当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode练习及自己理解记录(1)
LeetCode练习及自己理解记录(1)
2022-08-05 05:24:00 【monkeyhlj】
文章目录
LeetCode练习及自己理解记录(1)
516. 最长回文子序列
来源:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence/solution/dai-ma-sui-xiang-lu-dai-ni-xue-tou-dpzi-dv83q/
1、确定dp数组以及其下标的含义
dp[i][j]:字符串s在[i, j]范围内最长的回文子序列的长度为dp[i][j]。
2、确定递推公式
如果s[i]与s[j]相同,那么dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2;
因为相同的话子序列里就有2个数字,也就是2个长度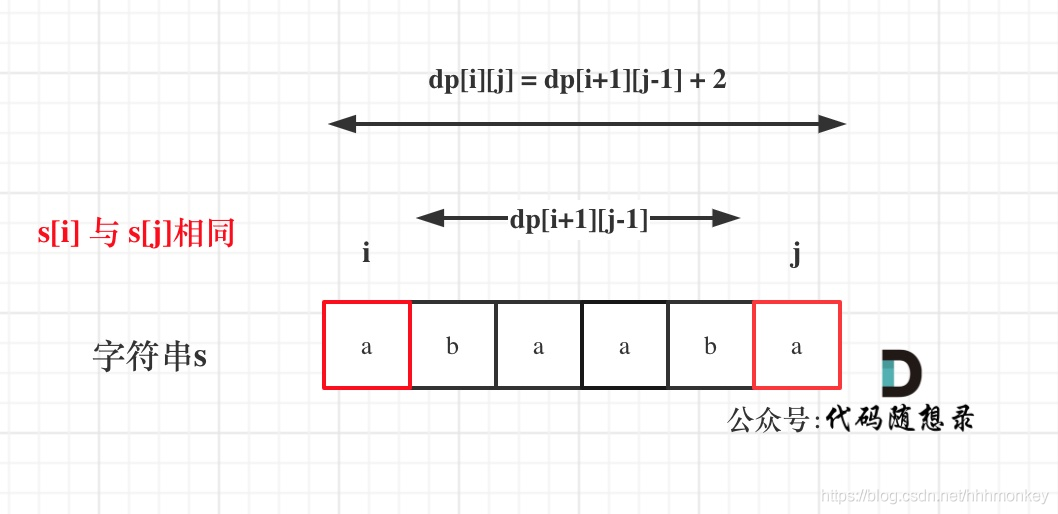
如果s[i]与s[j]不相同,说明s[i]和s[j]的同时加入并不能增加[i,j]区间回文子串的长度,那么分别加入s[i]、s[j]看看哪一个可以组成最长的回文子序列。
加入s[j]的回文子序列长度为dp[i + 1][j]。
加入s[i]的回文子序列长度为dp[i][j - 1]。
那么dp[i][j]一定是取最大的,即:dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);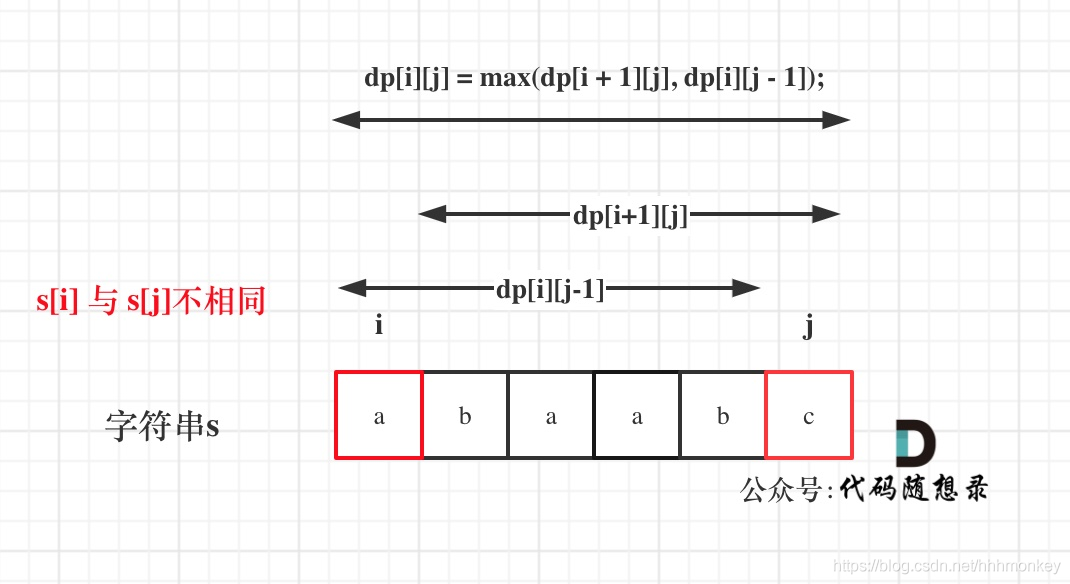
3、dp数组如何初始化
首先要考虑当i 和j 相同的情况,从递推公式:dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2; 可以看出 递推公式是计算不到 i 和j相同时候的情况。
所以需要手动初始化一下,当i与j相同,那么dp[i][j]一定是等于1的,即:一个字符的回文子序列长度就是1。
其他情况dp[i][j]初始为0就行,这样递推公式:dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]); 中dp[i][j]才不会被初始值覆盖。
4、确定遍历顺序
从递推公式dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2 和 dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) 可以看出,dp[i][j]是依赖于dp[i + 1][j - 1] 和 dp[i + 1][j],
也就是从矩阵的角度来说,dp[i][j] 下一行的数据。 所以遍历i的时候一定要从下到上遍历,这样才能保证,下一行的数据是经过计算的。
递推公式:dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2,dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) 分别对应着下图中的红色箭头方向,如图: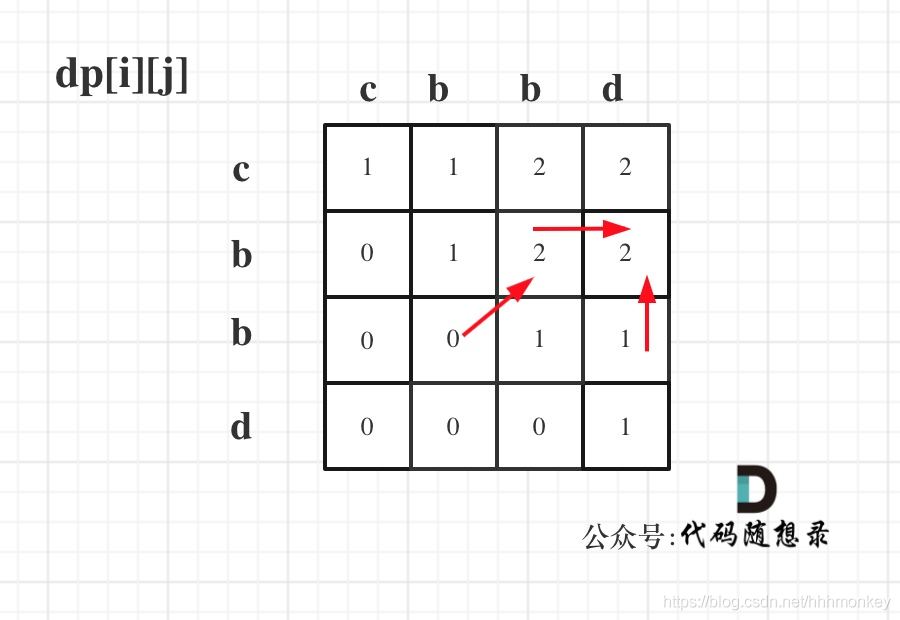
5、举例推导dp数组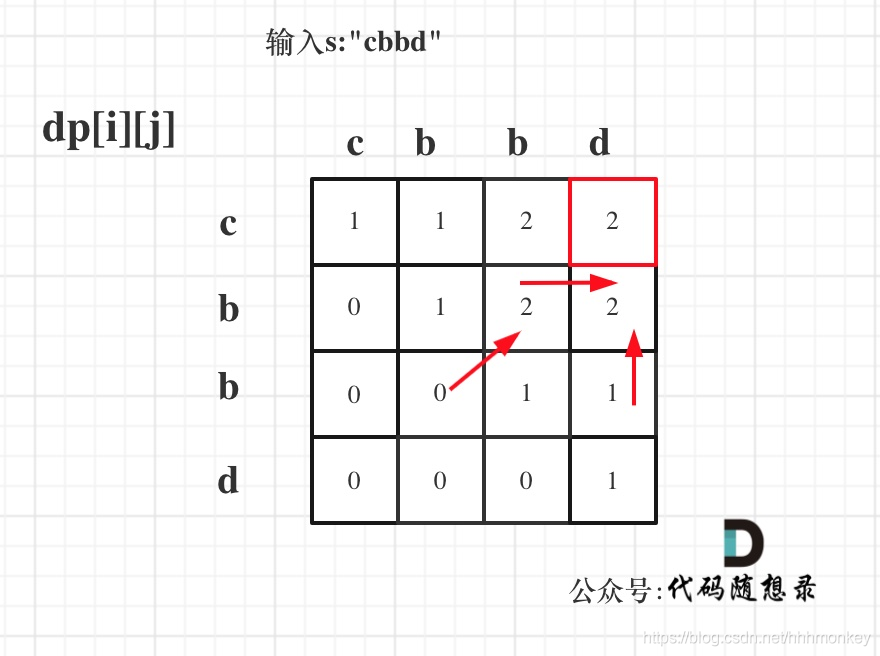
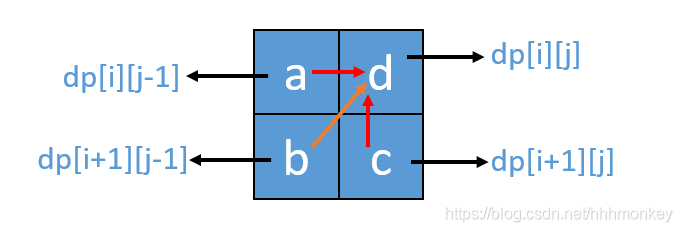
如果上面过程没懂可以结合上面这个田字格的图形去看,看箭头流向的一个过程,就应该能明白整个动态规划的过程了。
class Solution {
public int longestPalindromeSubseq(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int dp[][] = new int[n][n];
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
dp[i][i]=1;
char a=s.charAt(i);
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
char b=s.charAt(j);
if(a==b){
dp[i][j]=dp[i+1][j-1]+2;
}else{
dp[i][j]=Math.max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i+1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][n-1];
}
}
class Solution(object):
def longestPalindromeSubseq(self, s):
""" :type s: str :rtype: int """
n = len(s)
dp = [[0] * n for i in range(n)]
for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):
dp[i][i]=1
for j in range(i+1,n):
if s[i]==s[j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1]+2
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i+1][j],dp[i][j-1])
return dp[0][n-1]
/** * @param {string} s * @return {number} */
var longestPalindromeSubseq = function(s) {
var n = s.length;
var dp = new Array(n).fill(0).map(()=>new Array(n).fill(0));
for(var i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
dp[i][i] = 1;
var a = s.charAt(i);
for(var j=i+1;j<n;j++){
var b = s.charAt(j);
if(a==b){
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1]+2;
}else{
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i+1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][n-1];
};
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1E08ocgXThceqWEddOICoyg 密码: ts8t 推荐其写的关于动态规划的文章。
148. 排序链表
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return mergeSort(head,null);
}
public ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head,ListNode tail){
if(head == null){
return head;
}
if (head.next == tail) {
//这里刚开始忽略了
head.next = null;
return head;
}
//找出中点
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != tail) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast != tail) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
ListNode mid = slow;
ListNode l1=mergeSort(head,mid);
ListNode l2=mergeSort(mid,tail);
ListNode sorted = merge(l1,l2);
return sorted;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){
ListNode dumpHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp=dumpHead,temp1=head1,temp2=head2;
while(temp1 != null && temp2 != null){
if(temp1.val <= temp2.val){
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
}else{
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 != null) {
temp.next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 != null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dumpHead.next;
}
}
采用归并排序(递归)的方式,只是这种节点找中点的方式第一次用(快慢指针),偶数则是中点的后一个,奇数则是中点,上面忽略的地方是关键,否则会陷入死循环。合并就是采用比较两个节点的值的大小,最后返回有序链表的头节点。
56. 合并区间
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
if(intervals.length < 2){
return intervals;
}
Arrays.sort(intervals, new Comparator<int[]>() {
//新知识
public int compare(int[] a, int[] b) {
if(a[0] == b[0]) {
return a[1] - b[1];
}
return a[0] - b[0];
}
});
List<int[]> result = new ArrayList<int[]>();
for(int i=0;i<=intervals.length-1;i++){
int L = intervals[i][0],R = intervals[i][1];
if(result.size() == 0 || result.get(result.size()-1)[1] < L){
result.add(intervals[i]);
}else{
result.get(result.size()-1)[1] = Math.max(result.get(result.size()-1)[1], R);
}
}
return result.toArray(new int[result.size()][]);
}
}
上面就是直接用Arrays对二维数组排序,重写Comparator方法(第一次用,学到了),然后比较排序过后的[L,R],通过比较添加到ArrayList中,所以开始不要直接建二维数组,要建立链表,因为数组的大小是固定的。
57. 插入区间
class Solution {
public int[][] insert(int[][] intervals, int[] newInterval) {
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<int[]>();
List<int[]> result = new ArrayList<int[]>();
for(int i=0;i<intervals.length;i++){
list.add(intervals[i]);
}
list.add(newInterval);
int[][] arr = list.toArray(new int[list.size()][]);
Arrays.sort(arr,new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] a,int[] b) {
return a[0]-b[0];
}
});
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
int L = arr[i][0],R = arr[i][1];
if(result.size() == 0 || result.get(result.size()-1)[1] < L){
result.add(arr[i]);
}else{
result.get(result.size()-1)[1] = Math.max(result.get(result.size()-1)[1], R);
}
}
return result.toArray(new int[result.size()][]);
}
}
以上是在56题上改进的,不过不是最优,后面在题解里面看到更好的:
class Solution {
public int[][] insert(int[][] intervals, int[] newInterval) {
int left = newInterval[0];
int right = newInterval[1];
boolean placed = false;
List<int[]> ansList = new ArrayList<int[]>();
for (int[] interval : intervals) {
if (interval[0] > right) {
// 在插入区间的右侧且无交集
if (!placed) {
ansList.add(new int[]{
left, right});
placed = true;
}
ansList.add(interval);
} else if (interval[1] < left) {
// 在插入区间的左侧且无交集
ansList.add(interval);
} else {
// 与插入区间有交集,计算它们的并集
left = Math.min(left, interval[0]);
right = Math.max(right, interval[1]);
}
}
if (!placed) {
ansList.add(new int[]{
left, right});
}
int[][] ans = new int[ansList.size()][2];
for (int i = 0; i < ansList.size(); ++i) {
ans[i] = ansList.get(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
temp.add(root.val);
list.add(temp);
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queueTemp = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int levelSize = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
levelSize--;
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
queueTemp.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
queueTemp.offer(node.right);
}
if(levelSize == 0){
levelSize = queue.size();
List<Integer> temp2 = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queueTemp.isEmpty()){
TreeNode nodeTemp = queueTemp.poll();
temp2.add(nodeTemp.val);
}
if(!temp2.isEmpty()){
list.add(temp2);
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
temp.add(root.val);
list.add(0,temp); //get到了一个新方法
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queueTemp = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int levelSize = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
levelSize--;
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
queueTemp.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
queueTemp.offer(node.right);
}
if(levelSize == 0){
levelSize = queue.size();
List<Integer> temp2 = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queueTemp.isEmpty()){
TreeNode nodeTemp = queueTemp.poll();
temp2.add(nodeTemp.val);
}
if(!temp2.isEmpty()){
list.add(0,temp2);
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
662. 二叉树最大宽度
用到了双向队列。才可有getFirst()和getLsat()方法
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
// Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();//要双向队列才可
root.val = 0;
queue.offer(root);
int res = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
res = Math.max(res,queue.getLast().val-queue.getFirst().val+1);
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left != null){
node.left.val = 2*node.val;
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
node.right.val = 2*node.val+1;
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
559. N 叉树的最大深度
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> children; public Node() {} public Node(int _val) { val = _val; } public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int height = 0;
int levelSize = 1;
int sizetemp = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node node = queue.poll();
levelSize--;
for(int i=0;i<node.children.size();i++){
if(node.children.get(i) != null){
queue.offer(node.children.get(i));
sizetemp++; //记录每层的个数
}
}
if(levelSize == 0){
height++;
levelSize = sizetemp; //重新赋值
sizetemp = 0; //重新置为0
}
}
return height;
}
}
上面是自己的想法,跟题解的方法不太一样,不过运行效率差了点。
889. 根据前序和后序遍历构造二叉树
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructFromPrePost(int[] preorder, int[] postorder) {
if(preorder == null || preorder.length == 0){
return null;
}
return dfs(preorder,postorder);
}
public TreeNode dfs(int[] preorder, int[] postorder){
if(preorder == null || preorder.length == 0){
return null;
}
//数组长度为1时,直接返回即可!!!!!!
if(preorder.length==1) {
return new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
int n = preorder.length;
for(int i=0;i<postorder.length;i++){
if(preorder[1] == postorder[i]){
int line = i+1;
int[] pre_left = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,1,line+1);
int[] pre_right = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,line+1,n);
int[] post_left = Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,0,line);
int[] post_right = Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,line,n-1);
root.left = dfs(pre_left,post_left);
root.right = dfs(pre_right,post_right);
break;
}
}
return root;
}
}
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
class Solution {
public int rightMin(TreeNode root) {
//1.找到以某个结点为根节点的右子树最小值。
root = root.right;
while (root.left != null) root = root.left;//1.1循环往左找到最大值。
return root.val;
}
public int leftMax(TreeNode root) {
//2.找到以某个结点为根节点的左子树最大值。
root = root.left;
while (root.right != null) root = root.right;
return root.val;
}
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) {
//3.递归终止条件
return null;
}
if (key > root.val) {
//4.如果查找的结点比根节点大,继续在右子树查找删除该结点
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
} else if (key < root.val) {
//5.如果查找的结点比根节点小,继续在左子树查找删除该结点
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else {
//6.如果找到了该结点,删除它
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
//7.以叶子节点为根节点的二叉搜索树只有一个元素,可以直接删除。
root = null;
} else if (root.right != null) {
//8.如果有右子树,只要找到该右子树的最小值来替换,之后将它删除即可。
root.val = rightMin(root);
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, root.val);//9.将这个右子树的最小值替换根节点,此时存在两个相同节点,将这个节点删除即可。
} else {
//10.如果有左子树,只要找到该左子树的最大值来替换,之后将它删除即可。
root.val = leftMax(root);
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, root.val);//9.将这个左子树的最大值替换根节点,此时存在两个相同节点,将这个节点删除即可。
}
}
return root;
}
}
1361. 验证二叉树
class Solution {
public boolean validateBinaryTreeNodes(int n, int[] leftChild, int[] rightChild) {
int[] findFather = new int[n]; //先找出入度为0的节点,即为root
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(leftChild[i] != -1){
findFather[leftChild[i]]++;
}
if(rightChild[i] != -1){
findFather[rightChild[i]]++;
}
}
int root = -1;
int count = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(findFather[i] == 0){
root = i;
count++;
}
if(findFather[i] == 2){
return false;
}
}
if(root == -1 || count > 1){
return false;
}
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); //记录遍历的节点
queue.offer(root);
list.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int node = queue.poll();
if(leftChild[node] != -1){
if(list.contains(leftChild[node])){
return false;
}
list.add(leftChild[node]);
queue.offer(leftChild[node]);
}
if(rightChild[node] != -1){
if(list.contains(rightChild[node])){
return false;
}
list.add(rightChild[node]);
queue.offer(rightChild[node]);
}
}
return list.size() == n;
}
}
101. 对称二叉树
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return check(root.left,root.right); //递归检查
}
public boolean check(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p == null && q == null){
return true;
}
if(p == null || q == null){
return false;
}
return p.val == q.val && check(p.left,q.right) && check(p.right,q.left);
}
}
边栏推荐
- 有哪些事情是你做了运维才知道的?
- 线上问题排查流程
- Detailed explanation of ten solutions across domains (summary)
- 解决这三大问题,运维效率将超90%的医院
- [Problem has been resolved]-Virtual machine error contains a file system with errors check forced
- Spark source code-task submission process-6.2-sparkContext initialization-TaskScheduler task scheduler
- time complexity and space complexity
- By solving these three problems, the operation and maintenance efficiency will exceed 90% of the hospital
- Advantages of overseas servers
- 多线程之传递参数
猜你喜欢
One-arm routing and 30% switch
IP packet format (ICMP protocol and ARP protocol)
![[issue resolved] - jenkins pipeline checkout timeout](/img/3d/c14276d2b5ce18fc3d1288abb059c0.png)
[issue resolved] - jenkins pipeline checkout timeout
RAID磁盘阵列
What's the point of monitoring the involution of the system?
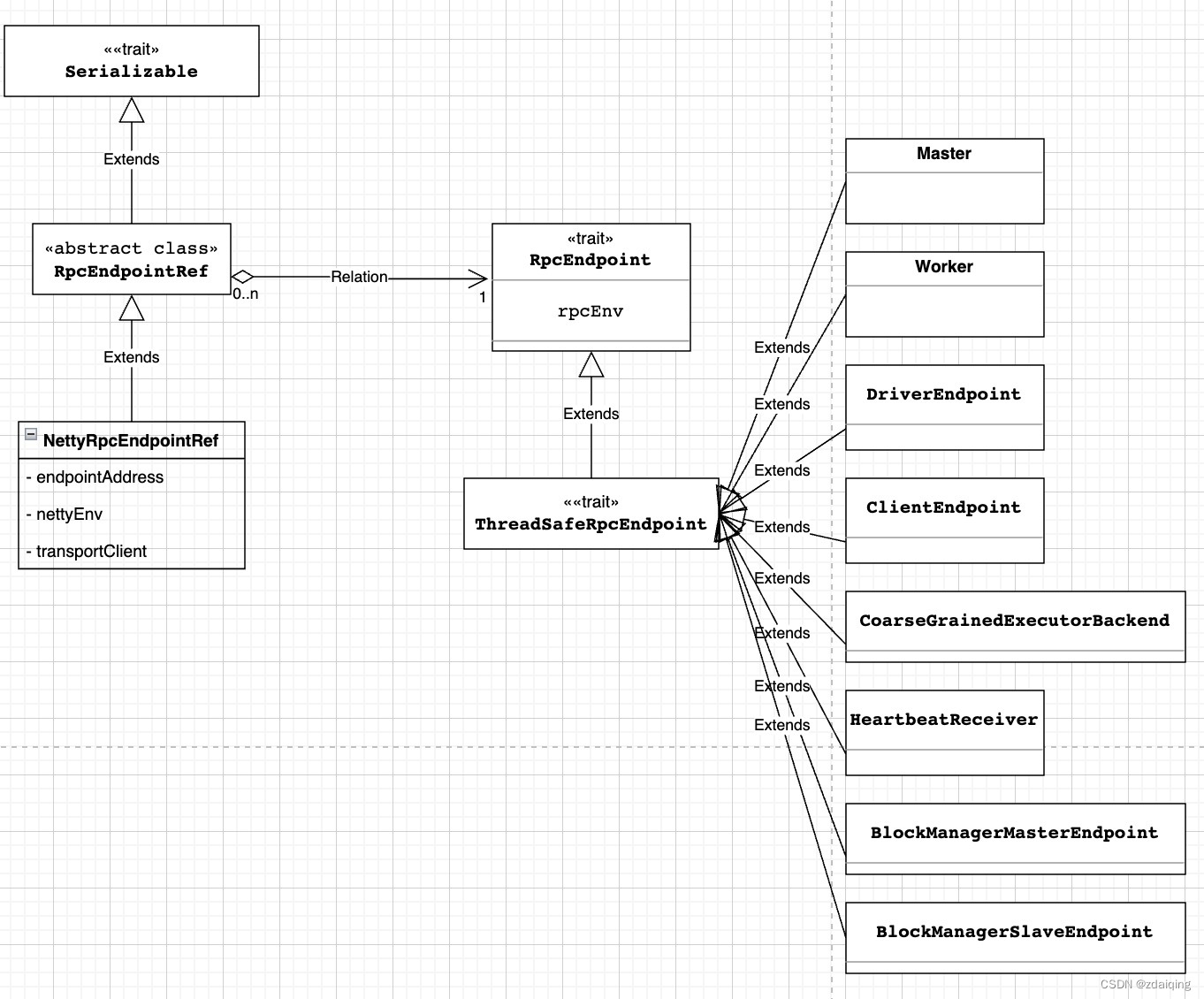
spark source code-RPC communication mechanism

初识网页与浏览器
The problem come from line screening process
el-progress implements different colors of the progress bar

LeetCode中常用语言的一些基本方法记录
随机推荐
Difference between link and @improt
增长:IT运维发展趋势报告
Met with the browser page
跨域的十种解决方案详解(总结)
Into the pre-service, thought they play so flowers
The idea of commonly used shortcut key
Cloud computing - osi seven layers and TCP\IP protocol
Advantages of overseas servers
Introduction to Network Layer Protocols
Mina的长连接和短连接
User and user group management, file permission management
Problems encountered in installing Yolo3 target detection module in Autoware
RAID disk array
Unity realizes first-person roaming (nanny-level tutorial)
NIO works is analysed
网络层协议介绍
TCP/IP four-layer model
监控系统的内卷,有什么讲究?
What's the point of monitoring the involution of the system?
The problem come from line screening process