当前位置:网站首页>MySQL index (1)
MySQL index (1)
2022-07-05 12:13:00 【ziyi813】
MySQL Indexes
The concept is introduced
What is index
An index is a data structure that stores records in a database in a special form . Through the index , Can significantly improve the efficiency of data query , So as to improve the performance of the server .
An index is an ordered list , In this list are stored the value of the index and the physical address of the row containing the data of this value . When the database is very large , Indexing can greatly speed up queries , This is because after using the index, you can locate the data of a row without scanning the whole table , Instead, we first find the corresponding physical address of the row data through the index table, and then access the corresponding data .
Indexes , It's not MySQL Database specific mechanism , There will be similar and different implementations in relational databases . Here we are just discussing MySQL Index implementation in database .
in fact , be supposed to MySQL The index is actually not accurate . Because in MySQL in , Indexes are implemented at the storage engine level, not at the server level . This means that the index we are talking about is exactly InnoDB Engine or MyISAM Engine or other storage engine .
So the index is even in MySQL There is no uniform standard in , The indexes implemented by different storage engines work differently . Not all storage engines support the same type of index , Even multiple engines support the same type of index , The underlying implementation may be different .
Why index is needed
The index seems to be adding a to the database 「 Catalog page 」, Can easily query data . But that's all the index does , Why do you need to spend a lot of time building and optimizing indexes ?
After using the index, you can locate the data of a row without scanning the whole table , Instead, we first find the corresponding physical address of the row data through the index table, and then access the corresponding data . This method naturally reduces the amount of data that the server needs to scan the database when responding .
More Than This , The scope of the database when the query is executed , If you don't use indexes , that MySQL It will first scan all row data in the database and filter out row records within the target range , Sort these row records and generate a temporary table , Then return the target row record of the user query through the temporary table . This process will involve the establishment of temporary tables and the sorting of row records , When there are many records in the target line , It will greatly affect the efficiency of range query .
So when you add an index , Because of the order of the index itself , When querying the range , The filtered row records have been sorted , This avoids the problems of re sorting and the need to establish temporary tables .
meanwhile , Due to the order of the underlying implementation of the index , So that when querying data , It can avoid random addressing in different sectors of the disk . After using the index, the access to data on the disk can be addressed roughly in order through disk pre reading . This is essentially based on the principle of locality .
** Locality principle :** When a data is used , Data in the vicinity is often used immediately . The data needed during program operation is usually centralized . Due to the high efficiency of disk sequential reading ( No seek time required , Only a small amount of rotation time is required ) , Therefore, for programs with local characteristics , Disk pre reading can improve I/O efficiency .
Disk read ahead is required to read ahead every time. The length is generally an integral multiple of the page . Moreover, the database system sets the size of a node equal to one page , In this way, each node only needs one time I/O You can load it completely . The page here is realized through page memory management , The concept is briefly mentioned here .
Paging mechanism Is to divide the memory address space into several small fixed size pages , The size of each page is determined by memory . This is done to map from a virtual address to a physical address , Improve memory and disk utilization .
To sum up . The existence of index has great advantages , The main performance is as follows :
- Indexing greatly reduces the amount of data that the server needs to scan
- Indexes can help the server avoid sorting and temporary tables
- Index can be random I/0 Into order I/0
The above three points can greatly improve the efficiency of database query , Optimize server performance . So in general , Adding efficient indexes to the database is one of the important work of database optimization .
Disadvantages of index
The existence of indexes can improve performance , Naturally, there will be additional costs in other ways .
The index itself is stored as a table , So it takes up extra storage space ; The creation and maintenance of index tables requires time and cost , This cost increases with the amount of data ; Building an index will reduce the modification of data ( Delete , add to , modify ) The efficiency of , Because you need to modify the index table as well as the data table ;
So for very small tables , The cost of using an index is greater than a direct full table scan , At this time, you don't have to use the index .
Classification of indexes
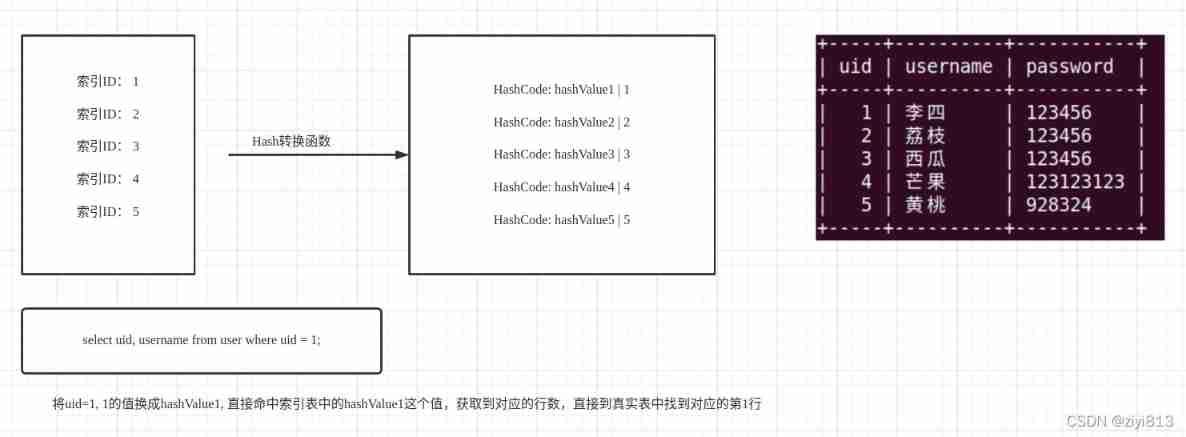
Index is a data structure used by storage engine to quickly find records , Classify according to the way of implementation , There are mainly Hash Index and B+Tree Indexes
Hash Indexes
Time complexity O(1)
principle :
According to the specific algorithm function , Generate hash The value stores the corresponding row position , When querying, it is converted into... According to the index value hash Value hit hash Value to get the corresponding row position , Avoid full table scanning .
B+Tree Indexes
Information to be supplemented
Index type
Single index :
An index contains only a single column , But you can have multiple single-column indexes in a table ,
Single column index can be divided into : General index , unique index , primary key
Composite index
Full-text index
Spatial index
Index operation
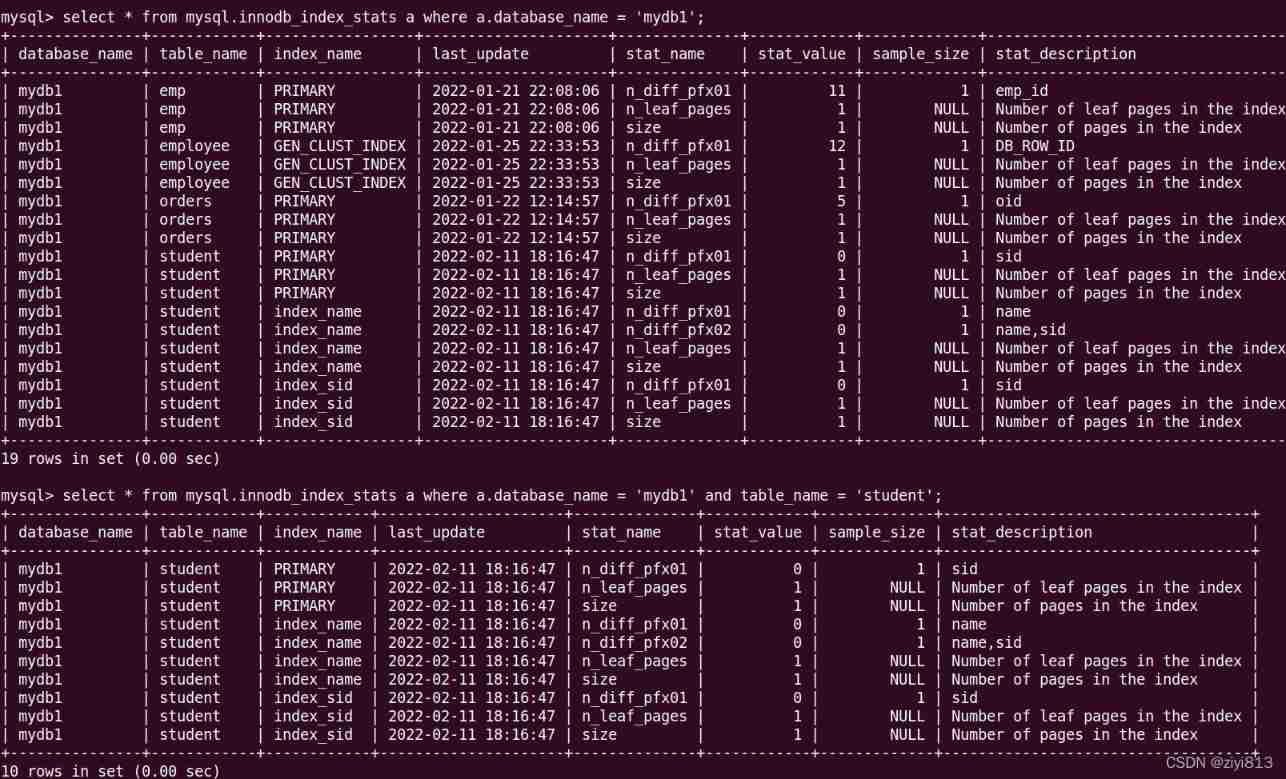
Index view
-- View all indexes of the database
-- grammar
select * from mysql.`innode_index_stats` a where a.`database_name` = ' Database name ';
-- Example 1, Inquire about mydb1 All indexes in the library
select * from mysql.`innodb_index_stats` a where a.`database_name` = 'mydb1';
-- Example 2, Inquire about mydb1 In the library student All indexes in the table
select * from mysql.innodb_index_stats a where a.database_name = 'mydb1' and table_name = 'student';
-- View all indexes in the table
-- grammar
show index from table_name;
-- Example
show index from student;
Delete index
-- The way 1
drop index Index name on Table name
-- The way 2
alter table Table name drop index Index name
Single index
Single column index can be divided into : General index , unique index , primary key
primary key
Each table usually has its own primary key , When we create a table ,MySQL The primary key column will be automatically created An index , This is the primary key index , The primary key index is unique and cannot be NULL.
General index
MySQL Basic index type , There are no restrictions , Allows you to insert duplicate and null values in a column that defines an index , Just to query the data a little faster .
There are three ways to create a normal index :
-- When creating a table
create table user(
uid int primary key,
name varchar(50),
index index_uid(uid) -- to uid Column to create a normal index
);
-- The way 2- Create directly
create index index_name on user(name); -- to user Tabular name Field creation index
-- The way 3 Modify table structure ( Add index )
-- alter table tableName add index index_name(cloumnname)
alter table user add index index_name(name);
unique index
The value of the index column must be unique , But you can have an empty value , If it's a composite index , The combination of column values must be unique .
-- The way 1, When creating a table Direct designation
create table stu(
sid int primary key,
card_id varchar(20),
name varchar(50),
age int,
phone varchar(11),
unique index_card_id(card_id) -- to card_id Column creates a unique index
);
-- The way 2, Create directly
-- create unique index Index name on Table name ( Name )
create unique index index_card_id on stu(card_id);
-- The way 3, Modify table structure
-- alter table Table name add unique [ Index name ] ( Name )
alter table stu add unique index_phone (phone)
Composite index
Composite index, also known as composite index , It means when building the index Multiple fields used , Similarly, it can be established as a common index or a unique index
The leftmost principle of composite index
Format :
-- The basic syntax for creating an index
create index indexname on table_name(column1(length), column2(length));
-- Example , Create a normal index
create index index_phone_name on stu(phone, name);
-- Example , Create unique index
create unique index unique_index on stu(phone, sid);
What is the leftmost principle ?
First match the first index field , You must match to the first field to hit the index . If it is and Then both can hit
Example
select * from stu where name = ' full name '; -- No hit index
select * from stu where phone = '15507551111'; -- Hit index
select * from stu where phone = '18888888888' and name = ' full name '; -- Hit index
select * from stu where name = ' full name ' and phone = '1888888888'; -- Hit index
Full-text index
The keyword of full-text index is fulltext, Not many scenes are used
Full text index is mainly used to find keywords in text , Instead of comparing directly with the values in the index , It's more like a search engine , Query based on similarity , Not simply where The parameters of the statement match
use like Fuzzy matching can be realized , Why full text indexing ?
like When there is less text The index is OK , But for a large number of text data retrieval , Efficiency and performance are not very good . Full text index is in front of a large amount of text data , Effect and performance ratio like better .
summary
Full text index in mysql5.6 Previous versions , Only MyISAM Storage engine support ,5.6 in the future MyISAM and InnoDB Storage engines support full-text indexing .
Only the data of the field is char, varchar, text Its series (longtext, etc. ) Before you can build a full-text index
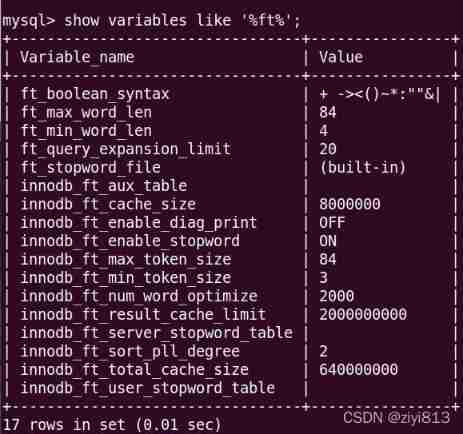
MySQL Full text index in , There are several key variables ,
Minimum search length and maximum search length , Less than the minimum search length and more than the maximum search length will not be indexed .
-- View the variables related to the global full-text index
show variables like '%ft%';
Operate full text index
Create full text index
The creation method is similar to the only one above , Keywords are fulltext
Use index
Use full-text indexing and common fuzzy matching like Different , Full text index has its own syntax format , Use match and agains keyword .
Format :
match(col1, col2, ...) against(expr [search_modifier])
Example :
select * from article where match(content) against(' Happy New Year! ');
Spatial index
stay MySQL5.7 Only later versions support spatial indexes .
Spatial index is to index the fields of spatial data type , Just know that you have this thing , Regular development doesn't work .
边栏推荐
- Reading notes of growth hacker
- 强化学习-学习笔记3 | 策略学习
- Take you two minutes to quickly master the route and navigation of flutter
- 7月华清学习-1
- 谜语1
- 15 methods in "understand series after reading" teach you to play with strings
- [HDU 2096] 小明A+B
- Mongodb replica set
- MVVM framework part I lifecycle
- Error modulenotfounderror: no module named 'cv2 aruco‘
猜你喜欢
![[mainstream nivida graphics card deep learning / reinforcement learning /ai computing power summary]](/img/1a/dd7453bc5afc6458334ea08aed7998.png)
[mainstream nivida graphics card deep learning / reinforcement learning /ai computing power summary]

什么是数字化存在?数字化转型要先从数字化存在开始

The most comprehensive new database in the whole network, multidimensional table platform inventory note, flowus, airtable, seatable, Vig table Vika, flying Book Multidimensional table, heipayun, Zhix

【yolov5.yaml解析】
自动化测试生命周期
Two minutes will take you to quickly master the project structure, resources, dependencies and localization of flutter
Embedded software architecture design - message interaction

Matlab imoverlay function (burn binary mask into two-dimensional image)

互联网公司实习岗位选择与简易版职业发展规划
Splunk configuration 163 mailbox alarm
随机推荐
MySQL splits strings for conditional queries
一类恒等式的应用(范德蒙德卷积与超几何函数)
【使用TensorRT通过ONNX部署Pytorch项目】
【Win11 多用户同时登录远程桌面配置方法】
Swift - add navigation bar
[calculation of loss in yolov3]
Vscode shortcut key
全网最全的新型数据库、多维表格平台盘点 Notion、FlowUs、Airtable、SeaTable、维格表 Vika、飞书多维表格、黑帕云、织信 Informat、语雀
Pytorch linear regression
【TFLite, ONNX, CoreML, TensorRT Export】
Principle of redis cluster mode
How to make your products as expensive as possible
Matlab superpixels function (2D super pixel over segmentation of image)
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)
【ijkplayer】when i compile file “compile-ffmpeg.sh“ ,it show error “No such file or directory“.
Why learn harmonyos and how to get started quickly?
A guide to threaded and asynchronous UI development in the "quick start fluent Development Series tutorials"
查看rancher中debug端口信息,并做IDEA Remote Jvm Debug
报错ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘cv2.aruco‘
Pytorch softmax regression

