当前位置:网站首页>Set (generic & list & Set & custom sort)
Set (generic & list & Set & custom sort)
2022-07-07 00:42:00 【A very lazy person】
This paper mainly introduces the indication of set , Including but not limited to the following knowledge :
- Generic
- Set system level
- Interfaces and their implementation classes in the collection system
- Collection custom sorting
aggregate
- 1. Generic
- 2. aggregate
- 3. Collection implements custom sorting
- 4. Double column set (Map)
1. Generic
(1) Concept
take data type As Parameters Conduct Pass on
( When using generics , What data type is received , What data type is this generic )
(2) Definition
1,<T>:T Declare a generic , You can use any letter , Refers to generic ,eg:<T>、<X>
2,<T,X,...>: Declare multiple generics ,T、X.....
(3) Use
Be careful :
- Generics must : First define , Reuse
- When using generics , What data type is received , What data type is this generic
- Generics can be defined at data types
- Generics defined in classes can only be used in classes , What is defined in a method can only be used in a method ( Generic scope )
- Classes that use generics , stay Create objects Please specify actual Data type of ( Only reference data types can be used )
- Use generic interfaces , Common abstract methods can use generics ( Statically decorated members cannot use generics )
- Realization Classes that use generic interfaces , You need to add generics after classes and interfaces , But generally, anonymous inner classes are used to create interface instances
eg01: Use... In methods
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = test(1);
String str = test("123");
Test t = new Test();
Test test = test(t);
}
/** * requirement , The parameter type passed in is the return value type * When using generics , What data type is received , What data type is this generic */
public static <X> X test(X str) {
return str;
}
/** * Any type can be passed in */
public static <X,Y> void test01(X str,Y y,Y y2) {
}
}
eg02: Use... In classes
- Define generics on class , It must be after the class name and before inheritance and implementation , Follow the class name
- When using generics , What data type is received , What data type is this generic
/** * Define generics on class , It must be after the class name and before inheritance and implementation , Follow the class name */
class Person<K,Y,Z> extends Object {
private K k;
private Y y;
private Z z;
private String str;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(K k, Y y, Z z, String str) {
super();
this.k = k;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
this.str = str;
}
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// When using generics , What data type is received , What data type is this generic
Person<Integer, String, Boolean> person = new Person<Integer, String, Boolean>();
Person<String, Integer, Integer> person2 = new Person<String, Integer, Integer>();
}
}
eg03: Used in an interface
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Anonymous inner classes use generics
MyInterfaceTest<String> test = new MyInterfaceTest<String>();
new MyInterface<Integer>() {
@Override
public void test01(Integer k) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public Integer test02(Integer k) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
};
}
}
interface MyInterface<K>{
void test01(K k);
K test02(K k);
}
//2. Class implements generic interfaces
/* You need to add generics after the interface and the implementation class */
class MyInterfaceTest<K> implements MyInterface<K>{
@Override
public void test01(K k) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public K test02(K k) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
}
2. aggregate
(1) Concept
Store a set of data with the same data type ( Reference data type ), Variable length
(2) System level
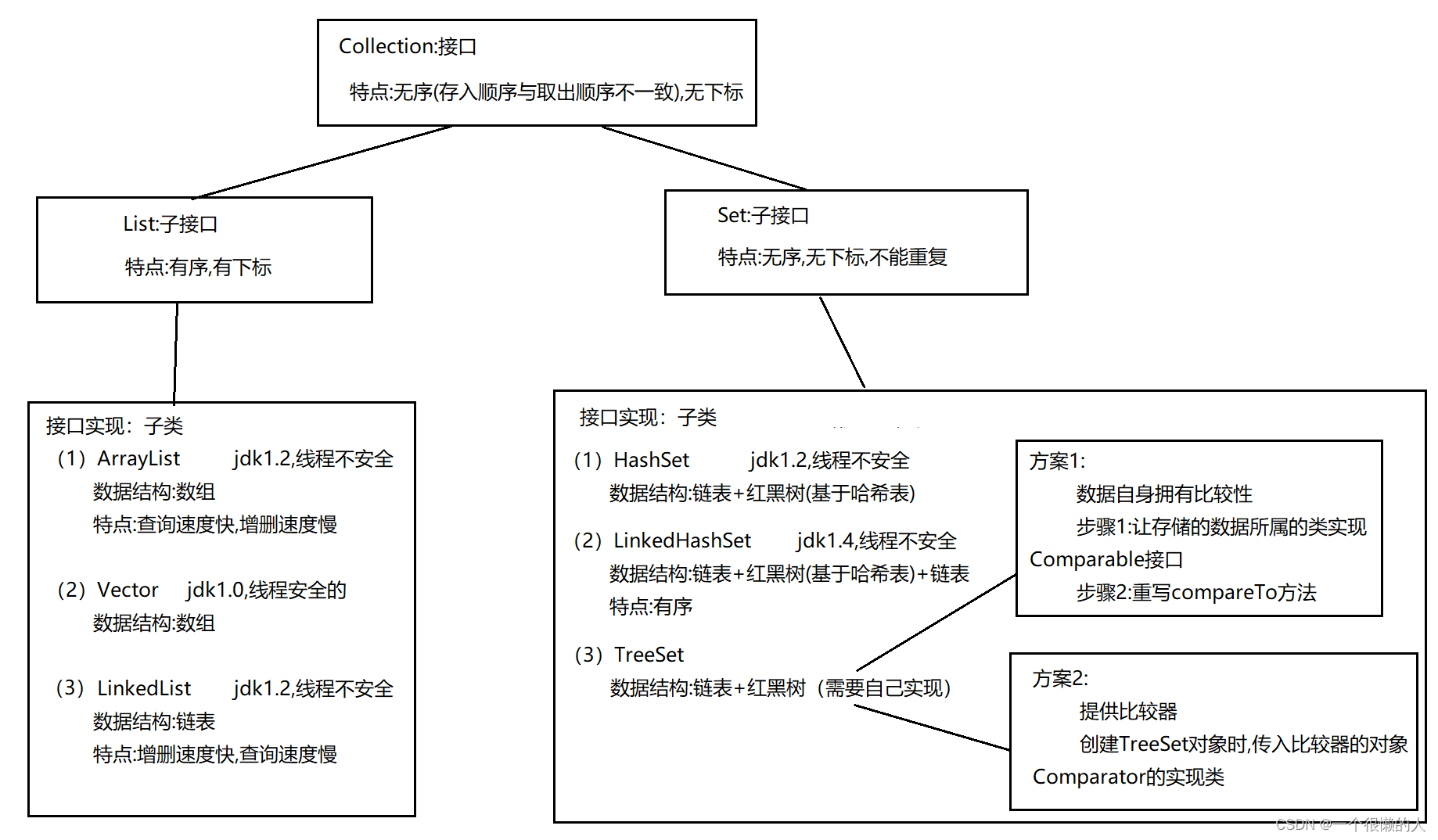
(3)Collection: Interface ( Set the first level parent class )
Collection: Interface
characteristic : disorder ( The order of deposit is inconsistent with that of withdrawal ), No subscript
Method :
increase
boolean add(E e): Add a data
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c): Add data from the subset to the set
Delete
boolean remove(Object o);: Delete a data
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c): Delete all data in the subset from the set
void clear(): Empty
Change
nothing
check
int size(): Get the number of elements in the collection
boolean contains(Object o): Determine whether the specified element exists in the collection
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c): Determine whether all data in the subset exists in the set
Iterator<E> iterator(): iterator
other
boolean isEmpty(): Determine whether there are elements in the set
Object[] toArray(): Convert collection to array
(4)List: A subinterface ( Set the secondary parent class )
List: A subinterface
characteristic : Orderly , With subscript
Subclass specific methods ( Remove inheritance Collection Methods )
increase
Insert data one at a time ,1 ginseng : Insertion position ,2 ginseng : Inserted data
void add(int index, E element);
Insert one set of data at a time ,1 ginseng : Insertion position ,2 ginseng : Inserted data
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);
Delete
Delete the data at the specified location according to the subscript
E remove(int index);
Change
modify :1 ginseng : Subscript ,2 ginseng : Modified elements
E set(int index, E element);
check
Get the element at the specified location , Parameters : Subscript
E get(int index):
(5)Set: A subinterface ( Set the secondary parent class )
Set
characteristic : disorder ( The order of deposit is inconsistent with that of withdrawal , But the output stored inside it is orderly ( From big to small or from small to large )), No subscript , Can't repeat
Subclass specific methods : nothing ( Remove inheritance Collection Method , There is no other way of your own )
(6) Sub interface implementation class ( aggregate )
List Sub interface implementation class
(1)ArrayList jdk1.2, Thread unsafe
data structure : Array
characteristic : Fast query speed , The speed of adding and deleting is slow
(2)Vector jdk1.0, Thread safe
data structure : Array
(3)LinkedList jdk1.2, Thread unsafe
data structure : Linked list
characteristic : The speed of adding and deleting is fast , Query speed is slow
Set Sub interface implementation class
(1)HashSet jdk1.2, Thread unsafe
data structure : Linked list + Red and black trees ( Based on hash table )
(2)LinkedHashSet jdk1.4, Thread unsafe
data structure : Linked list + Red and black trees ( Based on hash table ,jdk Source code encapsulation implementation )+ Linked list
characteristic : Orderly
(3)TreeSet
data structure : Linked list + Red and black trees ( You have to implement it yourself )
programme 1:
The data itself is comparative
step 1: Let the class to which the stored data belongs realize Comparable Interface
step 2: rewrite compareTo Method
programme 2:
Provide comparator
establish TreeSet Object time , The object passed into the comparator Comparator Interface implementation class
(7) Iterate through
- Get the iterator of the collection
- hasNext() Method to determine whether the position to be iterated contains elements
- iterator.next() Get the element indicating the position of the iterator , And move the iterator indication position down one position
- So circular , Until the elements in the iterator are traversed
// Iterate through
Iterator<Person> iterator=treeSet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Person person=iterator.next();
System.out.println(person);
}
3. Collection implements custom sorting
(1)Comparable Interface
- stay java Of jdk Provided in Comparable Interface , It provides an abstract method compareTo(T o), among T For generics , Using it with collections can realize custom sorting
- java Of 8 The basic data types in all implement classes Comparable Interface , Implement the methods in the class
1. With TreeSet For example , analysis Comparable Interface , Then realize custom sorting
- Person Realization Comparable Interface
- rewrite compareTo(Person o) Method
Among the methods this In the collection of substitutes add(e) Value , Compare them with the original elements in the set in turn , Make sure its location is in the data structure Position in , Then insert it into the data structure ( Use a certain data structure to realize the sequential storage of data values )- TreeSet Its storage is red black tree ,jdk Its sorting method is not implemented in , You have to implement it yourself , Make its stored class implement Comparable Interface is one of the methods to realize its sorting
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
private int height;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, String sex, int age, int height) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
}
/* ............ Other methods of the standard class are omitted */
// Custom comparison
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (this.height!=o.height) {
return this.height-o.height;
}else if (this.age!=o.age) {
return this.age-o.age;
}
else {
return this.name.compareTo(o.name)+this.sex.compareTo(o.sex);
}
}
}
(2)Comparator Interface
- Comparator The interface provides compare(T o1, T o2) Abstract method , among T For generics , It can be used with collections , Realize custom sorting of collections
2. With TreeSet For example , analysis Comparator Interface , Then realize custom sorting
- It can be seen as a custom comparator , Use in operation , There is no need to implement the interface for the class of its operation object
- Creating TreeSet When the collection , Incoming comparator (Comparator Implementation class of interface ), The following uses anonymous inner classes to create incoming
compare(T o1, T o2) Method in use , Its o1 The parameter represents that the collection is add(e) The object of ,o2 Represents the original object elements in the collection , take o1 It is in turn related to the original elements in the set (o2) Compare , Make sure its location is in the data structure Position in , Then insert it into the data structure ( Use a certain data structure to realize the sequential storage of data values )- TreeSet Its storage is red black tree ,jdk Its sorting method is not implemented in , You have to implement it yourself , Creating TreeSet Object time , Pass in a custom comparator (Comparator Interface implementation class ) It is one of the methods to realize the ordered sorting of its set
TreeSet<Person01> treeSet=new TreeSet<Person01>(new Comparator<Person01>() {
// Implement comparator
@Override
public int compare(Person01 o1, Person01 o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (o1.getHeight()!=o2.getHeight()) {
return o1.getHeight()-o2.getHeight();
}
else if (o1.getAge()!=o2.getAge()) {
return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
}
else {
return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName())+o1.getSex().compareTo(o2.getSex());
}
}
});
(3)Comparable Interface and Comparator Interface differences
Comparable Interface
- It can be regarded as a primary school from high to low row seats , The ranking method is to compare yourself with others , Determine your position
- It is abstracted as ,add(e) The object of is compared with the object that already exists in the collection , determine add(e) The location of the object stored in the underlying data structure
Comparator Interface
- It can be regarded as a primary school from high to low row seats , The ranking method is that the teacher gives you two comparisons , Then determine your position
- It is abstracted as ,add(e) The object of is compared with the object that already exists in the collection , Inside compare(T o1, T o2) In the method ,o1 representative add(e) The object of ,o2 Represents the existing objects in the union , Compare them to determine add(e) The location of the object stored in the underlying data structure
(4) The tool class that operates the collection :Collections( Implement custom sorting )
- Common methods
Collections.sort(list);// Sort
Collections.reverse(list);// Flip
Integer max = Collections.max(list);// Search for maximum
Integer min = Collections.min(list);// Find the minimum
- Collections in sort Method
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list)
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c)
The above two methods are Collections Two overloaded sort Method , From its parameters, we can see that the two ways to realize collection sorting are also and Comparable and Comparator of , That is, if you want to use this tool class to sort collections, there are two ways :
Scheme 1 : The data types stored in the collection have their own comparability
callCollections.sort(list)Yes list When sorting sets , requirement list The class of the data type stored in the collection implements Comparable Interface , I've rewritten one of them comparaTo MethodOption two : Provide custom comparator
callCollections.sort(list,new Comparator(compara Implementation method ))Yes list When sorting sets ,1 The parameter represents the set to be sorted ,2 The parameter represents the comparator you created ( Provides implementation of Comparator Implementation class of interface , It is required to rewrite compara Interface )
Use tool class Collections Code for sorting collections , You can refer to my other blog :
JAVA_ Custom sort (Comparable、Comparator) Detailed explanation
4. Double column set (Map)
(1) Concept
Concept : Store a set of data with the same data type , Variable length
Requirements for storing data : Key value corresponds to
(2) System level
Map( Interface )
- HashMap( class )
characteristic : Linked list + Red and black trees ( Hashtable ), Thread unsafe ,1.2
------- Inside it is Key value Key From small to large- HashTable( class )
characteristic : Linked list + Red and black trees ( Hashtable ), Thread safety ,1.0
------- Inside it is Key value Key From small to large
Properties( class )- TreeMap( class )
characteristic : Linked list + Red and black trees ( You need to provide it yourself )
------- There is no default sort inside , It is necessary to store data with comparability or provide comparator
Be careful : TreeMap Store the data , key (key) Or have comparability , Or create TreeMap Time is passed into the comparator ( similar TreeSet aggregate )
(3)Map Methods
increase
V put(K key, V value);
Be careful : If in the dictionary key non-existent , It's adding , If key There is , Then it will be modified key Corresponding value
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
Delete
V remove(Object key);
void clear();
Change
V put(K key, V value);
check
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean containsKey(Object key);
boolean containsValue(Object value);
V get(Object key);
Set<K> keySet();
Collection<V> values();
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
other :
Entry
getKey();
getValue();
(4)Map The traversal
Set<Integer> keySet = hashMap.keySet();
// Traverse the way 1
for (Integer key : keySet) {
String value=hashMap.get(key);
System.out.println(key+","+value);
}
// Traverse the way 2
Set<Entry<Integer,String>> entrySet = hashMap.entrySet();
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : entrySet) {
int key=entry.getKey();
String value=entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+","+value);
}
边栏推荐
- Three application characteristics of immersive projection in offline display
- Three methods to realize JS asynchronous loading
- Leecode brush questions record interview questions 32 - I. print binary tree from top to bottom
- C9高校,博士生一作发Nature!
- Idea automatically imports and deletes package settings
- Google, Baidu and Yahoo are general search engines developed by Chinese companies_ Baidu search engine URL
- Huawei mate8 battery price_ Huawei mate8 charges very slowly after replacing the battery
- 准备好在CI/CD中自动化持续部署了吗?
- After leaving a foreign company, I know what respect and compliance are
- On February 19, 2021ccf award ceremony will be held, "why in Hengdian?"
猜你喜欢

stm32F407-------DAC数模转换
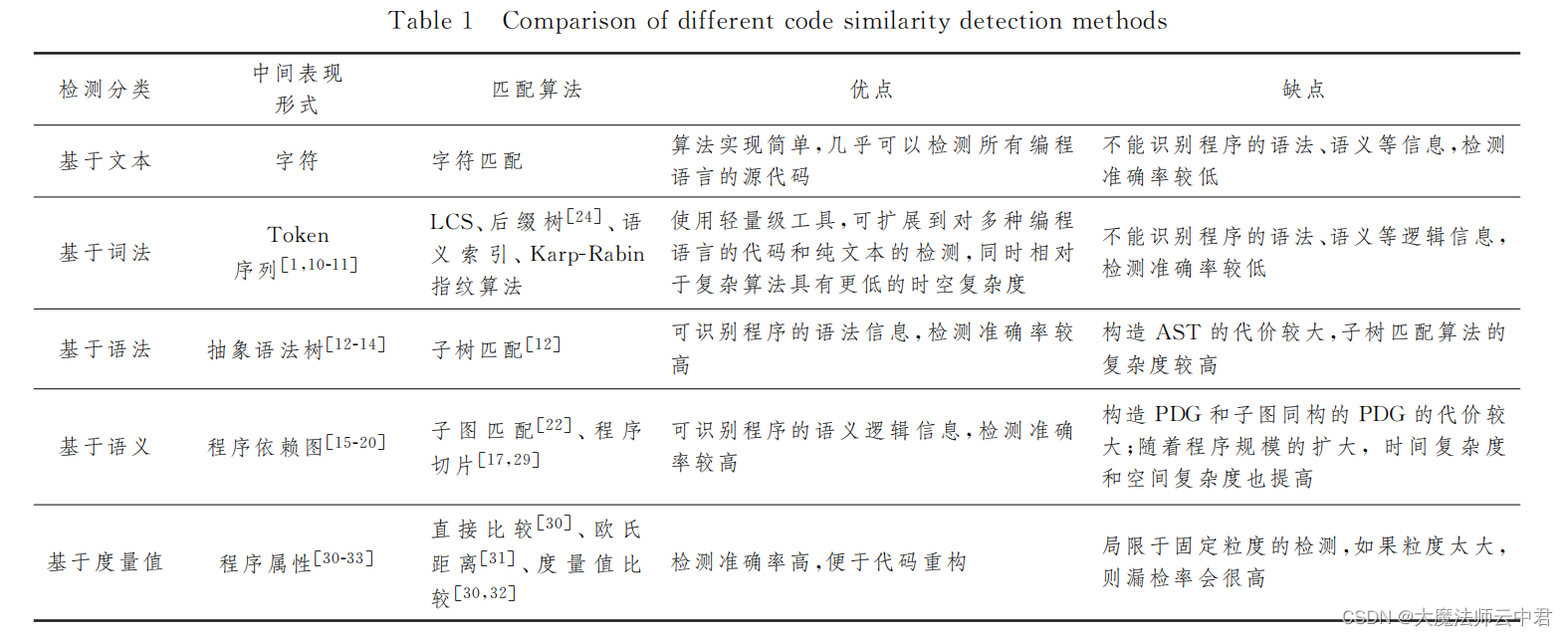
5种不同的代码相似性检测,以及代码相似性检测的发展趋势
学习使用代码生成美观的接口文档!!!
Lombok 同时使⽤ @Data 和 @Builder 的坑,你中招没?
Geo data mining (III) enrichment analysis of go and KEGG using David database
陀螺仪的工作原理
JS+SVG爱心扩散动画js特效

48页数字政府智慧政务一网通办解决方案
![[2022 the finest in the whole network] how to test the interface test generally? Process and steps of interface test](/img/8d/b59cf466031f36eb50d4d06aa5fbe4.jpg)
[2022 the finest in the whole network] how to test the interface test generally? Process and steps of interface test
Jenkins' user credentials plug-in installation
随机推荐
Encryption algorithm - password security
Value Function Approximation
代码克隆的优缺点
threejs图片变形放大全屏动画js特效
Typescript incremental compilation
Win10 startup error, press F9 to enter how to repair?
Everyone is always talking about EQ, so what is EQ?
Web project com mysql. cj. jdbc. Driver and com mysql. jdbc. Driver differences
Leecode brush questions record sword finger offer 11 Rotate the minimum number of the array
Alexnet experiment encounters: loss Nan, train ACC 0.100, test ACC 0.100
Clipboard management tool paste Chinese version
JWT signature does not match locally computed signature. JWT validity cannot be asserted and should
File and image comparison tool kaleidoscope latest download
Advanced learning of MySQL -- Fundamentals -- four characteristics of transactions
深度学习之数据处理
工程师如何对待开源 --- 一个老工程师的肺腑之言
System activity monitor ISTAT menus 6.61 (1185) Chinese repair
Personal digestion of DDD
A way of writing SQL, update when matching, or insert
Lombok 同时使⽤ @Data 和 @Builder 的坑,你中招没?