当前位置:网站首页>LAN communication process in the same network segment
LAN communication process in the same network segment
2022-07-06 05:51:00 【Creator of high-quality network system】
The process of communicating with a network segment in a LAN
It's needed at this time ENSP Simulator , It has been installed before , We go through ENSP To build an experimental environment , In this way, we can see the effect of the experiment and share the whole process by grabbing the bag , Let's first look at the communication process in the same network segment .
1、 preparation
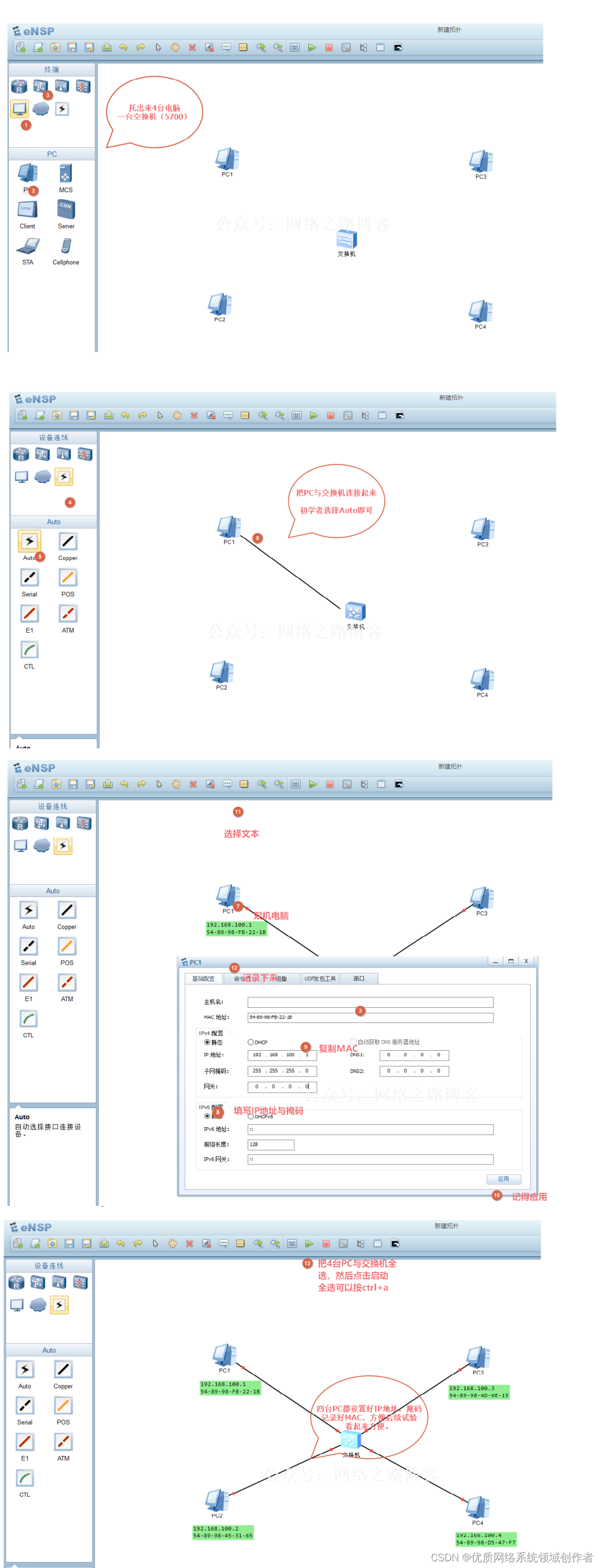
2、 Start testing
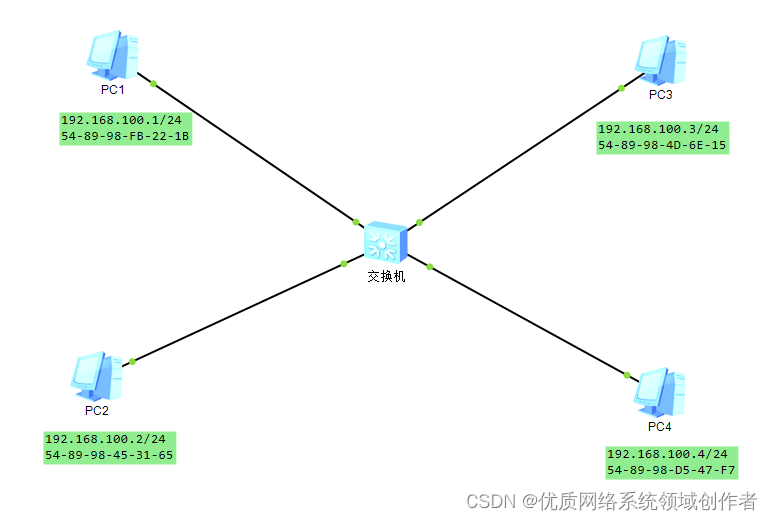
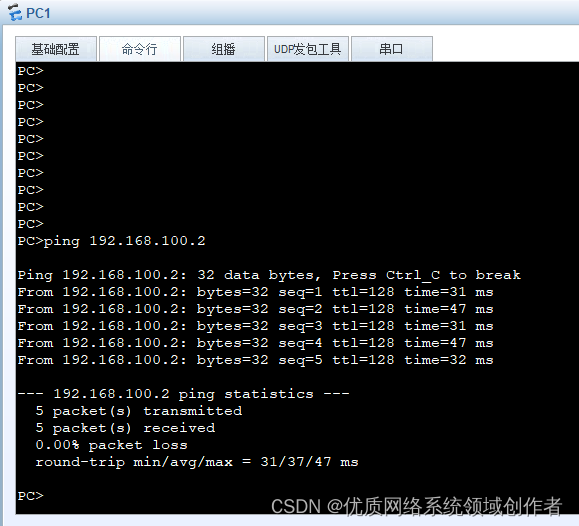
We use first PC1 Visit PC4, Let's look at the results first , Use of tests ICMP protocol ping Tools , The agreement hasn't been explained yet , And , This agreement is also an important agreement for subsequent troubleshooting .
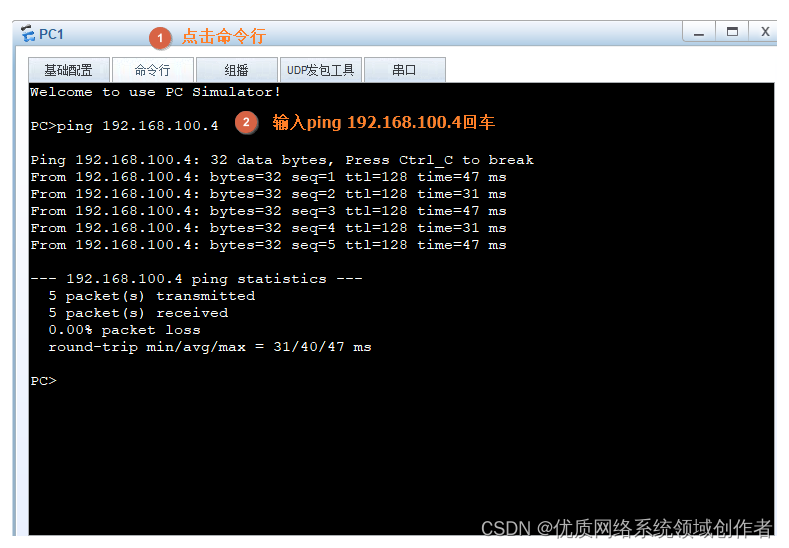
A simple test shows that , Indicates that the communication is normal , This is Ping Tools , Can detect the quality of the network 、 How about stability , Back to the point ,PC1 To PC4 Yes, it's already through , from IP In terms of address communication rules , Is in the same network segment , It's normal to get through , So what happens during its communication ?
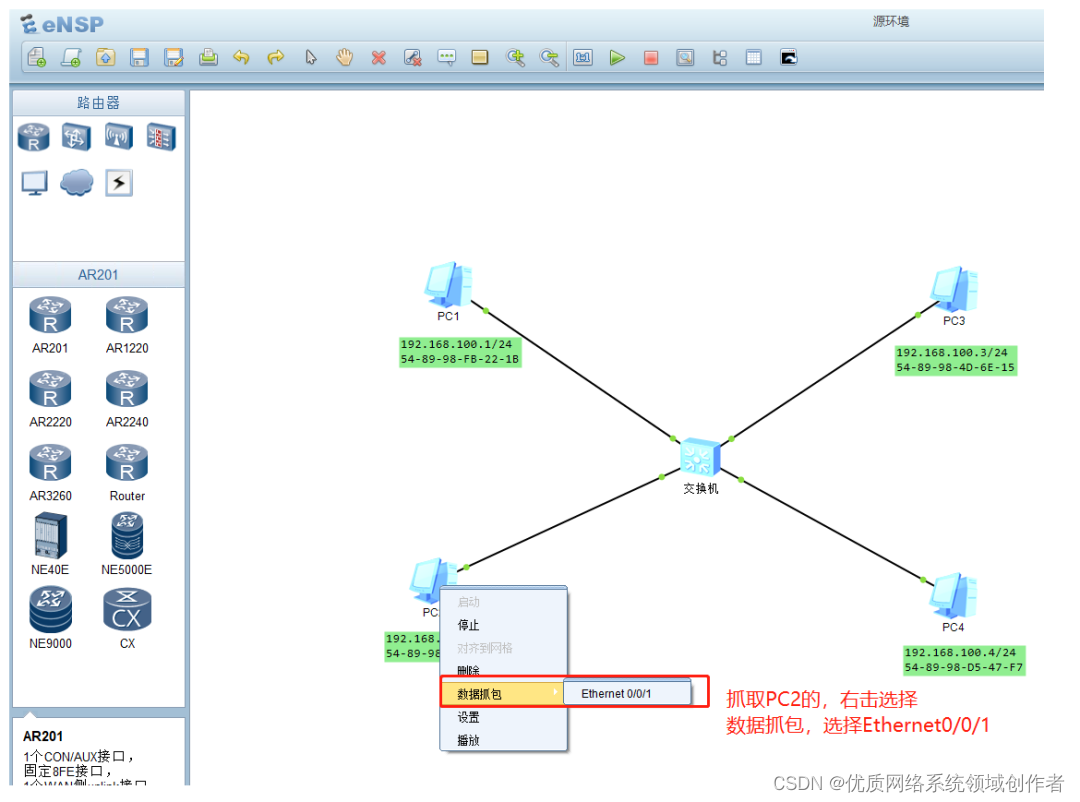
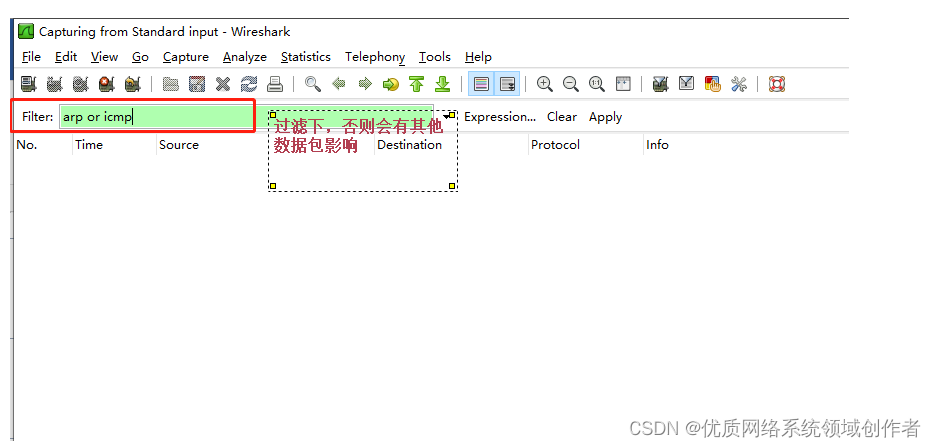
Open the grab bag ,PC1 visit PC2, Grab PC2 The data of , Let's see what happened during the communication ! because ping It only echoes the results , I don't know what happened in the middle , But this is the key to understand .
The result is obviously ok , Our focus is on what content is captured .
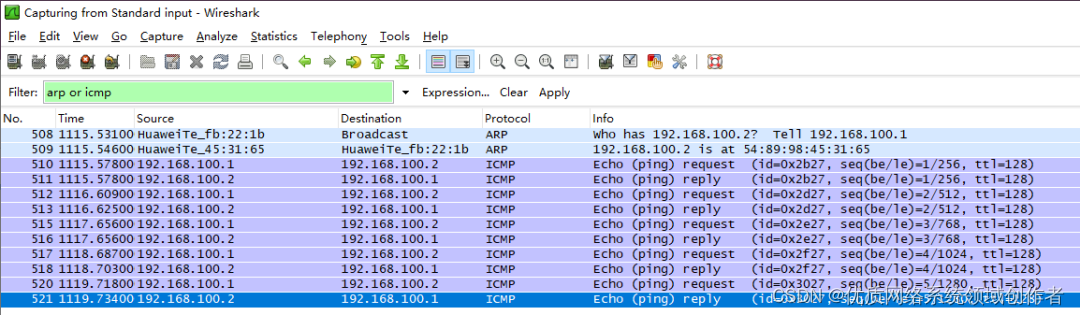
12 A packet ,protocol There are two types , One is ARP、 One is ICMP,ICMP As mentioned above , That's what we typed on the command line Ping,icmp in total 10 A package ( Back and forth 5 individual ), that ARP What is it for ? This needs to be integrated from what we have learned before , Only in this way can we understand the process thoroughly .
(1)IP Communication rules
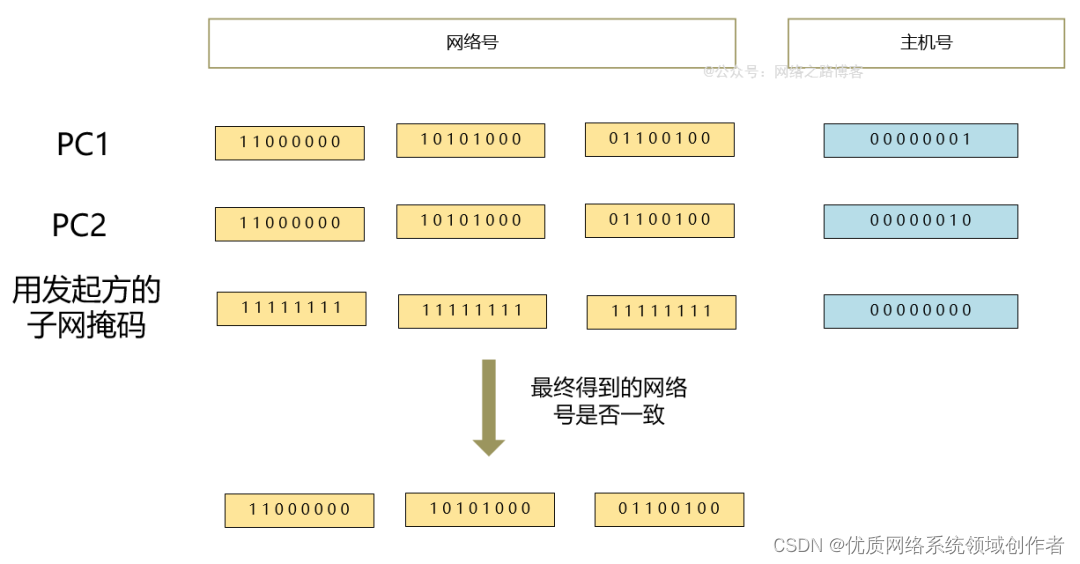
PC1(192.168.100.1/24) visit PC2(192.168.100.2) When ,PC1 Will use their own subnet mask to calculate their own network number , Then judge whether it is in a network segment according to the destination address , The judgment is based on whether the network numbers on both sides are consistent , Then there is a question ,PC1 It's impossible to know PC2 What is the mask of ,PC1 Only know your own , Because you can read the parameters of the network card , therefore PC1 The judgment is still calculated based on its own subnet mask PC2 What is the network number of your address , And then make a comparison , Obviously the same outlet number ,PC1 Will send data directly to PC2.( source address 192.168.100.1, Destination address 192.168.100.2)
(2) Data encapsulation
Now, through the calculation of the mask, it is found that the other party is in the same network segment with itself ,PC1 Will begin to encapsulate , The top is ICMP Protocol data , In the middle is the network layer , contain IP Head ( The source address is 192.168.100.1, The destination address is PC2 The address of 192.168.100.2), This is all known .( Here's how ,PC2 The address of , If only from PC1 I don't know , We send instructions to call ICMP Of ping The function is sent to 192.168.100.2,ICMP Call the network layer , Tell it what the destination address is , Many novices are confused , So here's more explanation )
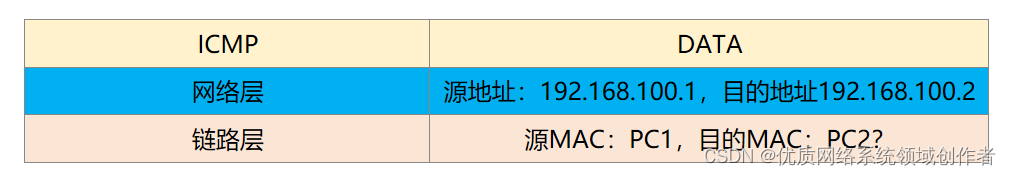
The problem now lies in the two-layer packaging , Source MAC, Naturally, it is PC1 Of MAC Address (54-89-98-FB-22-1B), however PC2 Of MAC How many? ,PC1 I don't know , If you don't know , Then you can't finish the packaging , So at this time, there must be an agreement to solve this problem , Give Way PC1 Can get the target MAC Address , Finish packaging , This agreement is ARP.
(3) From grasping the bag to understand ARP Message structure of
In understanding ARP Before the message structure , Let's get to know ARP How it works , Then in combination with the content of the packet capture , You can have a deeper grasp of ARP 了 .
ARP There are two types of messages ,ARP Request and ARP Respond to
PC1 Sending packets to PC2 When , I don't know PC2 Of MAC How much is the , therefore PC1 Will send a broadcast ARP Request , The content of this request package is request PC2 host IP Address corresponding MAC What's the address
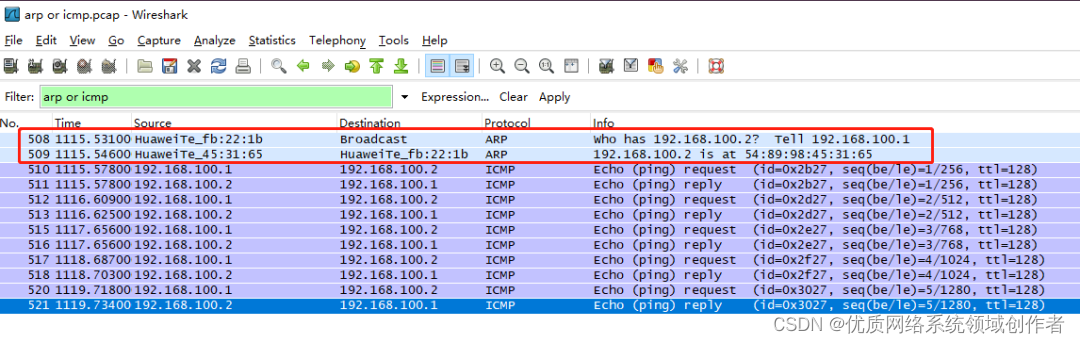
Look ahead first 2 individual , What do you think of packets , You can double-click the first , Will be displayed separately , This is also an important tool for us to further study the protocol , Can really see the whole process and content .
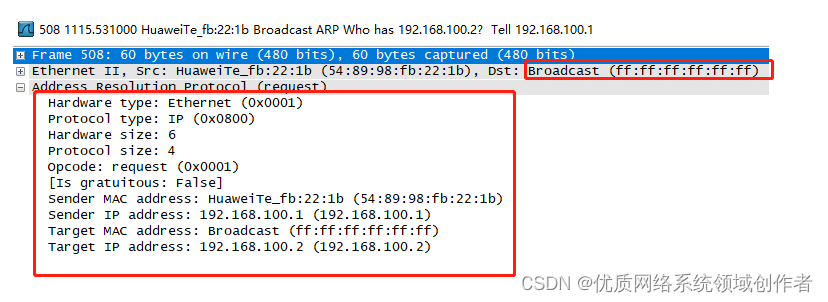
It's mentioned above that ARP There are two messages , The first package must be a request , Then it's in ARP The middle structure is as shown in the figure above .
Hardware Type: Usually the value is displayed as Ethernet (0x0001)
Protocol Type: Is this type familiar , stay IP There is also... In the agreement , stay ARP Indicate who to serve , Usually the value is IP(0x0800)
Hardware address and protocol address length : This means MAC Address and IP Byte length of address
Opcode:requeset(0x0001): This is used to identify this ARP Whether the package is a request package or a response package , When the operation value is 1 When , Said is ARP request
Sender MAC Address( The sender MAC): Indicates the sender's MAC Address ( Here for PC1 Of MAC 54-89-98-FB-22-1B)
Sender IP Address( The sender's IP): Indicates the sender's IP Address ( here PC1 Of IP yes 192.168.100.1)
Target MAC address( Target MAC): Target MAC Address , You will send some here is a special MAC Address , There is an error in the simulator , It's all. F, Show broadcast , But the standard format is all 0, It means unknown

Target IP address( Target IP): Indicate the purpose of IP What's the address , Also ask for the IP Of MAC
Useful information to master
The red part here indicates the key place , To master , First, let's have a special , The goal is MAC That field , Use all F It means , Mentioned above ,ARP The request packet is sent in the form of broadcast , The broadcast is in the Ethernet header , Purpose MAC The address means all F

Then why broadcast ? This goes back to the network characteristics of Ethernet , It is a typical structure of multiple access , From the topology , The switch is connected to several PC,PC1 Don't know 192.168.10.2 Which is it PC above , So it wants to know this MAC What's the address , The request can only be obtained by broadcasting , When this packet is broadcast , Everyone will receive , So when you get it , Who will respond ? That's what it is ARP Target in request message IP The meaning of existence , It indicates that this is what is requested IP Of MAC Address , Na Yuan MAC And IP What is the function of ? This is to enable the corresponding target to package back correctly , Or you send a request package , Don't tell others who is asking , The other party can't find anyone to ask for a response .
I saw ARP After the message structure content of , Combined with our tests , Is it easy to understand ,PC1 I do not know! PC2 Of MAC What's the address , So I sent ARP Request message , Source in message IP And MAC yes PC1, Requested target IP yes 192.168.100.2, The goal is MAC Unknown , So it's all in the form of radio F, Sent to all terminal devices in the same link area , Other equipment will disassemble this after receiving it ARP Request the contents of the package , If the target in the request package is found IP Address and own IP The address is consistent , Then the device will respond to the request , If not, discard ( Find that you're not looking for yourself )
therefore PC2 Find that the request package is asking yourself , So using ARP Respond to this request .( Let's look at the field content of the response message )
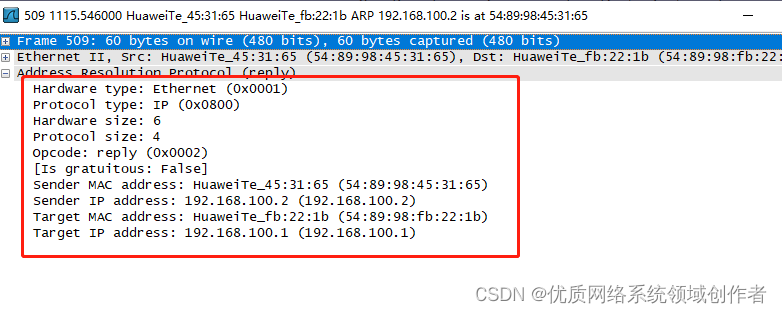
Most fields of the picture are the same , Let's look at the changes
Opcode:reply(0x0002): This becomes a response , The type is 2
Sender MAC Address( The sender MAC): This is PC2 Upon receipt of the request , Put your own... In the response package MAC The address is contained in the source MAC Inside
Sender IP Address( The sender's IP): Of the responding party IP Address , Here for 192.168.100.2(PC2 Of )
Target MAC address( Target MAC): The requester's goal MAC(PC1, It requests )
Target IP address( Target IP): Requestor's IP Address (PC1,192.168.100.1)
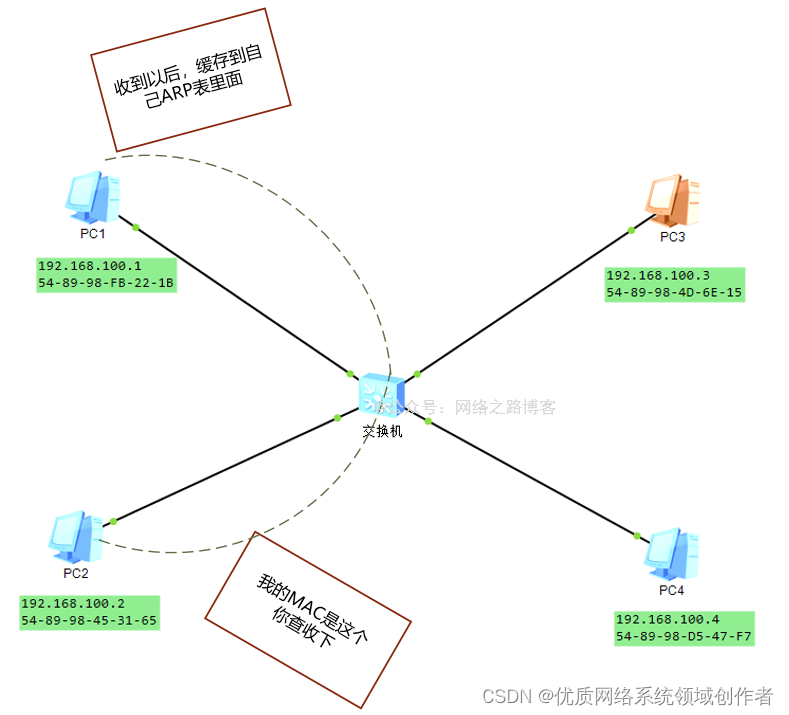
such PC1 You know the PC2 Of MAC What's the address , Then you can complete the packaging , Send a packet to PC2 了 , In addition, it can be found that unicast is used in response ( because PC2 got it PC1 Of MAC How much is the )
Now there's a problem ,PC1 Send data to PC2, Need to be ARP Please ?ARP The request packet is a broadcast message , Other unrelated terminals also need to view the contents of this package , If you send a packet every time ARP request , Once the network is large , It's not a waste of link bandwidth , To solve this problem , There is a table entry on terminal equipment and network equipment , be called ARP surface , Used to cache yourself through ARP Obtained by agreement IP And MAC The corresponding information of , In a certain amount of time , as long as ARP The table entry has this IP Corresponding MAC The entry of , You don't have to go ARP request .
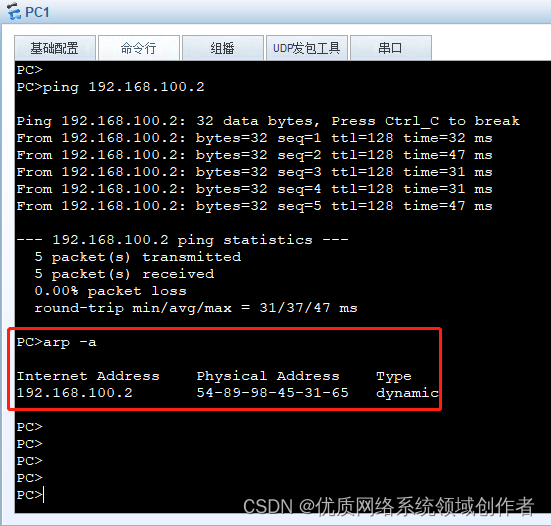
Through the command arp -a, You can see ,192.168.100.2 Corresponding MAC What's the address , also Type Is dynamic , Dynamic means that this record has time , Time goes by , Then it will disappear . image Windows The system default is 2 minute (arp -a It means to check arp cache ,Windows CMD The instructions inside )
(4) decapsulation
PC1 send out ICMP When the packet comes out , The switch will be based on MAC Table query found PC2 The location of (MAC It's recorded in the table PC2 Of MAC What's the address ), How switches work , In the third article, the link layer briefly mentioned , Go back and learn more about... After entering the exchange chapter ,PC2 Receive this packet , It will be unsealed , that PC2 How do you know that this packet is for yourself ? At this time, we need to take a look at the head of Ethernet .
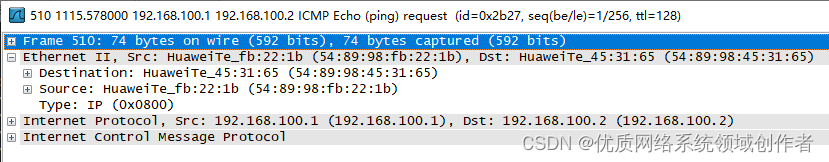
From the perspective of bag grabbing , The Ethernet header displays three fields
Destination( Purpose MAC): here MAC The address is PC2, If it is all F It means broadcast ( All hosts in the link area will be accepted )
Source( Source MAC): here MAC The address is PC1
Type( type ): Represents the content of the upper layer , In today's Network , The value of 0x0800( Express IP), If 0x86DD( Express IPV6)
You can't see the preamble and FCS Of , Because the captured packet is the result after the network card has been processed .
PC2 By reading the destination in the Ethernet header MAC Address , Find yourself , And from type The middle and upper levels are IP agreement , So when unpacking the three layers , Will use IP Protocol to read , Again, let's take a look at IP The head of
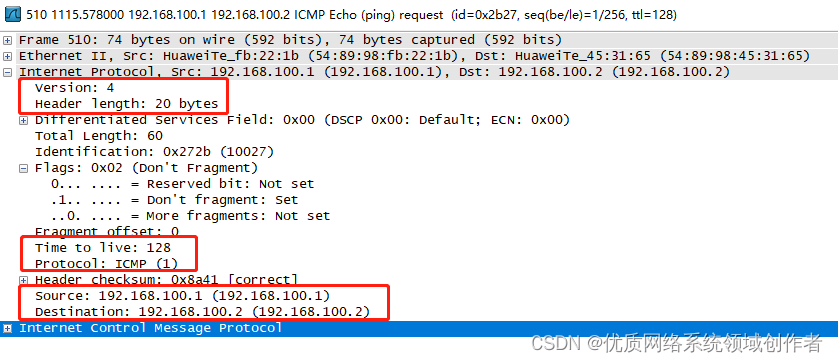
IP The fields in the protocol header have been described before , Here are some important fields , Review
version( edition ): Fixed as version 4, because IPV6 Baotou has changed
Header Length( Head length ) And Total Length( Total length ): The length of the head is 20 Bytes , This is a default size , And the total length is IP Head and back DATA The total length of the part , by 60 byte , That means ICMP Some have 40 Bytes (60-20).
Time to Live( Generation time ): here TTL by 128
Protocol( agreement ): Here for ICMP=1, That is, tell the receiver , What is the upper layer agreement
Source And Destination: Source order IP, The source of nature is PC1 The address of (192.168.100.1), The purpose is PC2(192.168.100.2)
PC2 By reading the IP The destination address in the agreement is found to be itself , Also from the Protocol The middle and upper layers use ICMP, Will eventually use ICMP To read these data , And then respond , This is the whole communication process .
The whole communication process of the same network segment is mainly reviewed
(1)PC1 Want to talk to PC2 signal communication , First, I will read the information on my network card IP、 Subnet mask parameters , Use this mask to calculate the network number of yourself and the other party , See if it's the same , The same is in the same network segment .
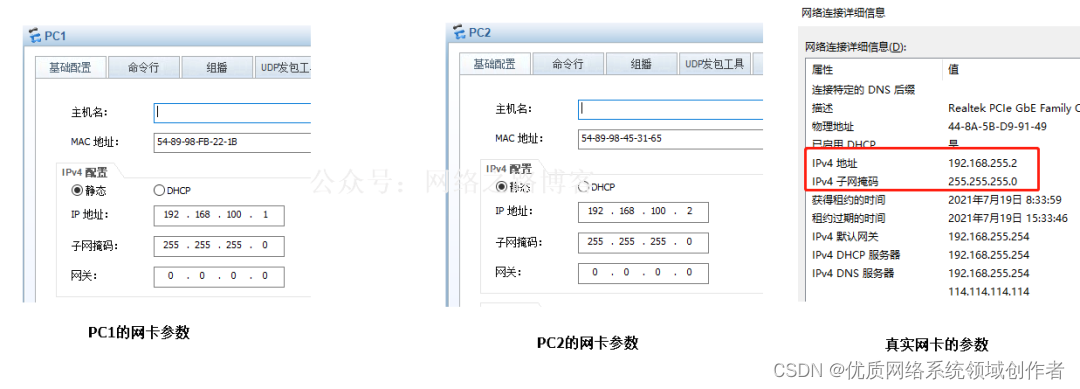
(2) It is determined that after the same network segment ,PC1 Because I don't know PC2 Of MAC What's the address , Unable to complete layer 2 encapsulation , So we must rely on ARP Request protocol to get , The content of this request package is request PC2 Of IP Of MAC What's the address , And send... In the form of broadcast ( Ethernet head Source MAC by PC1, Purpose MAC, whole F), The reason for broadcasting is PC1 I do not know! PC2 Where is the , Can only rely on the form of radio to ask PC2 Where is the ( As I said before, shit ” Roar ” The way ), In this way, the terminal in the whole LAN can receive this request , No PC2 Your terminal device has received , Find out ARP Asked in the message IP Not myself , Just throw it away , and PC2 You find yourself asking for IP Of MAC, Then start ARP Respond .
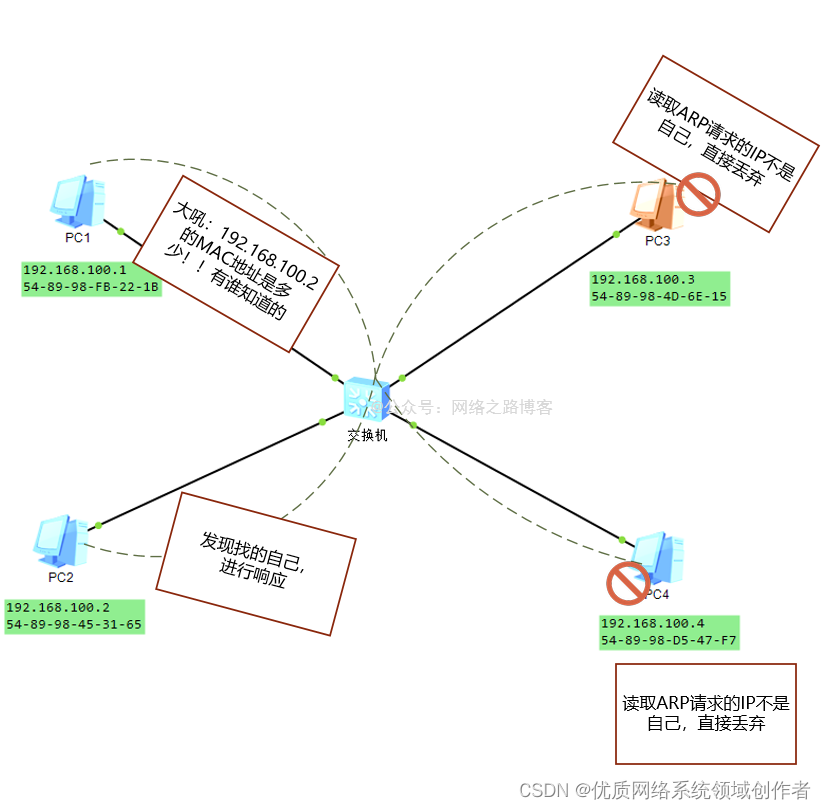
(3)PC2 Respond to this request ( Bring your own MAC), Ethernet head ( From PC2, The purpose is PC1), Unicast shape return ,PC1 After receiving it , Will cache this information to ARP In the table item , It won't disappear for a certain time , If a packet is sent again within this time , Call directly ARP Just the information in the table .
(4)PC1 Finally I know PC2 Of MAC, Start packaging , Ethernet head : Source MAC(PC1), Purpose MAC(PC2),IP Head : Source IP(PC1), Purpose IP(PC2), Final ICMP Header and data , And the Ethernet head is connected with IP The header will identify what the upper layer protocol uses .
(5)PC2 After receiving it , Start unpacking , The unpacking process passes through the purpose of the two-layer head MAC Find yourself looking for , And then through type Know what the upper layer protocol uses , Reading the upper layer with the corresponding protocol IP Head ,IP The purpose of the query in the header IP Field , Discovery is also for yourself , Then we know that the upper layer protocol is... Through the protocol number ICMP, Finally read the final data , And then respond to .
(6) The process of response is also a process of encapsulation and de encapsulation , And PC1 To PC2 equally , It just doesn't need to be executed in the middle ARP 了 , because PC1 use ARP obtain PC2 Of MAC At the address ,PC2 Also from the ARP I learned from the agreement PC1 Of MAC, It will also be cached to ARP In the list , Only after the cache disappears , Again, you need to rely on ARP Message to parse , The cache period is as long as ARP The list that exists in the table , There is no need to initiate again ARP request , Call directly .
(7) There is no explanation on how to handle packets received by the switch , This will be explained at the beginning of the switch chapter , So far, the LAN communication of the same network segment is completed .
边栏推荐
- Pytorch代码注意的细节,容易敲错的地方
- [C language syntax] the difference between typedef struct and struct
- How to get list length
- 嵌入式面试题(四、常见算法)
- Node 之 nvm 下载、安装、使用,以及node 、nrm 的相关使用
- B站刘二大人-反向传播
- 養了只小猫咪
- Li Chuang EDA learning notes 12: common PCB board layout constraint principles
- My 2021
- Luogu [Beginner Level 4] array p1427 number game of small fish
猜你喜欢
05. Security of blog project
Deep learning -yolov5 introduction to actual combat click data set training
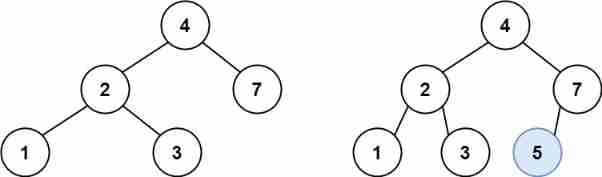
Leetcode 701 insertion operation in binary search tree -- recursive method and iterative method
![[Jiudu OJ 08] simple search x](/img/a7/12a00c5d1db2deb064ff5f2e83dc58.jpg)
[Jiudu OJ 08] simple search x
Migrate Infones to stm32

Li Chuang EDA learning notes 12: common PCB board layout constraint principles

How to use PHP string query function
ArcGIS application foundation 4 thematic map making

初识数据库
Node 之 nvm 下载、安装、使用,以及node 、nrm 的相关使用
随机推荐
[email protected] raspberry pie
Redis消息队列
Closure, decorator
Station B, Mr. Liu Er - multiple logistic regression, structure 7
Web Security (VI) the use of session and the difference between session and cookie
Leetcode 701 insertion operation in binary search tree -- recursive method and iterative method
Winter 2021 pat class B problem solution (C language)
High quality coding tool clion
[JVM] [Chapter 17] [garbage collector]
Query the standard text code corresponding to a work center (s) in the production order
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
清除浮动的方式
初识数据库
Anti shake and throttling are easy to understand
Station B, Master Liu Er - dataset and data loading
P2802 回家
Hongliao Technology: how to quickly improve Tiktok store
Sequoiadb Lake warehouse integrated distributed database, June 2022 issue
What impact will frequent job hopping have on your career?
29io stream, byte output stream continue write line feed