当前位置:网站首页>Data type of pytorch tensor
Data type of pytorch tensor
2022-07-07 01:04:00 【A traveler far away】
Processing data (Torch)
Tensor It's a special data structure , stay Pytorch in , Just use Tensor To encode the input of the model 、 Output and parameters of the model .
So you can think that if you want to use pytorch, Any data should be converted into tensor.
Data initialization
Method 1 :torch.tensor
function : Build general tensortorch.tensor(data, *, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False)
data: initialization tensor The data of , Can be a list (list)、 Tuples (tuple)、numpy Array of ndarray、 Numeric scalars and other types .
dtype: Appoint tensor Data type of , Usually, the data types are as follows
| dtype | Data type description |
|---|---|
| torch.float16 or torch.half | 16 Bit floating point type |
| torch.float32 or torch.float | 32 Bit floating point type |
| torch.float64 or torch.double | 64 Bit floating point type |
| torch.uint8 | 8 Bit unsigned integer |
| torch.int8 | 8 Long long |
| torch.int16 or torch.short | 16 Long long |
| torch.int32 or torch.int | 32 Long long |
| torch.int64 or torch.long | 64 Long long |
| torch.bool | bool type |
| torch.complex64 or torch.cfloat | 64 Bitwise complex |
The above are some commonly used data types , If this parameter is not specified , that torch Will be based on data Automatically infer data types , So if data The data types inside are unified , Can , So big can be ignored dtype, Let it automatically infer .
device: Specify where the data runs , Or cpu Or gpu
| Specify the running device | keyword |
|---|---|
| cpu | ‘cpu’ |
| gpu | ‘cuda:index’ |
If you have more than one on your computer gpu, Then you can pass index Appoint , Of course, you can also write one directly cuda
Next, let's talk about the method of specifying equipment , There are usually two ways to specify devices
The way 1: Define a devicedata = [[1,2],[3,4]] cpu_device = torch.device('cuda') tensor_data = torch.tensor(data,device=cpu_device)
The way 2: Direct designation data = [[1,2],[3,4]] tensor_data = torch.tensor(data,device='cuda')
requires_grad:bool type , Used to specify whether the data can be updated by gradient , In the process of model training , You can set it to True, When doing the reverse gradient like this , Parameters can be updated .
pin_memory:bool type , by True When , take tensor Allocate to fixed memory . It should be noted that , This parameter is only in device by cpu It's going to work next time .
`
Complete example
torch.tensor([[0.11111, 0.222222, 0.3333333]],dtype=torch.float64,device=torch.device(‘cuda:0’))** Method 2 :torch.sparse_coo_tensor**
function : initialization Build a sparse tensor
torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indices, values, size=None, *, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False)
`
Before explaining the parameters of this function , Let's first understand the principle of this function to build a sparse matrix , First post a picture drawn by the big guys on the Internet , More vivid 
As you can see from the diagram , On the left is a sparse matrix , But it can go through , The data on the right indicates . The first row represents the row of non-zero data , The second row represents the column of non-zero data , The third line represents the data size of the specific location .
With this basic design concept , You can explain the meaning of each parameter
Parameter description :
indices: Specify the position of non-zero elements , That is, the first and second lines on the right in the above figure . It can be list,tuple,ndarray, An integer
values: Non zero value at specific position , Its order is calculated line by line , The non-zero value of the first line is first , And then in order .
size: Specify matrix size , That is, the size of the matrix on the left of the above figure , It can be list perhaps tuple
dtype: Specify the data type , Refer to the above tensor
device : Designated equipment , Refer to the above tensor
requires_grad: Specify whether the data can be updated by gradient , Refer to the above tensor
Specific examples
The example above is implemented as follows i = torch.tensor([[0,0,1,1,2,2,2,3,3],[0,1,1,2,0,2,3,1,3]]) v = torch.tensor([1,7,2,8,5,3,9,6,4],dtype=torch.float32) spar_tensor = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i,v,size = [4,4],dtype=torch.float64,device=torch.device('cpu'))
Method 3 :tensor.asarray
function : initialization , Similar to the copy function torch.asarray(obj, *, dtype=None, device=None, copy=None, requires_grad=False)
Parameter description :
obj: It can be tensor,numpy array Other types
copy: bool type , If True when , Namely copy A copy of the data , If it is false, Is a quotation , Change a data , The other will change .
device: Designated equipment
requires_grad : Specifies whether gradients are supported
Specific examples a = torch.tensor([1,2,3]) b = torch.asarray(a) c = torch.asarray(a,copy=True,dtype=torch.float32,device = 'cpu')
Method four :torch.as_strided
function : Create a view , It is convenient to observe the data of specific location torch.as_strided(input, size, stride, storage_offset=0)
Parameter description :
input:tensor, The original input tensor
size: Define the size of the output data , It can be tuple perhaps int
stride: Specify the stride of the view , This parameter is actually quite abstract , Its function is not to be separated by much input Collect data on , It can be tuple perhaps int.
storage_offset: The starting position of data collection , Usually it is int.
Specific examples
`
x = torch.randn(3, 3)
t = torch.as_strided(x, (2, 2), (1, 1))
x,t
(tensor([[-0.0215, 0.3483, -1.4443],
[-0.3040, 1.3200, 2.0977],
[ 0.7380, 1.0222, -0.6579]]),
tensor([[-0.0215, 0.3483],
[ 0.3483, -1.4443]]))
`
Method five :torch.from_numpy
function : from ndarray In the initialization tensortorch.from_numpy(ndarray)
Other methods :
torch.zeros : establish 0 matrix
torch.zeros_like : establish 0 matrix , By inputting tensor The shape of the matrix creates the same shape 0 matrix tensor
torch.ones : establish 1 matrix
torch.ones_like : establish 1 matrix , By inputting tensor The shape of the matrix creates the same shape 1 matrix tensor
torch.range: and numpy Of range similar , Only the return value is tensor
torch.arange: and numpy Of arange similar , Only the return value is tensor
torch.linspace: and numpy Of linspace similar , Only the return value is tensor
torch.eye:: Create as 1 Diagonal matrix of
torch.empty: Define an empty tensor, Is equal to defining a variable
torch.empty_like: similar torch.ones_like
torch.full: Create a specified value filled tensor matrix
torch.full_like: similar torch.ones_like
tensor The index of 、 section 、 Connect 、 Mutation operation
torch.adjoint: For plural operations , Yes tensor Conjugate then transpose
torch.argwhere: return tensor Location index of non-zero value
torch.cat: Splicing tensor
torch.chunk: take tensor Split equally
torch.column_stac: It can be understood as transposing first , Then splice by column and row
torch.tensor_split: Split tensor
torch.hsplit: similar torch.tensor_split
torch.hstack: Vertical splicing tensor
torch.select: Returns a sliced tensor
torch.squeeze: Compress it into tensor by 1 Dimensions
torch.transpose:tensor Data exchange of different dimensions , So if it's two-dimensional data , When it is two-dimensional , After the exchange is transpose .
torch.t: Transposition , and torch.transpose similar
torch.take: obtain tensor Value of corresponding position , And then return the new tensor
torch.unsqueeze: increase tensor Dimensions
Mathematical operation
torch.acos: Calculation tensor The arccosine of
torch.cos: Cosine operation
torch.sin: Sinusoidal operation
torch.tan: Tangent operation
torch.add: Add operation
torch.sub: Reduction of operating
torch.mul:tensor Multiply the corresponding positions
torch.mm:tensor matrix multiplication
torch.div: Division operation
torch.pow: Power operation
torch.exp: Index operation
torch.log:log operation
torhc.sqrt: Root operation
torch.ceil: Rounding up
torch.floor: Rounding down
torch.abs: return tensor The absolute value
torch.neg:tensor Take the opposite
torch.frac: Get the decimal part
torch.imag: Take the imaginary part of the complex number
torch.real: Take the real part of the complex number
torch.round: Round to the nearest whole
torch.trunc: Take out the decimal point
torch.deg2rad: Angle turns to amplitude
torch.rad2deg: The amplitude changes to angle
torch.clip: Same as torch.clamp, Limit the size of an array to a range , Greater than the maximum , Replace with the maximum , If it is less than the minimum value, use the minimum value instead
torch.argmax: Index that takes the maximum value of different dimensions
torch.argmin: Index that takes the minimum value of different dimensions
torch.amax: Take the maximum value of different dimensions
torch.amin: Take the minimum value of different dimensions
torch.aminmax: Take the maximum and minimum values of different dimensions
torch.all: Whether all values are true
torch.any: Is there any one for true
torch.max: Find the maximum of all values
torch.min: Find the minimum of all values
torch.mean: Calculating mean
torch.nanmean: Find the mean value of non null values
torch.median: Find the median
torch.nanmedian: Find the median of non null value
torch…mode: Find the mode and the last index position where the mode appears
torch.nansum: Sum nonzero values
torch.sum: Sum up
torch.prod: Value multiplication
torch.std: Mean square error
torch.unique: Find the only value
torch.var: Variance estimation
torch.argsort: Return the index sorted by dimension
torch.eq: Compare whether the corresponding positions are equal
torch.equal: Why compare all values
torch.ge: The corresponding position is greater than or equal to
torch.gt: The corresponding position is greater than
torch.le: The corresponding position is less than or equal to
torch.lt: The corresponding position is less than
torch.ne: The corresponding position is not equal to the operation
torch.isin: Inclusion relation
torch.sort: The sorting operation
torch.topk: seek topK
边栏推荐
- 界面控件DevExpress WinForms皮肤编辑器的这个补丁,你了解了吗?
- 【批处理DOS-CMD命令-汇总和小结】-字符串搜索、查找、筛选命令(find、findstr),Find和findstr的区别和辨析
- Meet the level 3 requirements of ISO 2.0 with the level B construction standard of computer room | hybrid cloud infrastructure
- Advantages and disadvantages of code cloning
- 新手如何入门学习PostgreSQL?
- Windows installation mysql8 (5 minutes)
- build. How to configure the dependent version number in the gradle file
- Periodic flash screen failure of Dell notebook
- Dell笔记本周期性闪屏故障
- 重上吹麻滩——段芝堂创始人翟立冬游记
猜你喜欢

重上吹麻滩——段芝堂创始人翟立冬游记
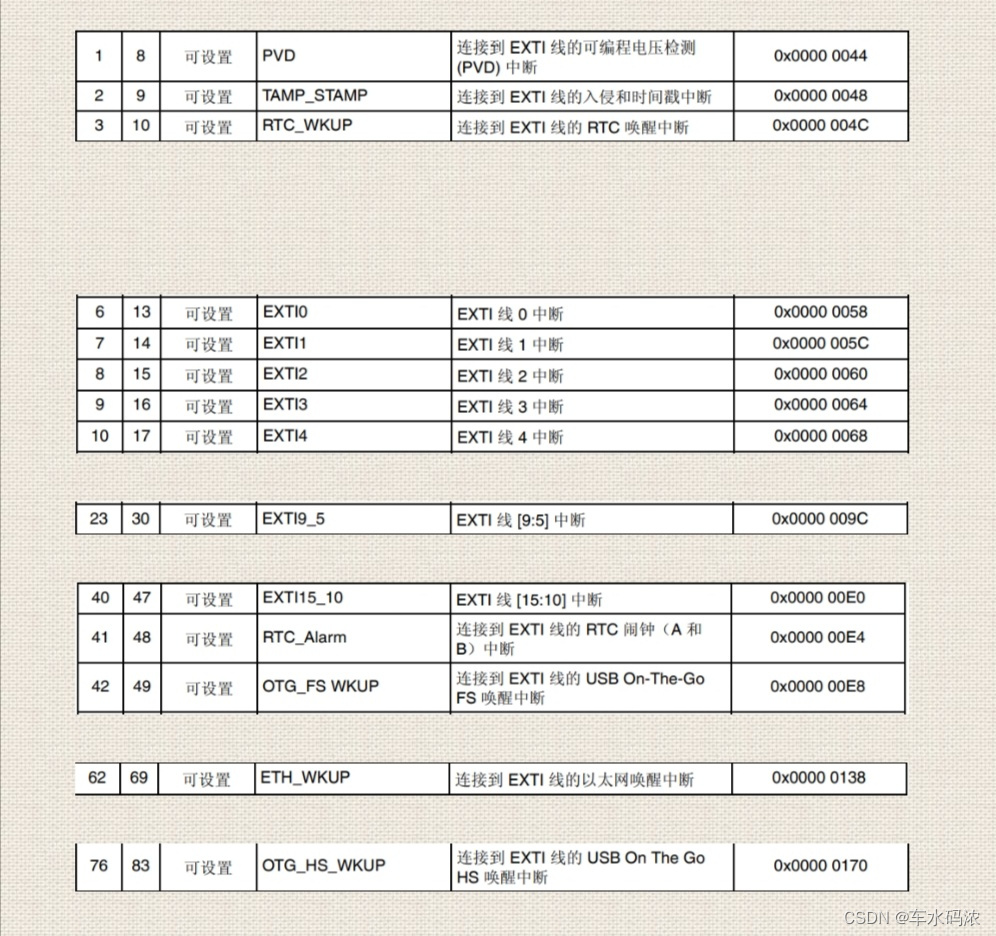
Part IV: STM32 interrupt control programming
![[100 cases of JVM tuning practice] 04 - Method area tuning practice (Part 1)](/img/7a/bd03943c39d3f731afb51fe2e0f898.png)
[100 cases of JVM tuning practice] 04 - Method area tuning practice (Part 1)
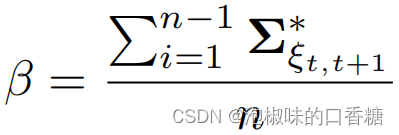
Slam d'attention: un slam visuel monoculaire appris de l'attention humaine

Batch obtain the latitude coordinates of all administrative regions in China (to the county level)

筑梦数字时代,城链科技战略峰会西安站顺利落幕
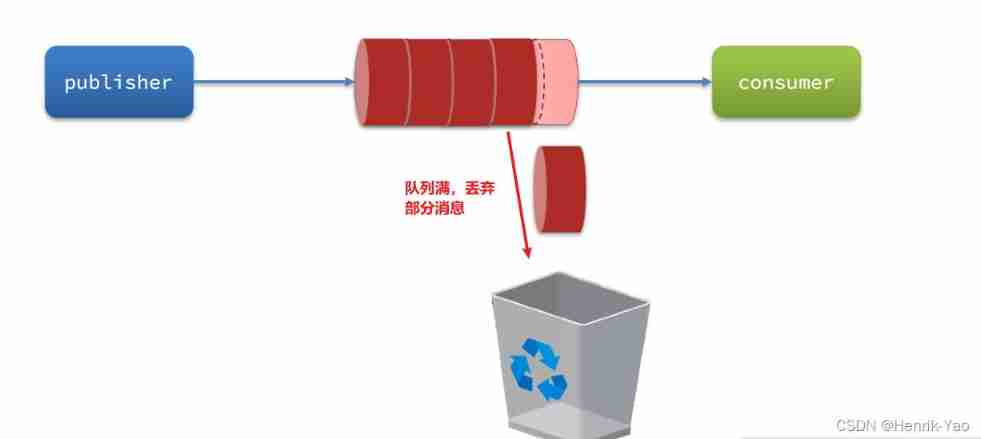
Service asynchronous communication
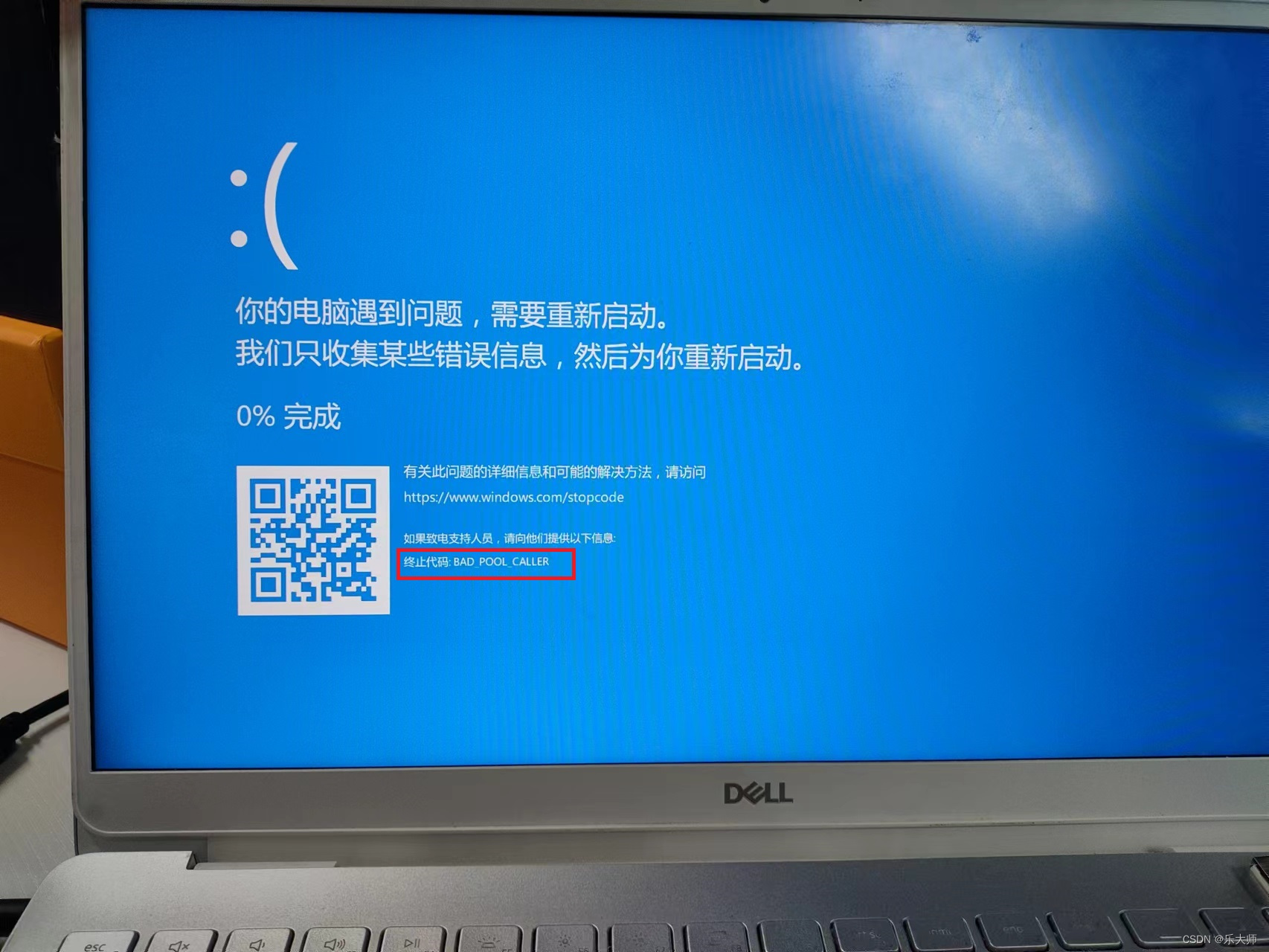
Dell筆記本周期性閃屏故障
【JVM调优实战100例】05——方法区调优实战(下)
深度学习之环境配置 jupyter notebook
随机推荐
New feature of Oracle 19C: automatic DML redirection of ADG, enhanced read-write separation -- ADG_ REDIRECT_ DML
Distributed cache
详解OpenCV的矩阵规范化函数normalize()【范围化矩阵的范数或值范围(归一化处理)】,并附NORM_MINMAX情况下的示例代码
新手如何入门学习PostgreSQL?
建立自己的网站(17)
【批处理DOS-CMD命令-汇总和小结】-字符串搜索、查找、筛选命令(find、findstr),Find和findstr的区别和辨析
【批處理DOS-CMD命令-匯總和小結】-字符串搜索、查找、篩選命令(find、findstr),Find和findstr的區別和辨析
以机房B级建设标准满足等保2.0三级要求 | 混合云基础设施
OSPF configuration command of Huawei equipment
Windows installation mysql8 (5 minutes)
In rails, when the resource creation operation fails and render: new is called, why must the URL be changed to the index URL of the resource?
Maidong Internet won the bid of Beijing life insurance to boost customers' brand value
ActiveReportsJS 3.1中文版|||ActiveReportsJS 3.1英文版
.class文件的字节码结构
Tencent cloud webshell experience
「精致店主理人」青年创业孵化营·首期顺德场圆满结束!
Informatics Olympiad YBT 1171: factors of large integers | 1.6 13: factors of large integers
Slam d'attention: un slam visuel monoculaire appris de l'attention humaine
BFS realizes breadth first traversal of adjacency matrix (with examples)
Learning notes 5: ram and ROM