当前位置:网站首页>[hand tearing code] single case mode and producer / consumer mode
[hand tearing code] single case mode and producer / consumer mode
2022-07-06 13:37:00 【Li bohuan】
The singleton pattern
The singleton pattern (Singleton Pattern): Ensure that a class has only one object , And provide a global access point to access it .
Advantages of singleton mode :
Because the singleton mode only generates one instance , Reduced system performance overhead , When more resources are needed to generate an object , Such as read configuration 、 When other dependent objects are generated , You can start... In the application Directly generate a singleton object , Then permanent resident memory to solveThe singleton mode can set the global access point in the system , Optimize ring shared resource access , For example, you can design A singleton class , Responsible for the mapping of all data tables
Code implementation :
Hungry Chinese style : Create before use , Thread safety , Take up memory .
public class SingleClassA {
//1. Privatized construction method , So that this method cannot be called outside the class , Limit the generation of multiple objects
private SingleClassA(){ }
//2. Create an instance of the class inside the class
// Class initialization , Load this object now ( There is no advantage of delayed loading ). When loading a class , Naturally, it's thread safe !
private static final SingleClassA instance = new SingleClassA();
//3. Call methods to external providers : Return the created object to , Can only be called through a class
// Method is not synchronized , High call efficiency !
public static SingleClassA getInstance(){
return instance;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleClassA a = getInstance();
SingleClassA b = getInstance();
System.out.println(a == b);
}
}Output results :

Slacker type : Created when used , Thread unsafe ( When creating or getting a singleton object ), Locking will affect efficiency .
public class SingleClassB {
//1. Privatized construction method , So that this method cannot be called outside the class , Limit the generation of multiple objects
private SingleClassB(){ }
//2. Create an instance of the class inside the class
private static SingleClassB instance ;
//3. Call methods to external providers : Return the created object to , Can only be called through a class
public static synchronized SingleClassB getInstance(){
if(instance == null) {
instance = new SingleClassB();
}
return instance;
}
// test
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleClassB a = SingleClassB.getInstance();
SingleClassB b = SingleClassB.getInstance();
System.out.println(a==b);
}
}Output results :
 The difference between lazy man mode and hungry man mode :
The difference between lazy man mode and hungry man mode :
- Lazy style will not instantiate by default , Wait until the method is called externally before , The object is instantiated in the hungry class loading stage
- Thread safe , Hungry man style must be thread safe , Because the object was instantiated before the thread appeared , Lazy is thread unsafe , Because in multithreading , If a thread judges that the finished instance is null Sleep or interrupt , Then another thread also enters the method , The judgment example is also null, Then the thread will create an instance object , After the original dormant thread resumes , Execute instantiation directly new Object step , Then there will be multiple instances .
- Analyze the thread safety above , Next is performance , Maybe you already have , The hungry man style doesn't need to be locked , High execution efficiency , Lazy style needs to be locked , Inefficient execution
- Occupy memory , Hungry man style whether you use its instance object or not , He was instantiated there from the beginning , Occupy memory space , The lazy type is instantiated only when it is used , It doesn't waste memory
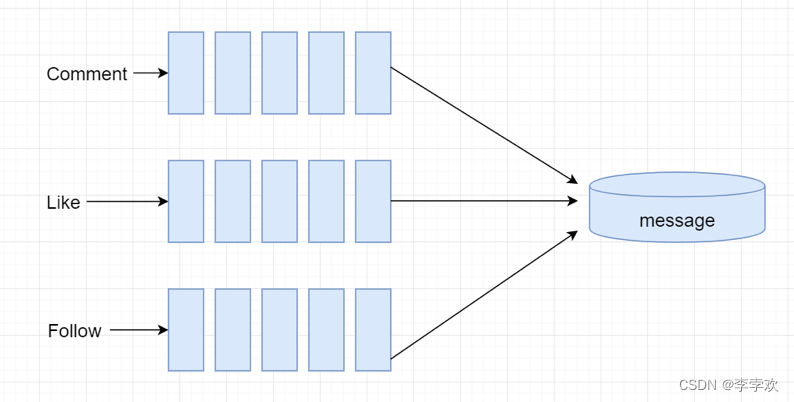
producer / Consumer model
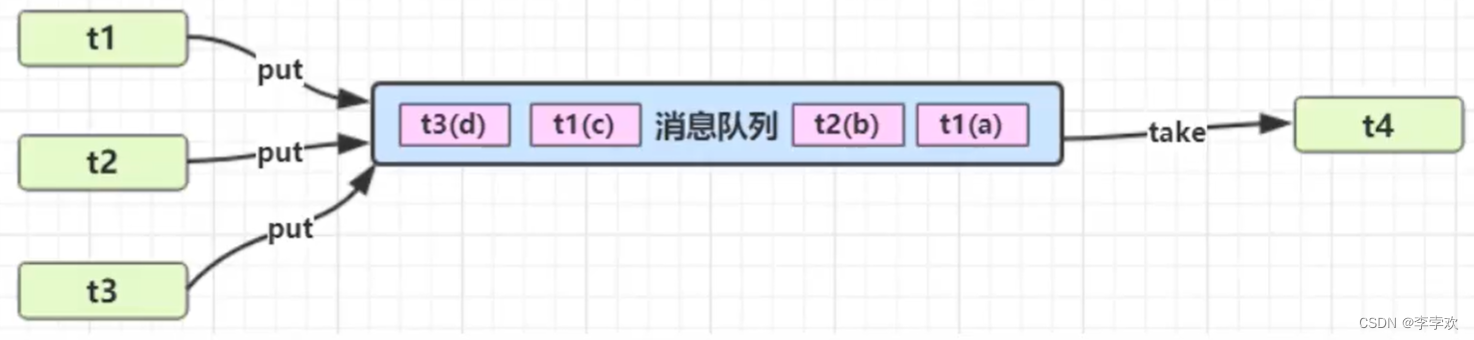
The producer-consumer pattern solves the problem of strong coupling between producer and consumer through a container . Producers and consumers do not communicate directly with each other , Instead, it communicates by blocking the queue , So producers don't have to wait for consumers to process their data , Throw it directly into the blocking queue , Consumers don't ask producers for data , I'm going to take it directly from the blocking queue , Blocking a queue is like a buffer , Balancing the processing power of producers and consumers . As shown in the figure below :
 Code implementation :
Code implementation :
@Slf4j(topic = "ProductAndConsumer")
public class ProductAndConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageQueue messageQueue = new MessageQueue(2);
// 3 Producer threads
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int id = i;
new Thread(() -> {
messageQueue.put(new Message(id, " value " + id));
}, " producer " + i).start();
}
// 1 Consumer threads , Processing results
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
sleep(1000);
Message message = messageQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, " consumer ").start();
}
}
final class Message {
private int id;
private Object message;
public Message(int id, Object message) {
this.id = id;
this.message = message;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public Object getMessage() {
return message;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Message{" +
"id=" + id +
", message=" + message +
'}';
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "MessageQueue")
class MessageQueue {
private LinkedList<Message> queue;
private int capacity;
public MessageQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
public Message take() {
synchronized (queue) {
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
log.debug(" The queue is empty , Consumer thread waiting ");
try {
queue.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Message message = queue.removeFirst();
log.debug(" Consumed news {}",message);
queue.notifyAll();
return message;
}
}
public void put(Message message) {
synchronized (queue) {
while (queue.size() == capacity) {
try {
log.debug(" Inventory has reached the upper limit , Producer thread waiting ");
queue.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
queue.addLast(message);
log.debug(" The message has been produced {}",message);
queue.notifyAll();
}
}
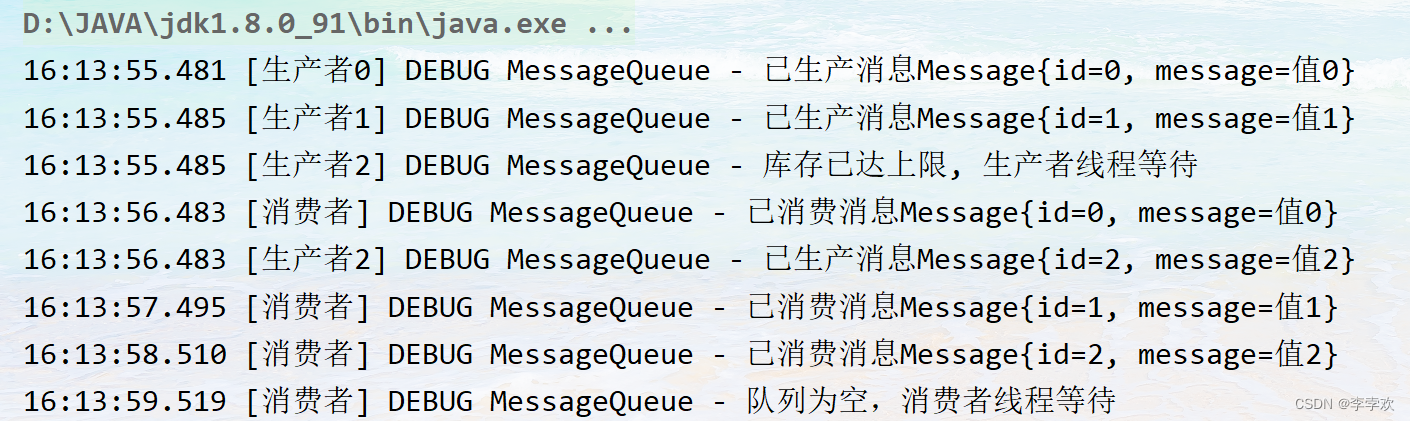
}The output is as follows :
边栏推荐
- [中国近代史] 第六章测验
- Arduino+ water level sensor +led display + buzzer alarm
- 4.分支语句和循环语句
- C language to achieve mine sweeping game (full version)
- FileInputStream和BufferedInputStream的比较
- C语言入门指南
- [中国近代史] 第九章测验
- 【九阳神功】2017复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
- System design learning (III) design Amazon's sales rank by category feature
- 2.C语言初阶练习题(2)
猜你喜欢
System design learning (III) design Amazon's sales rank by category feature
20220211-CTF-MISC-006-pure_ Color (use of stegsolve tool) -007 Aesop_ Secret (AES decryption)

西安电子科技大学22学年上学期《基础实验》试题及答案

5. Download and use of MSDN
Arduino+ water level sensor +led display + buzzer alarm

View UI plus released version 1.2.0 and added image, skeleton and typography components
2.C语言矩阵乘法
仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(三)
Mortal immortal cultivation pointer-2
Relational algebra of tyut Taiyuan University of technology 2022 database
随机推荐
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2017 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
Summary of multiple choice questions in the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
Tyut outline of 2022 database examination of Taiyuan University of Technology
fianl、finally、finalize三者的区别
仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(一)
string
ArrayList的自动扩容机制实现原理
Tyut Taiyuan University of technology 2022 "Mao Gai" must be recited
5. Download and use of MSDN
IPv6 experiment
12 excel charts and arrays
The latest tank battle 2022 full development notes-1
Floating point comparison, CMP, tabulation ideas
The latest tank battle 2022 - full development notes-3
View UI plus released version 1.2.0 and added image, skeleton and typography components
5. Function recursion exercise
【九阳神功】2019复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
稻 城 亚 丁
【话题终结者】
关于双亲委派机制和类加载的过程