacks
![[FPGA tutorial case 14] design and implementation of FIR filter based on vivado core](/img/fc/5162bbb0746f8af2d6c7d63ade571a.png)
[FPGA tutorial case 14] design and implementation of FIR filter based on vivado core
Introduction to yarn (one article is enough)
随机推荐
vim映射大K
ETCD数据库源码分析——从raftNode的start函数说起
软件测试的几个关键步骤,你需要知道
Value range of various datetimes in SQL Server 2008
开发者别错过!飞桨黑客马拉松第三期链桨赛道报名开启
从“跑分神器”到数据平台,鲁大师开启演进之路
FlexRay通信协议概述
Introduction to yarn (one article is enough)
软件测试知识储备:关于「登录安全」的基础知识,你了解多少?
JMeter's own functions are not enough? Why don't you develop one yourself
Understand the deserialization principle of fastjson for generics
postgresql 数据库 timescaledb 函数time_bucket_gapfill()报错解决及更换 license
Check point: the core element for enterprises to deploy zero trust network (ztna)
go-microservice-simple(2) go-Probuffer
[FPGA tutorial case 13] design and implementation of CIC filter based on vivado core
Redisl garbled code and expiration time configuration
Talking about reading excel with POI
360织语发布7.0新品 为党政军、央国企打造专属“统一数字工作空间”
cf:C. Column Swapping【排序 + 模擬】
计算模型 FPS