当前位置:网站首页>N++ is not reliable
N++ is not reliable
2022-07-04 13:09:00 【Brother Xiaokun】

Xiao Ming went to the interview again today , I was asked another strange interview question :
n := 0
for i := 0; i < 1000000; i++ {
go func() {
n++
}()
}
fmt.Println(n)
It's time for you to think , What results are output ?
Xiao Ming thought for a long time , Gave his answer : I do not know! , Then the interviewer told him : You passed .
Isn't it a little crazy , you 're right , The result of this code is that I don't know , The result of each execution is different , Look at it all cpu How to dispatch .
Let me tell you something slowly .
One 、 The original prototype
According to the interview code , Roll back a little , Look at this code :
n := 0
for i := 0; i < 1000000; i++ {
func() {
n++
}()
}
fmt.Println(n)
Let's get rid of Xie Cheng , Now the result is not very good to know , Yes, it's the number of cycles 1000000.
Two 、 The pit inside
Let's go back to the interview code , There are actually two pits :
The first pit : He didn't wait for it , So it is likely to sweep away , The main program is over before it has been cycled several times , Even quit without doing a cycle .
But in the interview , Generally, this pit is not mentioned , This is not the point of the interview , Of course, you can also mention .
The second pit is the focus of the interview :
Without considering the early exit of the main thread , After joining the process ,n++ The result of is not accurate .
Why? ?
because n++ Not atomic , He wants to finish n++ He needs to do three steps :
Get the value from memory perform +1 operation Assign back
Because it's not atomic , So it is likely that other line layers are also taking values when you take values , Also calculating , The last assignment will be overwritten , Thus, random and unpredictable results appear .
3、 ... and 、 How to guarantee the result ?
because n++ It's not atomic , If we want him to become an atom , There are two common operations :
1、 Lock
First of all, we want to ensure that he can finish the cycle , I need to add one wait:
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
n := 0
for i := 0; i < 1000000; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
n++ // It's not atomic 1、 Read from memory 2、n++ 3、 assignment
}()
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println(n)
In this way, he can finish the execution , Then add our thread layer lock :
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
locker := sync.Mutex{}
n := 0
for i := 0; i < 1000000; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
// lock
defer locker.Unlock()
locker.Lock()
n++ // It's not atomic 1、 Read from memory 2、n++ 3、 assignment
}()
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println(n)
The result of this execution , Each time is the number of executions .
2、 Use atomic
We occasionally use atomic Package to handle such operations , But there are certain limitations , The data types he supports are limited .
Go straight to the code :
var n int32 = 0
for i := 0; i < 1000000; i++ {
func() {
atomic.AddInt32(&n, 1) // Atomic manipulation
}()
}
fmt.Println(n)
Here we put n Turned into int32 type , Such operation result can also guarantee the number of cycles .
边栏推荐
- 【云原生 | Kubernetes篇】深入了解Ingress(十二)
- 数据库锁表?别慌,本文教你如何解决
- Detailed explanation of mt4api documentary and foreign exchange API documentary interfaces
- [data clustering] section 3 of Chapter 4: DBSCAN performance analysis, advantages and disadvantages, and parameter selection methods
- Excuse me, have you encountered this situation? CDC 1.4 cannot use timestamp when connecting to MySQL 5.7
- MDK在头文件中使用预编译器时,#ifdef 无效的问题
- 再说rsync+inotify实现数据的实时备份
- WPF双滑块控件以及强制捕获鼠标事件焦点
- Meituan Ali's Application Practice on multimodal recall
- CTF竞赛题解之stm32逆向入门
猜你喜欢

众昂矿业:为保障萤石足量供应,开源节流势在必行

I want to talk about yesterday
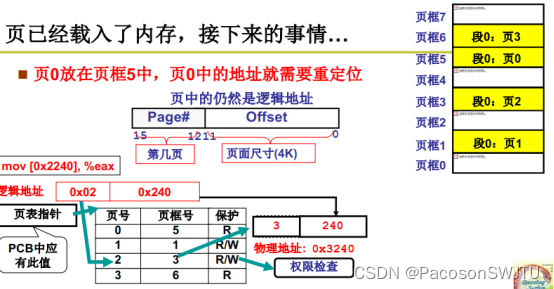
17. Memory partition and paging
![[leetcode] 96 and 95 (how to calculate all legal BST)](/img/d5/788c88064bce6a7c4499017908b3f2.jpg)
[leetcode] 96 and 95 (how to calculate all legal BST)
干货整理!ERP在制造业的发展趋势如何,看这一篇就够了
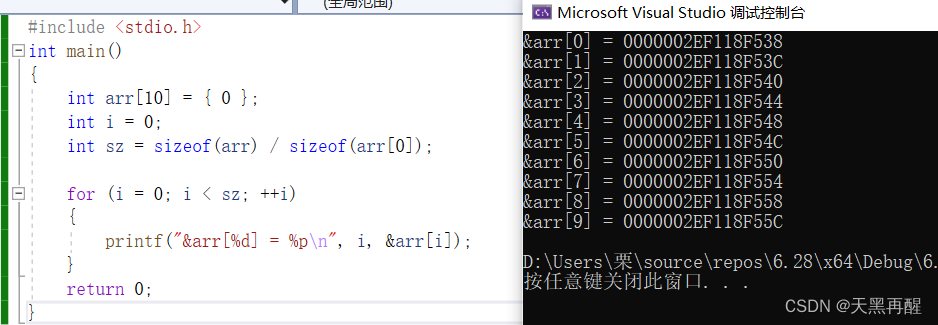
C language array
Reptile exercises (I)

比量子化学方法快六个数量级,一种基于绝热状态的绝热人工神经网络方法,可加速对偶氮苯衍生物及此类分子的模拟
DVWA range exercise 4

Read the BGP agreement in 6 minutes.
随机推荐
Peak detection of measured signal
C fonctions linguistiques
《天天数学》连载57:二月二十六日
Rsyslog配置及使用教程
AI 绘画极简教程
强化学习-学习笔记1 | 基础概念
比量子化学方法快六个数量级,一种基于绝热状态的绝热人工神经网络方法,可加速对偶氮苯衍生物及此类分子的模拟
C#/VB. Net to add text / image watermarks to PDF documents
C语言数组
WPF双滑块控件以及强制捕获鼠标事件焦点
Agile development / agile testing experience
【AI系统前沿动态第40期】Hinton:我的深度学习生涯与研究心法;Google辟谣放弃TensorFlow;封神框架正式开源
golang 设置goproxy代理的小细节,适用于go module下载超时,阿里云镜像go module下载超时
go-zero微服务实战系列(九、极致优化秒杀性能)
WPF double slider control and forced capture of mouse event focus
使用 NSProxy 实现消息转发
Transformer principle and code elaboration (tensorflow)
Solution: how to delete the information of Jack in two tables with delete in one statement in Oracle
WPF双滑块控件以及强制捕获鼠标事件焦点
ISO 27001 Information Security Management System Certification