当前位置:网站首页>(1) Introduction Guide to R language - the first step of data analysis
(1) Introduction Guide to R language - the first step of data analysis
2022-07-06 12:20:00 【EricFrenzy】
notes : This blog aims to share personal learning experience , Please forgive me for any irregularities !
Catalog
R Language
Simply speaking ,R Language is a free open source 、 Powerful programming language for data analysis and visualization .R Please go to R Language website . Download the R After language , It is recommended to download, install and use RStudio This development environment .
When the download is complete , open RStudio, You will see the interface shown in the figure below :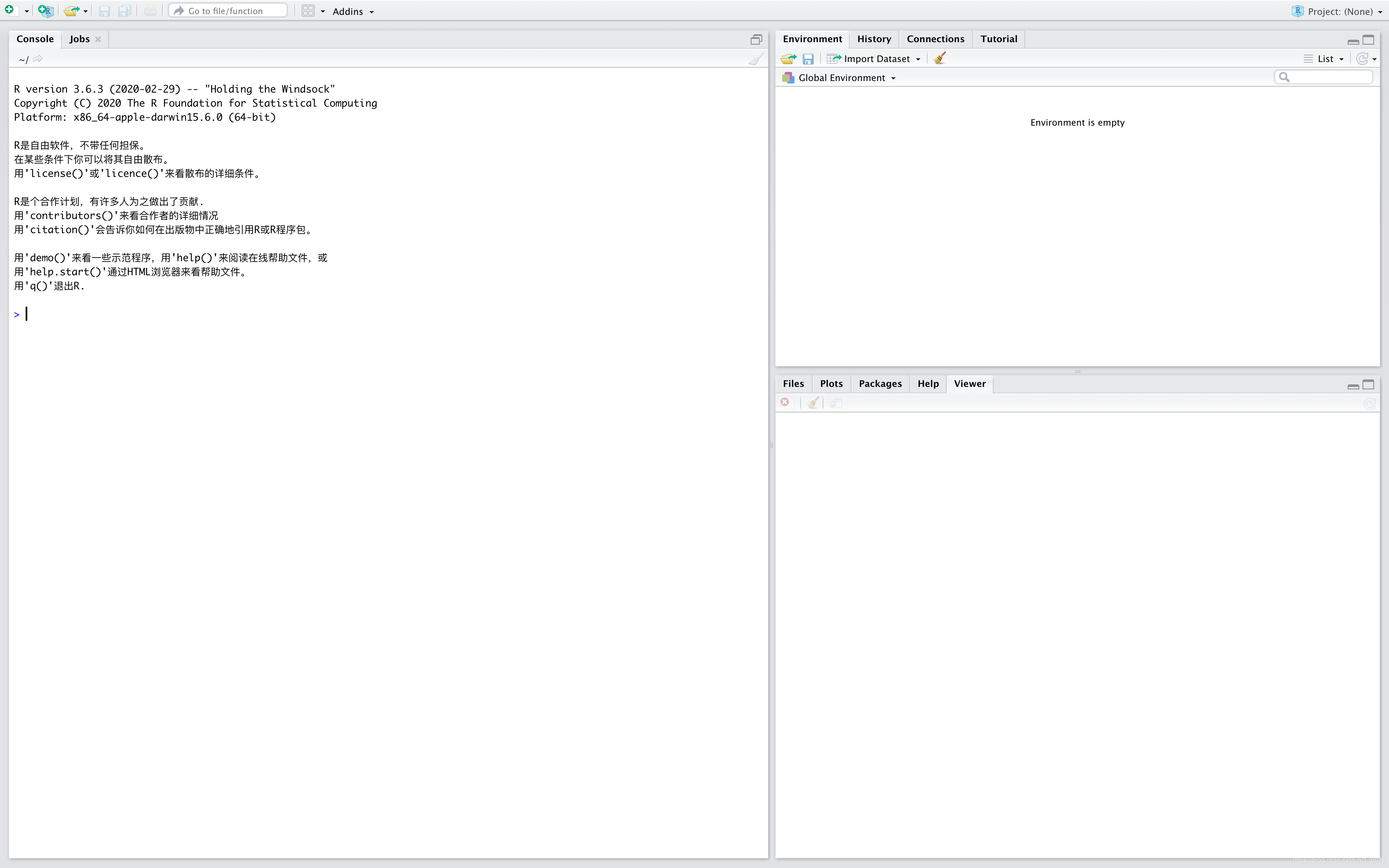
On the left is Console, You can directly enter the order . If you want to create files and write code , Click the pull-down menu in the top left corner to select . It's commonly used R Script file .
Next, the operation of bloggers can be all in Console in .
Numeric and logical operators
use R It's easy to calculate , Just in Console Type the order in and then enter .
Common numerical operators are shown in the following table :
| Symbol | meaning | give an example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition operation | 5+3 Output is 8 |
| - | Subtraction | 7-4 Output is 3 |
| * | Multiplication | 2*5 Output is 10 |
| / | Starting operation | 10/4 Output is 2.5 |
| ^ | Index of operation | 2^5 Output is 32 |
| %% | model / Take over operations | 5%%2 Output is 1 |
| %/% | Division operation | 11%/%3 Output is 3 |
The logical operators commonly used in the following tables :
| Symbol | meaning | explain | give an example |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | be equal to | If the symbols are equal twice , Return to true | 4==3 Output is F |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | If the front of the symbol is greater than or equal to the back of the symbol , Return to true | 4>=3 Output is T |
| <= | Less than or equal to | If the front of the symbol is less than or equal to the back of the symbol , Return to true | 4<=3 Output is F |
| != | It's not equal to | If the symbols are not equal twice , Return to true | 4!=3 Output is T |
| > | Greater than | If the front of the symbol is greater than the back of the symbol , Return to true | 4>3 Output is T |
| < | Less than | If the front of the symbol is less than the back of the symbol , Return to true | 4<3 Output is F |
| && | Logic and | If the symbol is true before and after , Return to true | (4==4)&&(3==2) Output is F |
| || | Logic or | If at least one before or after the symbol is true , Return to true | (4>3)||(4>6) Output is T |
Variable type and assignment
R Language variables are generally created without declaring types . In Computational Biology , The following five types of data are the most common :
| type | explain | give an example |
|---|---|---|
| character | character string | “abc” |
| numeric | Floating point numbers Inf Express R The upper limit of NaN Representational image 0/0 Undefined value of | 1.02 |
| integer | integer When assigning values, add L, No, the default is numeric | 15L |
| complex | The plural | 1+2i |
| logical | Logical value or Boolean value Case sensitive | T or TRUE F or FALSE |
The following commands are used to create variables and assign values to variables / Update value :
x <- 4
x <- x + 1
After this order is executed , stay Console hit x enter , Will return the current variable x Value (5). stay RStudio On the right side of the Environment I will go out x And its value (5). If you want to know all variables , Please be there. Console Use the following command :
rm(list= ls())
Complex data structure , Such as vector and data.frame, It will be explained in the subsequent use .
Logical decision and cycle
R Linguistic if else、for、while Grammar and C The language is similar , See the following example for details :
#if(){}else{}
# If the condition in brackets is true , Then execute the code in curly brackets and end , Otherwise, skip the code in curly brackets
# Can be in a if Nested in another if, Used to make more complex condition judgments
# there print() Function can output the contents in parentheses
# Try at Console Li Da ?print() or ? Add any function you are not sure about and enter , Instructions will appear on the lower right
x <- 20
y <- 30
if(x<y && y-x>15){
print("Condition 1")
} else {
print("Condition 2")
}
# The output should be "Condition2"
#for(){}
# Determine the number of times the code in curly braces is repeatedly executed according to the range in brackets
# For example, the following code i in 1:5, You mean for i=1,2,3,4,5
# That is to say, the code will be executed five times
# Again , Can be in a for loop Nested in another for loop
for(i in 1:5){
print(i^2)
}
# The output should be 1 4 9 16 25
#while(){}
# Loop through the code in curly braces , Until the condition of parentheses is false
# it is to be noted that , The condition in brackets is always true, and many words will loop
x <- 1
while(x < 10){
print(x)
x <- x + 1
}
# The output should be 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Conclusion
R That's all for language introduction . I'll explain it in detail next time vector、matrix、list These data structures , Coming soon ! If you have any questions or suggestions, please leave messages and comments !
边栏推荐
- Problèmes avec MySQL time, fuseau horaire, remplissage automatique 0
- js题目:输入数组,最大的与第一个元素交换,最小的与最后一个元素交换,输出数组。
- Keyword inline (inline function) usage analysis [C language]
- RuntimeError: cuDNN error: CUDNN_ STATUS_ NOT_ INITIALIZED
- RT thread API reference manual
- ESP learning problem record
- Basic operations of databases and tables ----- view data tables
- Pytoch implements simple linear regression demo
- level16
- I2C bus timing explanation
猜你喜欢
(五)R语言入门生物信息学——ORF和序列分析
ES6语法总结--上篇(基础篇)
Kaggle competition two Sigma connect: rental listing inquiries (xgboost)
Cannot change version of project facet Dynamic Web Module to 2.3.

数据库课程设计:高校教务管理系统(含代码)
NRF24L01故障排查
MySQL時間、時區、自動填充0的問題
Whistle+switchyomega configure web proxy

Symbolic representation of functions in deep learning papers
The dolphin scheduler remotely executes shell scripts through the expect command
随机推荐
OSPF message details - LSA overview
ESP8266使用arduino连接阿里云物联网
The first simple case of GNN: Cora classification
I2C bus timing explanation
Esp8266 connects to onenet cloud platform (mqtt) through Arduino IDE
arduino获取随机数
Page performance optimization of video scene
ESP8266连接onenet(旧版MQTT方式)
如何给Arduino项目添加音乐播放功能
单片机蓝牙无线烧录
Comparison of solutions of Qualcomm & MTK & Kirin mobile platform USB3.0
Cannot change version of project facet Dynamic Web Module to 2.3.
Basic operations of databases and tables ----- classification of data
(五)R语言入门生物信息学——ORF和序列分析
ES6语法总结--上篇(基础篇)
MP3mini播放模块arduino<DFRobotDFPlayerMini.h>函数详解
Fashion-Gen: The Generative Fashion Dataset and Challenge 论文解读&数据集介绍
Esp8266 connect onenet (old mqtt mode)
js题目:输入数组,最大的与第一个元素交换,最小的与最后一个元素交换,输出数组。
Selective sorting and bubble sorting [C language]