当前位置:网站首页>Manhattan distance and Manhattan rectangle - print back font matrix
Manhattan distance and Manhattan rectangle - print back font matrix
2022-07-06 06:08:00 【starnight531】
Manhattan distance and Manhattan rectangle
Food Guide :
Leetcode The column opens , Because the blogger is closed at the end of the period , So only one question per day Try to solve more than one problem , First say the train of thought. , Then the code realizes , Necessary comments will be added Grammar or STL The content will be highlighted at the attention point , Novice friendly Welcome to the blogger's magic tricks column , Detailed explanation of connotation algorithm foundation and code template
Title Description :
Input integer N, Output one N Two dimensional array of order glyphs .
The outermost layer of the array is 1, The outer layer is 2, And so on .
Input format
The input contains multiple lines , Each line contains an integer N.
When the input behavior N=0 when , End of input , And the bank doesn't need to do anything .Output format
For each input integer N, Output one that meets the requirements N Order two-dimensional array .
Each array takes N That's ok , Each row contains N Integers separated by spaces .
After the output of each array , Output a blank line .Data range
0≤N≤100
sample input :
1
2
3
4
5
0
sample output :
11 1
1 11 1 1
1 2 1
1 1 11 1 1 1
1 2 2 1
1 2 2 1
1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1
1 2 2 2 1
1 2 3 2 1
1 2 2 2 1
1 1 1 1 1Title source :https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/755/
Topic analysis :
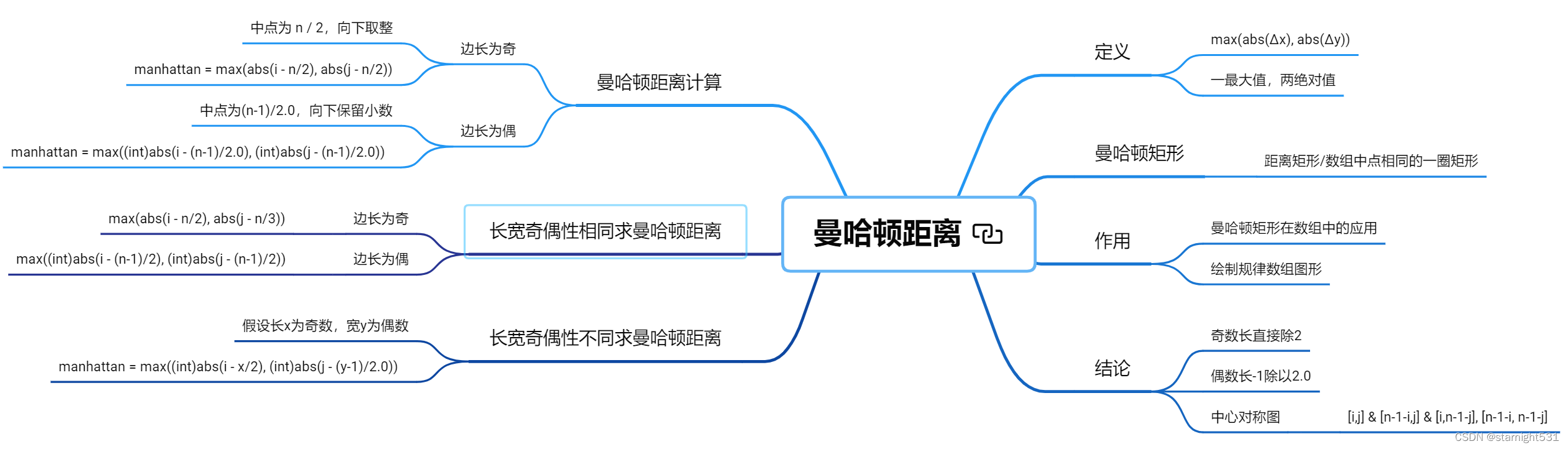
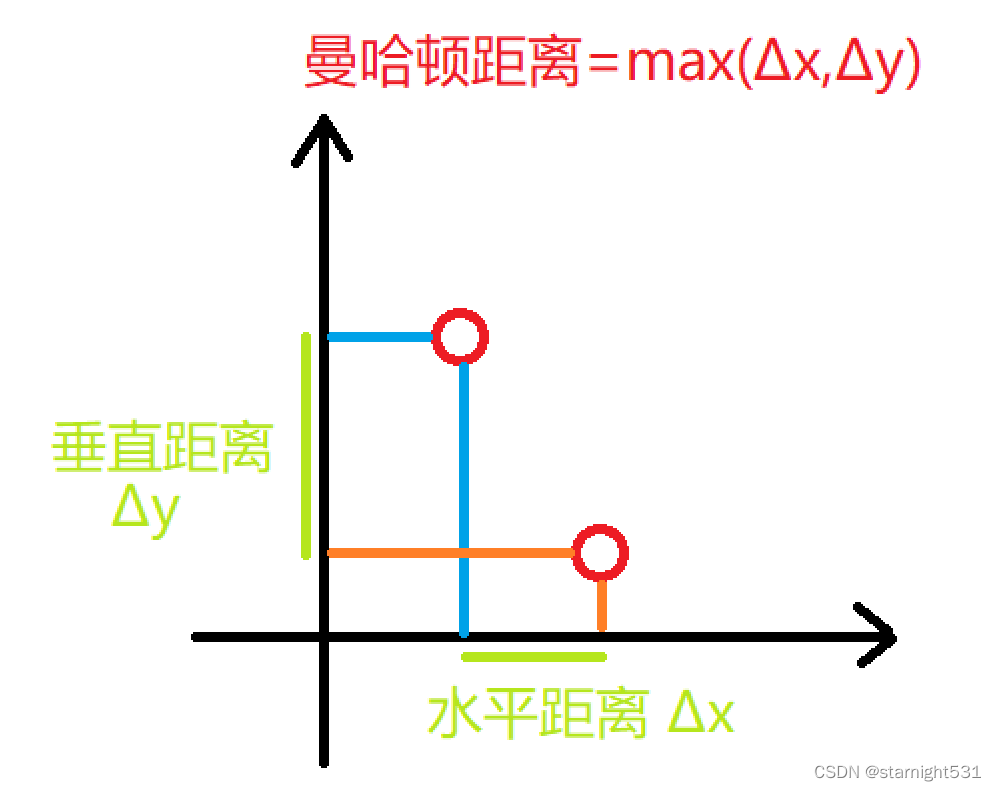
Law 1 : Manhattan distance
Manhattan distance is two points in the vertical coordinate system ,x & y Direction Maximum projection distance
Apply to array / Matrix , Manhattan sets points at the same distance into A circle of rectangles around the center of the matrix ,
When calculating Manhattan distance , Number of district branches required / Parity of column numbers :
Law two : The relationship between array subscript and value
Manhattan distance is actually the conclusion of the research on the relationship between array subscripts and values
When you don't know the distance from Manhattan , Try exploring manually , Other conclusions of non Manhattan distance may be drawn
Direction 1: Deduce the relationship with distance
- The graph is symmetrical about the center
Points that do not cross the center line are used i Calculation , Cross the center line with n-1-i Calculation ,
be For all points , or i and n-1-i/n-i Calculate once each , Take the largest of the two / Small value , Or use absolute value
2. For points that do not cross the center line , Use examples to explore
n = 5 when ,n/2 = 2, Midpoint is (2, 2)
The first point arr[0][0] = 1, Distance to midpoint Δx = Δy =2
Second points arr[1][0] = 1, From the end Δx = 2, Δy =1
The third point arr[0][1] = 1, From the end Δx = 1, Δy =2
Determine the calculation formula :n/2 - max(abs(x-n/2) , abs(y-n/2)) + 1
3. For the point passing the center line , Use examples to explore
n = 5 when ,n/2 = 2, Midpoint is (2, 2)
The first point arr[4][4] = 1, Distance to midpoint Δx = Δy =2
Second points arr[3][4] = 1, From the end Δx = 1, Δy =2
The third point arr[4][3] = 1, From the end Δx = 2, Δy =1
Determine the calculation formula :n/2 - max(abs(x-n/2) , abs(y-n/2)) + 1
- After completing the derivation with distance , You will find that you are pushing Manhattan distance ,
Direction 2: Just look at the relationship between subscript and value
- n = 5 when :
- For points that do not cross the center line , Use examples to explore :
The first point arr[0][0] = 1,1 = max/min(x + 1, y + 1)
Second points arr[1][0] = 1,1 = min(x + 1, y + 1)
The third point arr[0][1] = 1,1 = min(x + 1, y + 1)
The stone hammer adopts min(x + 1, y + 1) - For the point passing the center line , Use examples to explore :
The first point arr[4][4] = 1,1 = max/min(n-x, n-y)
Second points arr[3][4] = 1,1 = min(n-x, n-y)
The third point arr[4][3] = 1,1 = min(n-x, n-y)
The stone hammer adopts min(n-x, n-y)
3. Look at all points as a whole :
Now there are two options :min(x + 1, y + 1) & min(n-x, n-y)
Check to see if / What kind of ?
For point arr[3][4],min(x + 1, y + 1) = 4, min(n-x, n-y) = 1
For point arr[0][0],min(x + 1, y + 1) = 1, min(n-x, n-y) = 5
It is found that the minimum value of the two schemes is taken for each point , So come to the conclusion :
- For points that do not cross the center line , Use examples to explore :
- So for all points :arr[i][j] = min(min(x + 1, y + 1) , min(n-x, n-y));
Law three : Symmetric simplification ( Strictly speaking, it belongs to skill rather than method )
Centrosymmetric image , Filling in a little is equivalent to filling in 4 spot .
With n = 5 Rectangle of , View symmetrical 4 Dot subscript relation :

When filling in the value of a quadrant , Manhattan matrix method can be used / The relationship between subscript and value
This technique increases the time complexity , Reduce the time to a quarter of the original
It can also be used as a starting point for thinking when simplifying and finding rules in the following topics
Algorithm template :
- Manhattan distance + Law of central symmetry Itself is the basic algorithm , No template
Code implementation :
Law 1 :
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
int n = sc.nextInt();
if (n == 0) return; // Read the termination exit
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
if(n % 2 == 1)
// Manhattan is closer , Large value , A distance of 0 The value is (n+1)/2
System.out.print((n+1)/2 - Math.max(Math.abs(n/2-i), Math.abs(n/2-j)) +" ");
else
// Manhattan is closer , Large value , A distance of 0 The value is n/2
System.out.print((n/2) - Math.max((int)Math.abs((n-1)/2.0-i), (int)Math.abs((n-1)/2.0-j)) +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Law two :
- Subscript and value relationship :Math.min(Math.min(i+1, j+1), Math.min(n-i, n-j))
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
int n = sc.nextInt();
if (n == 0) return; // Read the termination exit
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
System.out.print(Math.min(Math.min(i+1, j+1), Math.min(n-i, n-j))+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Law three :
- Manhattan distance filling :
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
int n = sc.nextInt();
if (n == 0) return; // Read the termination exit
int[][] arr = new int[n][n];
// Even rows , Such as 4 That's ok 4 Column , Just fill in 0~1 That's ok & 0~1 Column
if(n % 2 == 0){
for(int i=0; i<n/2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n/2; j++){
arr[i][j] = arr[n-1-i][n-1-j]
= arr[n-1-i][j] = arr[i][n-1-j]
= n/2 - Math.max(Math.abs((int)((n-1)/2.0 - i)), Math.abs((int)((n-1)/2.0 - j)));
}
}
}
// Odd row , Such as 5 That's ok 5 Column , It needs to be filled in 0~2 That's ok & 0~2 Column
else{
for(int i=0; i<=n/2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<=n/2; j++){
arr[i][j] = arr[n-1-i][n-1-j]
= arr[n-1-i][j] = arr[i][n-1-j]
= (n+1)/2 - Math.max(Math.abs(n/2 - i), Math.abs(n/2 - j));
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
- Fill in the relationship between subscript and value :
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
int n = sc.nextInt();
if (n == 0) return; // Read the termination exit
int[][] arr = new int[n][n];
// Even rows , Such as 4 That's ok 4 Column , Just fill in 0~1 That's ok & 0~1 Column
if(n % 2 == 0){
for(int i=0; i<n/2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n/2; j++){
arr[i][j] = arr[n-1-i][n-1-j] = arr[n-1-i][j] = arr[i][n-1-j] = Math.min(Math.min(i+1, j+1), Math.min(n-i, n-j));
}
}
}
// Odd row , Such as 5 That's ok 5 Column , It needs to be filled in 0~2 That's ok & 0~2 Column
else{
for(int i=0; i<=n/2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<=n/2; j++){
arr[i][j] = arr[n-1-i][n-1-j] = arr[n-1-i][j] = arr[i][n-1-j] = Math.min(Math.min(i+1, j+1), Math.min(n-i, n-j));
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Be careful :
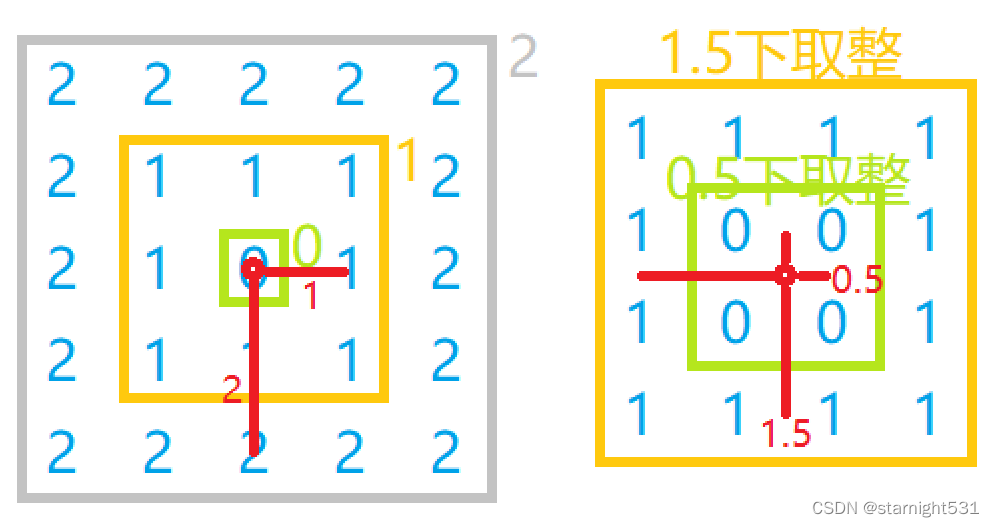
Manhattan distance formula :
- That's ok / The number of columns is odd :
manhattan = max(abs(x - n/2), abs(y - n/2));
The midpoint n/2 Rounding down , And the result itself is an integer - That's ok / The number of columns is even :
manhattan = max((int)abs(x - (n-1)/2.0), (int)abs(y-(n-1)/2.0));
That is, the midpoint is a decimal without rounding , and x - (n-1)/2.0 The result is rounded down - It can be abbreviated as , Divide the midpoint of an odd number directly 2, Even midpoint -1 Divide 2.0
- That's ok / The number of columns is odd :
For those with high safety requirements Java
double and int operation , Is first Int Integer raised to double And again double operation
take Double use (int) The explicit type is converted to int, It is also rounded down by default
边栏推荐
- [ram IP] introduction and experiment of ram IP core
- Memory and stack related concepts
- About PHP startup, mongodb cannot find the specified module
- Some easy-to-use tools make your essay style more elegant
- [web security] nodejs prototype chain pollution analysis
- Baidu online AI competition - image processing challenge: the 8th program of handwriting erasure
- isam2运行流程
- Web服务连接器:Servlet
- 查詢生產訂單中某個(些)工作中心對應的標准文本碼
- IDEA 新UI使用
猜你喜欢
![[paper reading] nflowjs: synthetic negative data intensive anomaly detection based on robust learning](/img/9c/2753f68ecec3555aaca23800dada1e.png)
[paper reading] nflowjs: synthetic negative data intensive anomaly detection based on robust learning
![[untitled]](/img/5d/028b9d19e9a2b217f40198d4631db2.png)
[untitled]

The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
How to use the container reflection method encapsulated by thinkphp5.1 in business code
C language learning notes (mind map)
nodejs实现微博第三方登录
请求转发与重定向
SQLMAP使用教程(三)实战技巧二

Sqlmap tutorial (III) practical skills II
【Postman】Monitors 监测API可定时周期运行
随机推荐
H3C S5820V2_ Upgrade method after stacking IRF2 of 5830v2 switch
Configuring OSPF GR features for Huawei devices
Eigen sparse matrix operation
Practice sharing: how to safely and quickly migrate from CentOS to openeuler
As3013 fire endurance test of cable distribution system
Yunxiaoduo software internal test distribution test platform description document
Buuctf-[gxyctf2019] no dolls (xiaoyute detailed explanation)
【Postman】Collections-运行配置之导入数据文件
【C语言】qsort函数
请求转发与重定向
Application du Groupe Li dans gtsam
在线问题与离线问题
异常检测方法总结
Buuctf-[[gwctf 2019] I have a database (xiaoyute detailed explanation)
Memory and stack related concepts
ICLR 2022 spotlight | analog transformer: time series anomaly detection method based on correlation difference
华为BFD的配置规范
Baidu online AI competition - image processing challenge: the 8th program of handwriting erasure
【Postman】测试(Tests)脚本编写和断言详解
[course notes] Compilation Principle