当前位置:网站首页>Isam2 and incrementalfixedlagsmooth instructions in gtsam
Isam2 and incrementalfixedlagsmooth instructions in gtsam
2022-07-06 06:12:00 【Zhan Miao】
1. Parameters
1.1. Configuration parameters ISAM2Params
struct ISAM2Params {
typedef boost::variant<ISAM2GaussNewtonParams, ISAM2DoglegParams>
OptimizationParams; ///< Either ISAM2GaussNewtonParams or
///< ISAM2DoglegParams
typedef boost::variant<double, FastMap<char, Vector> >
RelinearizationThreshold; ///< Either a constant relinearization
///< threshold or a per-variable-type set of
///< thresholds
/** Optimization parameters, this both selects the nonlinear optimization
* method and specifies its parameters, either ISAM2GaussNewtonParams or
* ISAM2DoglegParams. In the former, Gauss-Newton optimization will be used
* with the specified parameters, and in the latter Powell's dog-leg
* algorithm will be used with the specified parameters.
*/
OptimizationParams optimizationParams;
/** Only relinearize variables whose linear delta magnitude is greater than
* this threshold (default: 0.1). If this is a FastMap<char,Vector> instead
* of a double, then the threshold is specified for each dimension of each
* variable type. This parameter then maps from a character indicating the
* variable type to a Vector of thresholds for each dimension of that
* variable. For example, if Pose keys are of type TypedSymbol<'x',Pose3>,
* and landmark keys are of type TypedSymbol<'l',Point3>, then appropriate
* entries would be added with:
* \code
FastMap<char,Vector> thresholds;
thresholds['x'] = (Vector(6) << 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5).finished();
// 0.1 rad rotation threshold, 0.5 m translation threshold thresholds['l'] =
Vector3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); // 1.0 m landmark position threshold
params.relinearizeThreshold = thresholds;
\endcode
*/
RelinearizationThreshold relinearizeThreshold;
int relinearizeSkip; ///< Only relinearize any variables every
///< relinearizeSkip calls to ISAM2::update (default:
///< 10)
bool enableRelinearization; ///< Controls whether ISAM2 will ever relinearize
///< any variables (default: true)
bool evaluateNonlinearError; ///< Whether to evaluate the nonlinear error
///< before and after the update, to return in
///< ISAM2Result from update()
enum Factorization { CHOLESKY, QR };
/** Specifies whether to use QR or CHOESKY numerical factorization (default:
* CHOLESKY). Cholesky is faster but potentially numerically unstable for
* poorly-conditioned problems, which can occur when uncertainty is very low
* in some variables (or dimensions of variables) and very high in others. QR
* is slower but more numerically stable in poorly-conditioned problems. We
* suggest using the default of Cholesky unless gtsam sometimes throws
* IndefiniteLinearSystemException when your problem's Hessian is actually
* positive definite. For positive definite problems, numerical error
* accumulation can cause the problem to become numerically negative or
* indefinite as solving proceeds, especially when using Cholesky.
*/
Factorization factorization;
/** Whether to cache linear factors (default: true).
* This can improve performance if linearization is expensive, but can hurt
* performance if linearization is very cleap due to computation to look up
* additional keys.
*/
bool cacheLinearizedFactors;
KeyFormatter
keyFormatter; ///< A KeyFormatter for when keys are printed during
///< debugging (default: DefaultKeyFormatter)
bool enableDetailedResults; ///< Whether to compute and return
///< ISAM2Result::detailedResults, this can
///< increase running time (default: false)
/** Check variables for relinearization in tree-order, stopping the check once
* a variable does not need to be relinearized (default: false). This can
* improve speed by only checking a small part of the top of the tree.
* However, variables below the check cut-off can accumulate significant
* deltas without triggering relinearization. This is particularly useful in
* exploration scenarios where real-time performance is desired over
* correctness. Use with caution.
*/
bool enablePartialRelinearizationCheck;
/// When you will be removing many factors, e.g. when using ISAM2 as a
/// fixed-lag smoother, enable this option to add factors in the first
/// available factor slots, to avoid accumulating nullptr factor slots, at the
/// cost of having to search for slots every time a factor is added.
bool findUnusedFactorSlots;
};1.2. Update parameters ISAM2UpdateParams
struct ISAM2UpdateParams {
ISAM2UpdateParams() = default;
/** Indices of factors to remove from system (default: empty) */
FactorIndices removeFactorIndices;
/** An optional map of keys to group labels, such that a variable can be
* constrained to a particular grouping in the BayesTree */
boost::optional<FastMap<Key, int>> constrainedKeys{boost::none};
/** An optional set of nonlinear keys that iSAM2 will hold at a constant
* linearization point, regardless of the size of the linear delta */
boost::optional<FastList<Key>> noRelinKeys{boost::none};
/** An optional set of nonlinear keys that iSAM2 will re-eliminate, regardless
* of the size of the linear delta. This allows the provided keys to be
* reordered. */
boost::optional<FastList<Key>> extraReelimKeys{boost::none};
/** Relinearize any variables whose delta magnitude is sufficiently large
* (Params::relinearizeThreshold), regardless of the relinearization
* interval (Params::relinearizeSkip). */
bool force_relinearize{false};
/** An optional set of new Keys that are now affected by factors,
* indexed by factor indices (as returned by ISAM2::update()).
* Use when working with smart factors. For example:
* - Timestamp `i`: ISAM2::update() called with a new smart factor depending
* on Keys `X(0)` and `X(1)`. It returns that the factor index for the new
* smart factor (inside ISAM2) is `13`.
* - Timestamp `i+1`: The same smart factor has been augmented to now also
* depend on Keys `X(2)`, `X(3)`. Next call to ISAM2::update() must include
* its `newAffectedKeys` field with the map `13 -> {X(2), X(3)}`.
*/
boost::optional<FastMap<FactorIndex, KeySet>> newAffectedKeys{boost::none};
/** By default, iSAM2 uses a wildfire update scheme that stops updating when
* the deltas become too small down in the tree. This flagg forces a full
* solve instead. */
bool forceFullSolve{false};
};1.3. Returns the parameter ISAM2Result
/**
* @addtogroup ISAM2
* This struct is returned from ISAM2::update() and contains information about
* the update that is useful for determining whether the solution is
* converging, and about how much work was required for the update. See member
* variables for details and information about each entry.
*/
struct ISAM2Result {
/** The nonlinear error of all of the factors, \a including new factors and
* variables added during the current call to ISAM2::update(). This error is
* calculated using the following variable values:
* \li Pre-existing variables will be evaluated by combining their
* linearization point before this call to update, with their partial linear
* delta, as computed by ISAM2::calculateEstimate().
* \li New variables will be evaluated at their initialization points passed
* into the current call to update.
* \par Note: This will only be computed if
* ISAM2Params::evaluateNonlinearError is set to \c true, because there is
* some cost to this computation.
*/
boost::optional<double> errorBefore;
/** The nonlinear error of all of the factors computed after the current
* update, meaning that variables above the relinearization threshold
* (ISAM2Params::relinearizeThreshold) have been relinearized and new
* variables have undergone one linear update. Variable values are
* again computed by combining their linearization points with their
* partial linear deltas, by ISAM2::calculateEstimate().
* \par Note: This will only be computed if
* ISAM2Params::evaluateNonlinearError is set to \c true, because there is
* some cost to this computation.
*/
boost::optional<double> errorAfter;
/** The number of variables that were relinearized because their linear
* deltas exceeded the reslinearization threshold
* (ISAM2Params::relinearizeThreshold), combined with any additional
* variables that had to be relinearized because they were involved in
* the same factor as a variable above the relinearization threshold.
* On steps where no relinearization is considered
* (see ISAM2Params::relinearizeSkip), this count will be zero.
*/
size_t variablesRelinearized;
/** The number of variables that were reeliminated as parts of the Bayes'
* Tree were recalculated, due to new factors. When loop closures occur,
* this count will be large as the new loop-closing factors will tend to
* involve variables far away from the root, and everything up to the root
* will be reeliminated.
*/
size_t variablesReeliminated;
/** The number of factors that were included in reelimination of the Bayes'
* tree. */
size_t factorsRecalculated;
/** The number of cliques in the Bayes' Tree */
size_t cliques;
/** The indices of the newly-added factors, in 1-to-1 correspondence with the
* factors passed as \c newFactors to ISAM2::update(). These indices may be
* used later to refer to the factors in order to remove them.
*/
FactorIndices newFactorsIndices;
/** Unused keys, and indices for unused keys,
* i.e., keys that are empty now and do not appear in the new factors.
*/
KeySet unusedKeys;
/** keys for variables that were observed, i.e., not unused. */
KeyVector observedKeys;
/** Keys of variables that had factors removed. */
KeySet keysWithRemovedFactors;
/** All keys that were marked during the update process. */
KeySet markedKeys;
}2. Function description
2.1. ISAM2::marginalizeLeaves
Marginalize out variables listed in leafKeys. These keys must be leaves in the BayesTree. Throws MarginalizeNonleaf Exception if non-leaves are requested to be marginalized. Marginalization leaves a linear approximation of the marginal in the system, and the linearization points of any variables involved in this linear marginal become fixed. The set fixed variables will include any key involved with the marginalized variables in the original factors, and possibly additional ones due to fill-in.
If provided, 'marginalFactorsIndices' will be augmented with the factor graph indices of the marginal factors added during the 'marginalizeLeaves' call
If provided, 'deletedFactorsIndices' will be augmented with the factor graph indices of any factor that was removed during the 'marginalizeLeaves'
2.2. ISAM2::recalculateIncremental
2.3. ISAM2::recalculateBatch
2.4. recursiveMarkAffectedKeys
stay IncrementalFixedLagSmoother.cpp In this file , But it's not a member function .
Used to mark a key The subtree of
2.5. IncrementalFixedLagSmoother::update
2.6. ISAM2::update
2.7. BayesTree::removeSubtree
If the entry is a root group , Delete the regiment and all its descendants , stay node_ Also deleted in
If the input parameter is not the root node , First delete its parent group and its edge
Return all deleted groups
3. Member variable description
Values ISAM2::theta_
VectorValues ISAM2::delta_
VariableIndex ISAM2::variableIndex_
4. Auxiliary class
4.1. treeTraversalNode-inst.h
// Internal node used in DFS preorder stack
template<typename NODE, typename DATA>
struct TraversalNode {
bool expanded;
const boost::shared_ptr<NODE>& treeNode;
DATA& parentData;
typename FastList<DATA>::iterator dataPointer;
TraversalNode(const boost::shared_ptr<NODE>& _treeNode, DATA& _parentData) :
expanded(false), treeNode(_treeNode), parentData(_parentData) {
}
};4.2. EliminationTree.h
struct EliminationTree::Node {
typedef FastVector<sharedFactor> Factors;
typedef FastVector<boost::shared_ptr<Node> > Children;
Key key; ///< key associated with root
Factors factors; ///< factors associated with root
Children children; ///< sub-trees
sharedFactor eliminate(const boost::shared_ptr<BayesNetType>& output,
const Eliminate& function,
const FastVector<sharedFactor>& childrenFactors) const;
void print(const std::string& str, const KeyFormatter& keyFormatter) const;
};4.3. ClusterTree-inst.h
struct EliminationData {
// Typedefs
typedef typename CLUSTERTREE::sharedFactor sharedFactor;
typedef typename CLUSTERTREE::FactorType FactorType;
typedef typename CLUSTERTREE::FactorGraphType FactorGraphType;
typedef typename CLUSTERTREE::ConditionalType ConditionalType;
typedef typename CLUSTERTREE::BayesTreeType::Node BTNode;
// member variables
EliminationData* const parentData;
size_t myIndexInParent;
FastVector<sharedFactor> childFactors;
boost::shared_ptr<BTNode> bayesTreeNode;
// member functions
// Elimination pre-order visitor - creates the EliminationData structure for the visited node.
static EliminationData EliminationPreOrderVisitor(const typename CLUSTERTREE::sharedNode& node,
EliminationData& parentData) {
assert(node);
EliminationData myData(&parentData, node->nrChildren());
myData.bayesTreeNode->problemSize_ = node->problemSize();
return myData;
}
// ........
}4.4. VariableIndex
The VariableIndex class computes and stores the block column structure of a factor graph. The factor graph stores a collection of factors, each of which involves a set of variables. In contrast, the VariableIndex is built from a factor graph prior to elimination, and stores the list of factors that involve each variable. This information is stored as a deque of lists of factor indices.
The main variable is FastMap<Key, FactorIndices> index_, Used to store key And the index of the factor 边栏推荐
- Eigen sparse matrix operation
- The difference and usage between continue and break
- How to recover Huawei router's forgotten password
- 数字三角形模型 AcWing 1015. 摘花生
- 【Postman】动态变量(也称Mock函数)
- JDBC Requset 对应内容及功能介绍
- 【Postman】测试(Tests)脚本编写和断言详解
- H3C S5820V2_ Upgrade method after stacking IRF2 of 5830v2 switch
- Application of Lie group in gtsam
- 对数据安全的思考(转载)
猜你喜欢
【Postman】Collections配置运行过程
IPv6 comprehensive experiment
数据库-当前读与快照读
Caused by:org.gradle.api.internal.plugins . PluginApplicationException: Failed to apply plugin
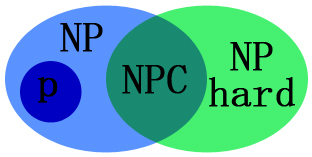
P问题、NP问题、NPC问题、NP-hard问题详解
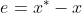
Basic knowledge of error
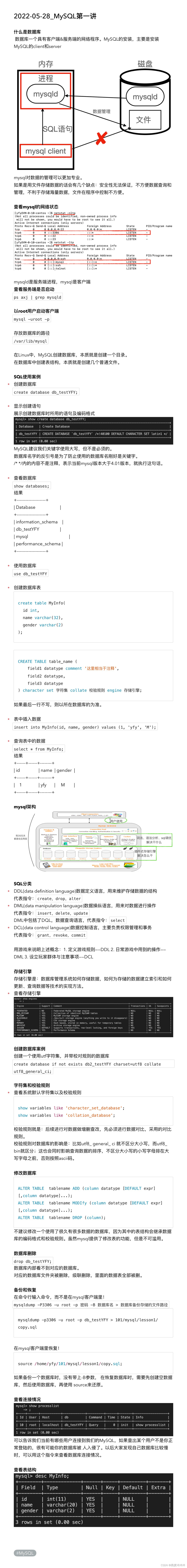
MySQL之基础知识
![[C language] string left rotation](/img/5f/66bcc8f992108bf3b7e455709d3174.png)
[C language] string left rotation

Digital triangle model acwing 1015 Picking flowers
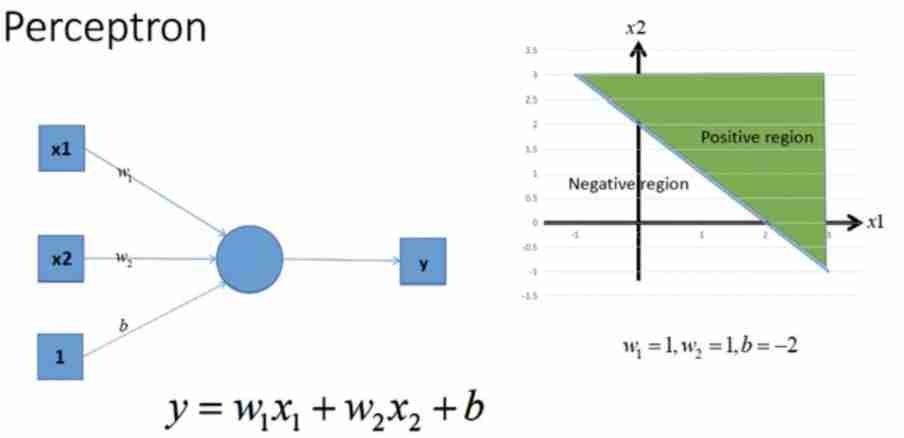
Function of activation function
随机推荐
【微信小程序】搭建开发工具环境
数学三大核心领域概述:几何
JDBC Requset 对应内容及功能介绍
数据库-当前读与快照读
Overview of three core areas of Mathematics: geometry
LeetCode 731. 我的日程安排表 II
数字三角形模型 AcWing 1015. 摘花生
曼哈顿距离与曼哈顿矩形-打印回字型矩阵
[postman] dynamic variable (also known as mock function)
Buuctf-[[gwctf 2019] I have a database (xiaoyute detailed explanation)
Cognitive introspection
How to use the container reflection method encapsulated by thinkphp5.1 in business code
测试周期被压缩?教你9个方法去应对
【Postman】动态变量(也称Mock函数)
黑猫带你学eMMC协议第10篇:eMMC读写操作详解(read & write)
Coordinatorlayout+nestedscrollview+recyclerview pull up the bottom display is incomplete
GTSAM中李群的运用
功能安全之故障(fault),错误(error),失效(failure)
职场进阶指南:大厂人必看书籍推荐
误差的基本知识