当前位置:网站首页>Mysql22 logical architecture
Mysql22 logical architecture
2022-07-06 10:37:00 【Protect our party a Yao】
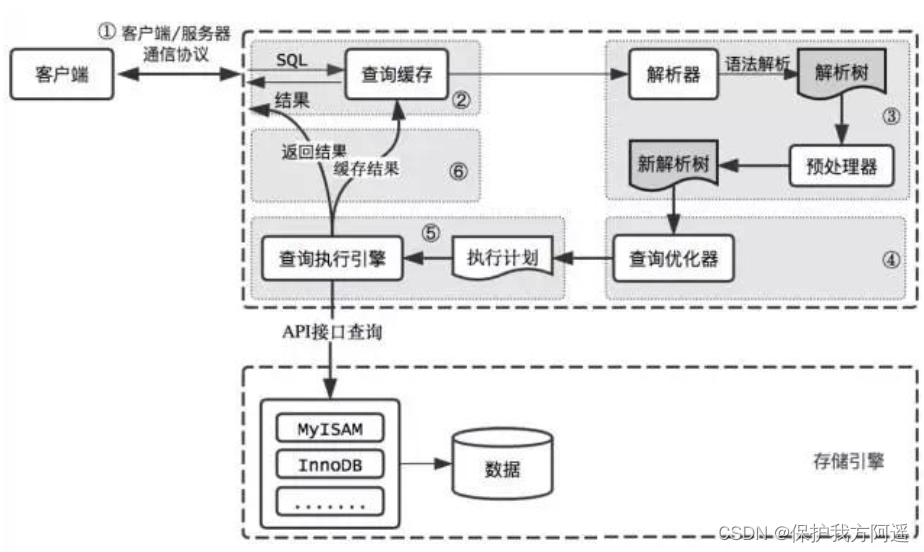
One . Logical architecture analysis
1.1. The server handles client requests
What does the server process do with the request sent by the client process , To produce the final processing result ? Here, take the query request as an example to show :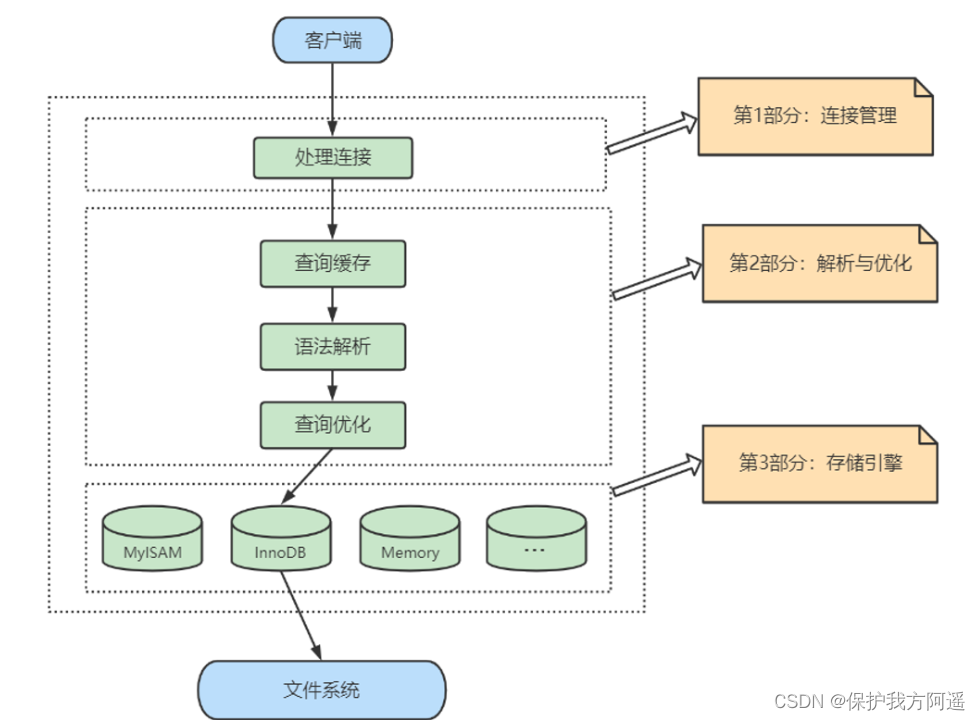 Let's take a look at :
Let's take a look at :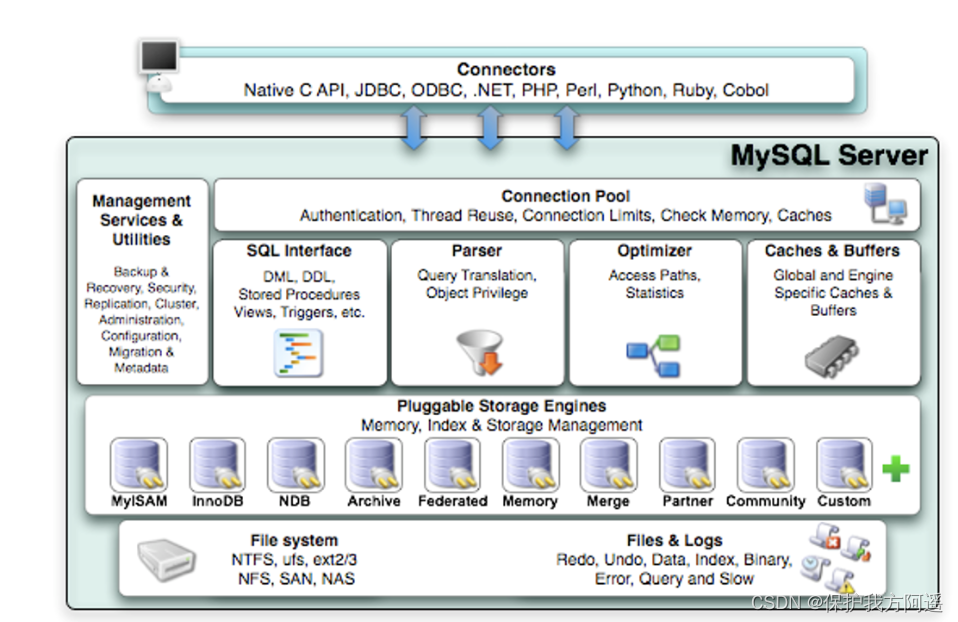
1.2. Connectors
1.3. The first 1 layer : adjoining course
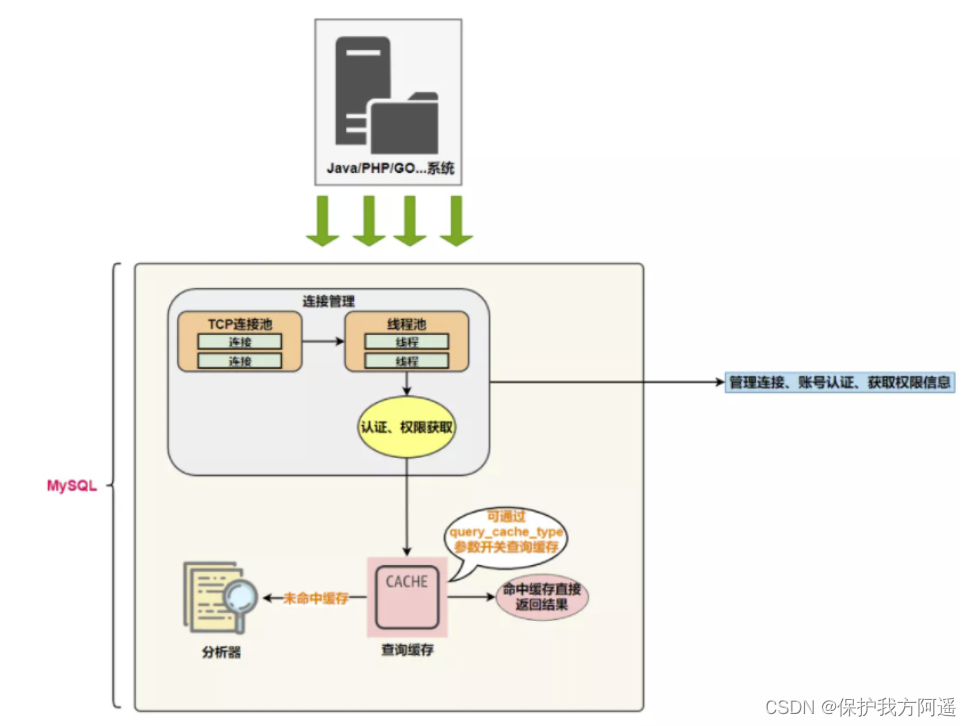
System ( client ) visit MySQL In front of the server , The first thing to do is to establish TCP Connect .
After three handshakes, the connection is established successfully , MySQL Server pair TCP The transmitted account and password are used for identity authentication 、 Access .
- Wrong user name or password , I'll get one Access denied for user error , The client program completes execution .
- User name password authentication passed , From the permission table, you will find out the permission of the account and the connection Association , The following permission judgment logic , Will depend on the permissions read at this time .
TCP After the connection receives the request , Must be assigned to a thread dedicated to the interaction with this client . So there will be a thread pool , Go to the later process . Each connection gets threads from the thread pool , Eliminates the overhead of creating and destroying threads .
1.4. The first 2 layer : Service layer
- SQL Interface: SQL Interface
- Receive the user's SQL command , And returns the result of the query that the user needs . such as SELECT … FROM It's called SQL Interface.
- MySQL Support DML( Data operation language )、DDL( Data definition language )、 stored procedure 、 View 、 trigger 、 User defined functions, etc SQL Language interface .
- Parser: Parser
- In the parser SQL Statement syntax analysis 、 Semantic analysis . take SQL Statements are decomposed into data structures , And pass the structure to the next step , in the future SQL Statements are passed and processed based on this structure . If you encounter an error in the decomposition composition , So that's it SQL The statement is unreasonable .
- stay SQL Commands are validated and parsed by the parser when they are passed to the parser , And create for it Grammar tree , And enrich the query syntax tree according to the data dictionary , Meeting Verify whether the client has permission to execute the query . After creating the syntax tree ,MySQL Will also be right SQl Query syntax optimization , Query rewriting .
- Optimizer: Query optimizer
- SQL Statement after syntax parsing 、 Before the query, the query optimizer will be used to determine SQL Statement execution path , Generate an execution plan .
- The implementation plan indicates that Which index to use The query ( Full table search or index search ), What is the connection order between tables , Finally, the method provided by the storage engine will be called according to the steps in the execution plan to truly execute the query , And return the query results to the user .
- It USES “ selection - Projection - Connect ” Strategy to query . for example :
SELECT id,name FROM student WHERE gender = ' Woman ';
This SELECT The query is based on WHERE The sentence goes on selection , Instead of querying all the tables and then gender Filter . This SELECT The query is based on id and name Make attributes Projection , Instead of taking all the attributes out and filtering them later , These two query criteria Connect Get up and generate the final query results .
- Caches & Buffers: Query cache component
- MySQL There's some internal maintenance Cache and Buffer, such as Query Cache Used to cache a SELECT Statement execution result , If the corresponding query result can be found in it , Then there is no need to query and parse 、 Optimization and execution of the whole process , Directly feed back the results to the client .
- The caching mechanism consists of a series of small caches . For example, table caching , Record the cache ,key cache , Authority cache, etc .
- The query can be cached in Sharing between different clients .
- from MySQL 5.7.20 Start , Query caching is not recommended , And in MySQL 8.0 Delete in .
1.5. The first 3 layer : Engine layer
Plug in storage engine layer ( Storage Engines), Really responsible MySQL The storage and extraction of data in , Perform operations on the underlying data maintained at the physical server level , Server pass API Communicating with the storage engine . Different storage engines have different functions , So we can choose according to our actual needs .
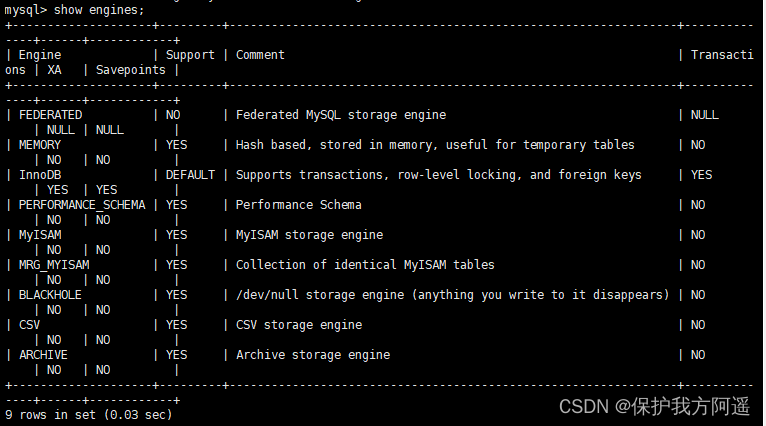
MySQL 8.0.25 The storage engines supported by default are as follows :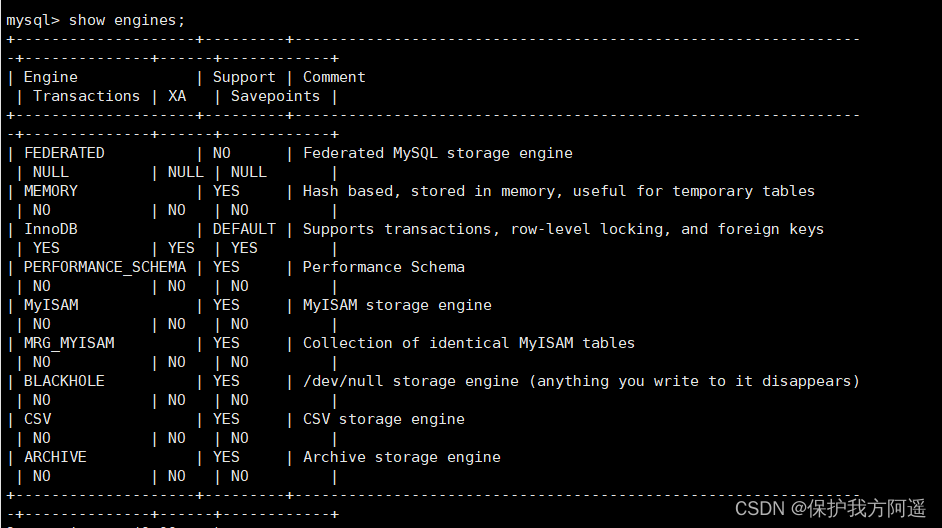
1.6. Storage layer
All data , database 、 The definition of the table , The contents of each row of the table , Indexes , All exist file system On , With file The way that exists , And complete the interaction with the storage engine . Of course, some storage engines, such as InnoDB, It also supports direct management of bare devices without using the file system , But the implementation of modern file systems makes this unnecessary . Under the file system , You can use a local disk , have access to DAS、NAS、SAN And other storage systems .
1.7. Summary
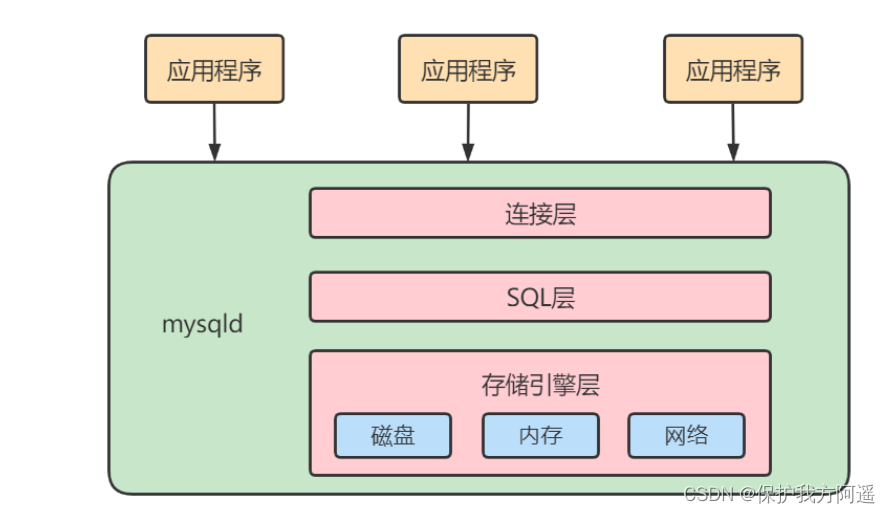 Simplified to a three-tier structure :
Simplified to a three-tier structure :
- adjoining course : Establish connection between client and server , The client sends SQL To the server side ;
- SQL layer ( Service layer ): Yes SQL Statement for query processing ; It has nothing to do with the storage mode of database files ;
- Storage engine layer : Dealing with database files , Responsible for data storage and reading .
Two . SQL Execute the process
2.1. MySQL Medium SQL Execute the process
MySQL The query process of :
- The query cache :Server If you find this in the query cache SQL sentence , The result will be returned directly to the client ; without , We're in the parser phase . It should be noted that , Because query caching is often inefficient , So in MySQL8.0 After that, I abandoned this function .
In most cases, query caching is a chicken rib , Why? ?
SELECT employee_id,last_name FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 101;
Query caching is to cache query results in advance , In this way, you can get the results directly without execution next time . It should be noted that , stay MySQL Query caching in , Not a cached query plan , Instead, query the corresponding results . This means that the query matches The robustness is greatly reduced , Only The same query operation will hit the query cache . The difference between two query requests in any character ( for example : Space 、 notes 、 Case write ), Will cause the cache to miss . therefore MySQL Of The hit rate of query cache is not high .
meanwhile , If the query request contains some system functions 、 User defined variables and functions 、 Some system tables , Such as mysql 、information_schema、 performance_schema Tables in the database , Then the request will not be cached . Take some system functions for example , Maybe two calls to the same function will produce different results , Like functions NOW , Each call produces the latest current time , If you call this function in a query request , Even if the text information of the query request is the same , Two queries at different times should also get different results , If it is cached on the first query , It is wrong to directly use the result of the first query in the second query !
Besides , Since it's a cache , Then there is it When the cache fails .MySQL The cache system of will monitor each table involved , As long as the structure or data of the table is modified , If this table is used INSERT 、 UPDATE 、 DELETE 、 TRUNCATE TABLE 、 ALTERTABLE 、 DROP TABLE or DROP DATABASE sentence , All cached queries that use this table become invalid and are removed from the cache ! about Update the database with high pressure Come on , The hit rate for the query cache will be very low .
- Parser : In the parser SQL Statement syntax analysis 、 Semantic analysis .
First do “ Lexical analysis ”. What you enter is a string with multiple Spaces SQL sentence ,MySQL You need to identify the strings in it , What is the . MySQL From what you typed "select" This keyword recognizes , This is a query statement . It also takes strings “T” Identify a “ Table name T”, Put the string “ID” Identify a “ Column ID”.
next , Want to do “ Syntax analysis ”. According to the result of lexical analysis , parsers ( such as :Bison) According to the rules of grammar , Judge the one you typed SQL Statement whether Satisfy MySQL grammar .
If SQL The statement is correct , A syntax tree like this will be generated :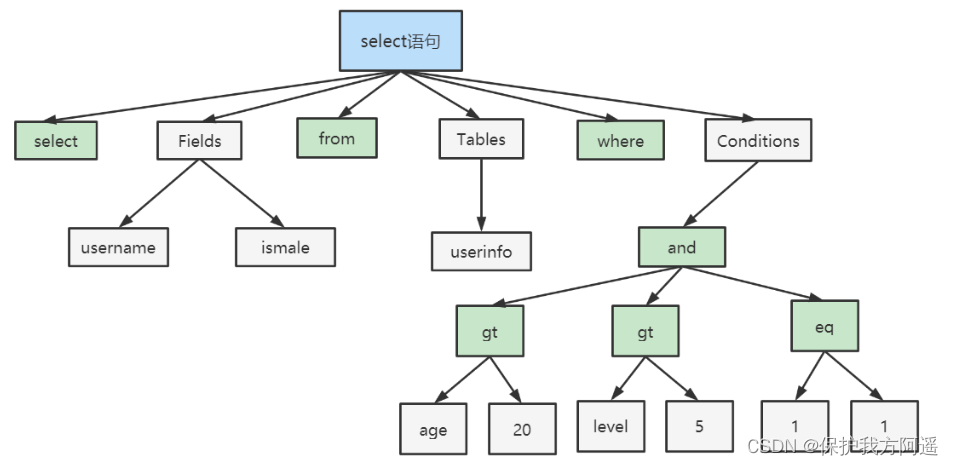
- Optimizer : It will be determined in the optimizer that SQL Statement execution path , For example, according to Full search , Or according to Index search etc. .
give an example : The following statement executes two tables join:
select * from test1 join test2 using(ID)
where test1.name='zhangwei' and test2.name='mysql Advanced courses ';
programme 1: You can start from the table test1 The inside out name='zhangwei’ The record of ID value , According to ID Values are associated to tables test2, To determine test2 Inside name Is the value of ‘mysql Advanced courses ’.
programme 2: You can start from the table test2 The inside out name=‘mysql Advanced courses ’ The record of ID value , According to ID The value associated with the test1, To determine test1 Inside name Is the value of zhangwei.
The logical result of the two execution methods is the same , But the efficiency of the execution will be different , The role of the optimizer is to decide which scheme to use . After the optimizer phase is complete , The execution of this statement is determined , Then we go to the executor phase .
In the query optimizer , Can be divided into Logical query Optimization phase and Physical query Optimization stage .
- actuator :
Up to now , I haven't really read and write real tables yet , It just produced an implementation plan . So I entered Actuator stage .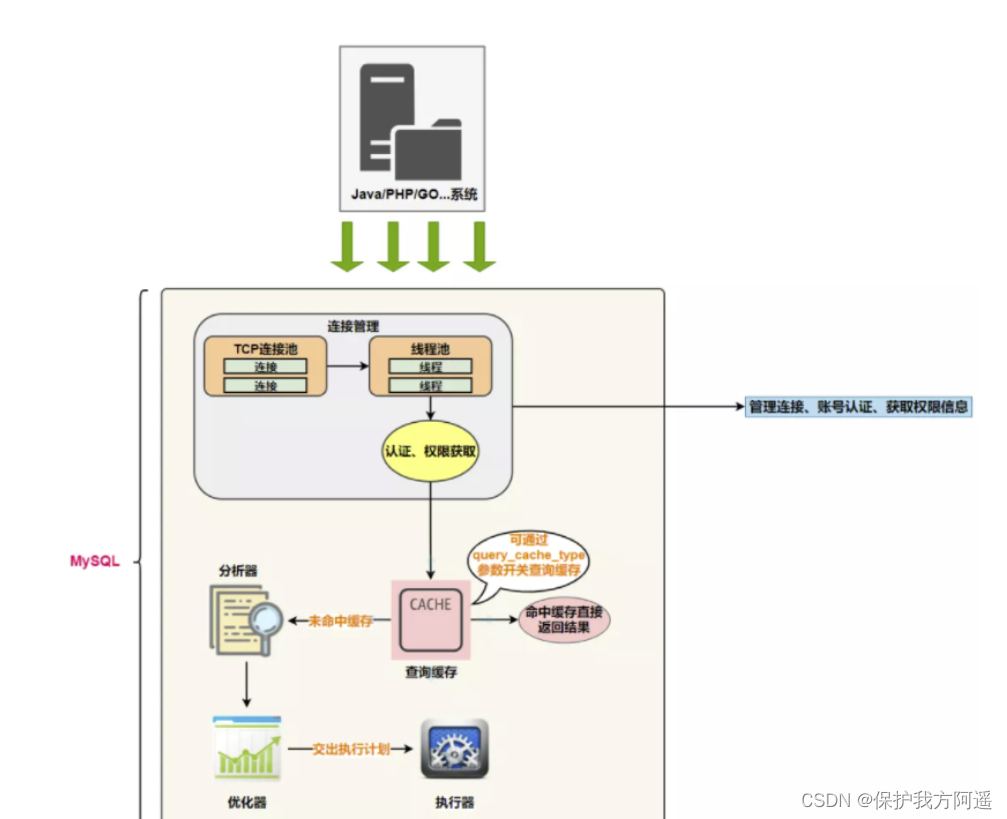
Before execution, you need to judge whether the user Have authority . without , A permission error will be returned . If you have permission , Is executed SQL Query and return the result . stay MySQL8.0 The following version , If query cache is set , At this time, the query results will be cached .
select * from test where id=1;
such as : surface test in ,ID Field has no index , So the execution process of the actuator is like this :
call InnoDB The engine interface takes the first row of this table , Judge ID Value is 1, If not, skip , If it is, the row will exist in the result set ;
Call the engine interface “ The next line ”, Repeat the same logic of judgment , Until you get to the last row of the table .
The executor returns the record set composed of all the rows that meet the conditions in the traversal process to the client as a result set .
thus , This statement is executed . For tables with indexes , The execution logic is similar .
SQL Statements in MySQL The process in is : SQL sentence → The query cache → Parser → Optimizer → actuator .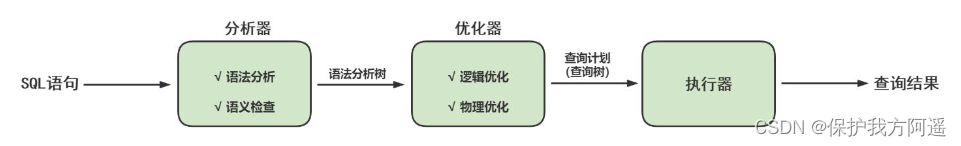
2.2. MySQL8 in SQL Execution principle
- confirm profiling Open or not
show @@profiling;
perhaps
show variables like 'profiling'
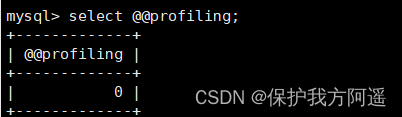
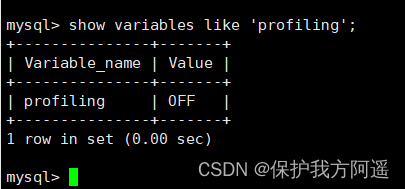
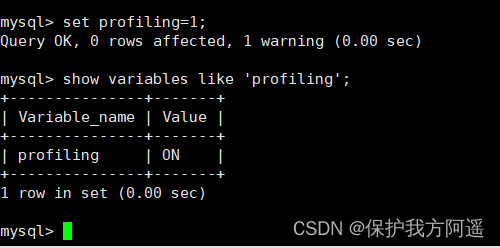
profiling=0 On behalf of closed , We need to take profiling open , It is set to 1:
set profiling=1;
- Perform the same many times SQL Inquire about
Then we execute a SQL Inquire about ( You can perform any SQL Inquire about ):
select * from employees;
- see profiles
View all generated by the current session profiles: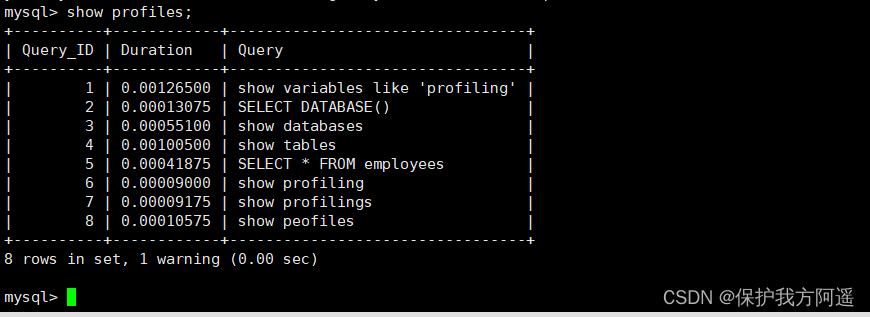
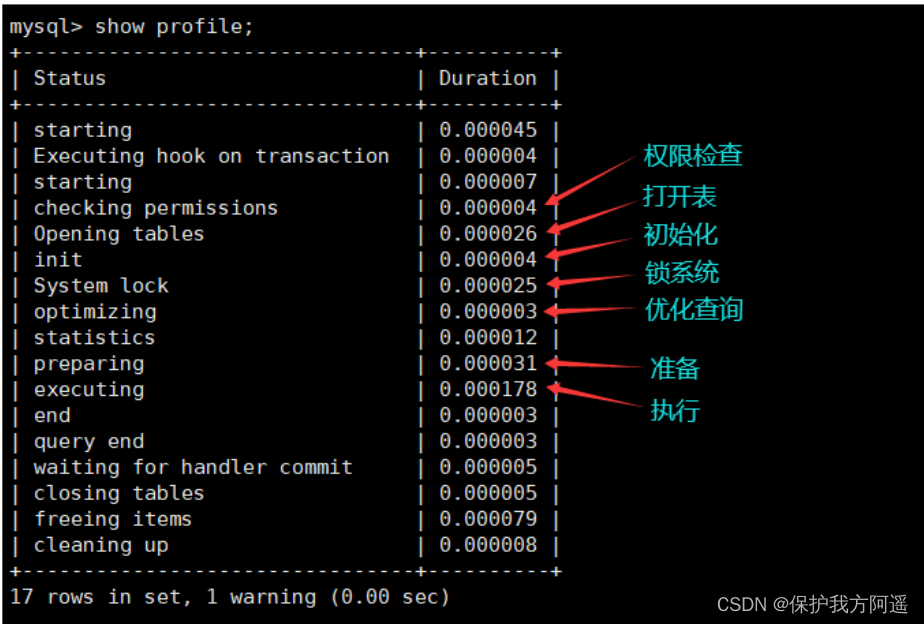
- see profile
Show execution plan , Check the execution steps of the program :
show profile;
Of course, you can also query the specified Query ID, such as :
show profile for query 5;
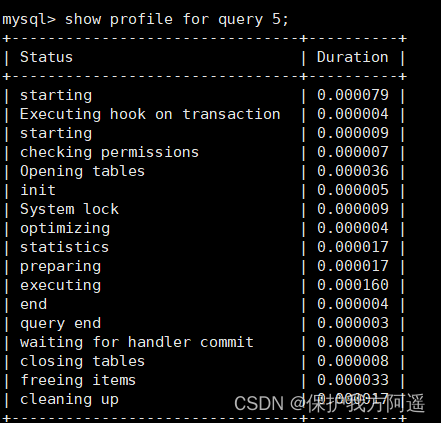
Inquire about SQL The result of execution time is the same as the above .
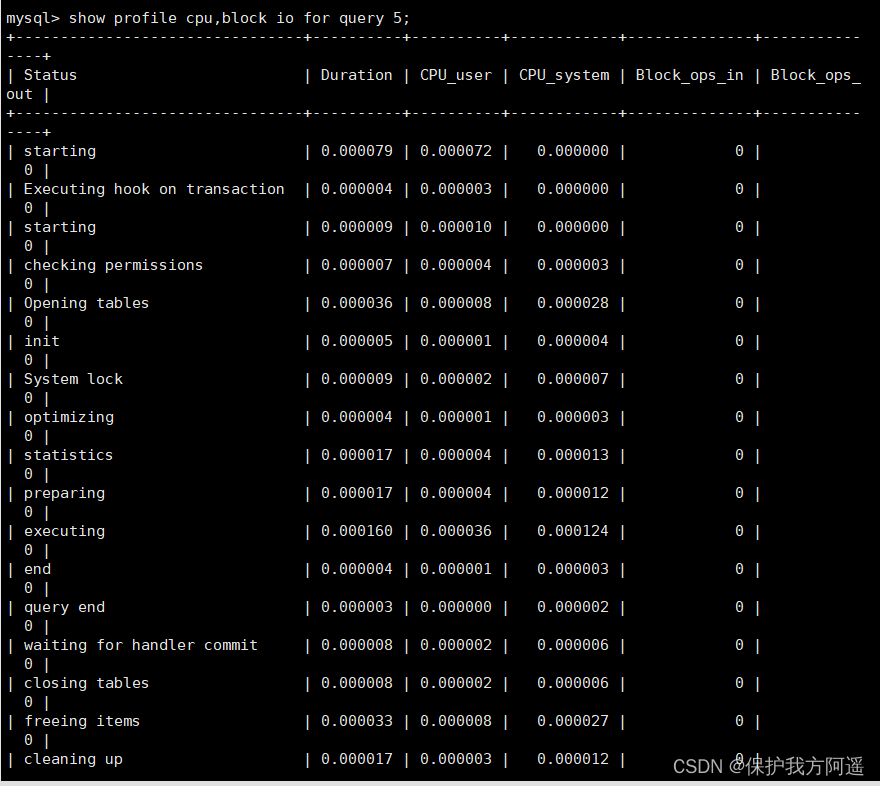
Besides , You can also query richer content :
SELECT PROFILE cpu,block io for query 5;
2.3. MySQL5.7 in SQL Execution principle
The above operation is in MySQL5.7 Medium test , Found the same two times before and after sql sentence , The query process is still the same . Don't you know how to use cache ? Here we need Explicitly turn on query cache mode . stay MySQL5.7 The settings are as follows :
- Open the query cache in the configuration file
stay /etc/my.cnf Add a new line :
query_cache_type=1
- restart mysql service
systemctl restart mysqld
- Open the query execution plan
Because the service has been restarted , The following instructions need to be executed again , Turn on profiling.
SET PROFILING=1;
- Execute the statement twice :
select * from employees;
select * from employees;
- see profiles
show profiles;
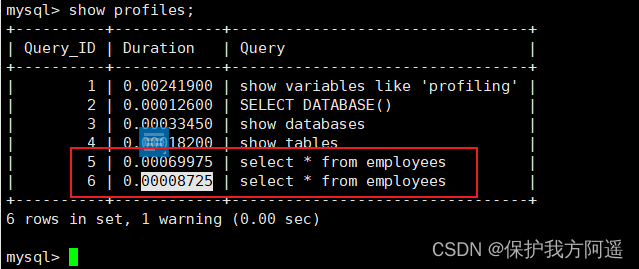
- see profile
Show execution plan , Check the execution steps of the program :
show profile for query 5;
show profile for query 6;
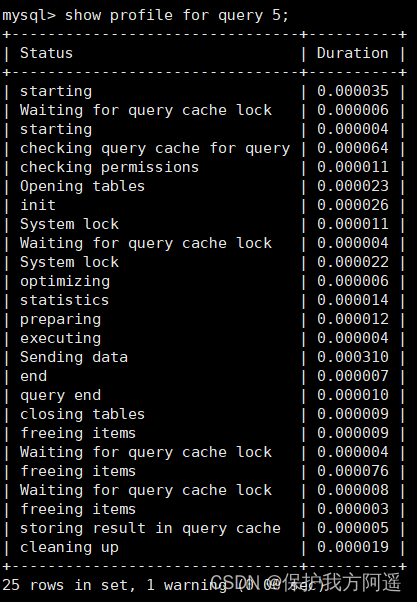
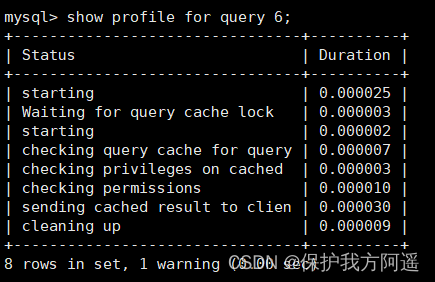
The conclusion is self-evident . Execution number 2 when , Ratio execution number 1 A lot of information is missing , As can be seen from the screenshot, the query statement directly obtains data from the cache .
2.4. SQL Grammatical order
With Mysql Version update , Its optimizer is also constantly upgrading , The optimizer will analyze the performance consumption caused by different execution order and dynamically adjust the execution order .
demand : Query each department older than 20 The number of years old is higher than 20 The number of people aged cannot be less than 2 people , Display the information of the first department with the largest number of people .
Here is the order of queries that often appear :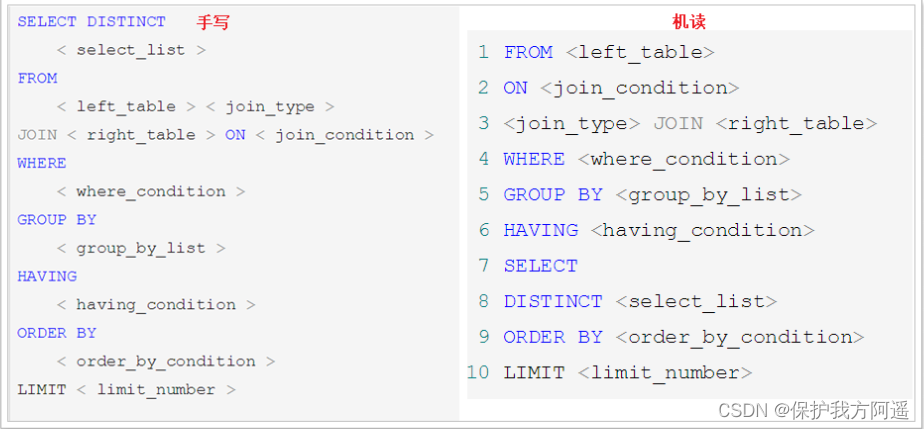
2.5. Oracle Medium SQL Execute the process ( understand )
Oracle Have adopted the Shared pool To judge SQL Whether the statement has a cache and execution plan , Through this step, we can know whether we should use hard parsing or soft parsing .
So let's see SQL stay Oracle The implementation process in :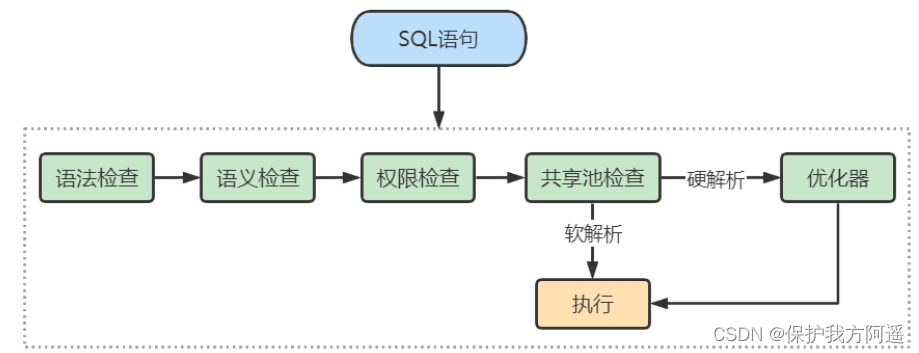
As can be seen from the picture above ,SQL Statements in Oracle The following steps have been taken in .
- Syntax check : Check SQL Is the spelling correct , If not ,Oracle Can report grammatical errors .
- Semantic check : Check SQL Whether the access object in exists . For example, we are writing SELECT At the time of statement , The name is wrong , The system will prompt an error . The function of grammar check and semantic check is to ensure SQL There is no mistake in the statement .
- Permission check : See if the user has access to the data .
- Shared pool check : Shared pool (Shared Pool) Is a memory pool , The main function is to cache SQL Statement and its execution plan .Oracle By checking that the shared pool exists SQL Statement execution plan , To judge for soft parsing , Or hard parsing . How to understand soft parsing and hard parsing ?
In a shared pool ,Oracle First of all, SQL The sentence goes on Hash operation , And then according to Hash Values are cached in the library (Library Cache) Search for , If There is SQL Statement execution plan , It's going to be executed directly , Go straight into “ actuator ” Link , This is it. Soft parsing . If not found SQL Statement and execution plan ,Oracle You need to create a parse tree to parse , Generate execution plan , Get into “ Optimizer ” This step , This is it. Hard parsing . - Optimizer : In the optimizer, hard parsing is needed , That is to decide what to do , For example, create a parse tree , Generate execution plan .
- actuator : When you have the parse tree and the execution plan , You know the SQL How to be executed , In this way, the statement can be executed in the executor .
The shared pool is Oracle Terms in , Including library cache , Data dictionary buffer, etc . We've already talked about the library cache , It mainly caches SQL Statement and execution plan . and Data dictionary buffer What's stored is Oracle Object definition in , Such as table 、 View 、 Index and so on . When the SQL When parsing a statement , If you need relevant data , Will extract... From the data dictionary buffer .
Library cache This one step , To determine the SQL Whether the statement needs to be hard parsed . In order to improve SQL Efficiency of execution , We should try to avoid hard parsing , Because in SQL During the execution of , Create a parse tree , Generating an execution plan is very resource consuming .
stay Oracle in , Bound variable It's a big feature . Binding variables is in SQL Use variables in statements , Through different variable values to change SQL The results of the implementation of . The advantage of this is that it can Improve the possibility of soft parsing , The disadvantage is that the generated execution plan may not be optimized , Therefore, whether you need to bind variables depends on the situation .
for instance , We can use the following query statement :
select * from player where player_id = 10001;
You can use bound variables , Such as :
select * from player where player_id = :player_id;
The efficiency of these two query statements is Oracle It's totally different . If you are inquiring player_id = 10001 after , Also query 10002、10003 Data like that , Then each query will create a new query resolution . The second method uses bound variables , So after the first query , There will be execution plans for such queries in the shared pool , That is, soft parsing .
therefore , We can reduce hard parsing by using bound variables , Reduce Oracle The workload of parsing . But there are also drawbacks to this approach , Usage dynamics SQL The way , Because the parameters are different , It can lead to SQL The efficiency of implementation is different , meanwhile SQL Optimization can also be difficult .
Oracle The architecture of the figure :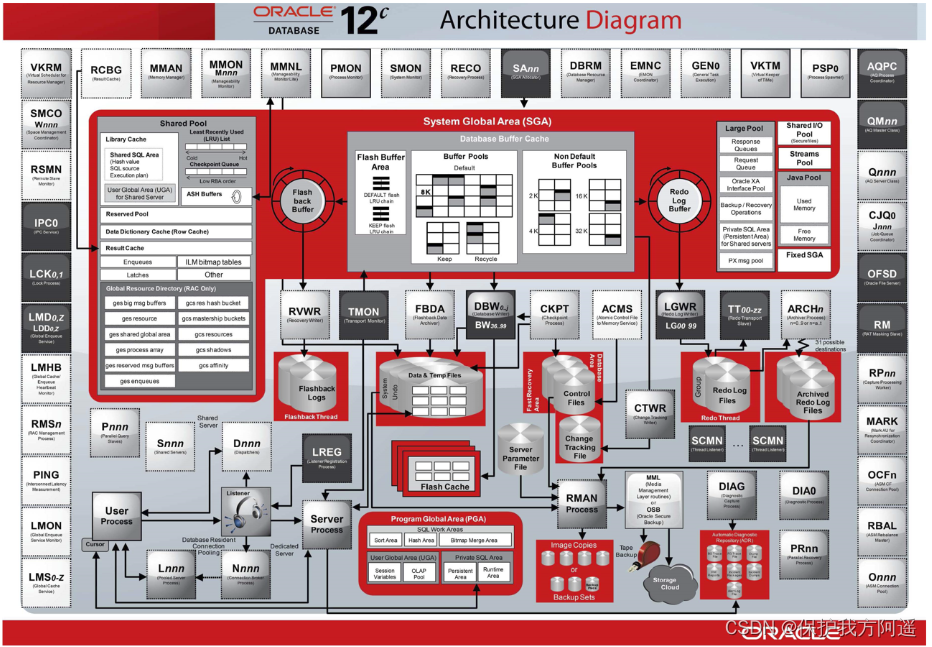
Schematic diagram :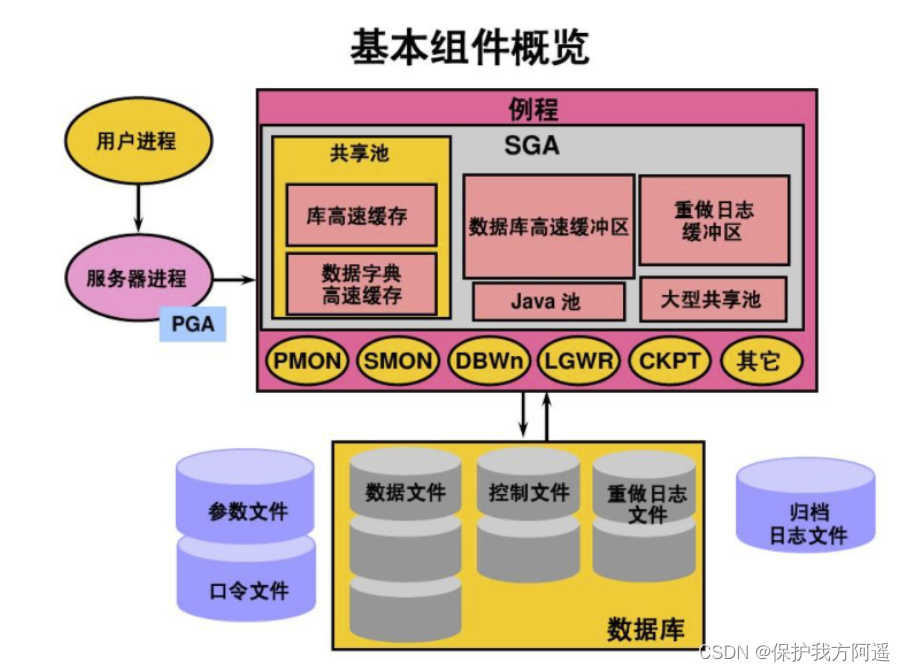
Summary :
Oracle and MySQL It's going on SQL There are differences in software implementation on the query of .Oracle The concept of shared pool is proposed , Determine whether soft parsing is performed through the shared pool , Or hard parsing .
3、 ... and . Database buffer pool (buffer pool)
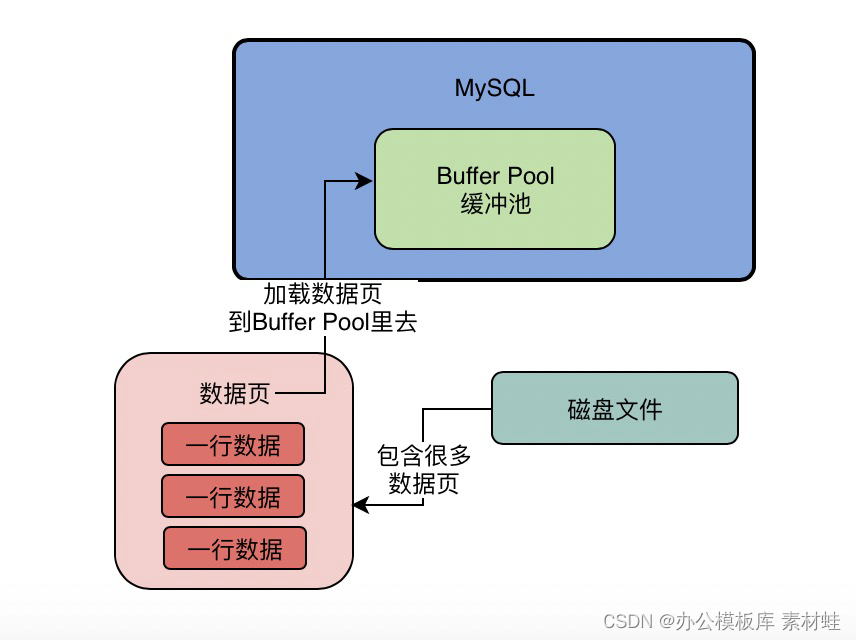
InnoDB The storage engine manages the storage space on a page by page basis , In fact, our operations of adding, deleting, modifying and querying are essentially visiting the page ( Including reading pages 、 Write page 、 Create a new page ). And disk I/O It takes a lot of time , And operate in memory , Efficiency will be much higher , In order to make the data in the data table or index be used by us at any time ,DBMS Will apply for Occupy memory as a data buffer pool , Before actually accessing the page , You need to cache pages on disk into memory Buffer Pool Then you can access .
The advantage of this is that it minimizes disk activity , thus Reduce direct communication with disk I/O Time for . Need to know , This strategy is important to improve SQL Statement is critical to query performance . If the indexed data is in the buffer pool , Then the cost of access will be reduced a lot .
3.1. Buffer pool vs The query cache
Are buffer pools and query caches the same thing ? No .
3.1.1. Buffer pool (Buffer Pool)
First of all, we need to understand in InnoDB In the storage engine , What are included in the buffer pool .
stay InnoDB Some data in the storage engine will be put into memory , The buffer pool accounts for most of this memory , It is used to store a cache of various data , As shown in the figure below :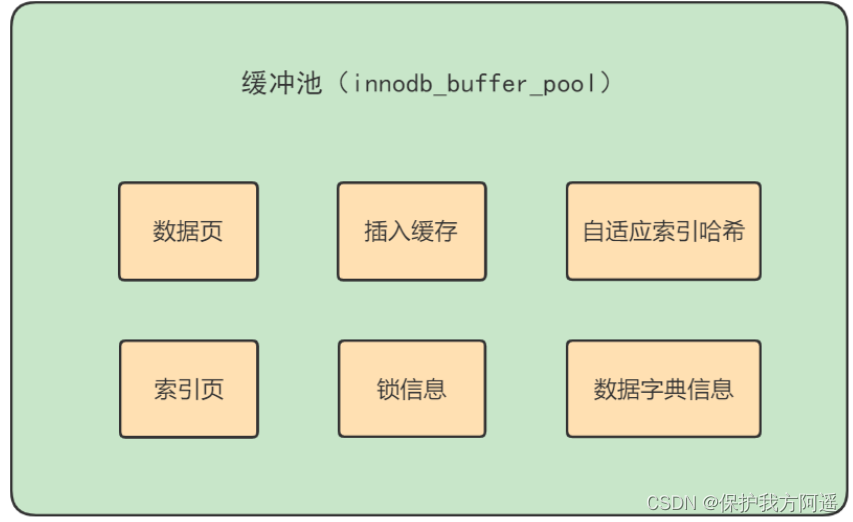
From the picture , You can see InnoDB The buffer pool includes data pages 、 Index page 、 Insert buffer 、 Lock information 、 The adaptive Hash And data dictionary information .
The importance of cache pools :
Caching principle :
“ Location * The frequency of ” This principle , It can help us deal with I/O Optimize access efficiency .
First , Location determines efficiency , Buffer pool is provided to directly access data in memory .
secondly , Frequency determines priority . Because the size of the buffer pool is limited , For example, the disk has 200G, But only memory 16G, The buffer pool size is only 1G, You can't load all the data into the buffer pool , Here comes the priority order , Meeting The thermal data with high frequency of use shall be preferentially loaded .
3.1.2. The query cache
So what is query caching ?
Query caching is to put Query result cache get up , In this way, you can get the results directly without execution next time . It should be noted that , stay MySQL Query caching in , Not a cached query plan , Instead, query the corresponding results . Because the hit conditions are harsh , And as long as the data sheet changes , The query cache will fail , So the hit rate is low .
3.2. How the buffer pool reads data
The buffer pool manager will try to save frequently used data , When the database reads pages , First, it will judge whether the page is in the buffer pool , If it exists, read it directly , If it doesn't exist , The page will be stored in the buffer pool through memory or disk, and then read .
The structure and function of cache in the database are shown in the figure below :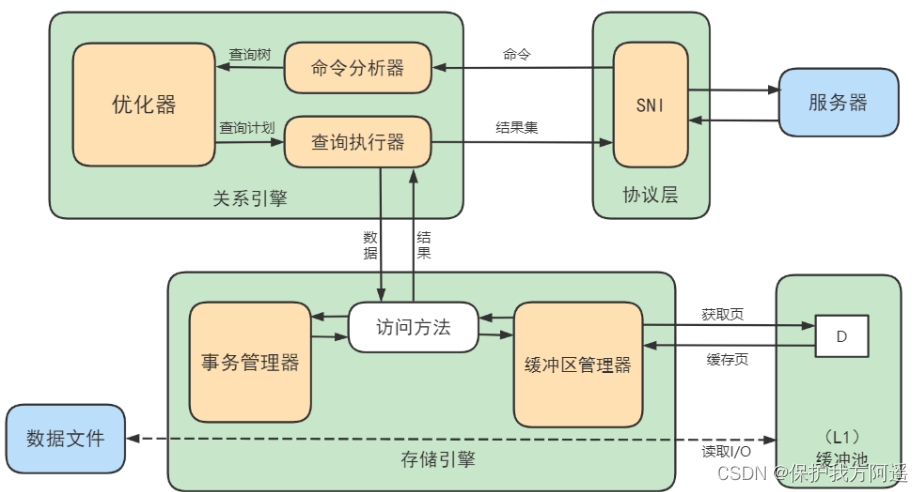
If we implement SQL Statement updates the data in the cache pool , So will these data be synchronized to the disk immediately ?
3.3. see / Set the size of the buffer pool
If you're using InnoDB Storage engine , By looking at innodb_buffer_pool_size Variable to see the size of the buffer pool . The order is as follows :
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'innodb_buffer_pool_size';
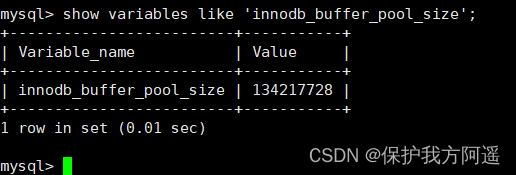
You can see at this time InnoDB The size of the buffer pool is only 134217728/1024/1024=128MB. We can modify the buffer pool size , For example, change to 256MB, The method is as follows :
set global innodb_buffer_pool_size = 268435456
perhaps :
[server]
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 268435456
3.4. Multiple Buffer Pool example
[server]
innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 2
This shows that we want to create 2 individual Buffer Pool example .
Let's see how to check the number of buffer pools , Use command :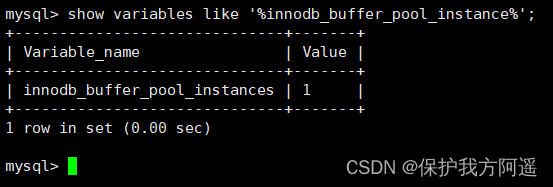
Then each Buffer Pool How much memory does the instance actually occupy ? Actually, it's calculated using this formula :
innodb_buffer_pool_size/innodb_buffer_pool_instances
That is, the total size divided by the number of instances , The result is every Buffer Pool The size occupied by the instance .
3.5. Extended question
Buffer Pool yes MySQL Memory structure is a very core component , You can think of it as a black box first .
Update data flow under black box 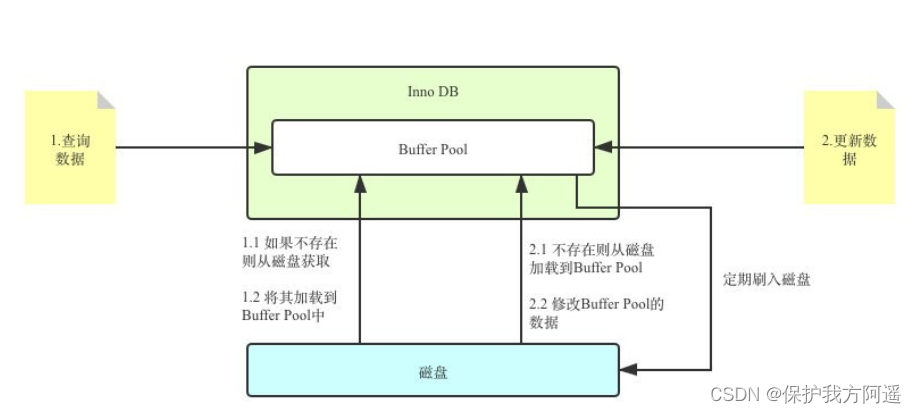
For example, an error occurred suddenly in the middle of the update , Want to roll back to the previous version , What should I do ? Even the guarantee of data persistence 、 There is no way to do transaction rollback, so we still talk about crash recovery ?
answer :Redo Log & Undo Log
边栏推荐
- PyTorch RNN 实战案例_MNIST手写字体识别
- MySQL combat optimization expert 03 uses a data update process to preliminarily understand the architecture design of InnoDB storage engine
- text 文本数据增强方法 data argumentation
- MySQL30-事务基础知识
- 13 medical registration system_ [wechat login]
- Introduction tutorial of typescript (dark horse programmer of station B)
- MySQL21-用户与权限管理
- MySQL24-索引的数据结构
- MySQL combat optimization expert 07 production experience: how to conduct 360 degree dead angle pressure test on the database in the production environment?
- MySQL real battle optimization expert 11 starts with the addition, deletion and modification of data. Review the status of buffer pool in the database
猜你喜欢
Mysql27 - Optimisation des index et des requêtes
Mysql23 storage engine
MySQL combat optimization expert 12 what does the memory data structure buffer pool look like?
![15 medical registration system_ [appointment registration]](/img/c1/27c7a5aae82783535e5467583bb176.png)
15 medical registration system_ [appointment registration]
MySQL20-MySQL的数据目录
Water and rain condition monitoring reservoir water and rain condition online monitoring
Mysql34 other database logs
![[C language] deeply analyze the underlying principle of data storage](/img/d6/1c0cd38c75da0d0cc1df7f36938cfb.png)
[C language] deeply analyze the underlying principle of data storage

实现微信公众号H5消息推送的超级详细步骤
Database middleware_ MYCAT summary
随机推荐
Unicode decodeerror: 'UTF-8' codec can't decode byte 0xd0 in position 0 successfully resolved
API learning of OpenGL (2004) gl_ TEXTURE_ MIN_ FILTER GL_ TEXTURE_ MAG_ FILTER
使用OVF Tool工具从Esxi 6.7中导出虚拟机
Nanny hand-in-hand teaches you to write Gobang in C language
Security design verification of API interface: ticket, signature, timestamp
[paper reading notes] - cryptographic analysis of short RSA secret exponents
Implement sending post request with form data parameter
Mysql34 other database logs
MySQL实战优化高手02 为了执行SQL语句,你知道MySQL用了什么样的架构设计吗?
MySQL的存储引擎
MySQL27-索引優化與查詢優化
[paper reading notes] - cryptographic analysis of short RSA secret exponents
Water and rain condition monitoring reservoir water and rain condition online monitoring
Const decorated member function problem
Anaconda3 installation CV2
Isn't there anyone who doesn't know how to write mine sweeping games in C language
text 文本数据增强方法 data argumentation
MySQL實戰優化高手04 借著更新語句在InnoDB存儲引擎中的執行流程,聊聊binlog是什麼?
MySQL combat optimization expert 02 in order to execute SQL statements, do you know what kind of architectural design MySQL uses?
该不会还有人不懂用C语言写扫雷游戏吧